Biology 110 Exam 2 Terms
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
membrane transport
the movement of ions and molecules across biological membranes
selective permeability
the property of membranes that allows the passage of certain ions or molecules but not others
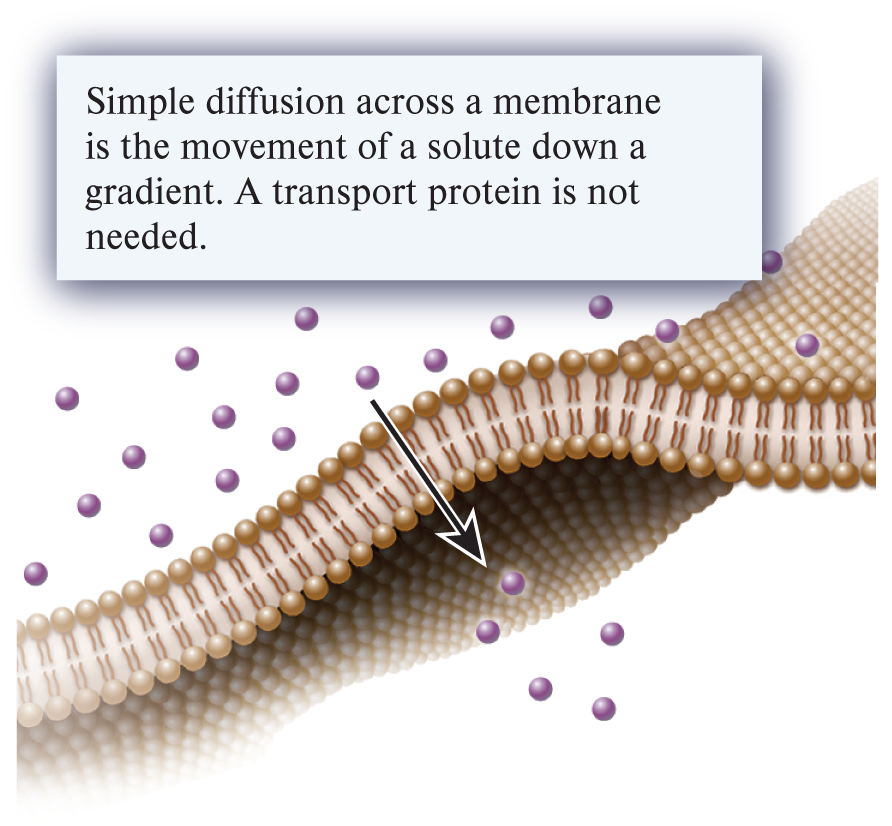
simple diffusion (1 of the 3 ways substances can move across a membrane)
When a substance moves across a membrane from a region of high concentration to a region of lower concentration by passing directly through the phospholipid bilayer; this movement can also be referred to as down a concentration gradient or downhill movement
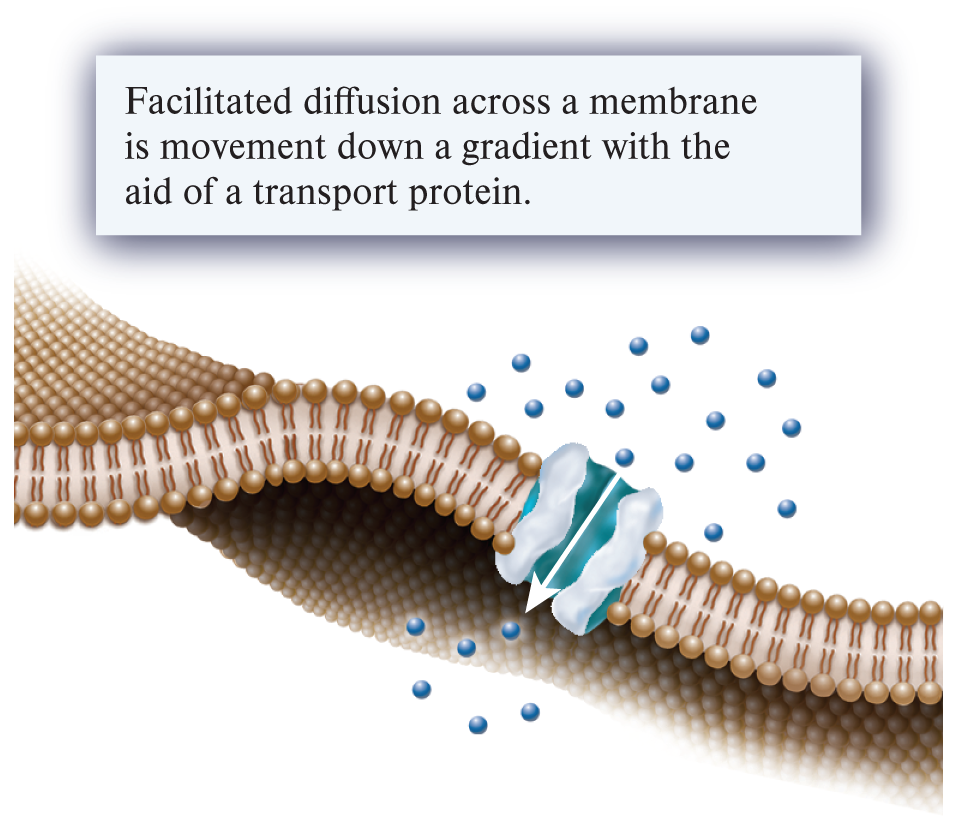
fascilated diffusion (1 of the 3 ways substances can move across a membrane)
A mechanism of passive transport in which a transport protein provides a passageway for a substance to cross a membrane from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration.
passive transport (ex. simple and fascilated diffusion)
The movement of a substance across a membrane from an area of high concentration to one of lower concentration; does not require an input of energy
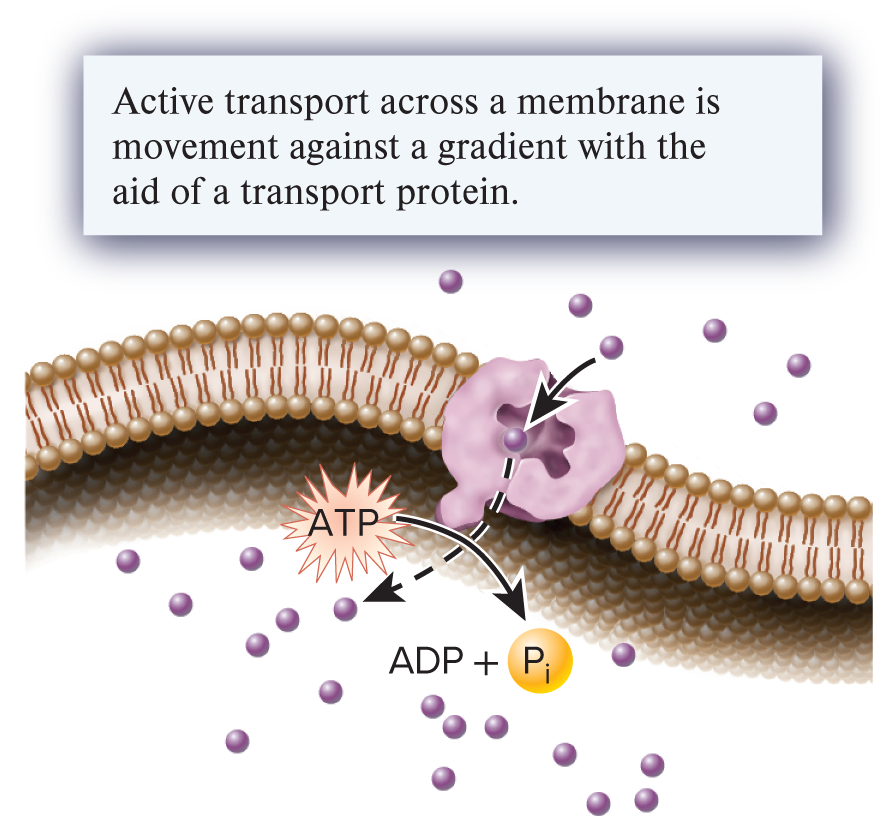
active transport (1 of the three ways substances can move across the membrane)
The transport of a substance across a membrane from an area of low concentration to one of higher concentration with the aid of a transport protein; requires an input of energy
solute
a substance dissolved in liquid
solvent
The liquid in which a solute is dissolved
4 factors that affect the ability of solutes to pass through a phospholipid bilayer
Size-small solutes cross bilayers faster than larger ones
Polarity-nonpolar solutes cross bilayers faster than polar ones
Charge-noncharged solutes cross bilayers faster than charged ones
Concentration-the rate of movement of a solute across a membrane will be higher when its concentration is higher
transmembrane gradient or concentration gradient
A situation in which the concentration of a solute is higher on one side of a membrane than on the other; universal feature for all living cells
electrochemical gradient
A dual gradient across a membrane, having both electrical and chemical components; determines the direction in which ions will move; occurs with solutes that have net positive or negative charge
isotonic
Condition in which the solute concentrations on both sides of a membrane are equal, which does not cause a cell to swell or shrink.
