SCIENCE 9 LESSON 2.1 RADIATION & HALF-LIFE
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
examples of radioactive materials in everyday life
smoke detectors (Americium-241), nuclear energy, Food irradiation
This man discovered and named invisible high-energy emissions as X rays in 1895
Wilhelm Roentgen
what numbers seem to favor nuclear stability?
even numbers and the "magic" numbers 2, 8, 20, 28, 50, 82, 126
Most common particles emitted by radioactive materials
alpha, beta, gamma, neutron
Types of Nuclear Radiation
alpha, beta, gamma
Electron Capture Equation and definition
basically same as beta emission except baliktad
-atomic nucleus absorbs one of its inner orbiting electrons causing a proton in the nucleus to convert into a neutron.
-emits X-rays
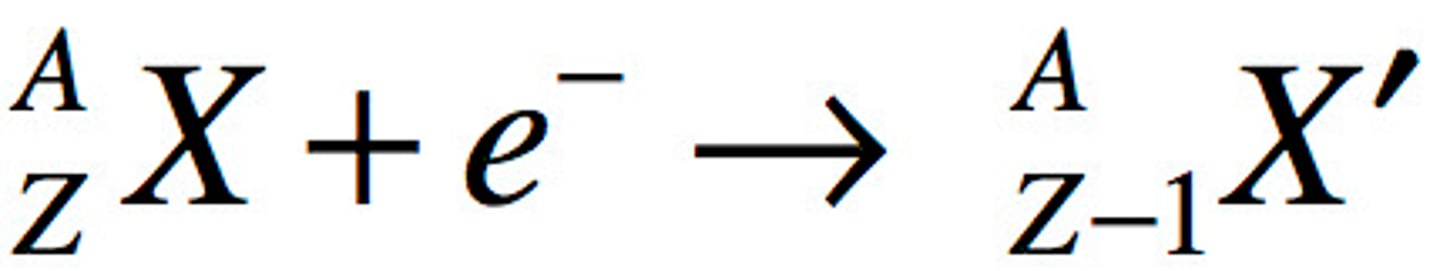
Transmutation
changing one element to another through radioactive decay
induced transmutation
Nucleus of an unstable isotope (radionuclide) is struck with a high velocity charged particle.
Half-life
amount of time for half of a sample of a radioactive element to decay into something else
t
elapsed time
This man accidentally discovered pitchblende emitted radiation on its own without any external energy source like sunlight.
Henri Becquerel
