Econ 206 - Chapter 16
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Canadian Payments System - Large Value Transfer System (LVTS)
Electronic, real time net settlement network operated by Payments Canada, designed for time critical transactions, allowing for people to know real time large value transactions
Account for less than 1% of total number of transactions, but account for 87% of value of transactions
How can a financial institution participate directly in LVTS?
Member of Payments Canada
Uses SWIFT
Maintains settlement account at BoC
Has agreements regarding borrowing from BoC and can pledge eligible collateral
Systemic risk and LVTS
the risk to the entire payments system due to the inability of one financial institution to fulfill its payment obligations in a timely fashion
How LVTS helps eliminate Systemic risk
LVTS participants can only make payments if they have real time
positive settlement balances in their accounts with BoC
posted collateral, OR explicit lines of credit with other LVTS participants
Multilateral Netting
when only the net credit or debit position of each participant vis-a-vis all other participants is calculated for settlement at the end of the payment cycle
Overnight Interest rate
At end of day, some LVTS members are short on settlement balances, and others have balances left over, they will borrow and lend to each other on the overnight money market
The interest rate on these overnight loans is the overnight interest rate
Canadian Payment Systems - Automated Clearing Settlement System (ACSS)
Electronic payment system also operated by Payments Canada
Provides settlement to paper-based payment items (cheques, money orders) and small value electronic payments (e.g debit card transactions)
ACSS aggregates payments and calculates net amounts to be sent to from settlement accounts with BoC
BoC Policy Rate
The target for the overnight interest rate that is announced by the BoC, also main target BoC adopts when conducting monetary policy
How BoC implements monetary policy with Policy Rate
by changing the policy rate in order to influence other short-term interest rates and the exchange rate
BoC’s overnight rate objective
Keep overnight rate within operating band of 50 basis points (half of 1%) or midpoint of operating band
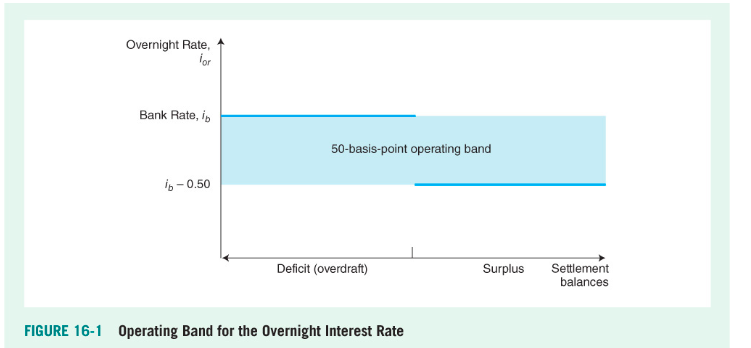
The Bank Rate
The upper limit of the operating band
The interest rate the BoC charges LVTS participants that require an overdraft loan (advance) to cover negative settlement balances with BoC at end of banking day
Lower limit of operating band is?
the rate the BoC pays to LVTS participants with positive settlement balances at the end of the day
BoC Standing Liquidity facilities - Lending Facility
LVTS participants can obtain overnight liquidity in case of shortage in order to bring settlement balance with BoC close to zero
BoC Standing Liquidity facilities - Deposit Facility
LTVS participants can make deposits in the case of excess liquidity in order to bring settlement balance with BoC close to zero
How BoC puts Ceiling and Floor on overnight rate
