Chemistry Unit 2 Test
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Democritus
developed the first idea of the atom
half of a glass of water: will there be a point where the water won’t be water any more?
philosophical idea
John Dalton
assumed the lowest ratio of atoms is 1:1
studied the idea of atoms (experimentally)
developed Atomic Theory
John Dalton’s Atomic Theory
atoms exist and are indivisible (needs revision)
each element had identical atoms, which are different from those of any other element (needs revision: isotopes)
Atoms physically mic, or chemically combine in whole # ratios to form compounds (correct)
chemical reactions are rearranging which atoms are combined, not changing the atoms
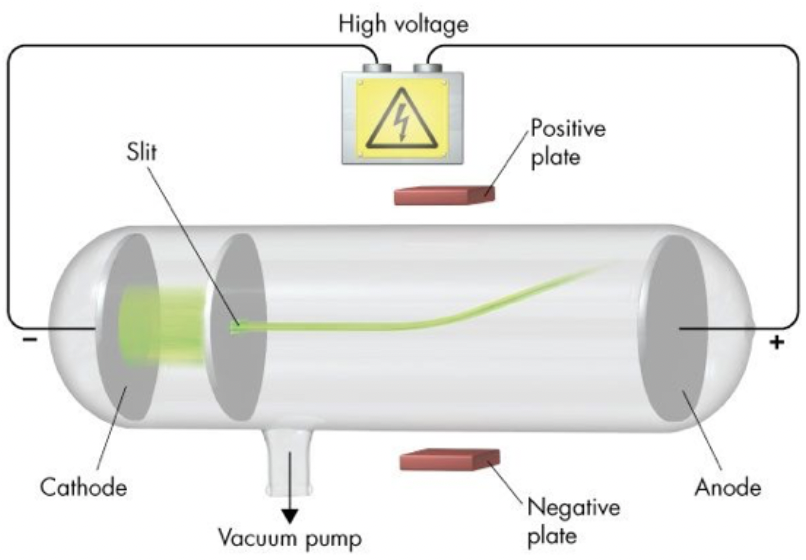
JJ Thomson
discovered the electron
high voltage can be passed through metal in a vacuum (cathode ray tube) → atoms are divisible
Plum Pudding Model
Plum Pudding Model
Thomson
atom is a uniform, positive charge
electrons embedded regularly within it
no nucleus
Saturnian Model
Nagaoka
The positive charge is at the center, and electrons move around like Saturn’s rings
