112.2 Parasitology
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
How are pinworm infections acquired
Direct hand to mouth an autoinfections
Name the patient specimen that best detects pinworm infections
Mature eggs on a scotch tape prep from the perianal area first thing in the morning
Where do adult pinworms live in humans
Hand to mouth and migrate from the colon to the perianal area and lay eggs in the perianal region
Describe patient symptoms of heavy Enterobius infections
Perianal itch and local irritation and scratching
List the infective and diagnostic stages of pinworm infections
Infective: mature egg with larva
Gravid stage: migrates from colon to perianal area (12 midnight to 2am) and lays eggs in perianal region
Diagnostic: The mature eggs on scotch tape prep
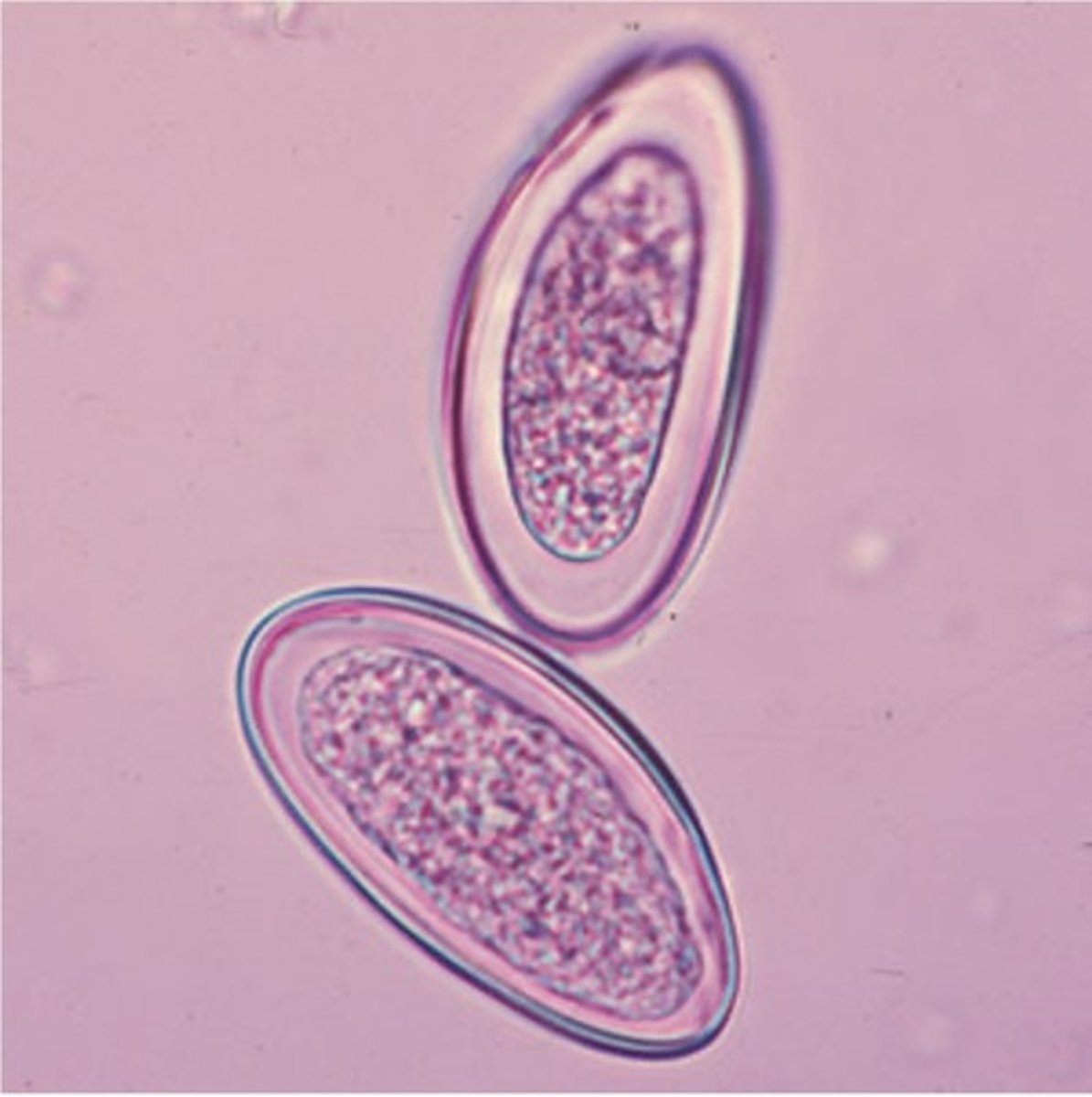
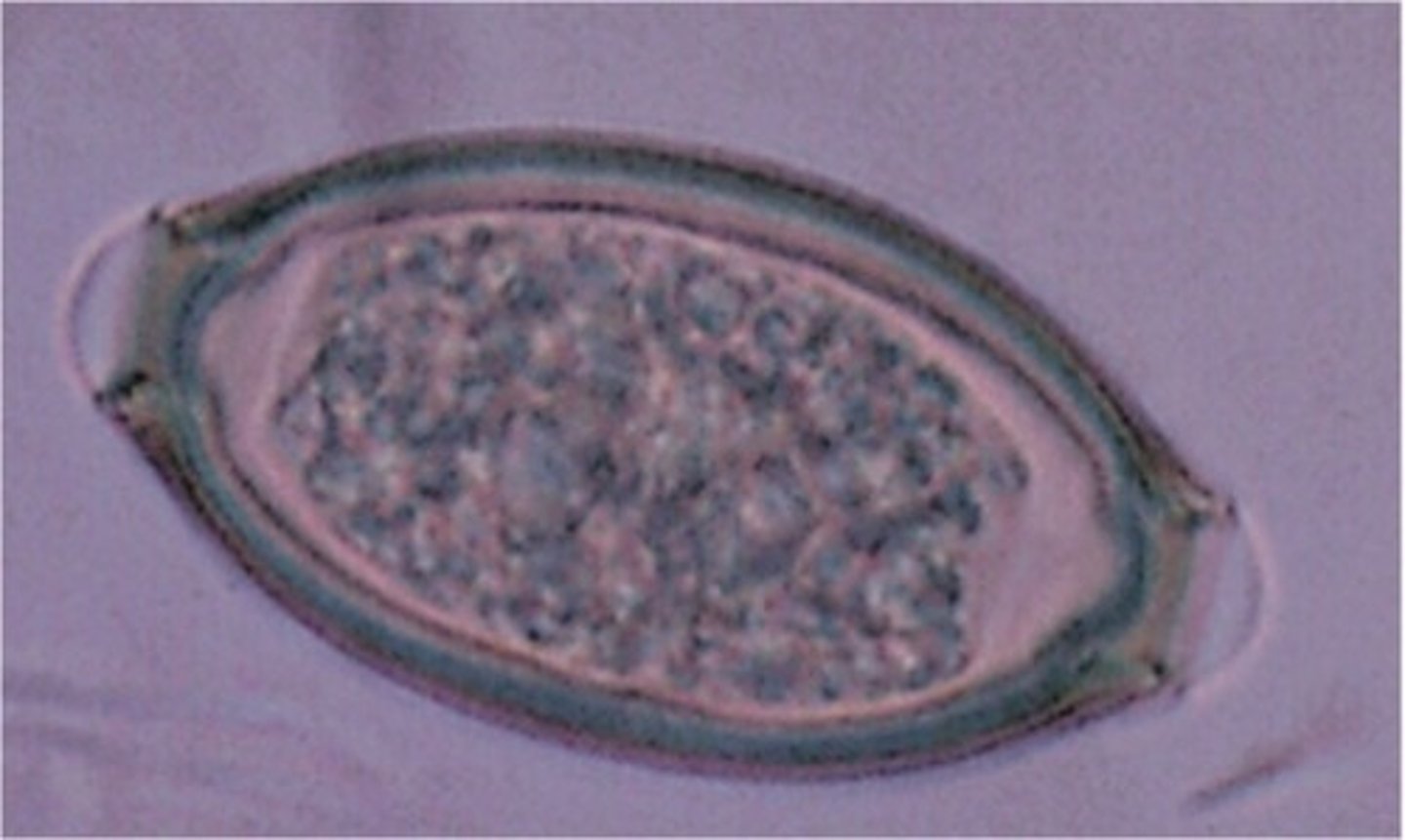
Describe and picture mature pinworm eggs
Eggs are oval, flattened on one side, thin, colorless shell, egg embryonated with C-shape larva
Explain why pinworm infections do not require development in the soil to become infective
Because it's immediately infective
Define autoinfection
Reinfection produced by a parasite that is already in the patients body
Which intestinal roundworms are autoinfective
Enterobius and Strongyloides
Which patient specimen is most commonly used to ID roundworm infections
Stool
