Bacterial Infections
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
1
New cards
What does C Diff stand for?
Clostridium difficile
2
New cards
What type of bacteria is C Diff?
Anaerobic, spore forming bacillus (Gram + and Rod Shaped)
3
New cards
In c diff, how long can spores survive for ? Does it need oxygen?
For several months and no, it’s anaerobic.
4
New cards
What’s one of the leading hospital acquired infections?
Clostridium difficile
5
New cards
C Diff route?
Primarily through Fecal oral route
6
New cards
C Diff is the leading cause of what type of infection?
Nosocomial Infections
7
New cards
What does C Diff manifest as ? And what can it lead to?
\
* Manifests as diarrhea (incontinent), but can lead to fatal inflammation of colon ( chronic loose stools and runny stools in the fecal matter)
* Manifests as diarrhea (incontinent), but can lead to fatal inflammation of colon ( chronic loose stools and runny stools in the fecal matter)
8
New cards
What is the risk group for C Diff?
- Antibiotic user
- \> 65 y/o
- Residing in room which housed C Diff pt 10-14 days prior
- \> 65 y/o
- Residing in room which housed C Diff pt 10-14 days prior
9
New cards
How to prevent C Diff?
* Contact Isolation
* BLEACH wipes >> 2 min air dry rule
* Need to use bleach wipes for whatever equipment you comin contact with the gait belts and such
* BLEACH wipes >> 2 min air dry rule
* Need to use bleach wipes for whatever equipment you comin contact with the gait belts and such
10
New cards
What is the treatment for C Diff?
Flagyl, vancomycin, probiotics
11
New cards
What type of bacteria is Staphylococcal Infections? Where does it reside?
Anaerobic bacteria that normally reside in skin
12
New cards
Staph infections is a leading cause of what?
Nosocomial and community acquired infections (Endocarditis, prosthetic device infection)
13
New cards
How does a person get a staph infection?
Direct contact transmission \>> not easily removed by scrubbing
14
New cards
What is the most common location for colonization for Staph infection?
Nares
15
New cards
What is Risk Group for Staph Infections?
- Surgical/burn pts
- IDDM
- Neutopenic
- Prosthetics
- Chronic Skin Disease
- RA
- Catheter
- Corticosteroid Rx
- IDDM
- Neutopenic
- Prosthetics
- Chronic Skin Disease
- RA
- Catheter
- Corticosteroid Rx
16
New cards
How to prevent Staph infection?
Hand washing/education
17
New cards
What is pathogenesis for Staph Infection? And what happens once it invades?
- Usually by traumatic inoculation
- Once invades, secrete membrane damaging enzymes and toxins
- Once invades, secrete membrane damaging enzymes and toxins
18
New cards
What does Staph Infections manifests as?
Local abscesses file w/ pus and bacteria
19
New cards
Staph Infections may lead to what?
* Infections anywhere via bloodstream
* Bones, Joints, Kidney, lung, Heart Valves (endocardinitis-lining of the cardiac is compromised)
* Bones, Joints, Kidney, lung, Heart Valves (endocardinitis-lining of the cardiac is compromised)
20
New cards
Symptoms of Staph Infection:
Fever, chills, pain, swelling over affected area, cellulitis
21
New cards
What is the most common Staph Infection?
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
22
New cards
What is treatment for MRSA?