energy would have been lost
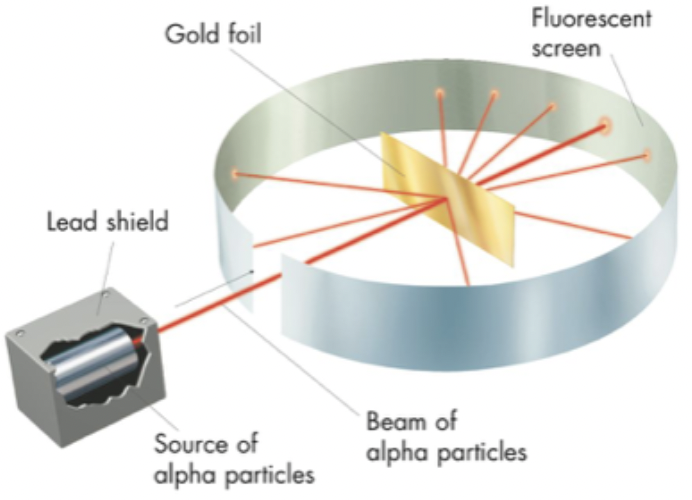
Earnest Rutherford
discovered the nucleus
gold foil experiment:
positive charge in atom is super, super small (nucleus) but very heavy
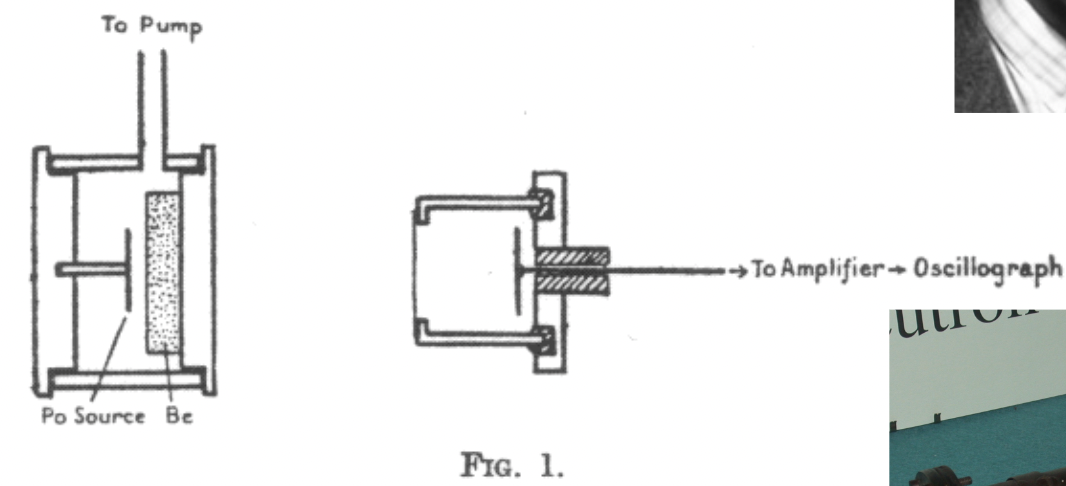
James Chadwick
discovered the neutron
nobel prize
Which Subatomic Particle?
Red- proton
Purple- neutron
Green- electron
Structure of an Electron
location: outside nucleus
mass: 1/1840 amu
charge: -1
Structure of a Proton
location: nucleus
mass: 1 amu
charge: +1
Structure of a Neutron
location: nucleus
mass: 1 amu
charge: 0
Nucleus of an Atom