Distinguish between immature and mature helminth eggs
Immature: oval with or without a thick coat
Mature: round to oval, thick, bumpy corticoid coat with a thick shell beneath it (some may or may not have a coat)
Name 2 roundworms whose infections are acquired by "eating dirt"
Ascaris lumbricoides and Trichuis trichiura
Where do Ascaris and Trichuis adult worms live
Colon and small intestines
Describe symptoms of heavy burdens of Ascaris
Transient pneumonia (they migrate through the lungs), diarrhea, obstruction of bile duct/intestines/ or aappendix
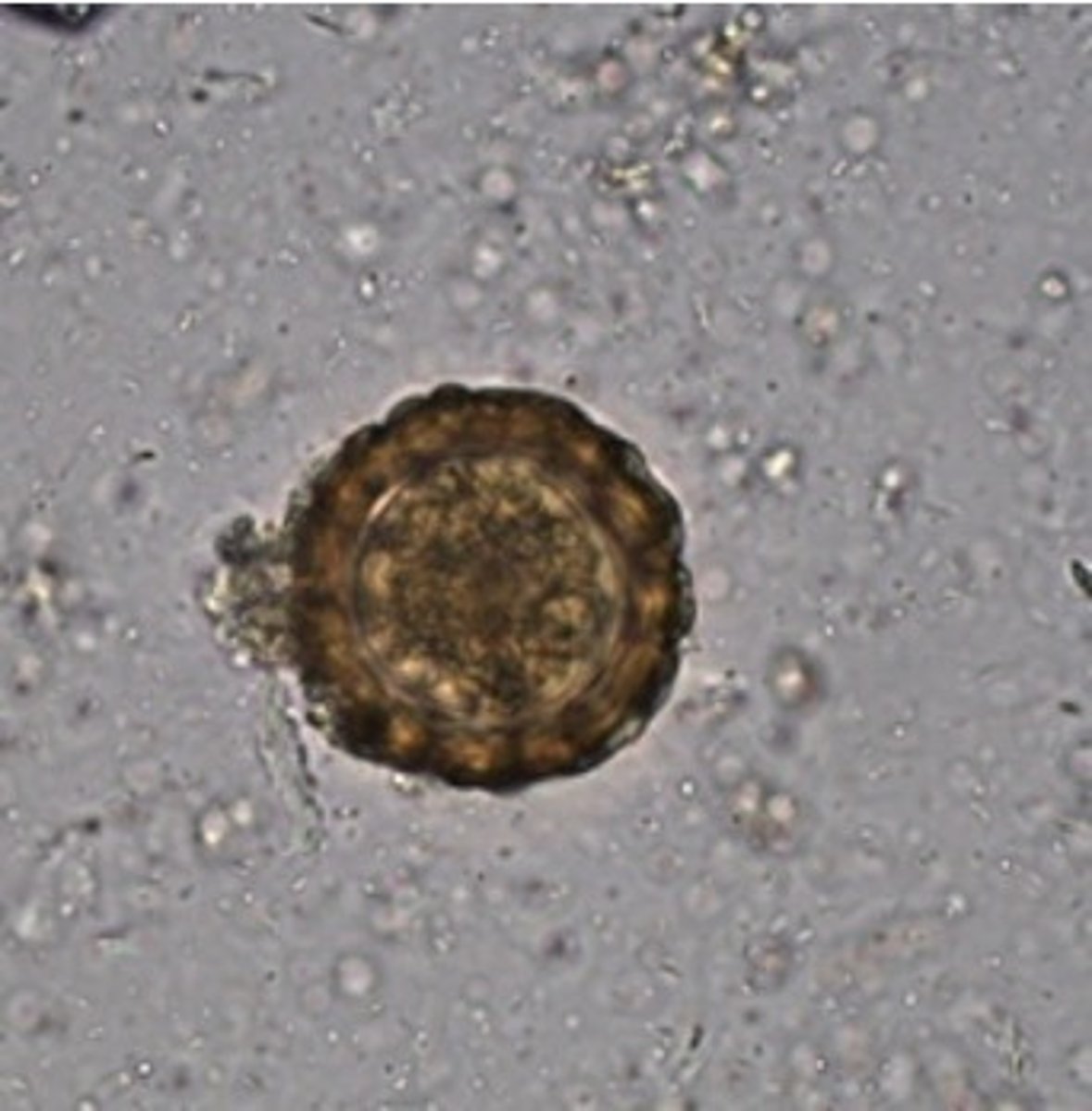
Describe and picture Corticated fertile Ascaris eggs
Round to oval, thick mammilated coat
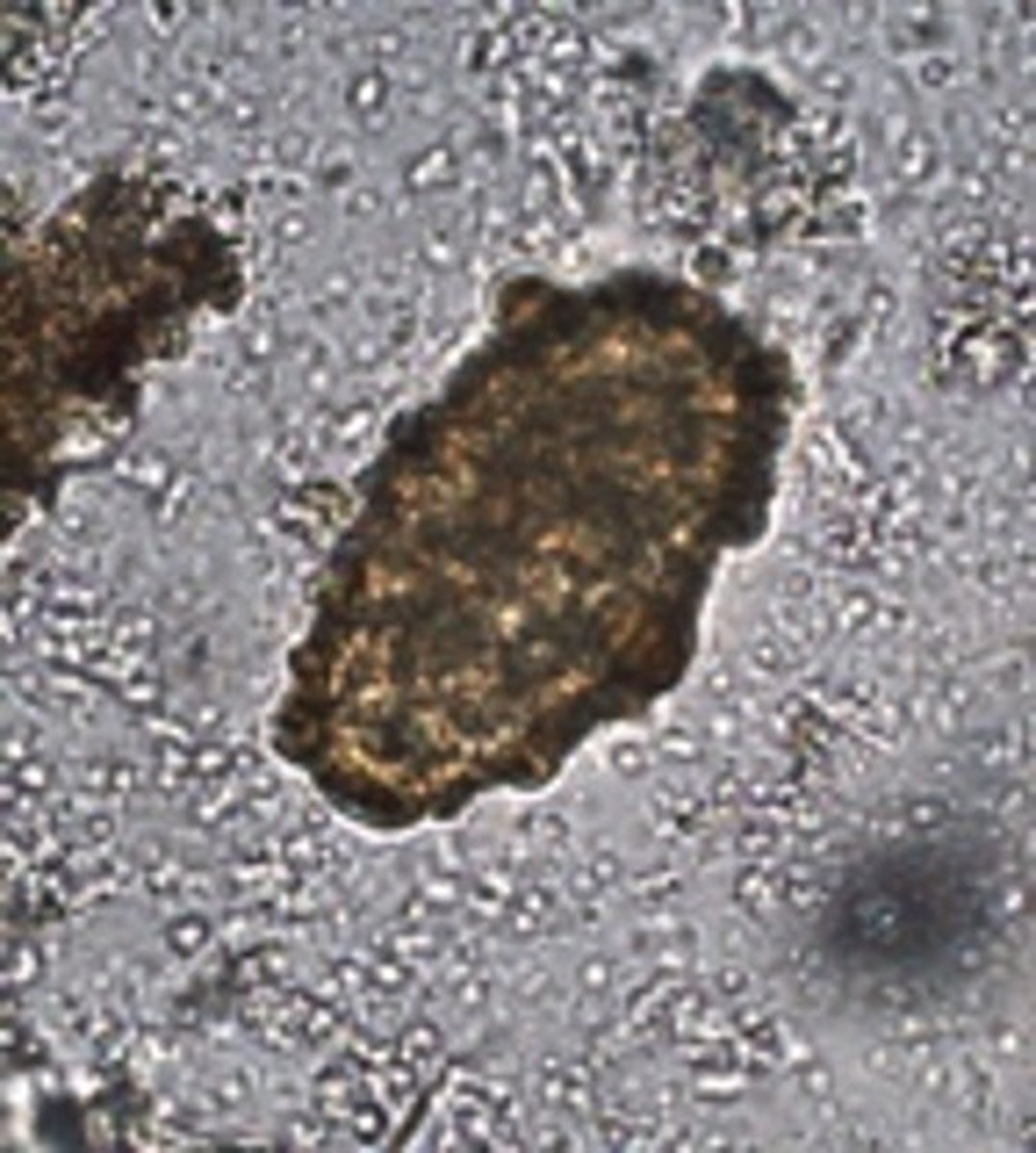
Describe and picture Decorticated fertile Ascaris eggs
Round to oval but no thick coat
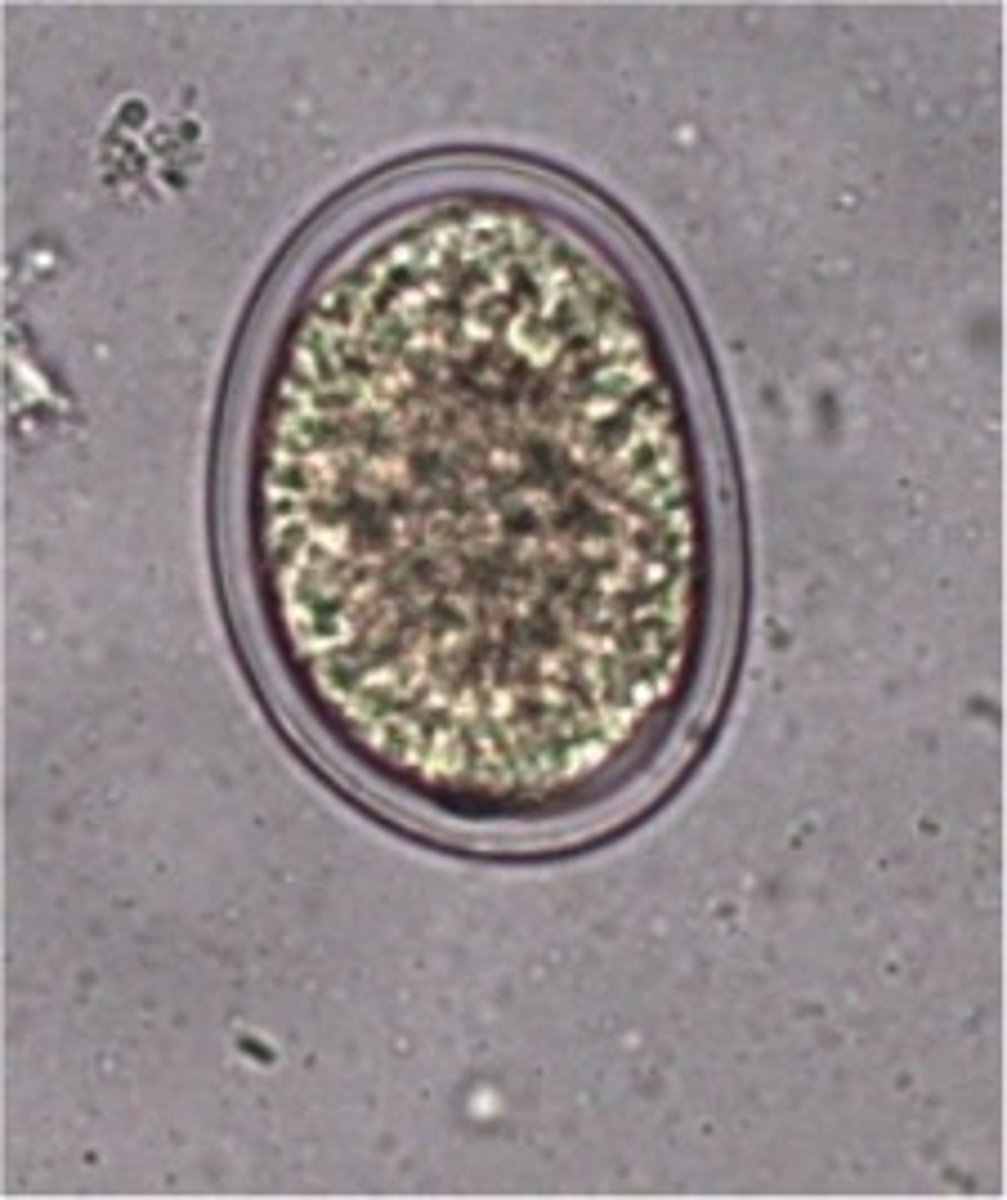
Describe and picture Infertile Ascaris eggs
Oval with or without a thick coat
Describe the symptoms of heavy burdens of Trichuris (whipworm)
Mimics ulcerative colitis in children and IBS in adults, diarrhea (bloody or mucoid), rectal prolapse (especially in children
Describe and picture eggs of Trichuris seen in patient stools
Barrel shaped egg, undeveloped unicellular embryo, smooth shell surface with thick yellow-brown shell color due to bile staining, hyaline plug at each pole
List the infective and diagnostic stages of Trichuris infections