Find antibiotic to fight strain (MRSA-Vancomycin)
23
New cards
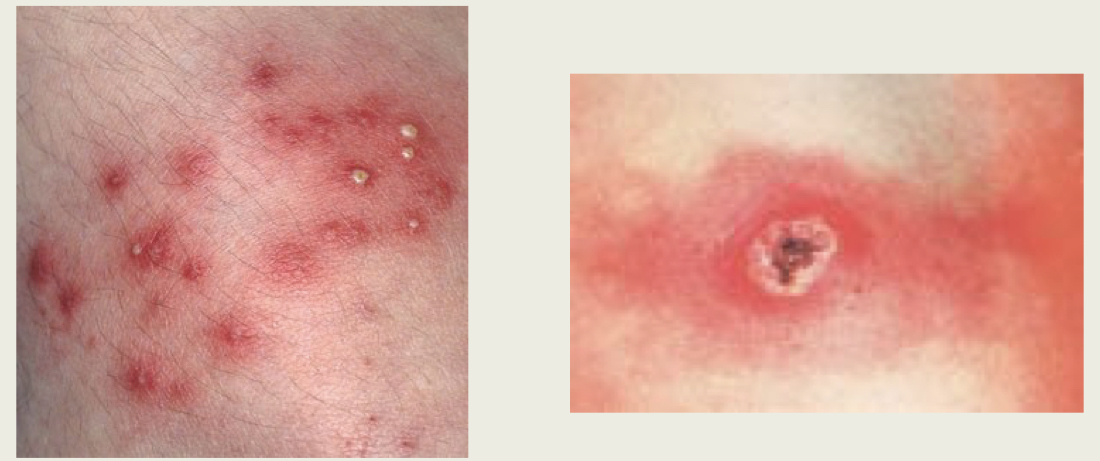
What is this ?
Staphylococcus Infection
24
New cards
What is GAS?
Streptococcal Infection - Group A
25
New cards
What is the most common pathogen that affects humans at any age and is an example of GAS?
S. Pyogenes
26
New cards
How is GAS transmitted?
Via contact w/ respiratory droplets
27
New cards
What are Signs and symptoms of GAS?
Dependent upon location of infection
28
New cards
GAS is also known as what?
Strep Throat
29
New cards
What is incubation period for GAS?
1-5 days
30
New cards
What is possible pt presentation if they have GAS?
Fever, sore throat, beefy red pharynx, swollen tonsils and lymph nodes, malaise, abdominal pain
31
New cards
What is treatment for GAS?
Antibiotics to avoid post strep syndromes
32
New cards
What does Post Strep secondary conditions include for Strep Throat?
Rheumatic fever or acute glomerulonephritis-(damaging the filtration system of your kidneys)
33
New cards
How can you get Scarlet Fever ?
When you leave strep throat untreated or wound infections
34
New cards
What does Strep Strain release?
A Pyrogenic Exotoxin = (fever)
35
New cards
What is Scarlet Fever common in?
2-10 y/o
36
New cards
How is Scarlet Fever Transmitted?
By direct inhalation or direct contact with oral secretions
(think about your contact precautions and what you need to wear)
(think about your contact precautions and what you need to wear)
37
New cards
What does a pt with Scarlet Fever present with?
* Fever
* Sore Throat
* Strawberry Tongue
* Rash that looks like Sand paper (it spreads from Chest to Extremities)
* Sore Throat
* Strawberry Tongue
* Rash that looks like Sand paper (it spreads from Chest to Extremities)
38
New cards
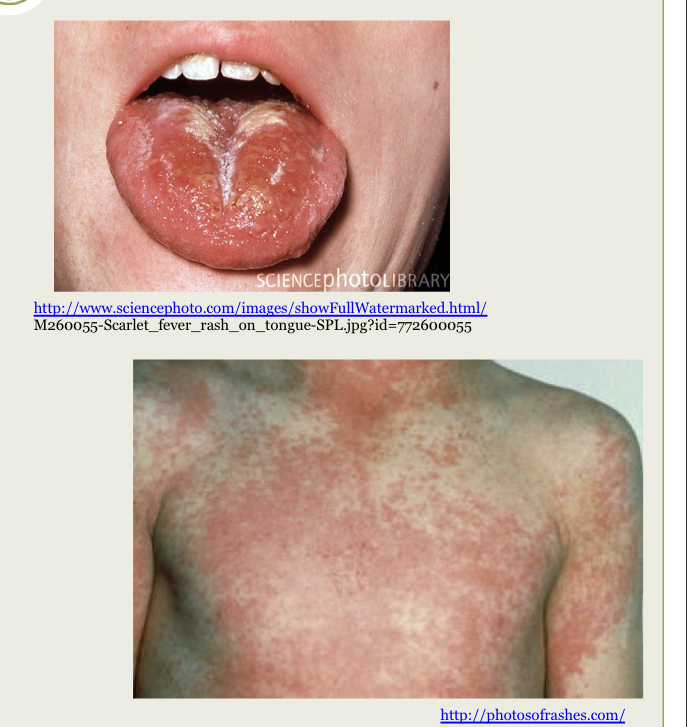
What infection is this?
