Databases - Nick
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Database
An organized collection of information or data that allows for flexibility in organization, displaying, and printing of information.
Purpose of Databases
They take up little room, can be easily edited, and facilitate easier searching and sorting.
Entity
A person, place, thing, or concept about which data can be collected.
Some examples of database tables might be:
a customer table
an employee
a movies table
a smartphone table
a car table
Attribute
Describes the facts, details, or characteristics of an entity.
Attribute Types
Different categories of data such as Text, Number, Date, Time, and Boolean.
Text Attribute
Stores characters or words, including combinations of text and numbers.
Number Attribute
Can store whole numbers (integers) or numbers with decimal places.
Date Attribute
Stores dates in various formats.
Time Attribute
Stores time of day, typically in 24-hour format.
Boolean Attribute
Stores true/false or yes/no answers.
Attribute Size
Limits applied to restrict the amount of storage space for data entries.
Entity Relationship Diagrams
Visual representations of entities (green), attributes (orange), and relationships (yellow).
entityName.attributeName and criteria = “searchCriteria”.
Example: Dog.dog name and criteria = “Olly”
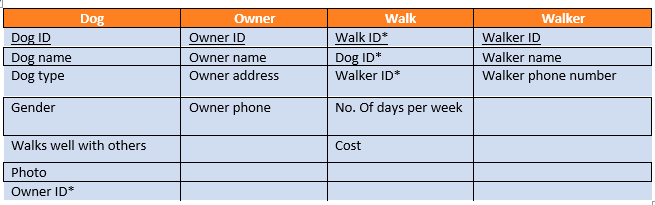
What is the query for the cost of the walk?
walk.cost
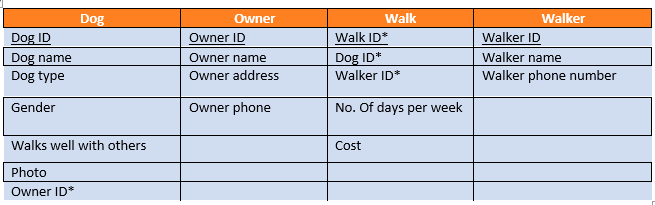
What is the query for dog’s gender if his name is Bruno?
Dog.gender and criteria = “Bruno”
One to Many Relationship
A relationship where a row in table A can have many matching rows in table B, but not vice versa.
Flat File Databases
Useful for small amounts of records but prone to data duplication and human error.
Relational Databases
Tables are linked to prevent data duplication, allowing for complex queries and easier data management.
Validation
Ensures data entered is allowable and sensible through various checks (range, restricted choice, length, presence).
Primary Key
A unique identifier for a single record in a database.
Foreign Key
A field in one table that links to the primary key in another table, creating a relationship.
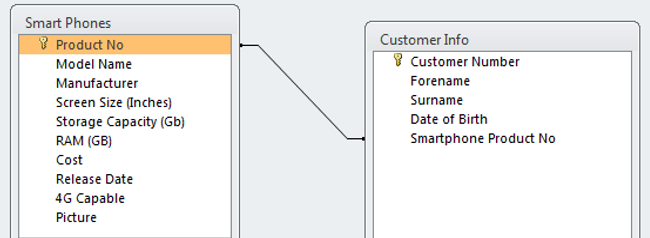
Identify the primary and foreign key
Product No.
Database Query
A request for information from a database, often performed using SQL.
SQL Code
Structured Query Language used to interact with databases, always ending with a semicolon.
SELECT Operation
Queries and retrieves data from one or more tables in a database.
Code Layout:
SELECT attributes (* means all)
FROM table_name
WHERE attribute = criteria
ORDER BY attribute ASC/DESC
Example:
SELECT name, age, house
FROM Pupils
WHERE age < 15
ORDER BY age DESC, house ASC;
This will print out the attributes name, age and house from the pupils table that are less than 15 years old. Results are sorted by the age attribute in descending order and house in ascending order.
INSERT INTO SQL
Command used to insert a new record into a database.
Code Layout:
INSERT INTO table_name
Values (value1, value2, value3, …); [IN ORDER OF ATTRIBUTE]
Example:
INSERT INTO Pupils
VALUES (6, "Jack Lawrie", 18, "Shiel");
UPDATE RECORD
Command used to update existing records in a database.
Code Layout:
UPDATE table_name
SET attribute1 = value1 etc.
WHERE attribute = criteria
Example:
UPDATE Pupils
SET house = “Ben Nevis”
WHERE house = “Nevis”;
DELETE RECORD
Command used to delete a record from a database.
Code Layout:
DELETE_FROM table_name
WHERE attribute = criteria
Example:
DELETE_FROM Pupils
WHERE name = “Bob Jordan”;