Chapter 3 - Organic compounds: Alkanes and their stereochemistry
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What is a functional group?
A group of atoms within a molecule that has a characteristic chemical behavior.
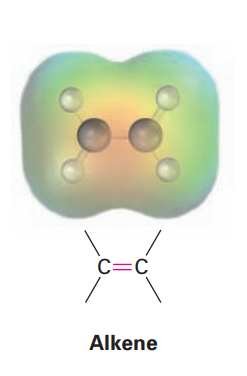
Alkene
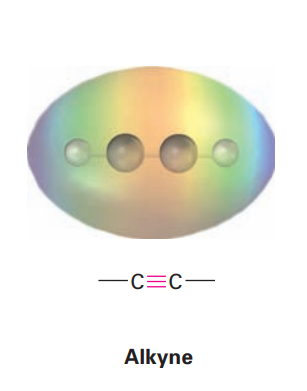
Alkyne
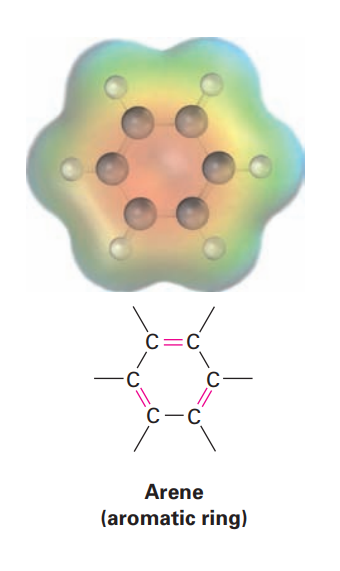
Arene
Halide
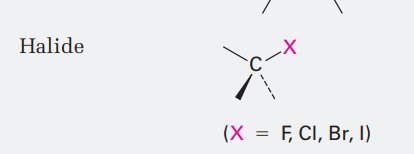
Alcohol
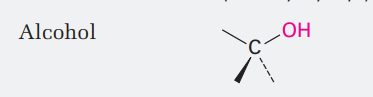
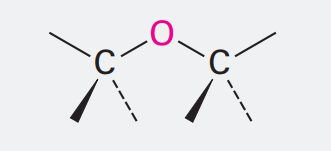
Ether
Ending: ether
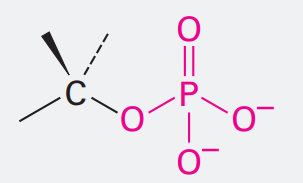
Monophosphate
Ending: phosphate
OPO32-
Diphosphate
Ending: diphosphate
OP2O63-
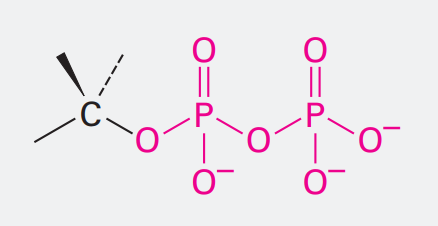
Amine
Ending: -amine
NH2
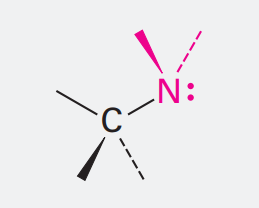
Imine
Ending: none
NH
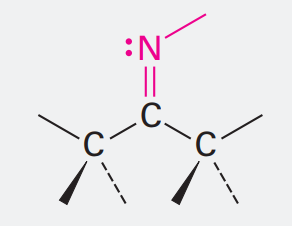
Nitrile
Ending: -nitrile
N

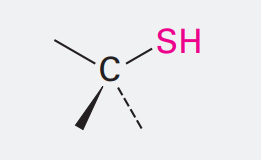
Thiol
Ending: -thiol
SH
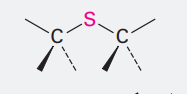
Sulfide
Ending: sulfide
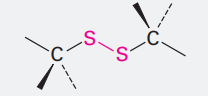
Disulfide
Ending: disulfide
SS
Sulfoxide
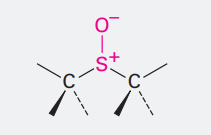
ending= -sulfoxide
SO-
Sulfoxide can also exist with double bond to O
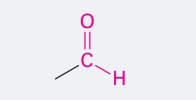
Aldehyde
ending -al
COH
Ketone
Ending: one
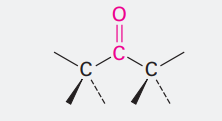
C=O
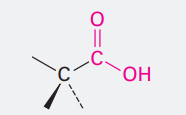
Carboxylic acid
Ending: -oic acid
COOH
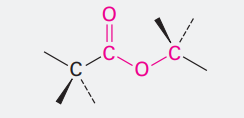
Ester
Ending = -oate
COOCH3
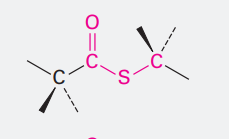
Thioester
Ending: -thioate
COSCH3
Amide
Ending: -amide
CONH2
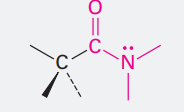
Acid chloride
Ending: -oyl chloride
COCl
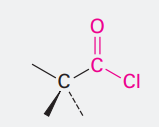
Carboxylic acid anhydride
Ending: -oic anyhydrided
COOCOCH3
Saturated hydrocarbonds
Hydrocarbon: consists of carbon and hydrogen only
Saturated: They have only C-C and C-H single bonds and thus contain the maximum possible number of hydrogens per carbon.
General formula alkane
CnH2n+2
Straight-chain alkanes vs. branched chain alkanes
Straight chain: All carbons are connected in one row.
Branched: Where the carbons branch off.
