2- AIDS/HIV
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
HIV mainly effects
Women at fertile age
17 Situations where it’s recommended to get AIDS blood test?

First AIDS cases were diagnosed in…
1980- US- detected aggressive pneumonias
Common presentation- severe decreases TCD4 cell rate
Why was the first disease initially called GRID, when and why did it change?
Seemed to only relate to gay people
1982- AIDS- affected people who received transfusions, haemophiliacs, lived in certain areas…
Who discovered that HIV-1 was the virus responsible for causing AIDS?
Montagnier and Barré (French)- 1984
Robert Gallo (American)
HIV-2 causes a disease similar to AIDS but…
Less aggressive and spreads slowly- easier to control
Most accepted explanation in spread of HIV?
Retrovirus infected monkey - monkey infected human- in 30s in central Africa
HIV structure
2 copies of RNA
Reverse transcriptase- transforms healthy cell to virus cell- causes DNA to change to RNA
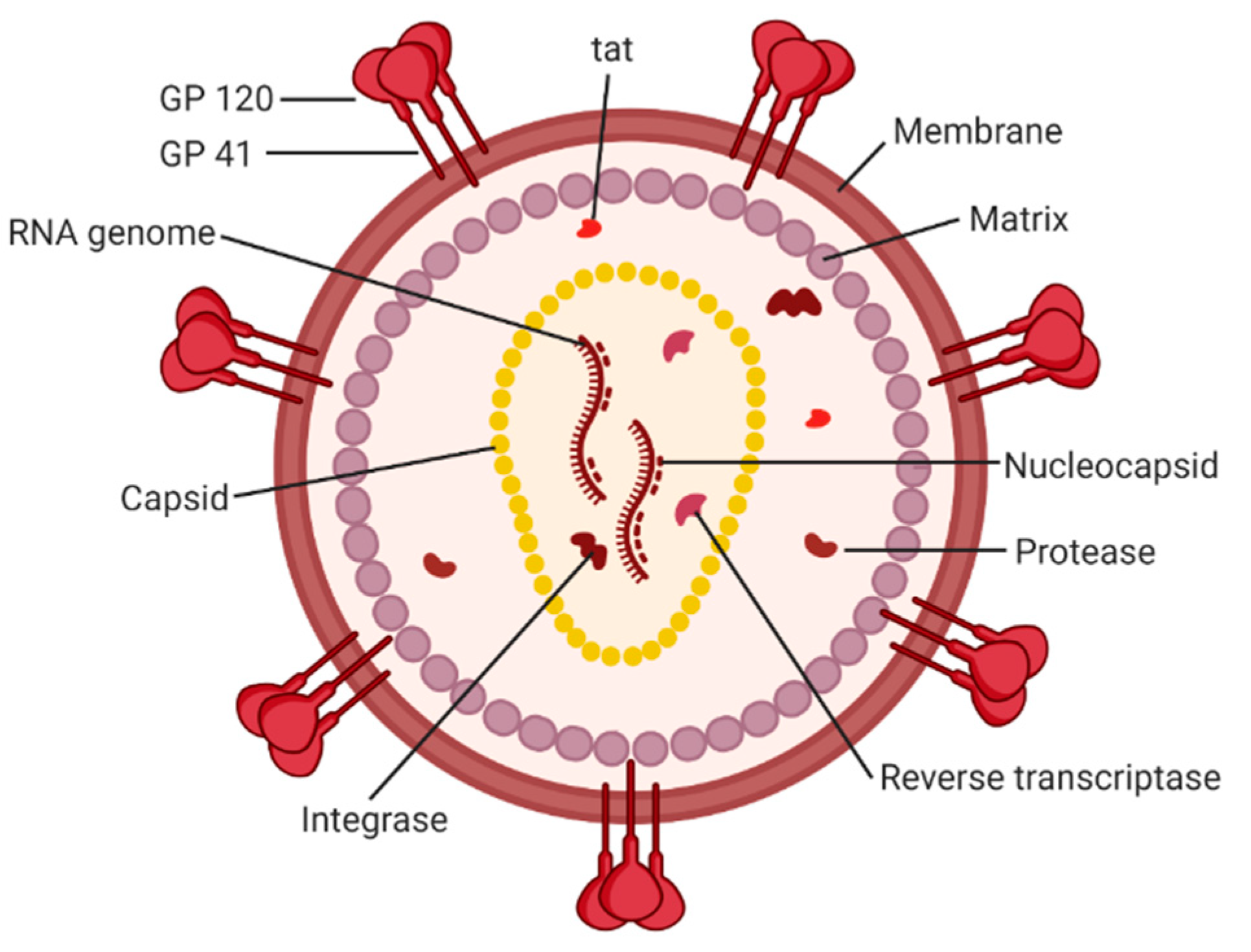
Many types of retrovirus infect animals but only 2 infect humans…
Oncovirus- related to tumours
Lentivirus- act silently like HIV
Lentivirus characteristics
Survive/dormant in an infected human for long time (10-15yrs)- no symptoms
Can replicate quickly- reach high level of copies until impossible to control
4 routes of transmission of retrovirus?
Blood
Semen
Vaginal fluids
Breast feeding
(Not through, air, dust or vomitting)
Etiopathogeneis of hiv
Condense slide 17 18 24 25
5 phases of infection of HIV TO cd4
4 Functions of T CD4 lymphocytes?
Macrophage activation
Induce formation of natural killer cells
Induce formation of B cells
Stimulates segregation of products- stimulates growth and differentiation of all types of lymphoid cells
When they decrease, opportunistic infections appear
What are the 3 phases of HIV infection
Primary- asymptomatic or symptomatic after 10-14 days
Viral replication
Silent period- up to 10 yrs, gradual deterioration of immune system, pre aids state
Symptoms of primary phase?
Fever
Adenopatías
Throat pain
Cutaneous rash

What occurs in the viral replication phase?
8-12 weeks- copies of virus visible in blood test
Copies distributed throughout body- specially lymphoid organs
Decreased rates of T CD4 lymphocytes
Natural immune response controls spread from 1 week to 3 months but doesn’t destroy virus completely
What are the symptoms of Pre- AIDS state?
Diahorrea
Fever
Oral candidiasis
Weight loss
What are opportunistic infections?
Severe infections by agents that usually don’t causes any diseases in immunocompetent individuals
Presence important in diagnosis
What are characteristics of AIDS?
Opportunistic infections
Kaposi sarcoma
B cells lymphoma
Neurological symptoms- caused by opportunistic infections in neurological cells or direct invasion of viral cells to brain- usually appears in final stages- dementia if advanced (common)
What factors effect when the disease is developed?
Age
Sex
Initial diagnosis
Immune status- t lymphocytes response decreases with time
Opportunistic infection- bacterial