Infective: eggs embyonate in soil by 1 month
Diagnostic stage: undeveloped eggs in feces
Which roundworm may cause a transient pneumonia in its host because it migrates through the lungs
Ascaris lumbricoides
How are primary infections of hookworm and Strongyloides infections acquired
Filariform larvae hatch in soil and penetrate skin, especially through the feet
Between hookworm and Strongyloides, which one causes autoinfection
Strongyloides stercoralis
List the two genera/species of hookworms
Necator americanus and Ancylostoma duodenale
Where do adult hookworms live in the body
Small intestine
How do hookworms feed in humans
They are bloodsuckers
Describe "ground itch" and explain what causes it
Dermatitis from repeat infections
Describe the blood disorder caused by heavy burdens of adult hookworms
Microcytic hypochromic anemia
Explain how adult hookworms cause microcytic hypochromic anemia
They cause chronic blood loss
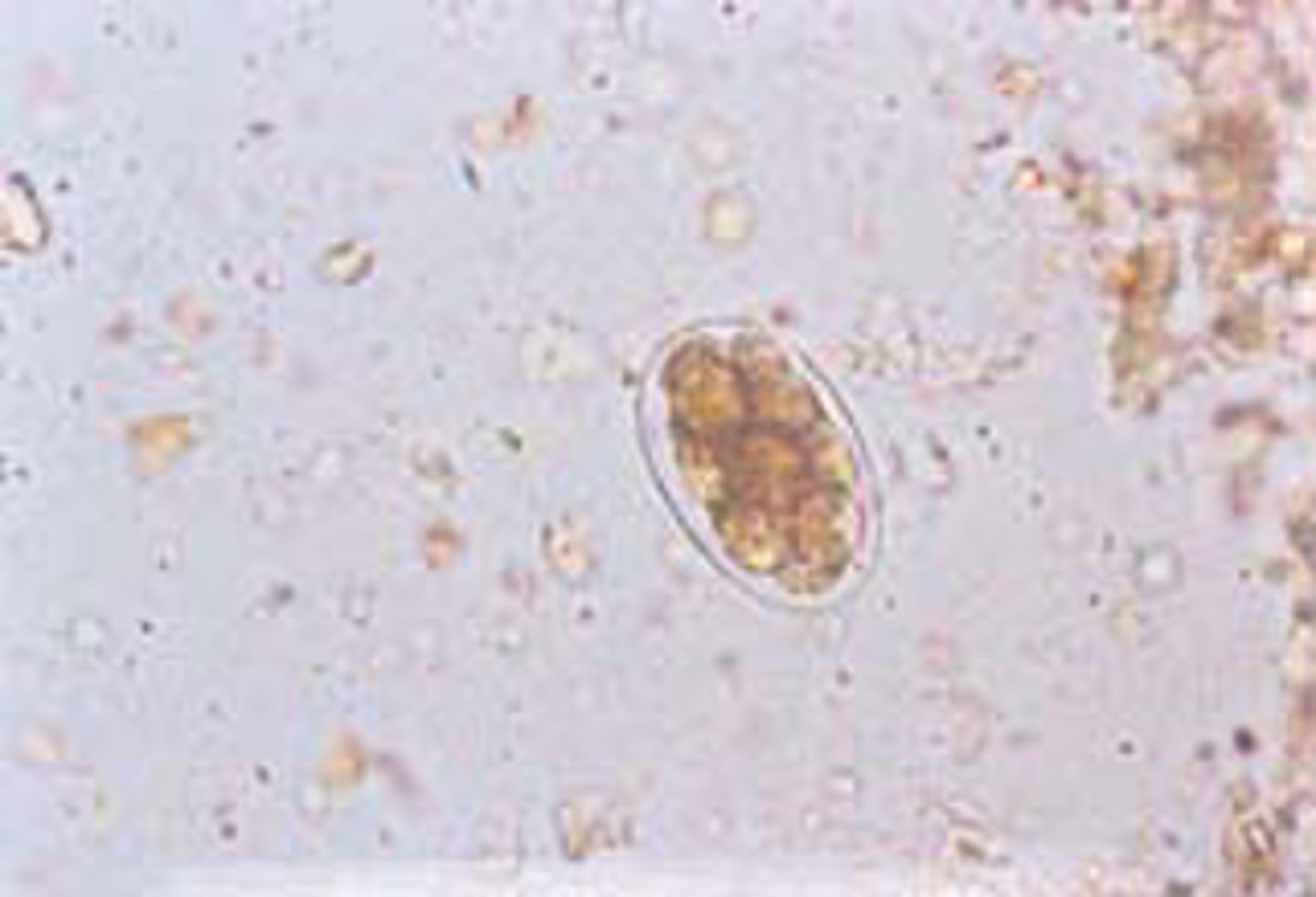
Describe and picture hookworms seen in patients stool
Eggs broadly oval, thin, colorless shell, 4-8 cell stage embryo when passed in stool (rhabditiform larvae rarely seen in stool)
Which other roundworm egg may be confused with a hookworm egg
Ascaris eggs, dercorticated
List the infective and diagnostic stage of hookworm infection