high mass, low volume
Structure of an element
Proton: changes element
Neutrons: changes mass/ isotope
Electrons: changes charge (ions)
Atomic #
# of protons in an atom of the element
Mass #
# of protons + neutrons in an atom of the specific isotope
Element Symbol
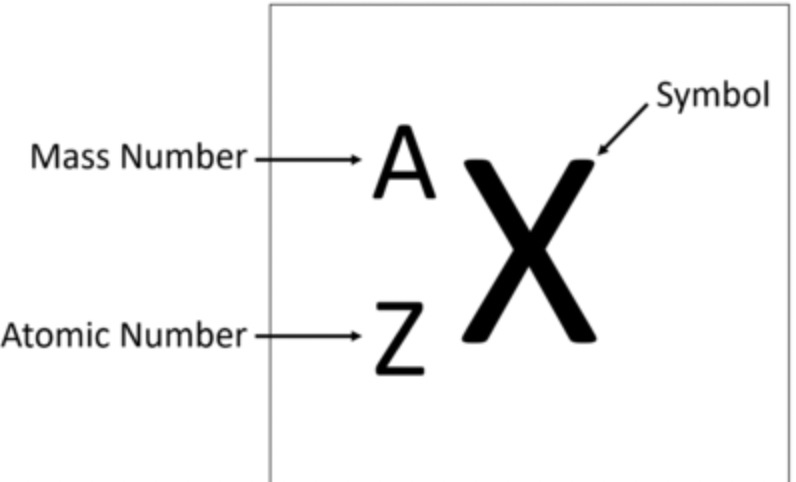
Naming Isotopes
element-mass#
ex: oxygen-16 ion (3+)
Atomic Spectrum
“finger print” of an element
atoms get energy from the sun (exciting) and release it as light
enables the identification of elements
The Photoelectric Effect
light has wave-particle duality
