BS1030 TOPIC 8: OXIDATIVE PHOPHORYLATION (LECTURE 1)
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
What are the three major metabolic pathways that produce high-energy electrons?
Glycolysis, Citric Acid Cycle (CAC/Krebs cycle), and Fatty Acid Oxidation (FAO).
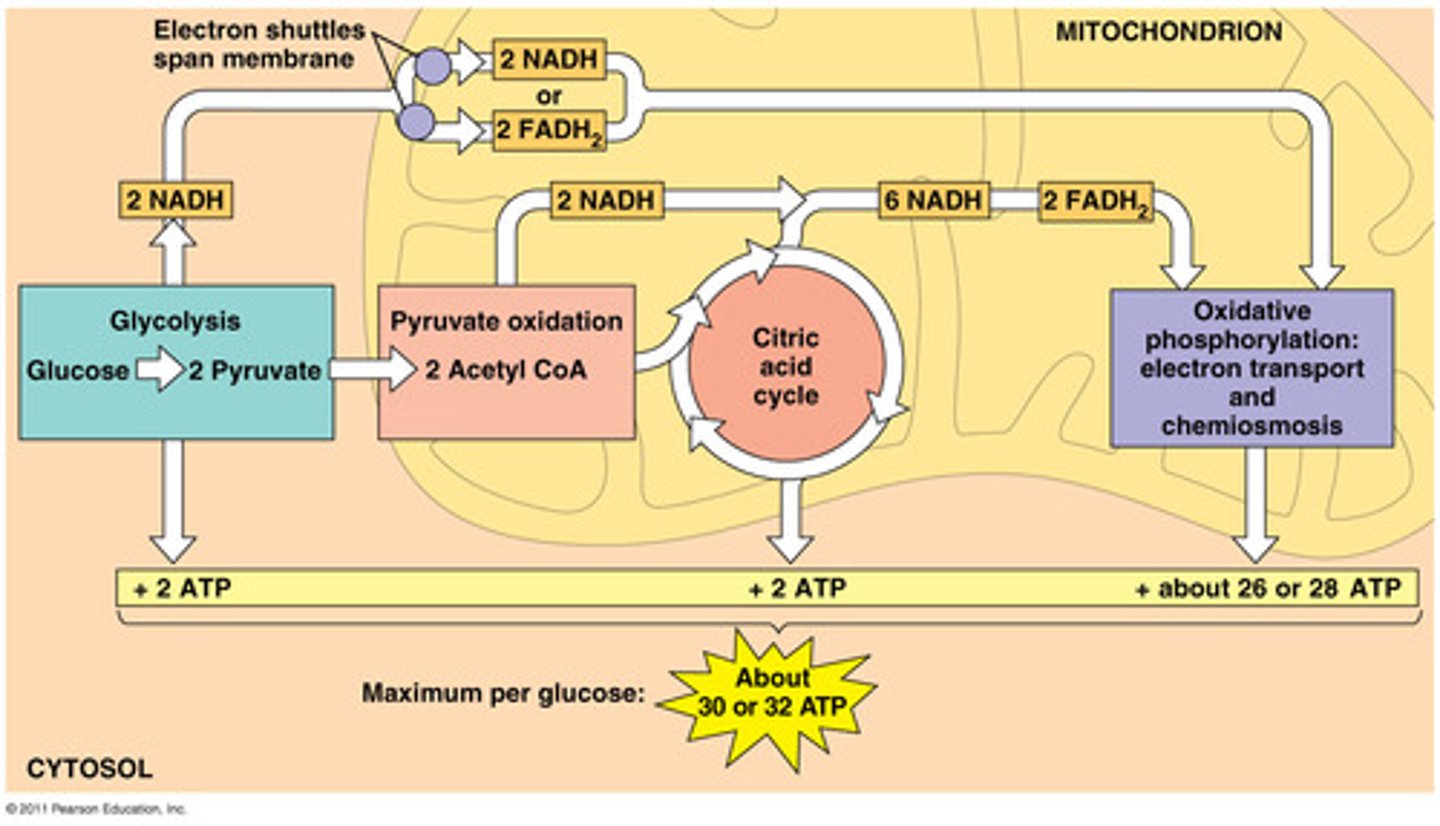
What are the reduced electron carriers produced during metabolism?
