boundary layers - water
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
δ
boundary layer thickness
what happens to δ as fluid flows over a plate?
it increases
what happens as fluid passes over a greater length?
- more fluid is slowed by friction between the fluid layers
- thickness of the slow layer increases
what are the 2 main mechanisms that cause a boundary layer?
viscous forces and rotation
describe the boundary layer caused by viscous forces
thin, with a large velocity gradient du/dy
by quoting newton's law of viscosity, describe what happens to shear stress if there is a large velocity gradient
τ = μ(du/dy) so shear stress is large, large enough to drag fluid in
what happens as the boundary layer thickens?
the velocity gradient reduces and shear stress decreases.
- eventually it is too small to slow fluid
the part of the boundary layer caused by viscous forces dragging fluid in is called what?
the laminar boundary layer
describe what happens in the second mechanism
the viscous forces cannot drag all the fluid along so the fluid starts to rotate
describe what happens to fluid motion and the effects of this as fluid starts to rotate
- fluid motion rapidly becomes turbulent
- momentum transfers between main flow and boundary layer
what is the effect of the momentum transfer?
an increase in momentum in the boundary layer
the boundary layer with increased momentum is known as what?
the turbulent boundary layer
a large velocity gradient causes a large viscous force, this is large enough to cause what?
a thin layer of viscous flow called the laminar sublayer
what can happen if the laminar sublayer is thicker than the roughness of a pipe?
it can smooth the pipe wall
what effect does roughness have in turbulent flow?
if roughness is higher than laminar sublayer, turbulence increases and there are energy losses
what effect does roughness have in laminar flow?
little effect
what kind of flow do high inertial forces give?
turbulent
what kind of flow do high viscous forces give?
laminar
what are the effects of divergent flow in terms of pressure?
- positive pressure gradient
- pressure increases in the direction of flow
- higher pressure can push against flow and possibly reverse it
what are the other effects of divergent flow?
increases turbulence
increases the energy loss
what kind of pressure gradients do convergent flows create?
negative
how do convergent flows affect pressure?
pressure decreases in the direction of flow
what are the other effects of convergent flows?
- fluid accelerates and the boundary layer is thinner
- flow remains stable
- turbulence reduces
does boundary layer separation occur in convergent flows?
no
what happens at a divergent duct?
- velocity drops
- pressure increases
- increase angle for more danger of boundary layer separation
what happens at a Tee-junction? (assume equal sized pipes)
- area increases, similar to divergent pipe flow
-velocities at 2 and 3 are smaller than 1
- pressures at 2 and 3 are greater than 1
- causes boundary layer separation
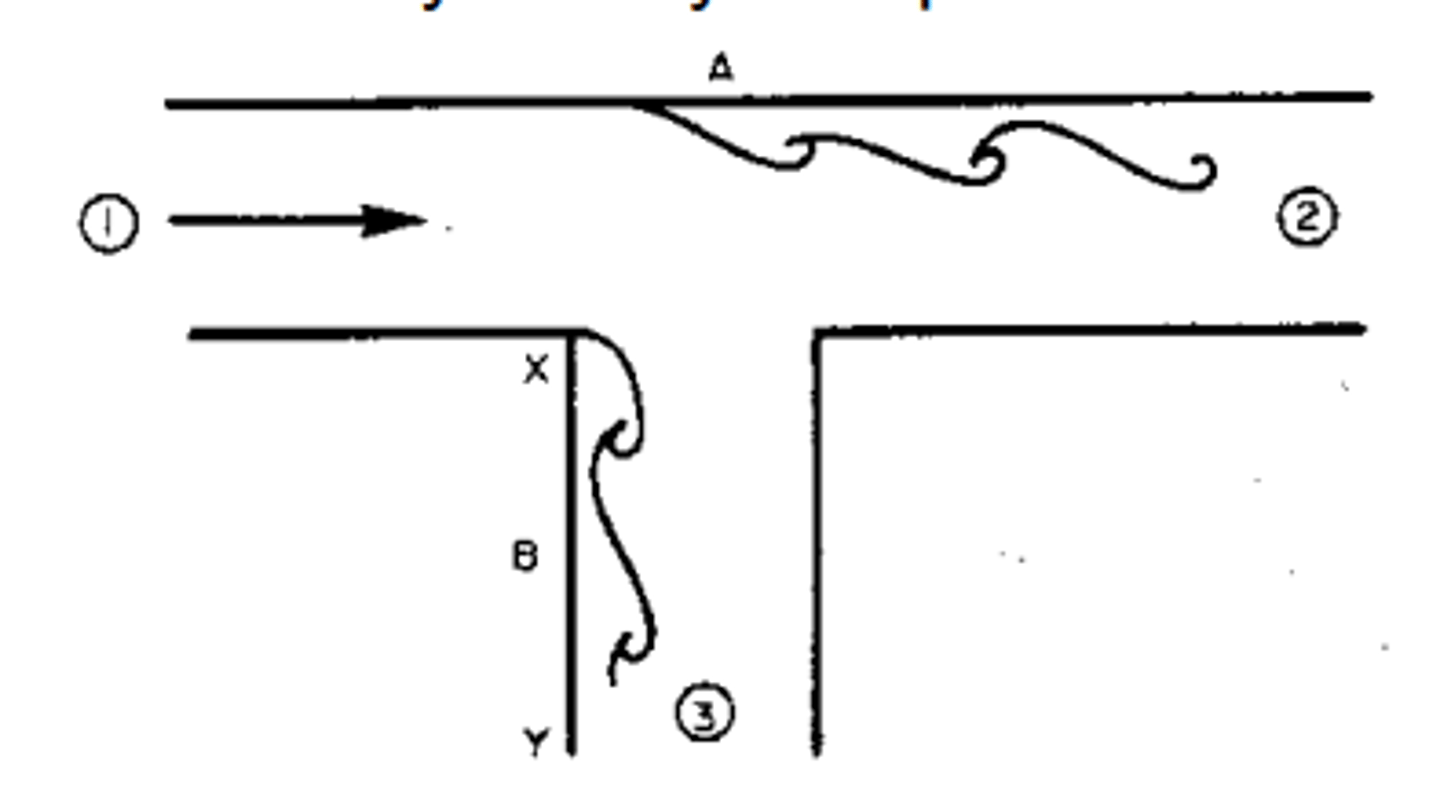
what happens if there is a bend in the pipe?