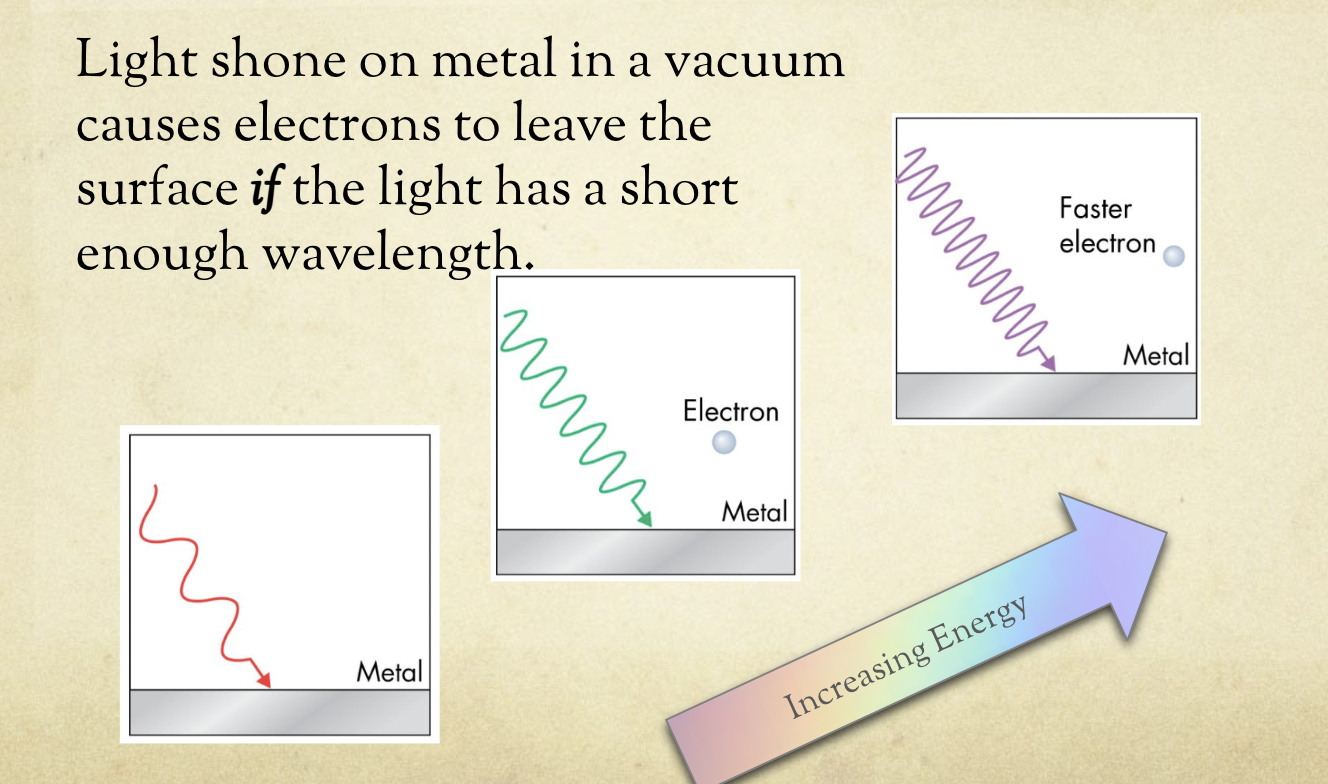
Photons
packets of waves
wave properties
wavelength: determines color+energy
particle properties
photons
Wavelength
smaller wavelength→ faster electrons
there is a cut off wavelength above which no electrons are released → depends on element
Photon Flux (brightness/frequency)
# of protons determines how many electrons are released (1 electron→ 1 photon)
does not impact speed of electron
Frequency + Wavelengths of light
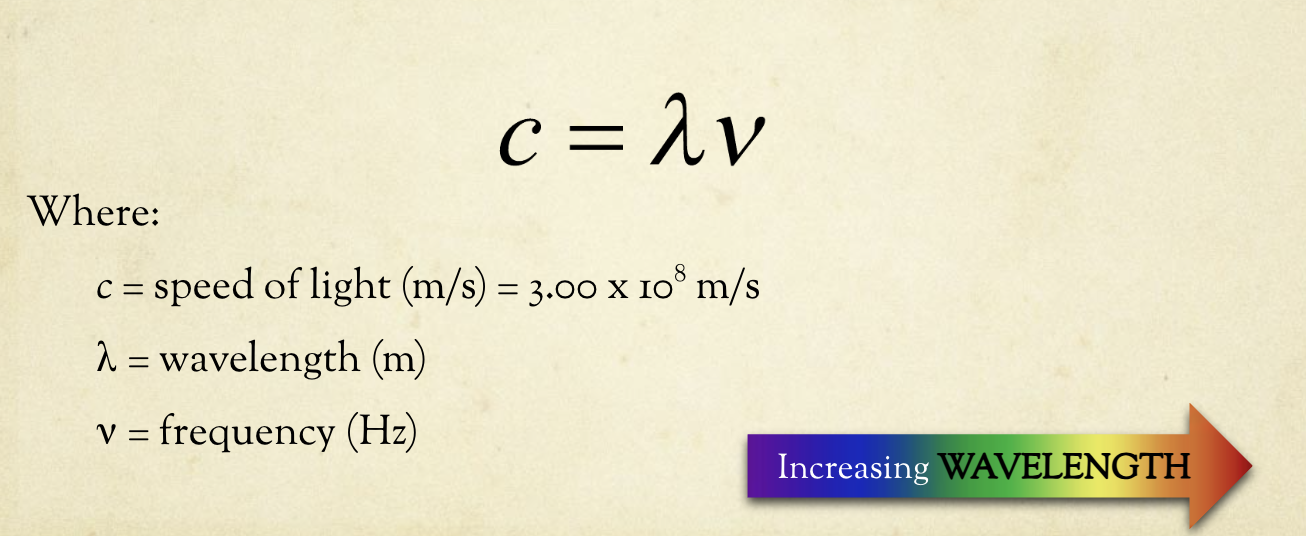
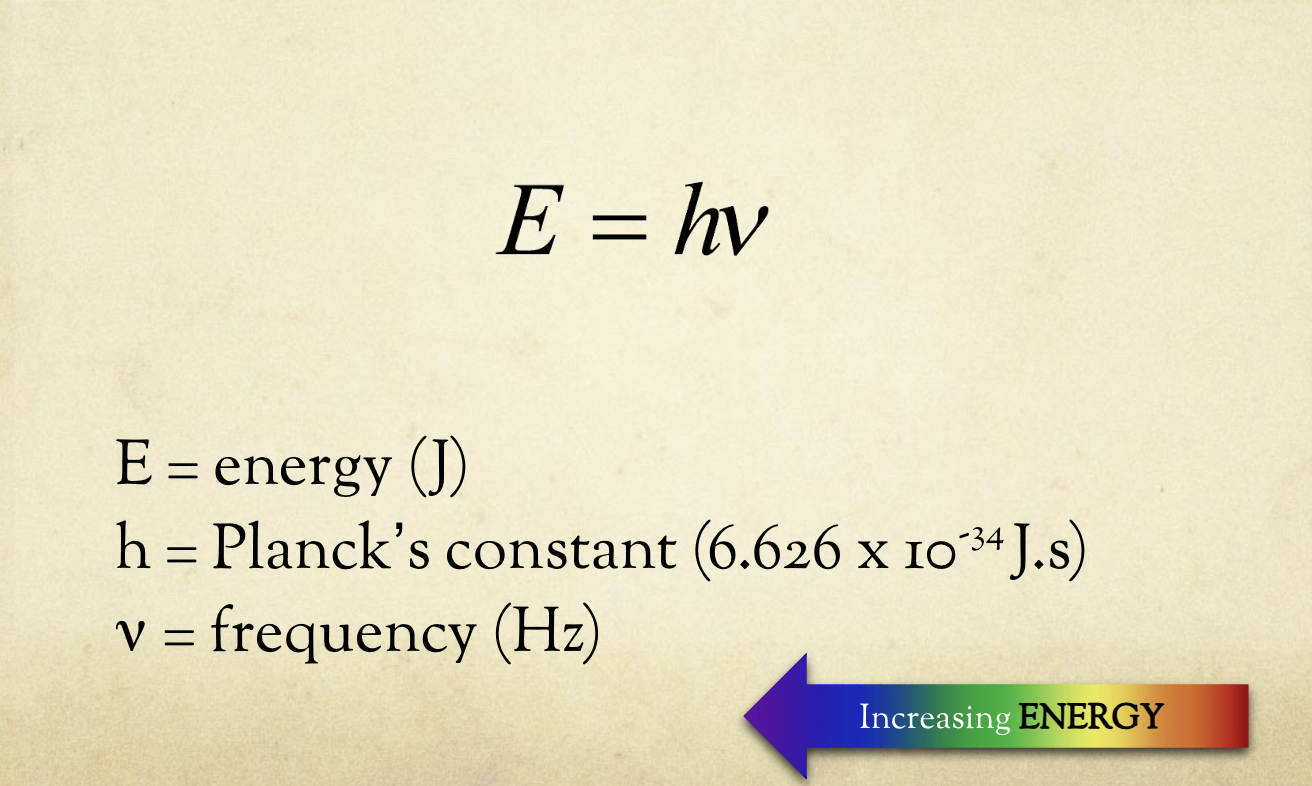
Energy of a Photon