Infective: filariform larva, eggs shed in stool and mature in soil; two larval staged develop in soil: rhabditiform and filariform; rhabditiform may been seen only if stools left at room temp for several days
Diagnostic: eggs in feces; embryo develops rapidly to rhabditiform larva and hatches in warm, moist soil (24-48 hours) and rapidly molts
Distinguish between the rhabditiform and filariform larvae of hookworm
Rhabditiform larva have a long buccal cavity and a small genital primordium. Filariform larva have a pointed tail and a esophageal intestinal ratio of 1:4
Why is the hookworm rhabditiform larvae not normally seen in a patients stool
Because they need time to hatch
Under what conditions may hookworm rhabditiform larva be seen in stool
If the stool is left at room temp for several days
List two ways Strongyloides infections may be acquired
Penetrate the skin and enter the lymphatic system or blood; autoinfection when larva develops to infective stage in intestine
Where do adult Strongyloides live in humans
Mucosa of the small intestine. Parthenogenic parasite is female only
Distinguish between the Strongyloides rhabditiform and filariform larvae
Rhabditiform is the first stage seen in stools. Short buccal cavity, large genital primordium. Filariform is the second stage. Infective form, notched tail and esophageal/intestinal ratio is 1:2
Which of the two larvae of Strongyloides is most commonly the diagnostic stage