hypertonic
Condition in which the concentration of solutes outside a cell is higher, which causes the cell to shrink due to osmosis of water out of the cell.
hypotonic
Condition in which the concentration of solutes outside a cell is lower, which causes the cell to swell due to the uptake of water via osmosis.
osmosis
The movement of water across a membrane to balance solute concentrations. Water diffuses from a solution that is hypotonic (lower solute concentration) into a solution that is hypertonic (higher solute concentration);
plasmolysis
The shrinkage of algal or plant cytoplasm that occurs when water leaves the cell by osmosis, with the result that the plasma membrane no longer presses on the cell wall.
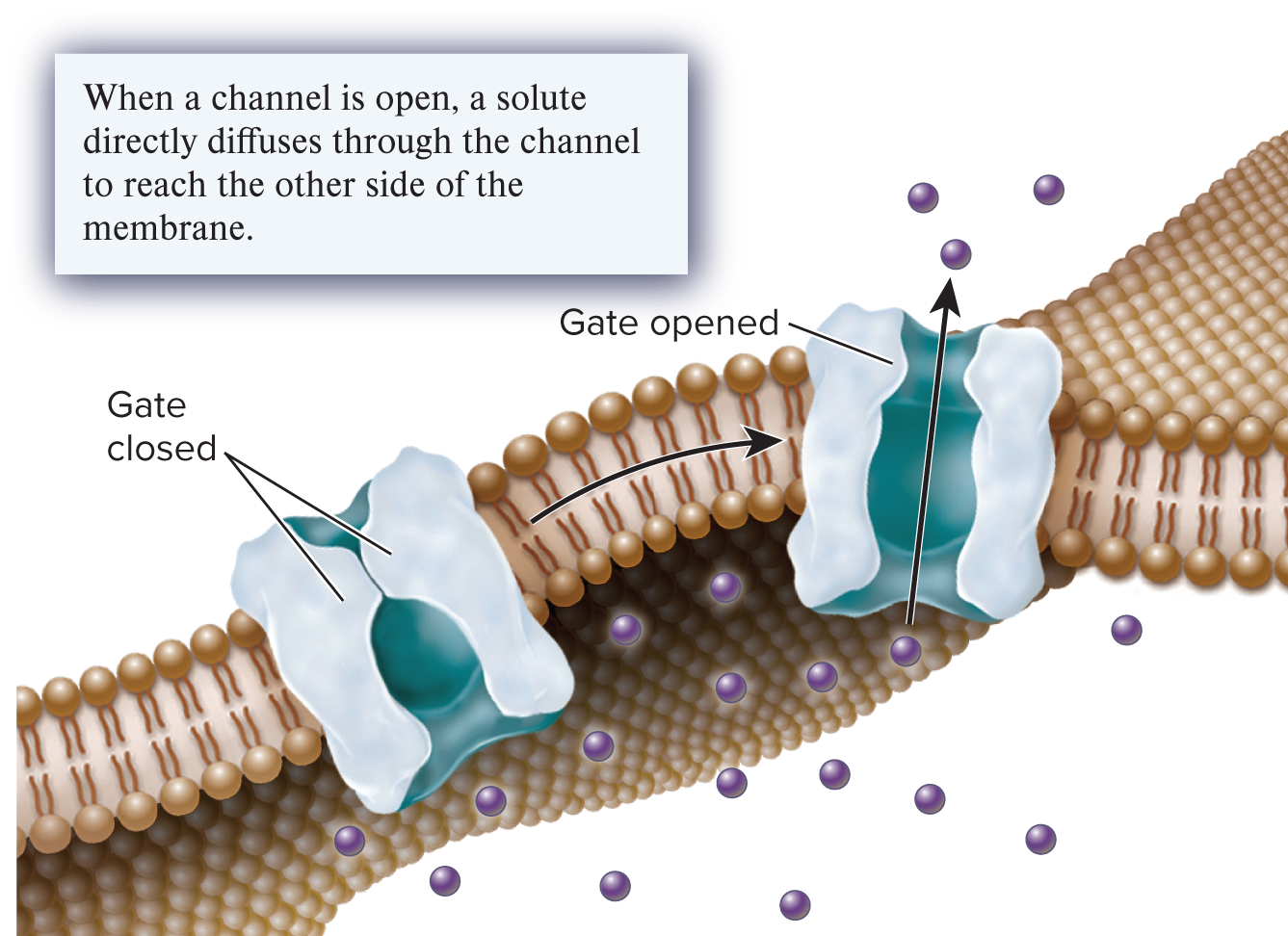
channel
A transmembrane protein that forms an open passageway for the facilitated diffusion of ions or molecules across a membrane.
What is the purpose of gating?
to regulate the function of channels, allowing them to be open or closed
gated
A property of many channels that allows them to open and close to control the movement of solutes across a membrane.
ligand
An ion or molecule that binds to a protein, such as an enzyme, a receptor, or a channel; the gated channels are controlled by these; important in the transmission of signals between neurons and muscle cells or two neurons
aquaporin
A transport protein in the form of a channel that allows the rapid diffusion of water across the cell membrane.