2 separation zones occur
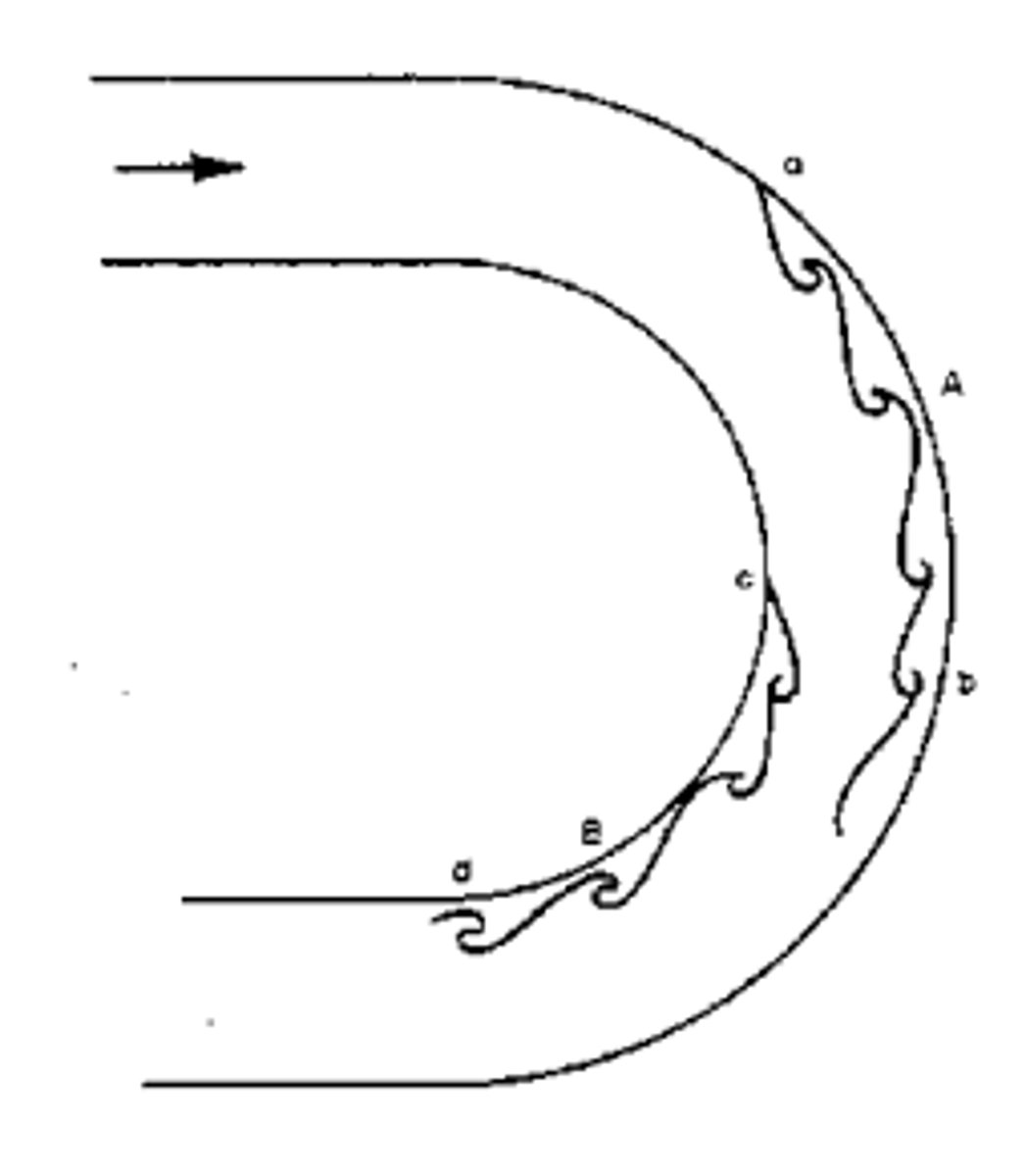
if flowing past a cylinder, what are the requirements for slow flow and what happens?
Re<0.5
no separation
if flowing past a cylinder, what are the requirements for moderate flow and what happens?
Re < 70
symmetric vortices
if flowing past a cylinder, what are the requirements for fast flow and what happens?
Re>70
alternate vortices fall from each side
what causes separation when flowing past a cylinder?
adverse pressure as fluid accelerates to get round
what happens in flow over an aerofoil?
velocity increases over the wing causing low pressure on the top
what happens if the aerofoil is at a steep angle?
the boundary layer can separate as most of the 'suction' pressure is lost
what are some solutions to prevent boundary layer separating when aerofoil is at too steep an angle?
- allow air through slot to get fast air on top
- put flap on wing to lengthen top surface