Rhabditiform
Under what conditions may a Strongyloides filariform larvae be seen in stool
If the patient has a heavy burden
Distinguish between rhabditform larvae of Strongyliodes and hookworm
-Strongyloides is short buccal cavity with large genital primordium
-Hookworm is long buccal cavity with small genital primordium
Describe patients symptoms of heavy burdens of Stongyloides infections
Larval dermatitis from repeat infections, transient pneumonia when migrating through the lungs, diarrhea, vomiting, moderate eosinophilia
What population are most susceptible to heavy Strongyloides infections
Immunocompromised hosts
Which roundworms are infective by ingesting mature eggs
Ascaris lumbricoides and Trichuris trichiura
Which roundworms are infective by filariform larvae penetrating the skin
Stronglyloides and Necator americanus
Which roundworm infection is not dependent on the soil for development of its infective stage because its egg is immediately infective
Enterobius vermicularis
Which two roundworms may cause a transient pneumonitis because its larvae migrates through the lungs
Ascaris and Strongyloides
Name the roundworm infections most commonly diagnosed by finding eggs in stool
Ascaris
Name the roundworm infections most commonly diagnosed by rhabditiform larvae in stool
Strongyloides
Name the roundworm infections most commonly diagnosed by eggs on scotch tape preps
Enterobius
Which roundworm egg would not be recovered by concentrating the stool by the Zinc sulfate flotation procedure
Ascaris eggs
Which of the intestinal roundworm infections are best controlled by good sanitary waste disposal methods
Necator americanus
Which of the intestinal roundworm infections are best controlled by good personal hygiene
Enterobius
Where do adult Trichinella live in humans
The intestines
Where do larval Trichinella forms live in humans
Encysted in striated (skeletal) muscle. "Nurse cells"
List the definitive and intermediate hosts of Trichinella spiralis
Definitive: Humans
Intermediate: Pigs, bear, deer, walrus, etc
How do humans acquire Trichinella spiralis infections
Eating undercooked pork or bear
Describe the symptoms of heavy Trichinella infections
Eye edema, blurred vision, eosinophilia, fever, headache, local muscle inflammation, epilepsy if in brain tissue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and headache
Describe the diagnostic stage an best specimen for diagnosing Trichinella
Larva encysted in striated muscle; gastrocenemuis, deltoid. Muscle biopsy is where diagnostic larva is; adults and larvae are not seen in stool
How do humans acquire Drancuculus infections
Infected copepod ingested in drinking water
How is the diagnosis made for Drancuculus
Visually observe skin blisters or emerging worms