Niels Bohr
discovered that electrons orbit the nucleus in specific radius orbits of specific energies
Bohr Model
electrons orbit the nucleus in specific radius orbits of specific energies
quantized: only certain values are allowed
ground state: n=1
n = ∞: electron has left the atom
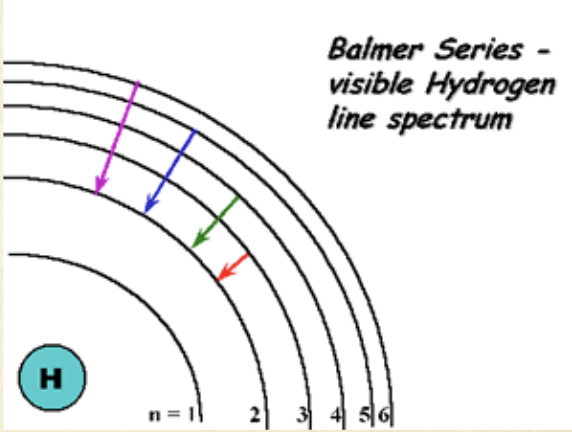
Absorption line spectrum
absorbed colors are absent
arrows pointing up
Emission line spectrum spectrum
emitted colors are present
arrows pointing down
ionization
n=1 → n=∞
absorption
n=2 → n=3,4,5…
Quantum Mechanical Model
Schrödinger
probability based