Scarlet fever
39
New cards
What is Impetigo caused by?
Mainly by GAS but also by other strep and staph species
40
New cards
What is Impetigo most common in?
Children 2-5 y/o especially in hot, humid weather
41
New cards
What are the risks for Impetigo?
Close contact, over crowding, poor skin hygiene, minor skin trauma
42
New cards
What is the best defense against Impetigo? And why?
Good Hygiene since colonization usually precedes infection
43
New cards
What does a pt with Impetigo present with?
Small macule \>> Vesicles (pus and encrust)
44
New cards
What may spread Impetigo? And what can it cause?
Scratching and can cause cellulitis/lymphadenitis
45
New cards
Does Impetigo pts with Impetigo have fever or pain?
NOOO Just uncomfortable and itchy
46
New cards
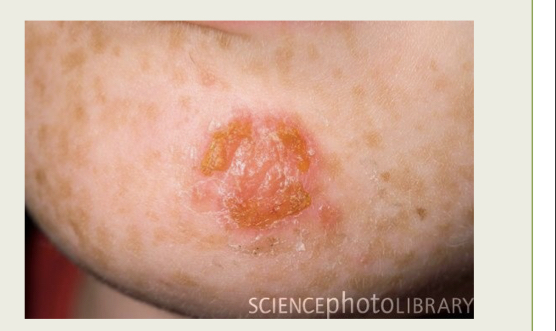
What infection is this?
Impetigo
47
New cards
What causes Erysipelas ?
It’s caused by Streptococcal Bacteria
48
New cards
What is Erysipelas?
Superficial cellulitis with fever and chills
49
New cards
Where is Erysipelas usually found on?
* Face and legs ( very well defined, you can see it where it starts and stops)
50
New cards
Erysipelas is most common in which gender?
Women
51
New cards
What does Erysipelas look like? And what can form in a couple of days?
- Skin is RED (well demarcated), shiny, and swollen
- Bullae (blisters) may form in couple of days
- Bullae (blisters) may form in couple of days
52
New cards
How is Erysipelas treated?
w/ antibiotics
53
New cards
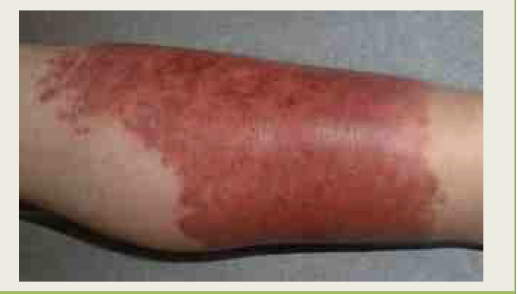
What infections is this?
Erysipelas
54
New cards
What is Streptococcal Cellulitis?
Inflammation of skin and subcutaneous tissues
55
New cards
Where is Streptococcal Cellulitis usually at?
Wound site, but entire site not always noted
56
New cards
Where can Streptococcal Cellulitis reoccur at?
In extremities w/ impaired lymph drainage
57
New cards
How does Lymphangitis present? (Streptococcal Cellulitis)
Red linear streak from affected area toward tender, swollen lymph nodes
58
New cards
What infection is this?
Streptococcal Cellulitis
59
New cards
What is Streptococcal Necrotizing Fasciitis (NF)?
Serious, rapidly progressive infection along fascial planes
60
New cards
In Streptococcal Necrotizing Fasciitis (NF), is it painful and what can you lose?