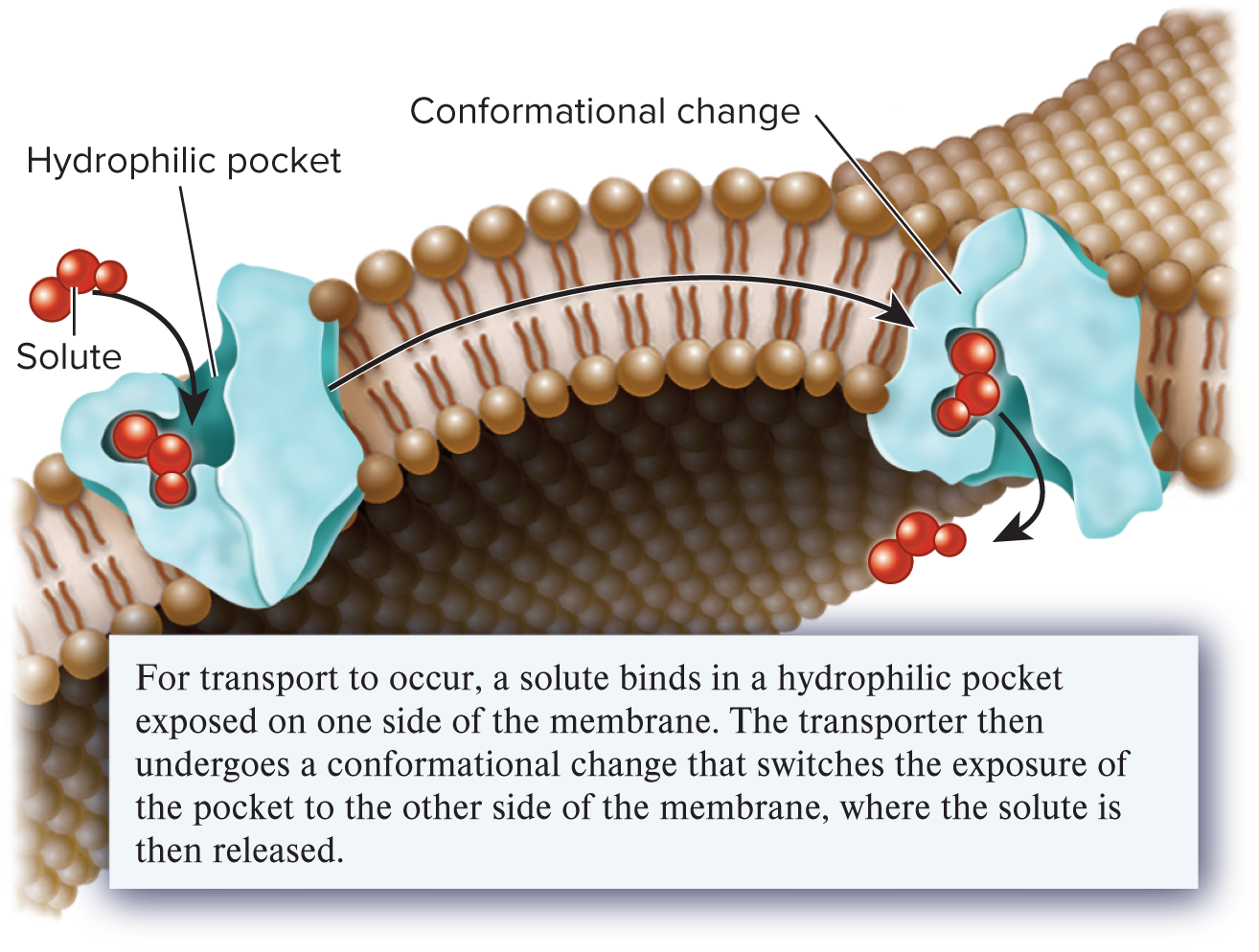
transporters
A transmembrane protein that binds a solute and undergoes a conformational change to allow the movement of the solute across a membrane; also called a carrier; provide the principle pathway for the uptake of organic molecules, such as sugars, amino acids, and nucleotides, into cells
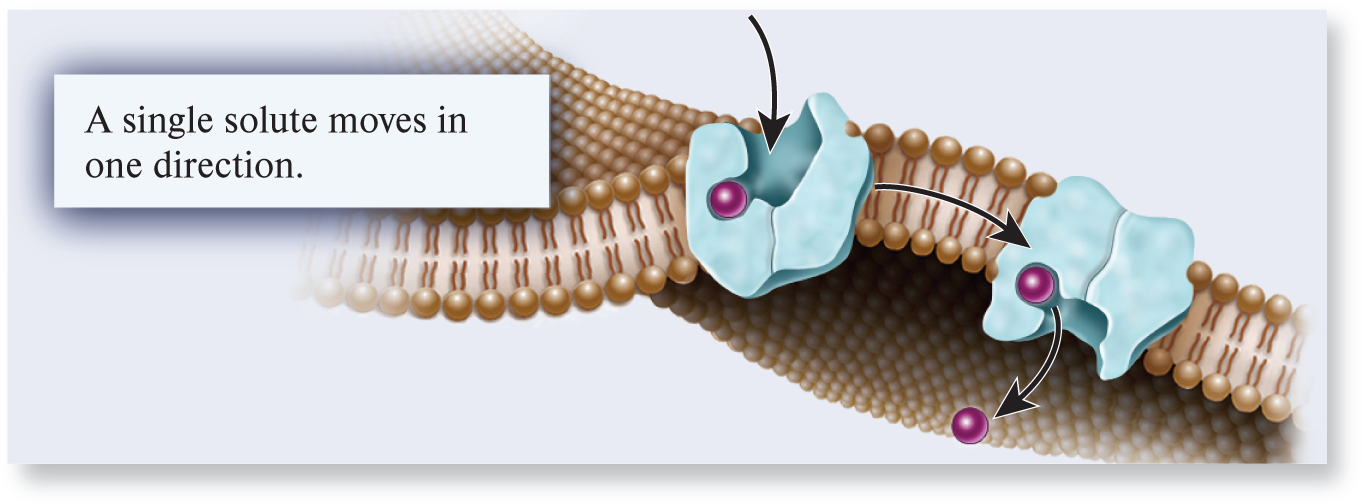
uniporter
A type of transporter that binds a single ion or molecule and transports it across a membrane
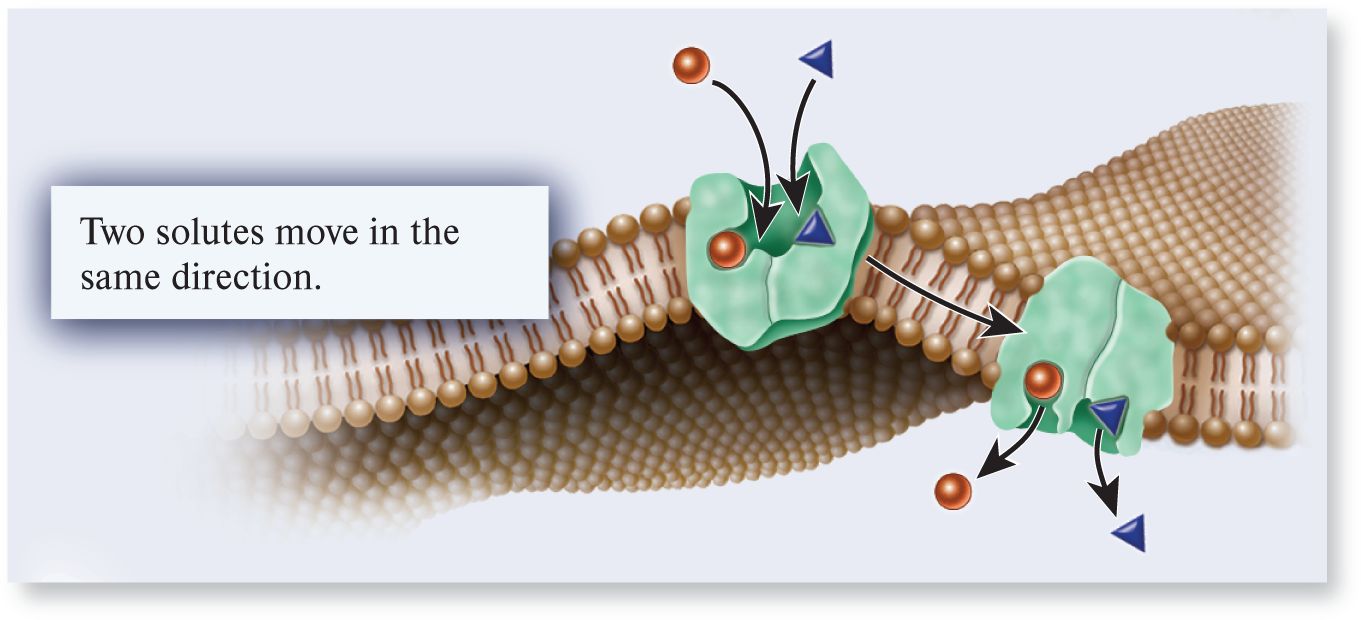
symporter
A type of transporter that binds two or more ions or molecules and transports them in the same direction across a membrane; also called a cotransporter.