If overnight rate increases towards upper limit of operating band, the BoC will lend at the bank rate (ceiling)
If the overnight rate falls towards lower limit of operating band, the BoC will accept deposits from LVTS participants at the lower limit rate (bank rate - 50 basis points) (floor)
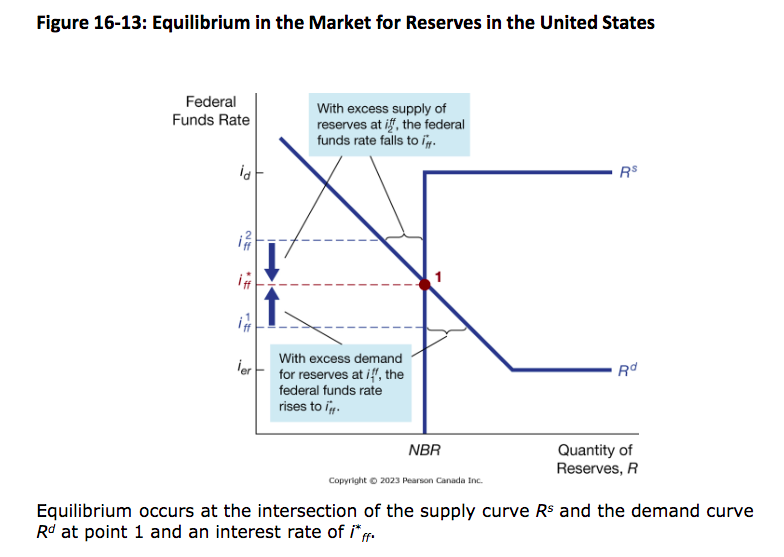
Market for Settlement Balances/Reserves
Where the overnight interest rate is determined, chosen through the market equilibrium where quantity of reserves demanded equals quantity supplied)
Demand Curve for Reserves
Inverse relationship between overnight interest rate and quantity demanded, but demand curve becomes flat at certain point since banks become indifferent to holding reserves beyond this point
Supply Curve Two components - Non-borrowed reserves
the amount of reserves that are supplied by BoC’s open market operations
Supply Curve Two components - Borrowed Reserves
the amount of reserves borrowed from the BoC
Supply Curve of Reserves - when Ior is less than Ib
Banks will not borrow from BoC since it is not worth it to borrow at a higher rate, hence supply of reserves = amount of NBR’s since no one is borrowing
Why is supply curve vertical at whatever the amount of NBR’s?
Since BR’s are zero, reserves only depend on NBR’s, which is fixed
Why is supply curve horizontal at Ior = Ib
happens at bank rate (ceiling), the interest rate has one above Ib, so banks borrow unlimited reserves from BoC at point Ib and lends them at a higher rate, and BoC supplies as many reserves as needed at Ib
How BoC Operating Procedure Limit Fluctuations in Overnight interest rate
By establishing a limit for the fluctuations to between the deposit rate (lower band) and the bank rate (upper band)
Leftward shift in demand curve lowers overnight rate to the minimum deposit rate
A rightward shift in demand curve raises overnight rate to the maximum bank rate
BoC approach to Monetary Policy - Inflation target
Keep inflation rate between target range of 1%-3%, with 2% being most desirable outcome
Inflation rates/targets in Canada trend
rate of inflation has significantly reduced over time and has achieved inflation targets
What determines monetary conditions in which the economy operates?
The level of short-term interest rates and the exchange rate of the CAD (all affected by changes in overnight interest rate)
*slide 19 come back to because prof is lazy and can’t finish slide explanations properly
Exchange rate
the units of foreign currency per one Canadian dollar
If amount of units of foreign currency decreases, implies CAD depreciates
How BoC keeps Inflation rate from falling below limit of target range
Decrease in target rate for overnight interest rate
causes dollar and interest rate to decrease
which causes Increase in aggregate demand, as prices/cost increases and so does inflation
How BoC keeps Inflation rate from moving above limit of target range
Increase in target for overnight interest rate
causes dollar and interest rates to increase
which causes decrease in aggregate demand, as prices/costs decrease, so does inflation
How is it that changes in short-term nominal interest rates affect real interest rates?