NADH and FADH₂.
Why are NADH and FADH₂ considered 'reduced'?
Because they are carrying high-energy electrons, similar to charged batteries.
Where do NADH and FADH₂ travel to release their energy?
To the mitochondrial inner membrane, where the electron transport chain (ETC) is located.
What happens to NADH during reoxidation in the ETC?
NADH is converted to NAD⁺, releasing electrons and H⁺.
What is the result of FADH₂ undergoing reoxidation?
FADH₂ is converted to FAD, releasing electrons and H⁺.
What does oxidative phosphorylation produce?
ATP.
How does the electron transport chain contribute to ATP production?
Energy released from electrons pumps protons (H⁺) across the membrane, creating a proton gradient.
What role does ATP synthase play in ATP production?
It uses the flow of protons back through the membrane to synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi.
Why is the process called oxidative phosphorylation?
Because electrons are passed to oxygen (oxidative) and ATP is made from ADP and Pi (phosphorylation).
What analogy is used to describe the proton gradient created during oxidative phosphorylation?
It is likened to water behind a dam.
What is the function of the Outer Mitochondrial Membrane (OMM)?
The OMM is permeable to small molecules and ions, allowing easy movement through it.
How does the OMM interact with the cytoplasm?
It acts almost like it's continuous with the cytoplasm due to the presence of porins (protein channels).
What is the permeability of the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane (IMM)?
The IMM is impermeable to most molecules, including small ions like H⁺.
Why is the impermeability of the IMM important?
It is essential for creating the proton gradient necessary for ATP production.
What key components are found in the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane?
The IMM contains electron transport chain (ETC) complexes and ATP synthase.
What is the Mitochondrial Matrix?
The central space enclosed by the IMM that contains enzymes for the Citric Acid Cycle and Fatty Acid Oxidation.
What does the Mitochondrial Matrix contain besides enzymes?
It contains mitochondrial DNA, ribosomes, and tRNAs.
What is the endosymbiotic theory?
It explains that mitochondria originated from bacteria that were engulfed by early eukaryotic cells.
Who proposed the endosymbiotic theory?
The theory was proposed by Lynn Margulis.
What evidence supports the endosymbiotic theory?
Mitochondria have their own DNA, divide by binary fission, have double membranes, and possess ribosomes similar to bacterial ribosomes.
What are the key characteristics of the Mitochondrial Genome?
It has 16,569 base pairs, is circular, double-stranded, and lacks chromatin.
How many genes are in the mitochondrial genome?
There are 37 genes total, including 13 protein-coding genes.
What do the mitochondrial genes encode?
They encode components of the respiratory chain (ETC), 22 tRNAs, and 2 rRNAs.
Why can mutations in mitochondrial DNA cause genetic diseases?
Because mitochondria produce essential ETC subunits, mutations can disrupt energy production.
What does sequencing mitochondrial DNA reveal about its origin?
It shows strong similarity to bacterial DNA, particularly with α-proteobacteria.
What is the significance of the double membranes of mitochondria?
The double membranes are consistent with the engulfment process described in the endosymbiotic theory.
What is the role of the Citric Acid Cycle in mitochondria?
It is involved in the metabolic pathway that produces ATP through oxidation of acetyl-CoA.
What is the function of ATP synthase in mitochondria?
ATP synthase synthesizes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate using the proton gradient.
What is the relationship between mitochondria and aerobic respiration?
Mitochondria are responsible for producing ATP through aerobic respiration.
What is the role of fatty acid oxidation in mitochondria?
Fatty acid oxidation is a metabolic process that breaks down fatty acids to produce energy.