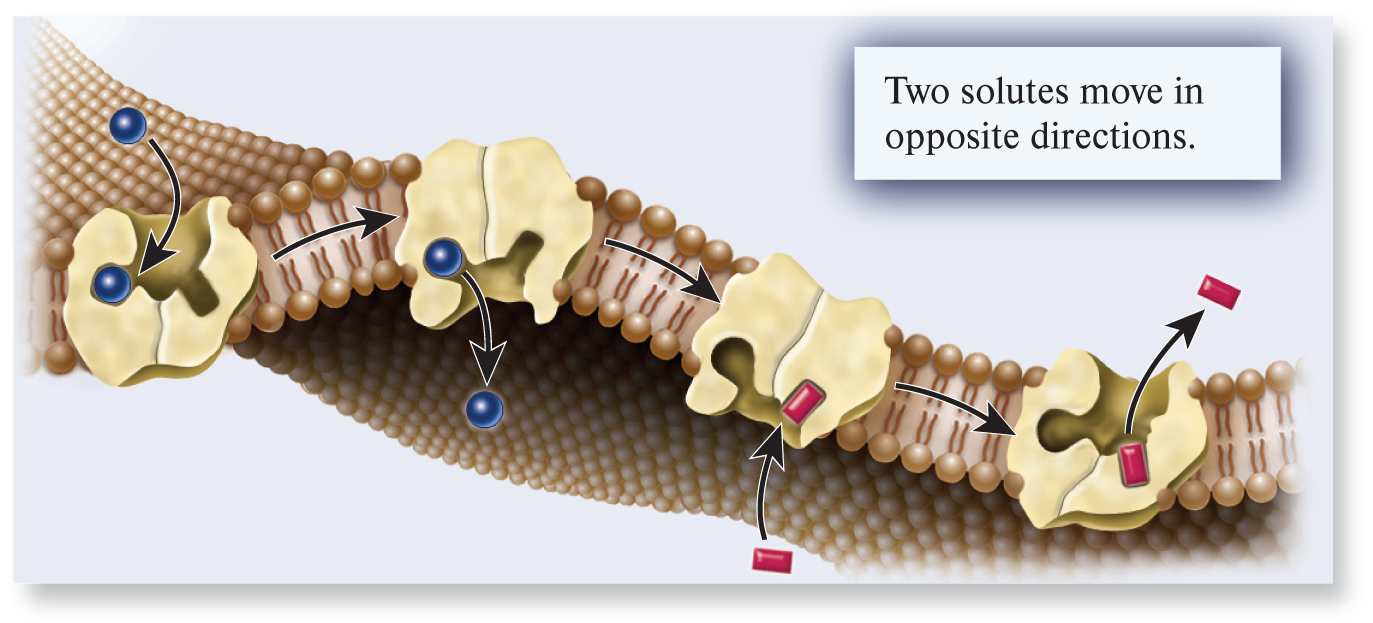
antiporter
A type of transporter that binds two or more ions or molecules and transports them in opposite directions across a membrane; also called an exchanger.
primary active transport
A type of transport that involves pumps that directly use energy to transport a solute against a gradient; ATP
sodium-potassium pump (type of primary active transport)
in animal cells; actively transports sodium and potassium against their gradients (low to high) using energy from ATP hydrolysis; 3 sodium move out, 2 potassium move in
pump
A transporter that directly couples its conformational changes to an energy source, such as ATP hydrolysis; found in endoplasmic reticulum
secondary active transport
A type of membrane transport that involves the utilization of a pre-existing gradient to drive the active transport of another solute.
proton pump
the main electrogenic pump of plants, fungi, and bacteria
electrogenic pump
a transport protein that generates a difference in charges across a membrane
Important Functions of Ion Electrochemical Gradients
transport of ions and molecules, production of energy intermediates, osmotic regulation, neuronal signaling, muscle contraction, and bacterial swimming
exocytosis (ex. hormones, digestive enzymes)
A process in which material inside a cell is packaged into vesicles and excreted into the extracellular environment.
endocytosis (ex. uptake of vital nutrients, root nodules, immune system)
A process in which the plasma membrane invaginates, or folds inward, to form a vesicle that brings substances or particles into the cell.
3 types of Endocytosis
receptor-mediated endocytosis, pinocytosis, phagocytosis
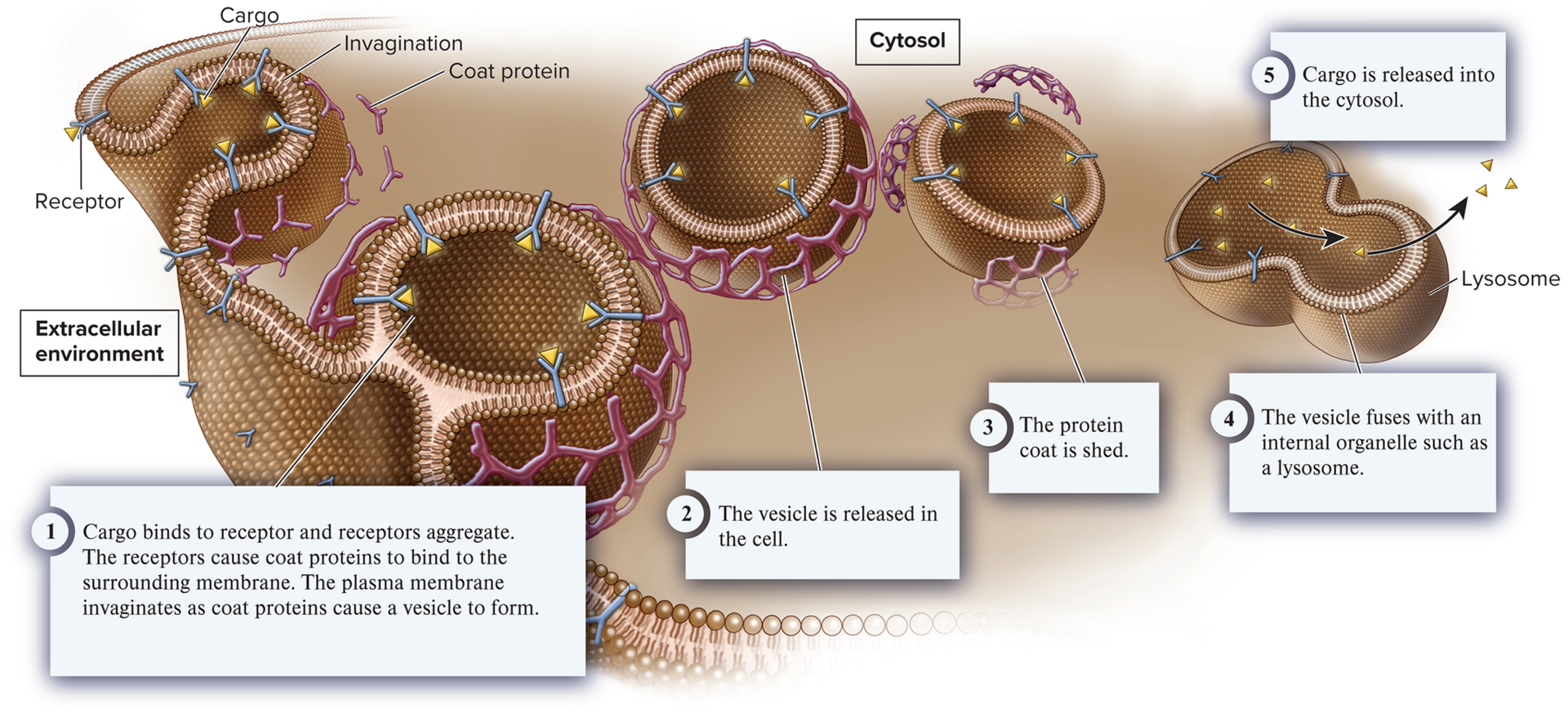
receptor-mediated endocytosis
A common type of endocytosis in which a receptor in the membrane is specific for a given cargo.
pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis that involves the formation of membrane vesicles from the plasma membrane as a way for cells to internalize the extracellular fluid.
phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis that involves the formation of a membrane vesicle, called a phagosome or phagocytic vacuole, which engulfs a particle such as a bacterium.
energy
The ability to do work or cause change.

kinetic energy
Energy associated with movement

potential energy
The energy that a substance possesses due to its structure or location; an electron in an outer shell has more potential energy than one in an inner shell
chemical potential energy (ex. organic molecules like glucose) (important type of energy)
The potential energy contained within atoms and the bonds between atoms.
Light (important type of energy)
light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the eye
Heat (important type of energy)
heat is the transfer of kinetic energy from one object to another or from an energy source to an object
Mechanical (important type of energy)
mechanical energy is the energy possessed by an object due to its motion or its position relative to other objects
electrical/ion gradient (important type of energy)
the movement of charge or the separation of charges can provide energy
thermodynamics
The study of energy interconversions
1st Law of Thermodynamics
the law of conservation of energy-energy cannot be created or destroyed; however, energy can be transferred from one place to another and can be transformed from one type to another
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
any energy transfer or transformation from one form to another increases the degree of disorder of a system, called entropy
entropy
The degree of disorder of a system; when a physical system becomes more disordered, the entropy increases
enthalpy (H)
The total energy of a system.
free energy (G)
The amount of a system's energy that is available and can be used to promote change or do work.
entropy (S)
the amount of unusable energy in a system
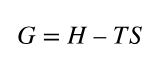
free energy equation
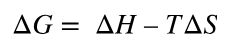
spontaneous chemical reaction equation
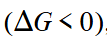
exergonic
Refers to chemical reactions that release free energy and occur spontaneously.
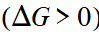
endergonic
Refers to chemical reactions that require an addition of free energy and do not proceed spontaneously.
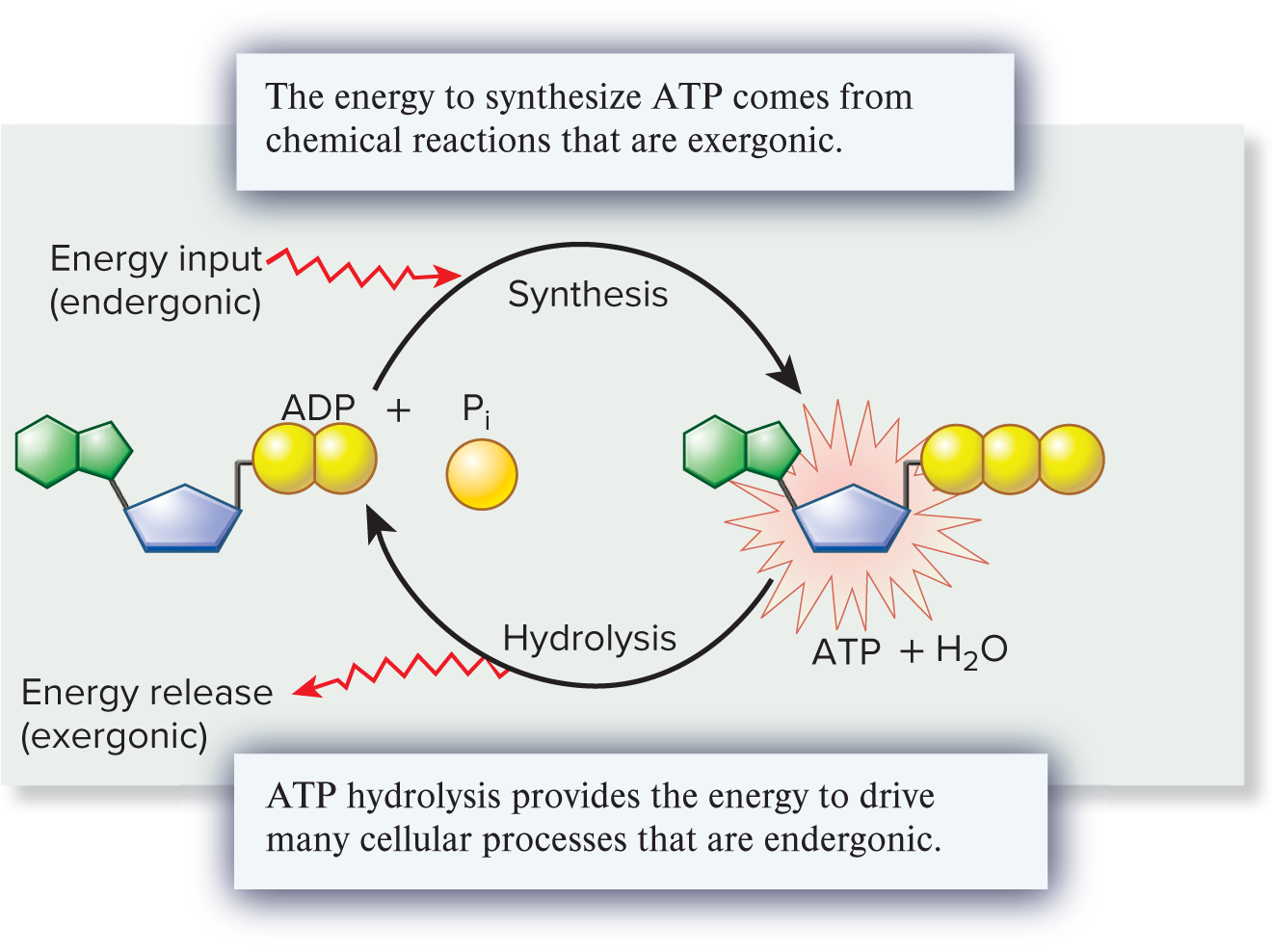
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
A molecule that is a common energy source for all cells.
hydrolysis of ATP (exergonic reaction)
Chemical reaction in which a water molecule is used to break ATP into ADP and inorganic phosphate; releases a large amount of free energy
phosphorylation
The attachment of a phosphate to a molecule
proteome
The complete complement of proteins that a cell or an organism makes
Proteins that use ATP for energy
metabolic enzymes, transporters, motor proteins, chaperones, DNA-modifying enzymes, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, protein kinases
catalyst
An agent that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without being permanently changed or consumed during the reaction.