Isomers
Same formula, different structures.
Isomers are compounds that have the same numbers and kinds of atoms but differ in the way the atoms are arranged.
Consists of constitutional isomers and stereoisomers.
Constitutional isomers.
Are isomers whose atoms are connected differently
How can a normal straight chain be represented?
putting: n- before the formula
e.g.: n-C4H10
Number of carbons
1: Meth
2: Eth
3: Prop
4: But
5: Pent
6: Hex
7: Hept
8: Oct
9: Non
10: Dec
Alkyl naming
Number (e.g. Meth) + yl
primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary carbon
Primary carbon: is bonded to one other carbon.
Secondary carbon: is bonded to two other carbons
etc.
e.g. a tertiary alcohol = has an alcohol functional group bonded to a carbon atom that is itself bonded to three other carbons.
Primary, secondary, … hydrogen
Primary hydrogen atoms are attached to primary carbons (RCH3), secondary hydrogens are attached to secondary carbons (R2CH2), and tertiary hydrogens are attached to tertiary carbons (R3CH)
(no quaternary hydrogen because then the carbon would have an expanded octet)
Steps of IUPAC
Find the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the molecule and use the name of that chain as the parent name. (if two chains with equal length are present choose the one that has the most branch points)
Number each carbon in the parent chain. Try to have the branches at low numbers
Identify and number the substituents
Write the name as a single word. Use hyphens to separate different prefixes. Cite prefixes in alphabetical order.
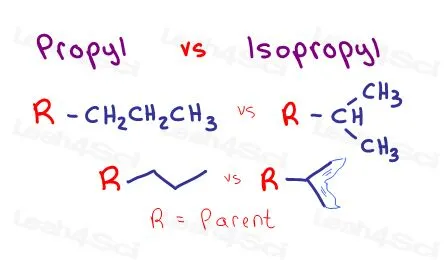
Propyl vs isopropyl
"iso-" signifies a specific type of branching pattern where the last two carbons of the chain are part of a terminal isopropyl group
Properties of alkanes
Have little affinity and are inert.
Reaction of alkane with oxygen
Reaction with oxygen occurs during combustion in an engine or furnace when an alkane is used as fuel.
Carbon dioxide and water are formed as products, and a large amount of heat is released.
Reaction of alkane with Cl2
Occurs when a mixture of the two is irradiated with ultraviolet light .
Depending on the time allowed and the relative amounts of the two reactants, a sequential substitution of the alkane hydrogen atoms by chlorine occurs.
This leads to a mixture of chlorinated products
Relation number of carbons to boiling/melting point
Higher number of carbons = higher melting/boiling point
Effect of increased branching on boiling point
Another effect seen in alkanes is that increased branching lowers an alkane’s boiling point.
e.g. pentane has no branches and boils at 46.1 C
Isopentane (2-methylbutane) has one branch and boils at 27.85 C
Stereochemistry
The branch of chemistry concerned with the three-dimensional aspects of molecules.
Conformation
The different arrangements of atoms that result from bond rotation are called conformations
Conformers
Another word for conformational isomers
Molecules that have different arrangements
Conformational isomers vs. constitutional isomers
Conformational isomer: Same molecular formula, same connectivity, but differ by rotation around single bonds
Constitutional isomer: Same molecular formula, but differ in connectivity (bonding sequence) of atoms
Newman projection vs. Sawhorse representation
Sawhorse: views carbon-carbon bond from an oblique angle and indicates spatial orientation by showing all C-H bonds.
Newman: Views the carbon-carbon bond directly end-on and represents the two carbon atoms by a circle.
Staggered conformation
A conformation where substituents on adjacent carbons are positioned as far apart as possible, minimizing steric hindrance.
Seen as the most stable conformation due to lower torsional strain.
Maximum distance
Lowest energy
Eclipsed conformation
A conformation where substituents on adjacent carbons are aligned directly with each other, causing increased steric hindrance.
Less stable due to increased repulsion and torsional strain between groups.
Minimum distance
Highest energy
What is the lowest-energy arrangement called?
The anti conformation, where the two methyl groups are as far apart as possible. (180 degrees)
Gauche conformation
When an energy minimum is reached at the staggered conformation where they methyl group are 60 degrees apart.
Has no eclipsing interaction
This energy difference occurs because the hydrogen atoms of the methyl groups are near one another in the gauche conformation, resulting in what is called steric strain.
How do molecules shift from eclipsed to staggered conformation?
Through rotation around a single sigma bond.
During rotation the molecule moves between energy states. It has to overcome a small energy barrier to go from one conformation to another.
In eclipsed conformation, this is a high-energy state because the electron clouds of substituent groups on adjacent carbons align directly with each other, causing torsional strain from steric repulsion.
In staggered conformation this is a low energy state where substituent groups are as far apart as possible, minimizing repulsive forces and making it more stable.
Steric strain
The repulsive interaction that occurs when atoms are forced closer together than their atomic radii alow.
Three types of cycloalkanes
Chrysanthemic acid
Prostaglandins
Steroids
Chrysanthemic acid
Active insecticidal
Constituents of chrysanthemum flowers
Prostaglandins
potent hormones
control physiological functions in humans
Steroids
naturally occurring hormones in plants and animals
Cis-trans isomerism in cycloalkanes
Two faces
Isomerism possible in substituted cycloalkanes.
Substituted cycloalkanes have substituents. Instead of just C and H.
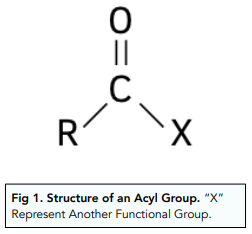
Acyl group