How is the adult worm of Drancuculus removed
Slow withdraw from blister by wrapping it around a revolving small stick over several days (process can be completed in a few days but usually requires weeks or even months; surgical removal of adults
How are Filariae infections acquired
Enter skin from arthropods feeding site, adults live in the lymphatic system or subcutaneous tissues, microfilariae are ingested by arthropods from blood or subcutaneous nodules, where they develop into the infective larval form
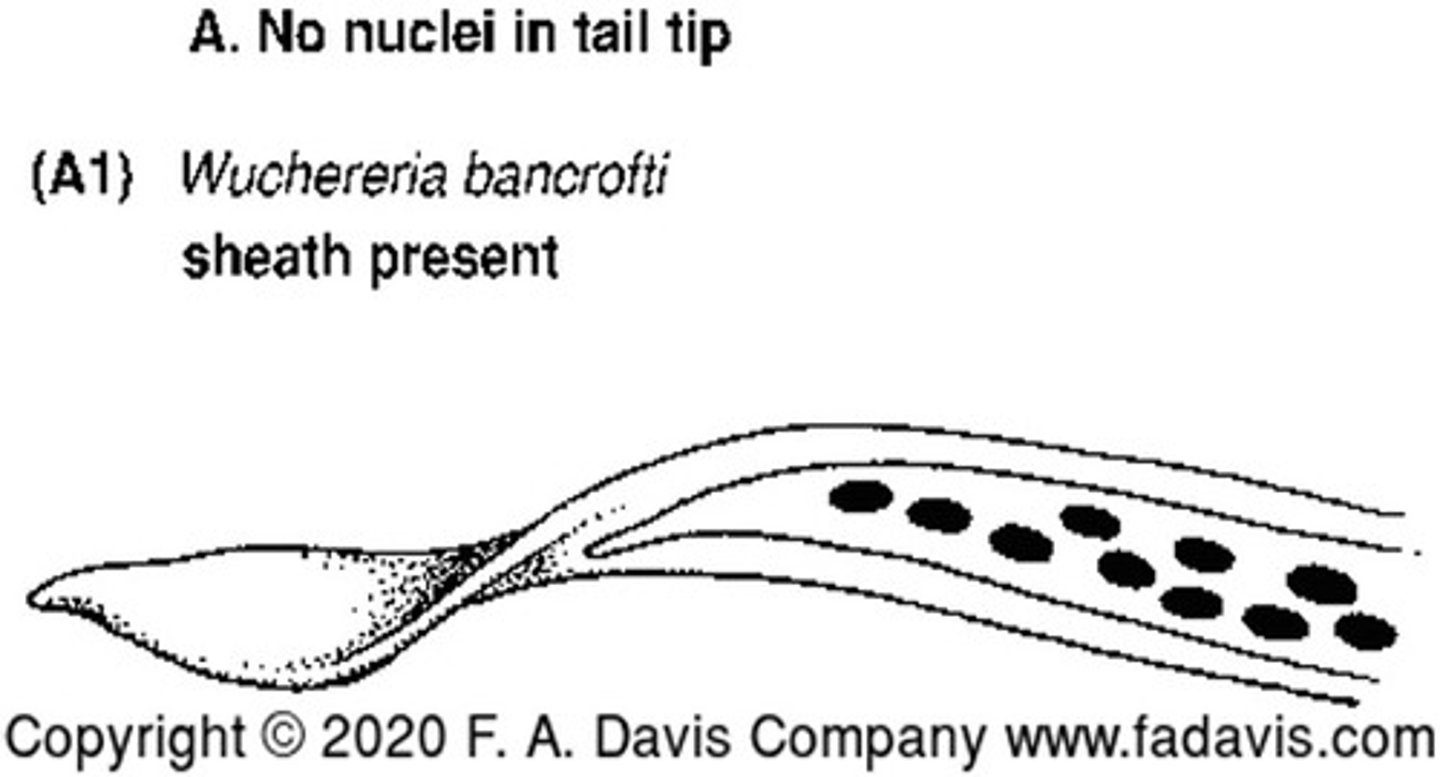
Describe and picture Wuchereia bancrofti
No nuclei in tail tip with a sheath present
Causes: granulomatous lesions, fever, chills, eosinophilia, and elephantiasis
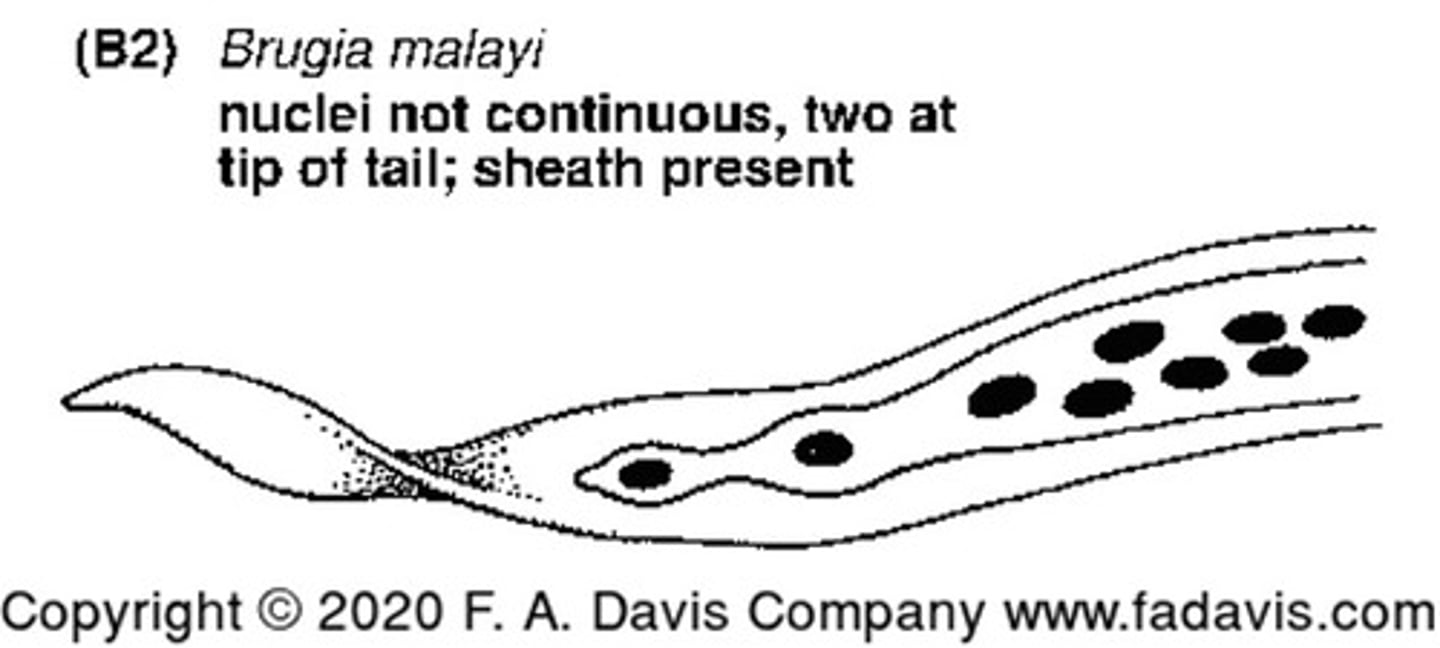
Describe and picture Brugia malayi
Nuclei in tail tip, no continuous nuclei with a sheath present
Causes: granulomatous lesions, fever, chills, eosinophilia and elephantiasis
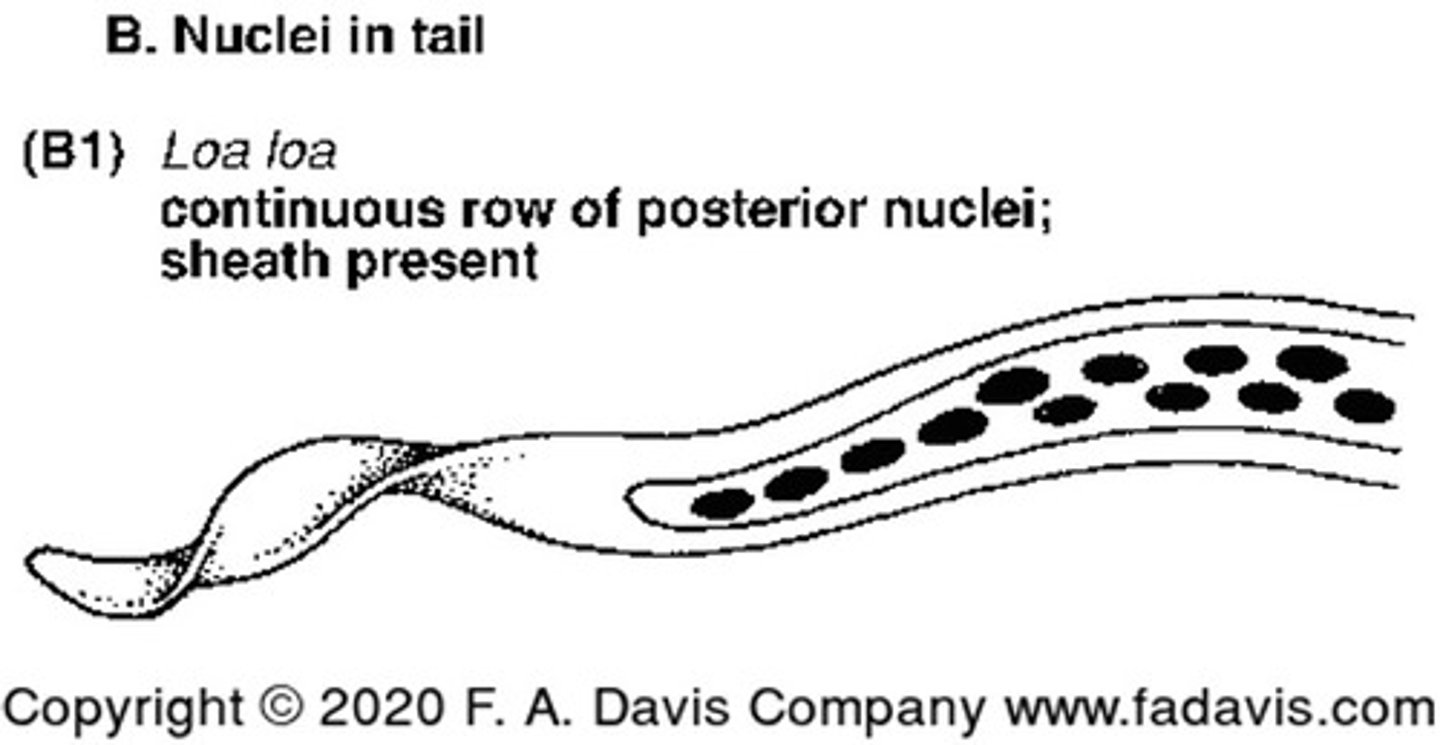
Describe and picture Loa loa
Nuclei in tail tip in a posterior continuous row with a sheath
Causes: Calabar swellings (eye edema), proteinuria and endomycardial fibrosis
Describe and picture Onchocerca volvulus
No nuclei in the tip with no sheath present
Causes: fibrotic skin nodules, blindness
How do humans acquire zoonotic nematode infections