enzymes (common catalyst in living cells)
A protein that acts as a catalyst to speed up a chemical reaction in a cell; discovered in 1876 by physiologist Wilhelm Kuhne
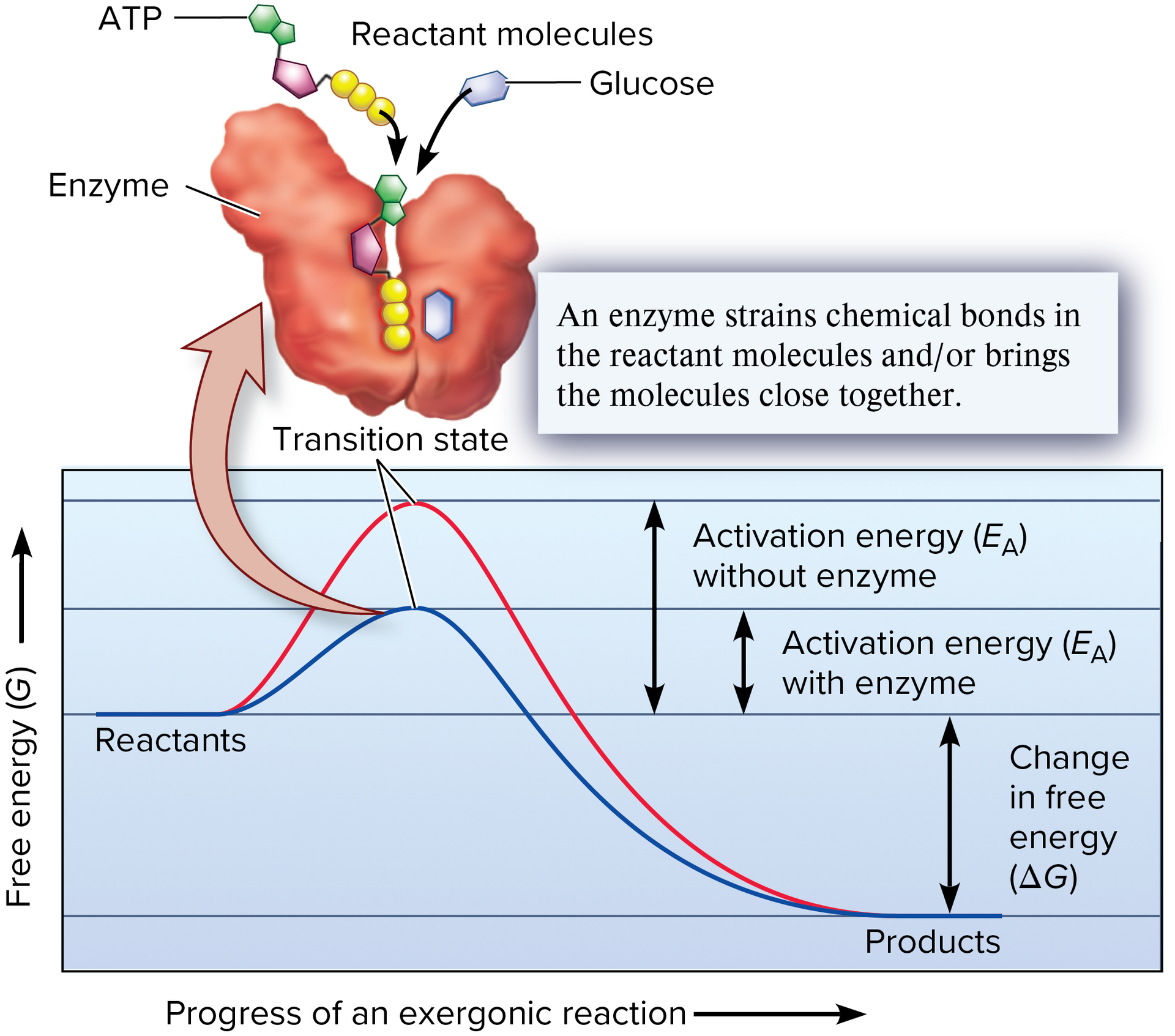
activation energy
An initial input of energy in a chemical reaction that allows the molecules to get close enough to cause a rearrangement of bonds
transition state
In a chemical reaction, a state in which the original bonds have stretched to their limit; once this state is reached, the reaction can proceed to the formation of products
straining reactants
enzymes are proteins that bind relatively small reactants. when reactant molecules are bound to an enzyme, their bonds can be strained, thereby making it easier for them to achieve the transition state
positioning reactants closer together
when a chemical reaction involves two or more reactants, the enzymes provide a site where the reactants are positioned close to each other in an orientation that facilitates the formation of new covalent bonds
active site
The location in an enzyme where a chemical reaction takes place
substrate
1. A reactant molecule that binds to an enzyme at the active site and participates in a chemical reaction.
2. The organic compounds such as soil or rotting wood that fungi use as food.
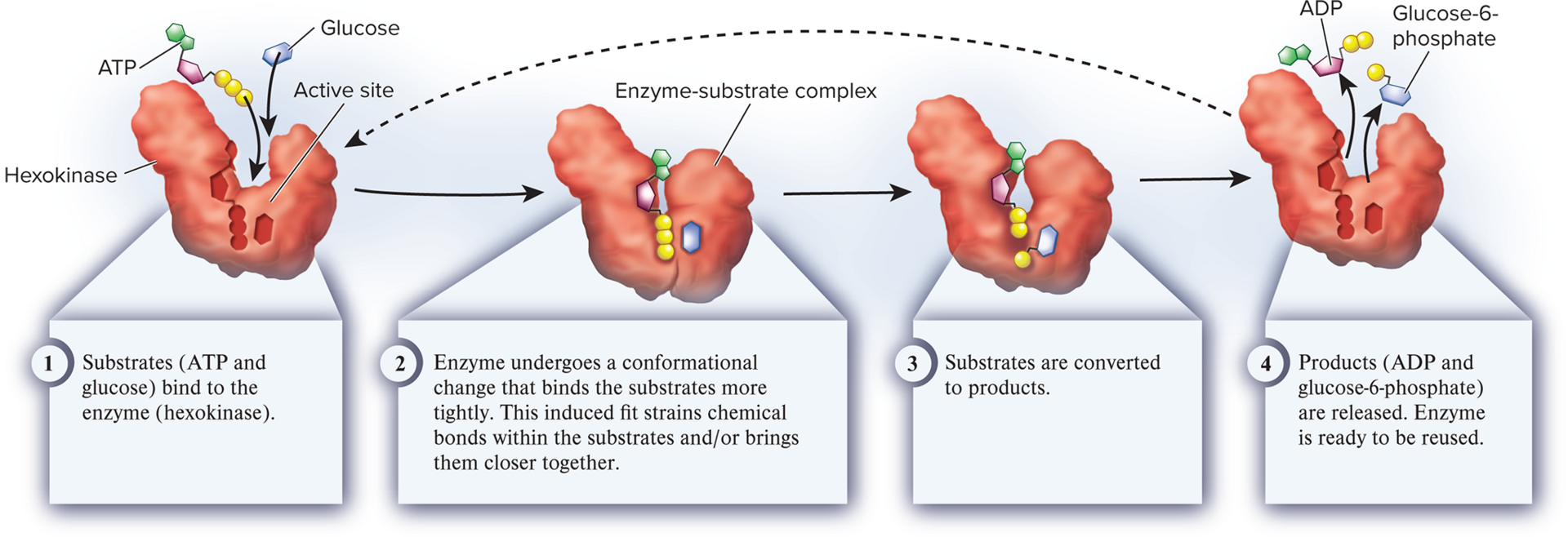
enzyme-substrate complex
The structure produced by binding an enzyme and its substrate(s)
induced fit
The phenomenon that occurs when the substrate(s) bind(s) to an enzyme and the enzyme undergoes a conformational change that causes the substrate(s) to bind more tightly to it; proposed by biochemist Daniel Koshland in 1958
affinity
The degree of attraction between an enzyme and its substrate(s)
KM
The substrate concentration at which an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is half of its maximal value.
competitive inhibitor
A molecule that binds noncovalently to the active site of an enzyme and inhibits the ability of the substrate to bind.
noncompetitive inhibitor
A molecule that binds noncovalently to an enzyme at a location that is outside the active site and inhibits the enzyme’s function.
allosteric site
A site on an enzyme where a molecule can bind noncovalently and affect the enzyme's function.