Assumption of ‘sticky prices’ meaning nominal prices don’t adjust immediately to changes in money supply, allowing the BoC some control over interest rates
4 Conventional Monetary Policy Tools
Open market purchases
Open market sales
Settlement balances management
BoC lending
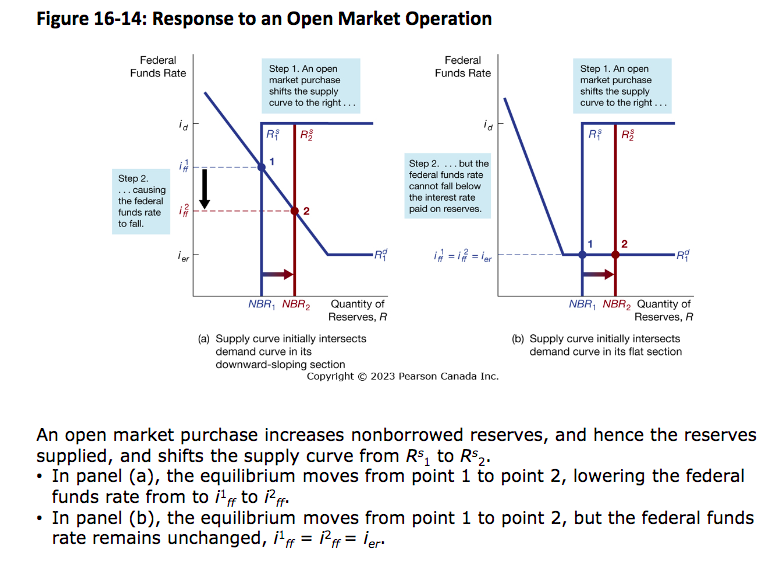
Open market purchase effects
expands bank reserves and monetary base
Lowers short-term interest rates
Raises money supply
Open market sales effects
Shrinks bank reserves and monetary base
Raises short-term interest rates
Lowers money supply
BoC Special Purchase and Resale agreement
BoC purchases securities that are repurchased by the seller the next day
if overnight funds are traded above target overnight interest rate, BoC enters into special purchase at the target price, and relives undesired upward pressure on the overnight interest rate
BoC Sales and Repurchase Agreement
BoC sells securities and then purchases it back the next day
If overnight funds are traded at a rate below the target overnight interest rate, BoC sells securities and removes cash from the market, which means banks need to borrow from each other more and undesired downward pressure on overnight interest rate is removed
Settlement Balances Management - Drawdowns
BoC moves deposits from commercial banks to its account
This removes money from the banking system (bank loses reserves) and settlement balances fall
Settlement Balances Management - Redeposits
BoC moves money from their account to commercial banks
This adds money to the banking system (banks gain reserves) and the settlement balances rise
How do standing lending facilities place a ceiling on the overnight interest rate?
Since banks can always borrow reserves from BoC as the bank rate, they will never pay more than that in the overnight market
BoC as lender of last resort
provides emergency lending assistance (against eligible collateral) preventing bank failures and financial panics
Zero-lower-bound problem
Banks typically lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth, but when the interest rate hits zero, interest rate changes become ineffective as people hoard cash since they will not get a good return with lower interest rates