when does alpha decay occur?
in nuclei with Z > 83
when does beta decay occur?
nuclei with a high neutron to proton ratio
when does electron capture decay occur?
heavier elements that have a low neutron to proton ratio
what should you base the number of SF on in solving for half life?
based on what is asked
nuclear chemistry
study of the structure of atomic nuclei and the changes they undergo
Isotopes
atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
Radioisotopes
emit radiation to attain more stable atomic configurations in a process called radioactive decay
Band of Stability
the location of stable nuclei when number of protons and neutrons are plotted
Location of radioactive isotopes on band of stability
outside band of stability
At what number protons do elements become unstable?
83
Alpha Decay definition and equation
- release of 2 protons and 2 neutrons
- largest and slowest, least penetrating
- changes an element to a different element with a lower atomic mass and number
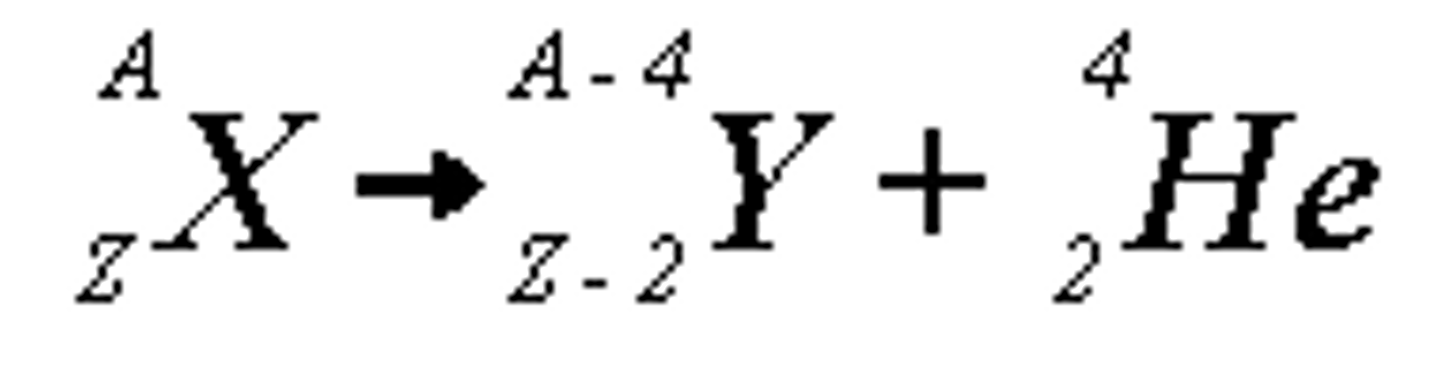
Beta Radiation definition
- Two types
- Decay of a neutron into proton and electron
- Decay of a proton into a neutron and positron
- faster than alpha particles
Beta Emission Equation