What is standard reduction potential (E₀')?
A measure of how easily a molecule gains electrons, indicating its tendency to be reduced.
What does a more positive E₀' indicate?
A stronger tendency to accept electrons.
What does a more negative E₀' indicate?
A weaker tendency to accept electrons.
What is the standard reduction potential of NAD⁺?
E₀' = -0.32 V, indicating it does not strongly want electrons.
What is the equation linking reduction potential to free energy?
ΔG₀' = -n F ΔE₀'.
What do the variables in the equation ΔG₀' = -n F ΔE₀' represent?
n = number of electrons transferred, F = Faraday constant (96,484 C mol⁻¹), ΔE₀' = difference in reduction potentials.
What is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain (ETC)?
Oxygen (O₂).
What is the overall reaction of NADH oxidation in the ETC?
½ O₂ + NADH + H⁺ ⇌ H₂O + NAD⁺.
How do you calculate ΔE₀'?
ΔE₀' = E₀'(acceptor) - E₀'(donor).
What is the ΔE₀' when comparing NADH and O₂?
ΔE₀' = 0.82 - (-0.32) = 1.14 V.
What does a large positive ΔE₀' value indicate?
Strong electron flow from NADH to O₂ and a lot of energy released.
How do you calculate ΔG₀' for NADH oxidation?
ΔG₀' = -n F ΔE₀', with n = 2 electrons and ΔE₀' = 1.14 V.
What is the approximate energy released when 1 mol of NADH is oxidized by oxygen?
ΔG₀' ≈ -220 kJ mol⁻¹.
How much energy is required to make 1 ATP from ADP + Pi?
ΔG₀' = +30.5 kJ/mol.
What is the theoretical maximum ATP yield from NADH oxidation?
Approximately 7 ATP (220 kJ ÷ 30.5 kJ).
What is the actual ATP yield from NADH in real cells?
Approximately 2.5 ATP due to non-standard conditions and energy losses.
What factors contribute to the lower ATP yield in cells compared to theoretical maximum?
Non-standard conditions, energy lost as heat, and proton leaks.
What is the primary function of the Electron Transport Chain (ETC)?
To transfer electrons in small steps to prevent energy loss as heat.
What happens if NADH transfers all its electron energy to O₂ in a single step?
Too much energy would be lost as heat.
How many main protein complexes are in the ETC?
There are 4 main protein complexes.
What are the mobile electron carriers in the ETC?
Ubiquinone (CoQ) and Cytochrome c.
What is the role of the proton gradient created by the ETC?
It stores energy used to synthesize ATP when protons flow back through ATP synthase.
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
The process of making ATP from ADP + Pi using the energy from the proton gradient.
What is the function of Complex I in the ETC?
It accepts electrons from NADH, transfers them to ubiquinone (CoQ), and pumps 4 H⁺ into the intermembrane space.
What does Complex II do in the ETC?
It accepts electrons from FADH₂, transfers them to ubiquinone (CoQ), but does not pump protons.
What is the significance of Complex III in the ETC?
It accepts electrons from CoQ, passes them to cytochrome c, and pumps 4 H⁺.
What occurs at Complex IV of the ETC?
It accepts electrons from cytochrome c, transfers them to oxygen (O₂), forming water, and pumps 2 H⁺.
What happens if oxygen (O₂) is absent in the ETC?
The entire ETC stops functioning.
What is the flow of electrons in the ETC starting from NADH?
NADH → Complex I → CoQ → Complex III → Cyt c → Complex IV → O₂ → H₂O.
What is the flow of electrons in the ETC starting from FADH₂?
FADH₂ → Complex II → CoQ → Complex III → Cyt c → Complex IV → O₂ → H₂O.
How do electrons move through the ETC?
Electrons always move from lower E₀' to higher E₀'.
Why does oxygen pull electrons through the ETC?
Oxygen has the highest E₀', which drives the movement of electrons.