Diisopropyl Phosphorofluoridate (DIFP)
a type of nerve gas that was developed as a chemical weapon
prosthetic groups (nonprotein molecule/ion)
A small molecule that is permanently attached to the surface of an enzyme and aids in the enzyme's function.
cofactor (nonprotein molecule/ion)
Usually an inorganic ion that temporarily binds to the surface of an enzyme and promotes a chemical reaction.
coenzyme (nonprotein molecule/ion)
An organic molecule that temporarily binds to an enzyme and participates in the chemical reaction that the enzyme catalyzes, but is left unchanged when the reaction is completed.
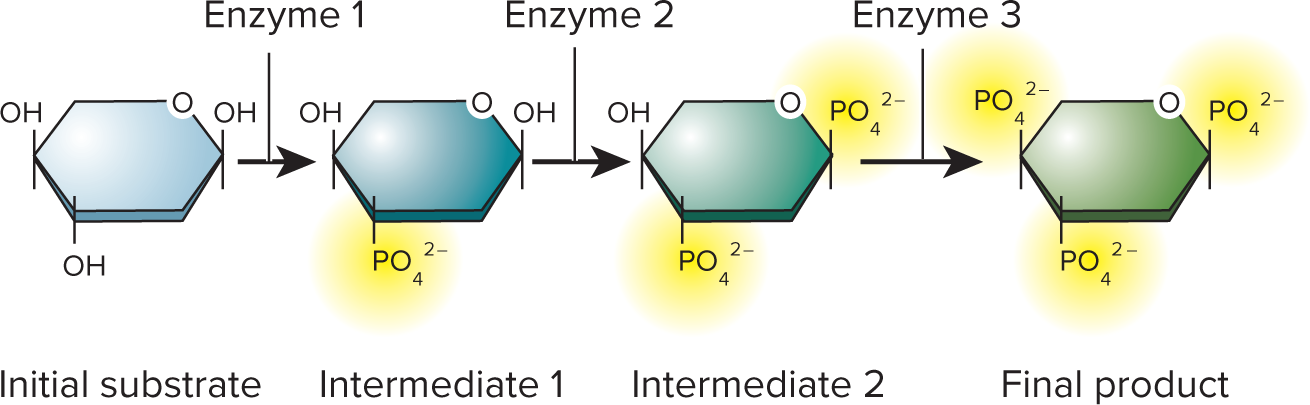
metabolic pathway
In living cells, a coordinated series of chemical reactions in which each step is catalyzed by a specific enzyme.
catabolic reaction
A chemical reaction in a metabolic pathway in which a molecule is broken down into smaller components, usually releasing energy.
anabolic reaction
A chemical reaction in a metabolic pathway that involves the synthesis of larger molecules from smaller precursor molecules. Such reactions usually require an input of energy.
energy intermediate
A molecule such as ATP or NADH that stores energy and is used to drive endergonic reactions in cells.
substrate-level phosphorylation
A method of synthesizing ATP that occurs when an enzyme directly transfers a phosphate from an organic molecule to ADP.
chemiosmosis
A process for making ATP in which energy stored in an ion electrochemical gradient is used to make ATP from ADP and Pi.
oxidation
The removal of one or more electrons from an atom or molecule; may occur during the breakdown of small organic molecules.
reduction
The addition of one or more electrons to an atom or molecule.
redox reaction
A type of reaction in which an electron that is removed during the oxidation of an atom or molecule is transferred to another atom or molecule, which becomes reduced; short for reduction-oxidation reaction
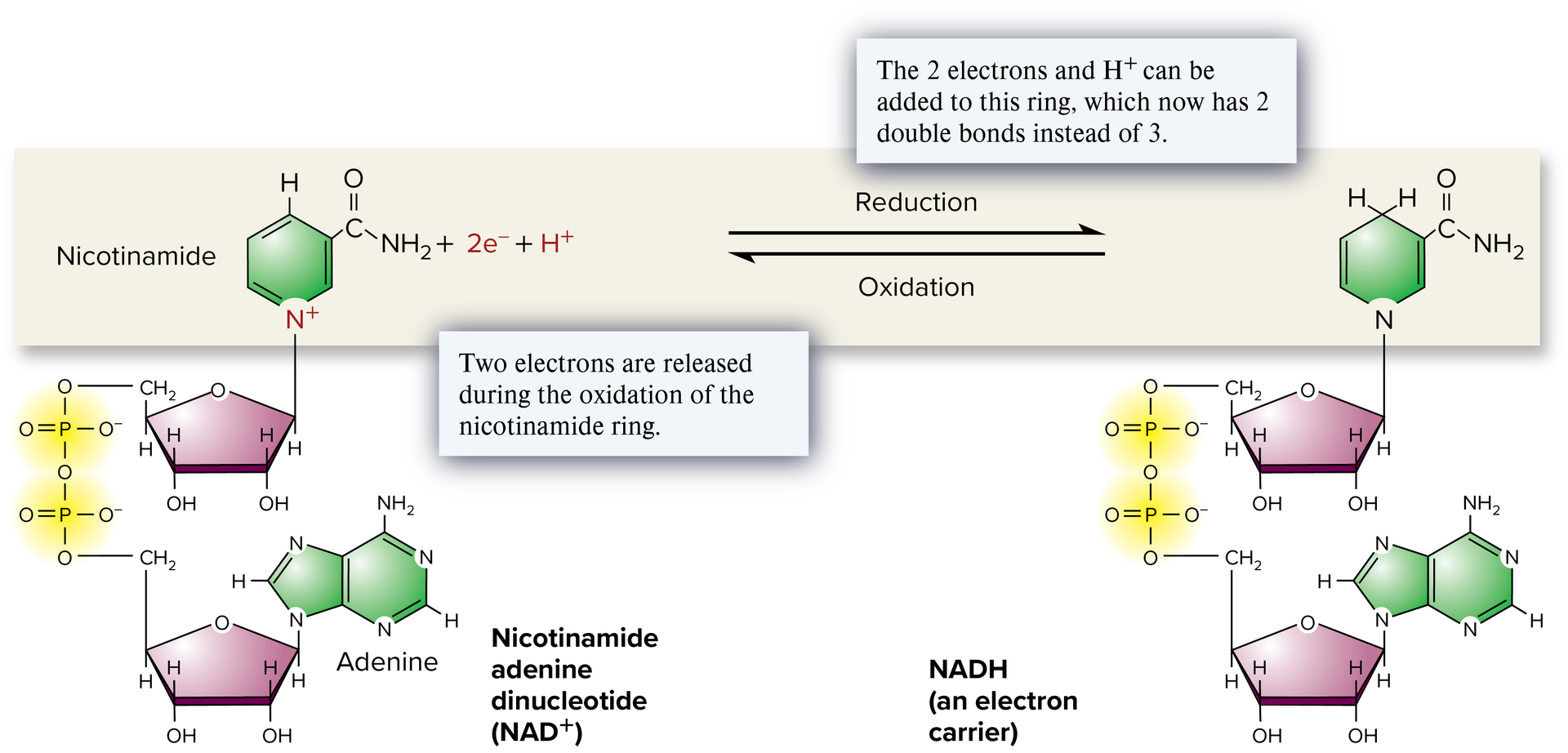
NAD+
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; an organic molecule that functions as an energy intermediate. It combines with two electrons and H+ to form NADH.
biosynthetic reaction
Also called an anabolic reaction; a chemical reaction in which small molecules are used to synthesize larger molecules.