mass number stays the same, proton number increases by one
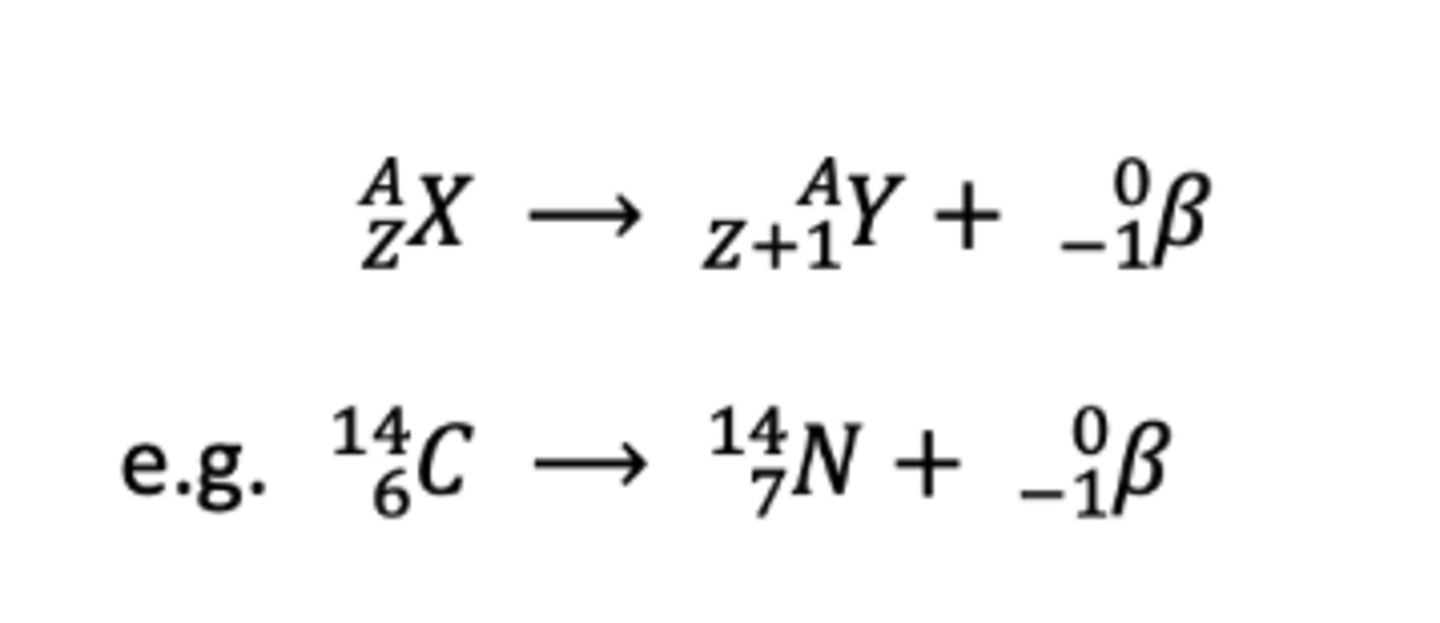
Positron Emission Equation
Mass number stays the same, proton number decreases by one
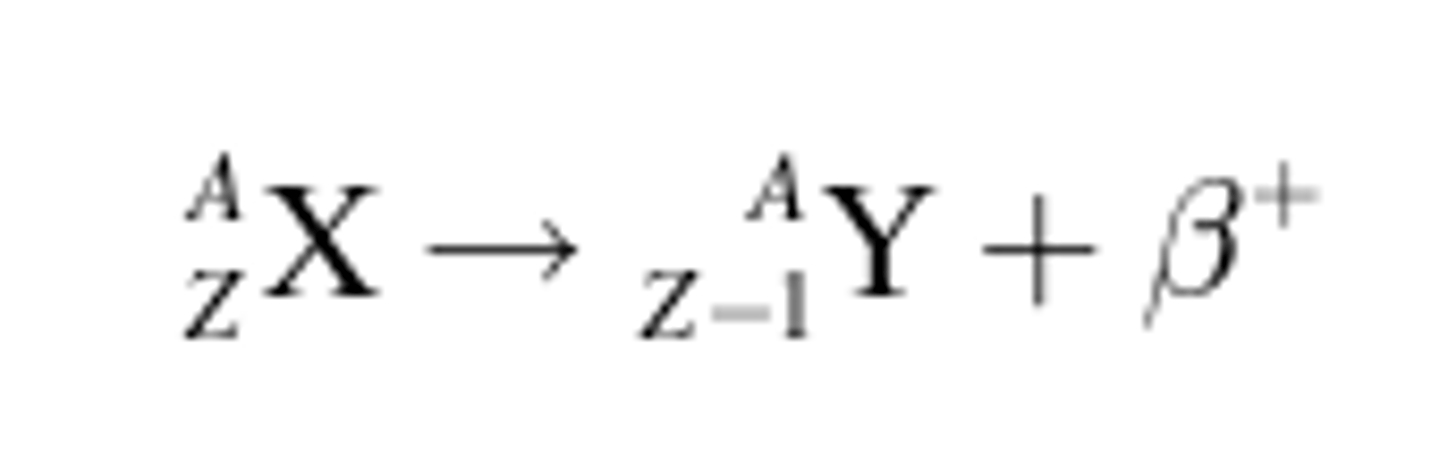
Gamma Radiation Emission Definition
- not a particle
- electromagnetic wave
- no mass no charge
- very fast
- follows other types of decay
what can stop gamma radiation
several centimeters of lead
Gamma radiation emission equation
Element -> Element + gamma ray
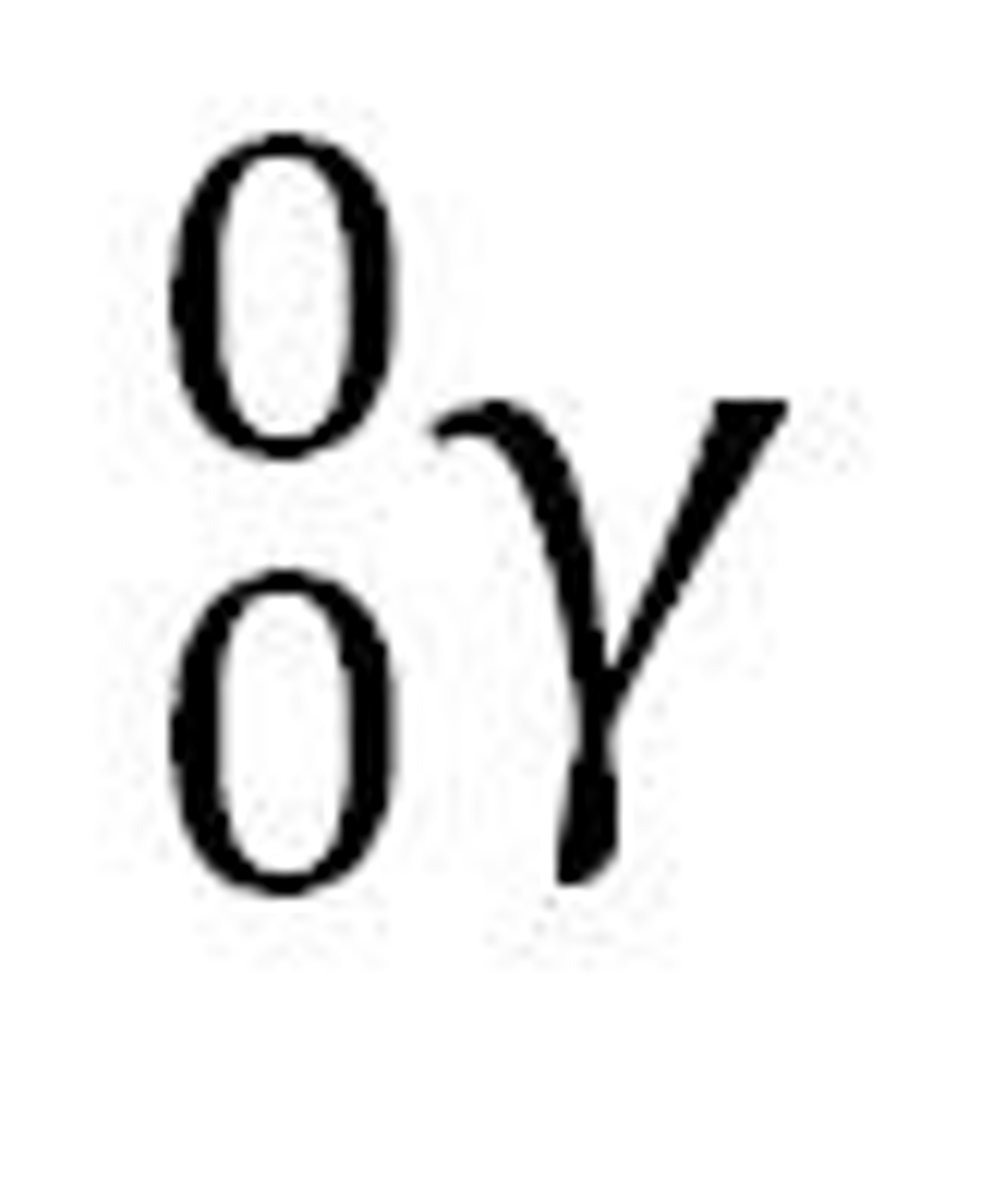
Natural Transmutation
➢Occurs naturally as a radioisotope decays to become more stable
Half-life formula
N(t) = No(1/2)^t/t1/2
N(t)
quantity remaining
No
Initial quantity
t1/2
half life of material
pitchblende
a uranium mineral which was found to produce a photographic image even through black paper without any external energy
These 2 scientists studied radioactive materials, specifically pitchblende
Marie and Pierre Curie
What did Marie and Pierre Curie deduce after studying pitchblende?
it must contain traces of some unknown radioactive component that was far more radioactive than uranium
when does positron decay occur?
low neutron to proton ratio
Still learning (15)
You've begun learning these terms. Keep up the good work!