What is the result of energy released at each step of the ETC?
It is used to pump protons (H⁺) across the membrane.
What is the role of Ubiquinone (CoQ) in the ETC?
It is a lipid-soluble molecule that carries electrons from Complex I and II to Complex III.
What is the role of Cytochrome c in the ETC?
It is a small soluble protein that carries electrons from Complex III to Complex IV.
What is the overall chemical equation for the ETC?
NADH and FADH₂ donate electrons to the chain, ultimately reducing O₂ to H₂O.
What is the significance of the proton gradient created by the ETC?
It drives ATP synthesis as protons flow back through ATP synthase.
What is the role of oxygen in oxidative phosphorylation?
Oxygen (O₂) is the final electron acceptor and is converted into water (H₂O).
What happens to the electron transport chain (ETC) if oxygen is absent?
The ETC stops functioning.
What is created as electrons flow through the electron transport chain?
A proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
What is the proton motive force (pmf)?
The energy stored in the proton gradient, consisting of a chemical gradient and an electrical gradient.
How do protons return to the mitochondrial matrix?
Protons can only return via ATP synthase.
What is the function of ATP synthase?
It converts ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) into ATP using the energy from protons flowing through it.
What process is powered by the mechanical rotation of ATP synthase?
Chemiosmosis.
What happens to protons during electron transport?
They are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, creating an electrochemical gradient.
What is the significance of the electrochemical gradient?
It creates stored energy that drives ATP synthesis.
What are the components of the proton motive force?
The chemical gradient (H⁺ concentration difference) and the electrical gradient (charge difference).
What is the result of the accumulation of protons in the intermembrane space?
The intermembrane space becomes high in H⁺ (positive), while the matrix becomes low in H⁺ (negative).
What initiates the flow of electrons through the electron transport chain?
Electrons from NADH and FADH₂.
What are the main complexes involved in the electron transport chain?
Complex I, CoQ, Complex III, Cyt c, Complex IV.
What is the outcome of the energy released during electron transport?
The energy is used to pump protons from the matrix to the intermembrane space.
What is the final product of oxidative phosphorylation?
ATP, produced from ADP and Pi through the action of ATP synthase.
What initiates the electron transport chain (ETC)?
Electrons start at high energy in NADH/FADH₂.
What is the sequence of complexes in the ETC?
I → II → III → IV → O₂
What is the role of the energy lost by electrons in the ETC?
It is used to pump protons (H⁺) across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
How many protons does Complex I pump into the intermembrane space?
4 H⁺
What is the difference in proton pumping between Complex I and Complex II?
Complex I pumps protons; Complex II does not pump protons.
What generates the proton motive force (pmf) in mitochondria?
The difference in H⁺ concentration across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
What are the two major parts of ATP synthase?
F₀ (in the inner mitochondrial membrane) and F₁ (in the matrix).
What is the function of the c-ring in ATP synthase?
It rotates when H⁺ enters, providing a proton channel.
What are the three states of the β subunits in ATP synthase?
Loose (L), Tight (T), and Open (O).
What happens in the T state of the β subunit?
It binds ADP + Pi and forms ATP.
How does the γ subunit affect ATP synthesis?
Its rotation changes the states of the β subunits, facilitating ATP release and binding.
What is the ATP yield from NADH and FADH₂?
NADH yields 2.5 ATP; FADH₂ yields 1.5 ATP.
What is respiratory control in oxidative phosphorylation?
It regulates ATP synthesis based on ADP availability; high ATP slows down ATP synthase.
What are uncouplers in oxidative phosphorylation?
They provide an alternative path for protons to flow back into the matrix, bypassing ATP synthase.
What is an example of a chemical uncoupler?
DNP (2,4-Dinitrophenol)
What is the role of protein uncouplers like UCP1?
They are used for thermogenesis, allowing heat production instead of ATP.
What is the effect of uncouplers on ATP production?
They collapse the proton gradient, speeding up the ETC but reducing ATP production.