Yes it is very painful and you can lose skin tissue
61
New cards
What is Type 1 NF?
- Polymicorbial infection - p/o complication
62
New cards
What is Type 2 NF?
Distal break in skin or transient bacteremia
63
New cards
Pt presentation of NF? (4) steps, what happens initially and then what does the skin become?
● Initially, pain and fever present while skin looks healthy
● Infection rapidly spreads \> edema and tenderness
● Thrombosis of blood vessels \> dark red and indurated
● Ultimately, skin becomes ischemic (black and friable)
● Infection rapidly spreads \> edema and tenderness
● Thrombosis of blood vessels \> dark red and indurated
● Ultimately, skin becomes ischemic (black and friable)
64
New cards
S/S of NF? (4)
- Hypotension
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Delirium
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Delirium
65
New cards
Does NF have a high mortality rate? And why?
* Yes, because of:
* Toxic Shock
* Kidney and Liver Failure
* Pulmonary Infiltrates
* Toxic Shock
* Kidney and Liver Failure
* Pulmonary Infiltrates
66
New cards
What is treatment for NF?
* Aggressive debridement w/ IV antibiotics
67
New cards
What is needed in order to determine antibiotic choice?And what does does it need? (NF)
- Culture and gram staining
- May need serial debridement
- May need serial debridement
68
New cards
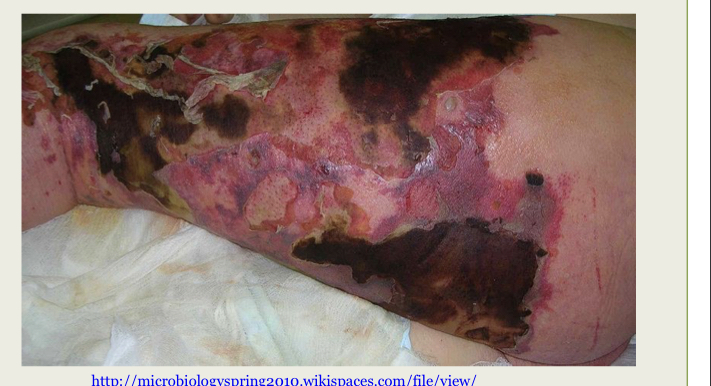
What infection is this ?
Streptococcal Necrotizing Fasciitis (NF)
69
New cards
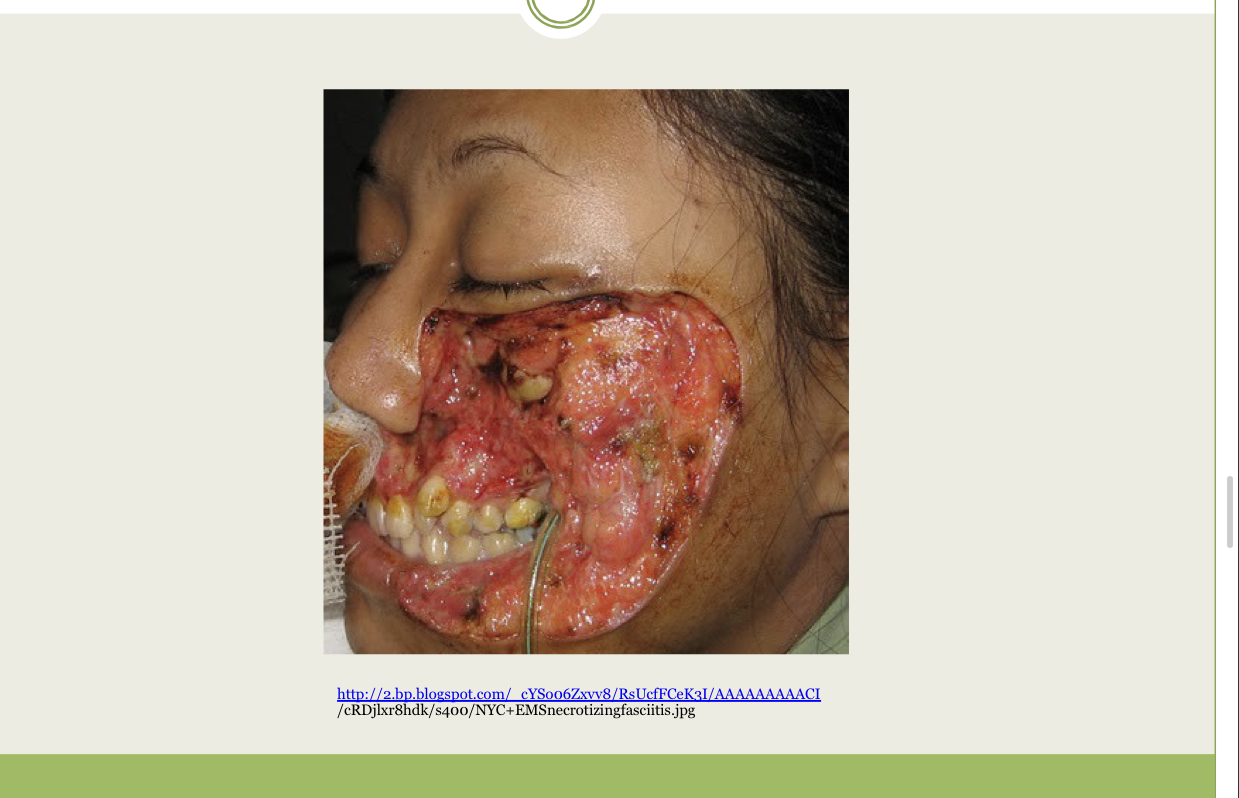
What infection is this?
Streptococcal Necrotizing Fasciitis (NF)
70
New cards
What is Streptococcus Pneumoniae a cause of? (4)
- PNA
- Sepsis
- Otitis Media
- Meningitis
- Sepsis
- Otitis Media
- Meningitis
71
New cards
How is Streptococcus Pneumoniae transmitted?
Direct contact or inhalation of respiratory secretions