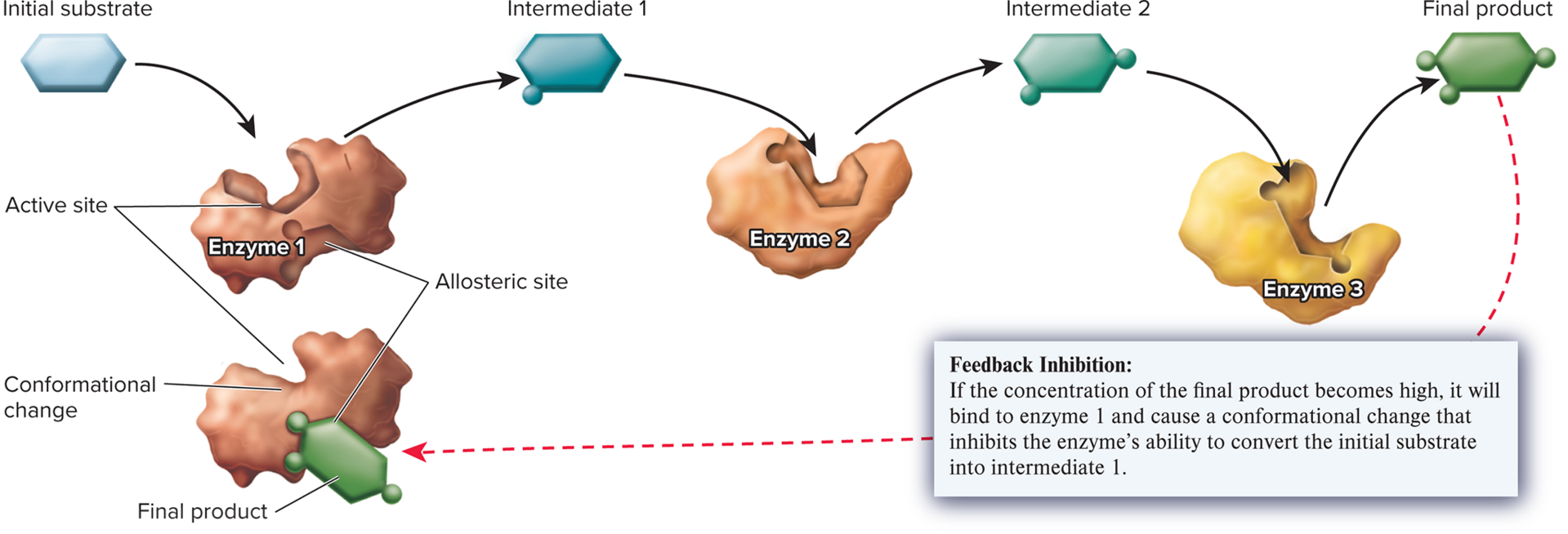
feedback inhibition
A type of regulation in which the product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an enzyme that acts early in the pathway, thus preventing the overaccumulation of the product.
rate-limiting step
The slowest step in a reaction pathway.
aerobic respiration
a type of cellular respiration in which O2 is consumed and CO2 is released.
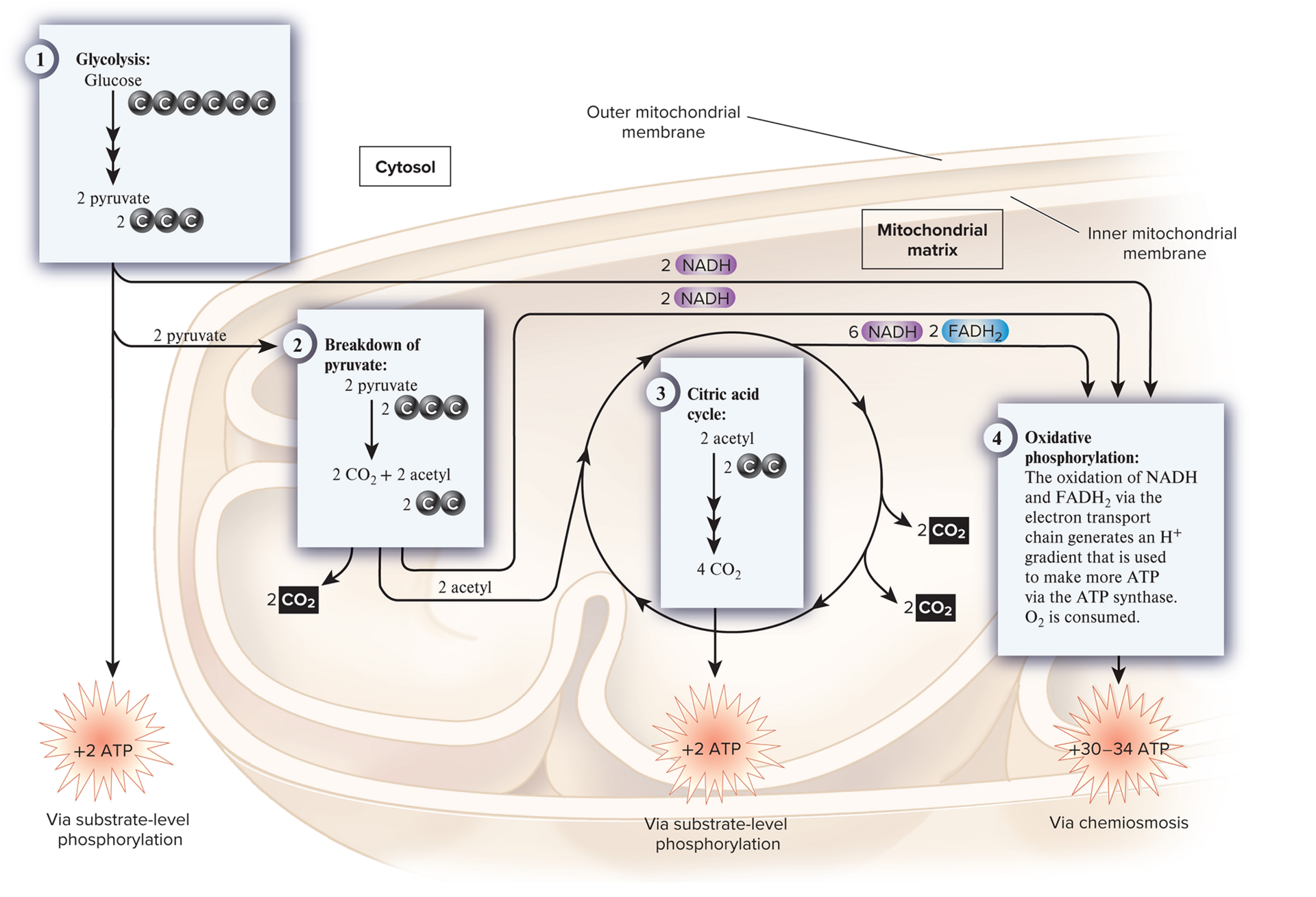
cellular respiration four metabolic pathways
glycolysis, breakdown of pyruvate to release an acetyl group, citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation
cristae
Projections of the highly invaginated inner membrane of a mitochondrion.