Accidentally acquired from contact with contaminated animal feces, contaminated soil, or encountering the larvae eggs
How are Zoonotic infections most commonly diagnosed
Based on patient's symptoms
How does the phrase "strangers in a strange land" describe Zoonotic infections
Migrating larvae that are unable to develop into adults in their foreign host (larvae eventually die off and symptoms subside
Describe viceral larval migrans
An infection by zoonotic helminth larvae that migrate aimlessly throughout the boy because they are in an aberrant host
Describe how humans acquire VLM
By ingesting things that have been contaminated by the eggs
How to humans acquire Dirofilaria infections
Mosquito bites
Where do adult Dirofilaria live in dogs
Heart
Describe cutaneous larval migrans
Red, itchy tracts under the skin on the legs as larvae migrates
How do humans acquire CLM
When people walk or sit on the beach sand or soil where infected dogs or cats have defecated
barrel-shaped, thick shell, bipolar plugs
Trichuris
round to oval, thick shell, mammalated
Fertile Ascaris
oval, flattened on one side, thin shell
Enterobius
large, oval, with thick coat or no coat
|
oval, thin shell, 4-8 cell embryo
Hookworm
What is Ascaris infective form
Egg
What is Strongyliodes infective form
Filariform larva
What is Hookworm infective form
Filariform larva
What is Enterobius infective form
Egg
What is Trichuris infective form
egg