72
New cards
Streptococcus Pneumoniae is the most common cause of what?
- Community-Acuired PNA
- Death by preventable bacterial diseases by vaccination
- Death by preventable bacterial diseases by vaccination
73
New cards
Streptococcus Pneumoniae vaccine is recommended for what population?
- \> 65 y/o
- Individuals w/ chronic diseases or compromised immunity
- Individuals w/ chronic diseases or compromised immunity
74
New cards
Streptococcus Pneumoniae pt presentation (7)
- fever
- pleuritis with pain
- dyspnea
- productive cough
- purulent sputum
- elderly with delerium
- slight cough
- pleuritis with pain
- dyspnea
- productive cough
- purulent sputum
- elderly with delerium
- slight cough
75
New cards
What are complications of Streptococcus Pneumoniae?
- Empymea
- Bacteremia
- Sepsis
- Meningitis
- Bacteremia
- Sepsis
- Meningitis
76
New cards
What is required to select appropriate antibiotic for Streptococcus Pneumoniae?
Culture fluid and Gram Staining
77
New cards
What is Gas Gangrene? And what is it caused by?
- Rare, painful
- Caused by Anaerobic Bacteria (Clostridial Myonecrosis)
- Caused by Anaerobic Bacteria (Clostridial Myonecrosis)
78
New cards
What happens to the muscles and subcutaneous tissues with Gangrene?
Muscles and subcutaneous tissues fill with gas and exudate
79
New cards
What does gangrene usually follow after?
Follows trauma or surgery
80
New cards
What can happen in a couple of hours with gangrene?
It spreads rapidly so death can follow within hours
81
New cards
Gangrene growth is uncommon in what?
Healthy human tissue UNLESS devitalized tissue w/ severe trauma present
82
New cards
Where is Gangrene usually found?
deep wounds
83
New cards
What gasses are produced subcutaneously when pt has Gangrene?
CO2 and H Gasses
84
New cards
Gangrene Incubation period?