Thus efforts to stimulate economy with lower interest rates is blocked which can hinder recovery from recessions/economic slowdown
Nonconventional monetary policy tools - Liquidity provision
Standing lending facility expansion
Standing term liquidity facility
New lending programs
Nonconventional monetary policy tools - Large-Scale Asset (bond) Purchase/Quantitative Easing
The large-scale purchase of Government of Canada bonds, leading to an increase in the monetary base
Non-conventional monetary policy tools - Forward Guidance/Management of Expectations
In order to lower long-term interest rates and provide more stimulus to the economy, the BoC commits to keeping the policy rate at zero for an extended period of time
This lowers market’s expectations of future short-term interest rates, also causing long-term interest rates to fall
Non-conventional monetary policy tools - Negative Interest rates on reserves
BoC can charge banks for depositing their funds, banks will look for better uses of their money and thus will lend it out more rather than losing money at the central bank
Monetary Policy Tools of the Federal Reserve (US)
Federal funds rate
Open market operations
Discount lending
Required reserves
Interest on reserves
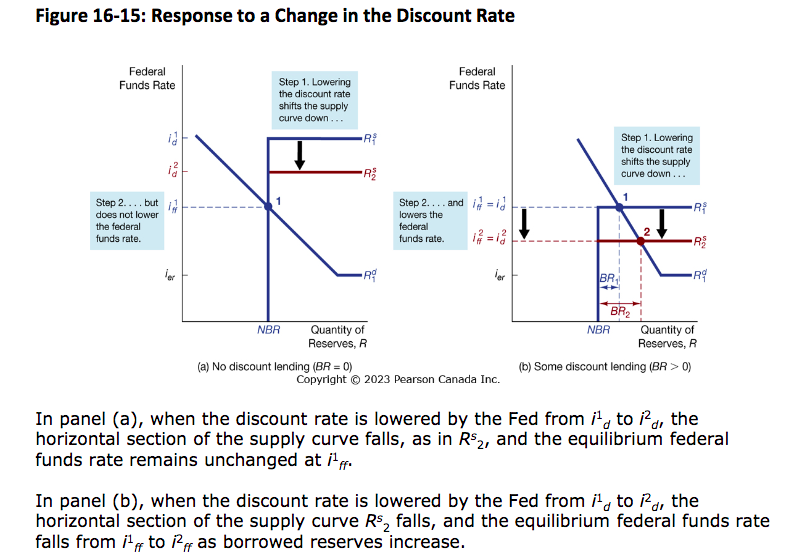
Discount window (US)
the facility at which US banks borrow reserves from the Federal Reserve
Discount rate (US)
the interest rate charged for loans from Discount window
Primary indicator of Monetary policy stance in US
the federal funds rate (interest rate on overnight loans of reserves that banks trade amongst themselves)
Equilibrium for market for reserves in US
Response to open market operation (US)
Response to change in discount rate (US)
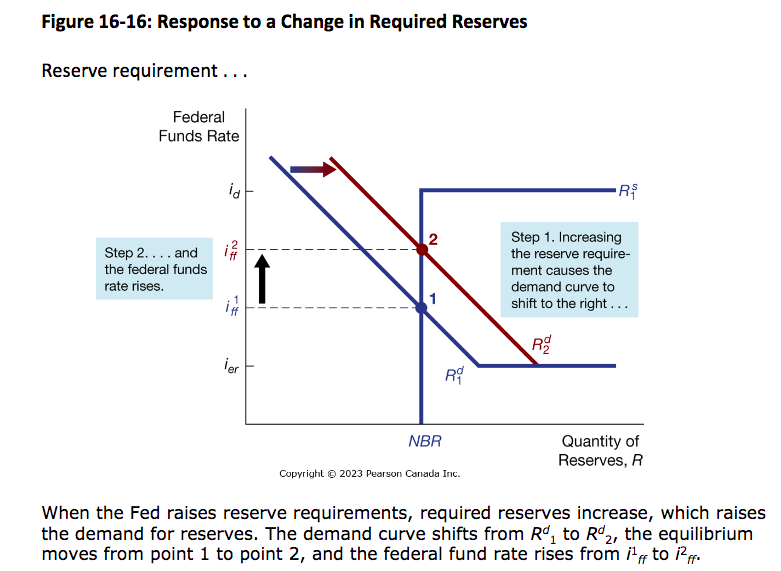
Response to a change in required reserves (US)
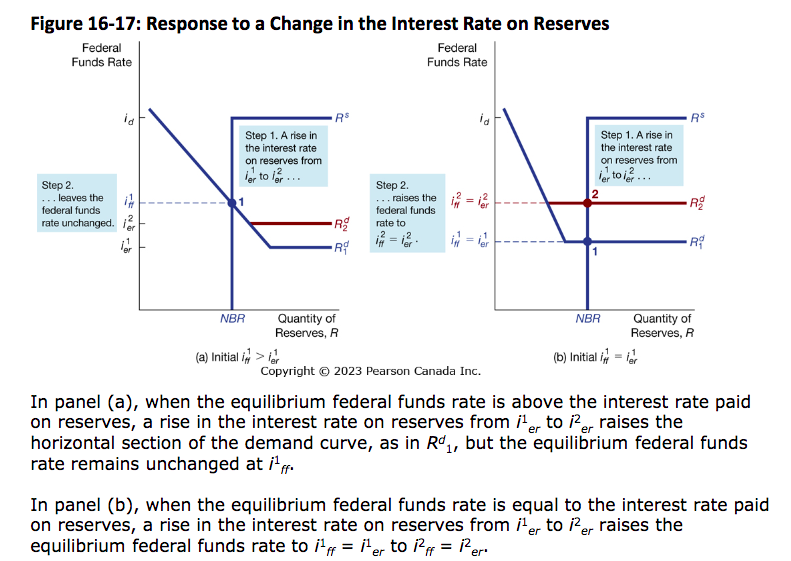
Response to a change in the interest rate on reserves (US)
How European Central Bank (ECB) signals stance of monetary policy
setting target financing rate which in turn sets a target for the overnight cash rate (interest-rate for very short term interbank loans)