< 3 days after injury
85
New cards
What are Signs and symptoms of Gangrene?
- Cool skin
- Pallor/Cyanosis
- Sudden/Sever Pain
- Sudden edema
- Loss of Extremity pulses
- Pallor/Cyanosis
- Sudden/Sever Pain
- Sudden edema
- Loss of Extremity pulses
86
New cards
What happens to the skin of Gangrene pt?
* Skin darkens because of cutaneous necrosis and hemorrhage
* Thick discharge w/ foul odor
* Thick discharge w/ foul odor
87
New cards
In gas gangrene, whats it called when you palpate the skin from gas bubbles?
Crepitation
88
New cards
What’s the key prevention to avoid Gangrene?
Cleaning Wounds
89
New cards
How can you treat gas gangrene?
surgical debridement and antibiotics
90
New cards
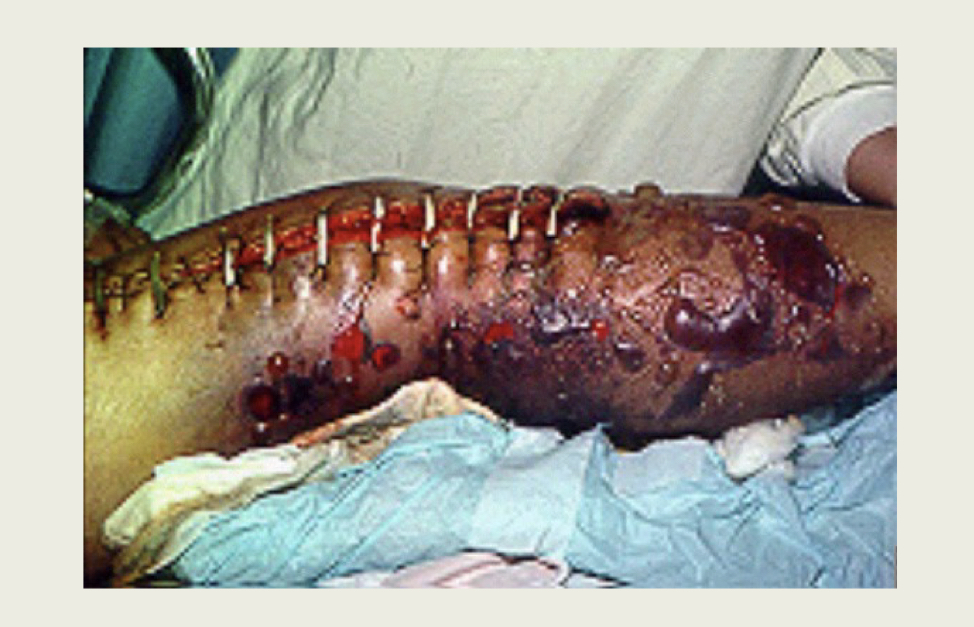
What infection is this?
Gas gangrene
91
New cards
What type of bacteria is Pseudomonas?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa-opportunistic bacteria
92
New cards
What does Pseudomonas cause?
PNA, wound infections, UTI, Sepsis
93
New cards
Where does Pseudomonas thrive in?
Moist environment surfaces
94
New cards
Is Pseudomonas antibiotic resistant?
YESS which is why it’s tough to treat
95
New cards
Pseudomonas aggressive growth often leads to what?
Sepsis in population with low immunity
96
New cards
How does a person contract Pseudomonas?
Contact transmission
97
New cards
What are the 3 ways to prevent Pseudomonas transmission?
- Proper hand hygiene
- Proper cleaning of equipment
- Strict Sterils techniques w/ wounds
- Proper cleaning of equipment
- Strict Sterils techniques w/ wounds
98
New cards
What does Pseudomonas produce?
Variety of proteins which helps to evade host's immune response
99
New cards
Pseudomonas damages what?
- Epithelial cells uncovering binding sites or P. Aeruginosa
100
New cards
What does Pseudomonas produce for protection?
Proteoglycan