electron energy is quantized
electrons have wave-particle duality
orbital
area in which there is a 90% chance of finding an electron
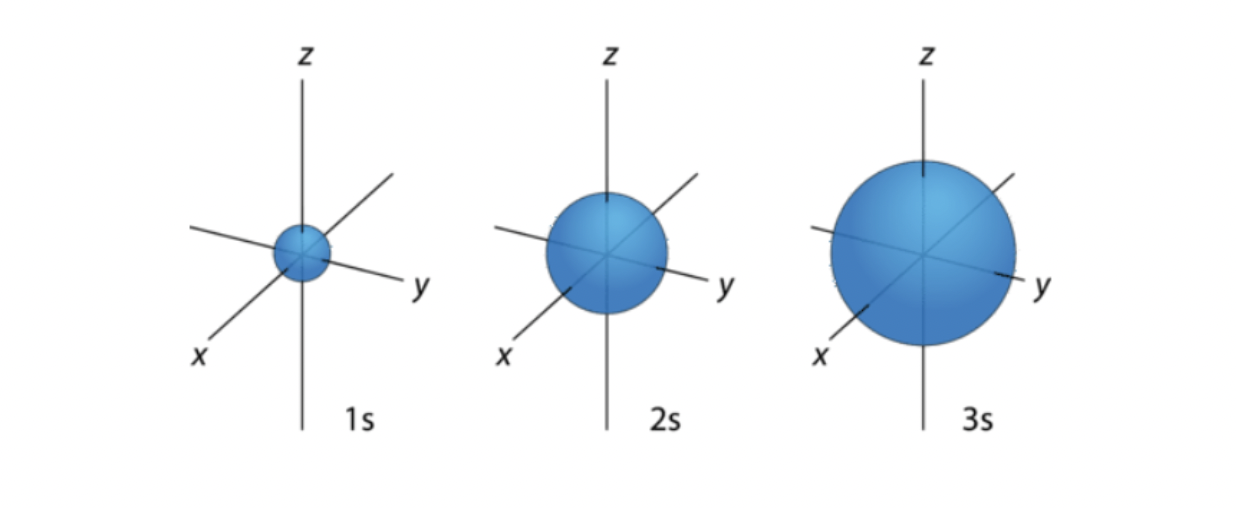
s orbitals
spherical
origin: nucleus
1s 2s 3s: principal energy level
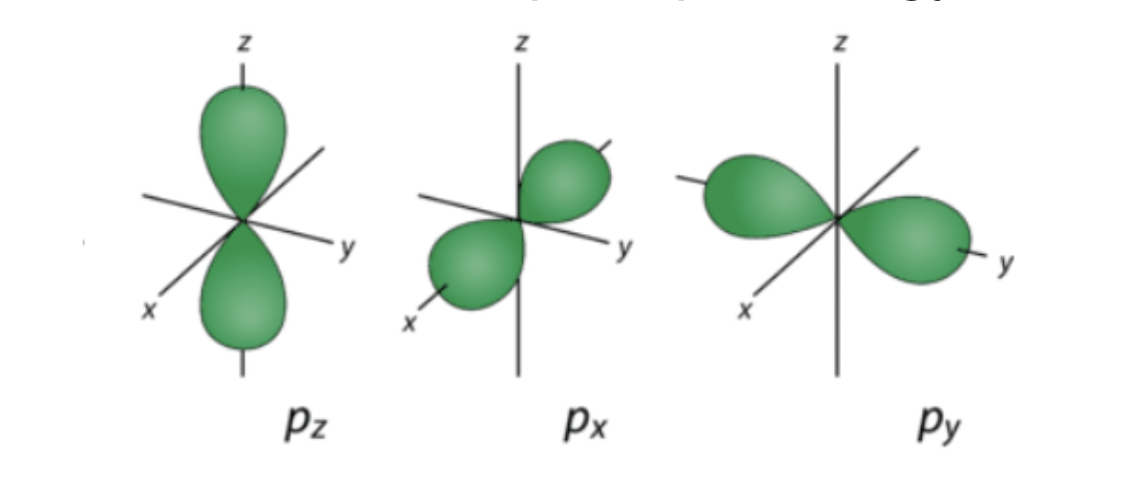
p orbitals
energy levels 2 and above
3 p orbitals: pz px py
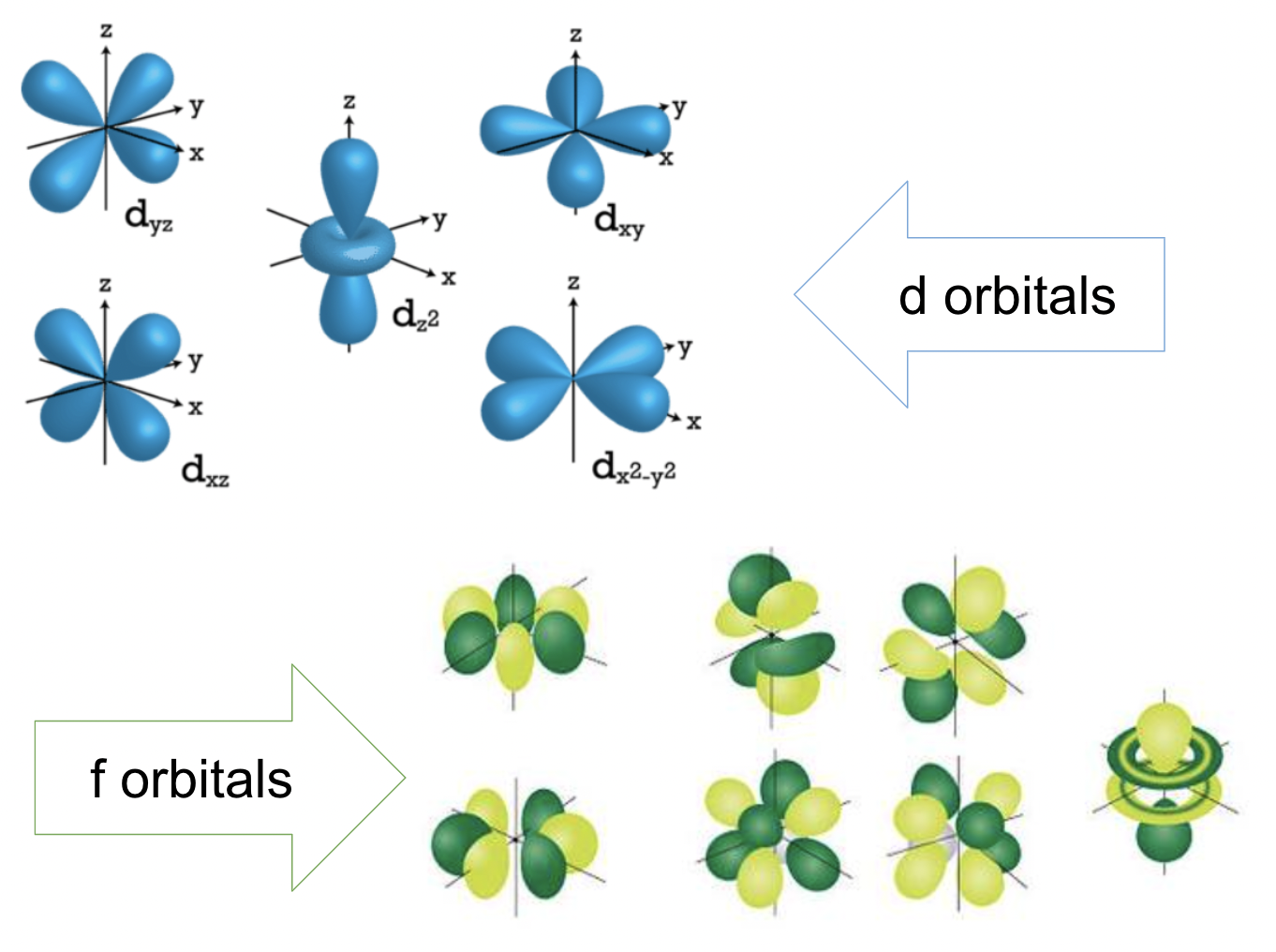
d and f orbitals
5 d orbitals, principal energy levels 3 and above
7 d orbitals, principal energy levels 4 and above
electron configurations
arrangement of electrons in an atom
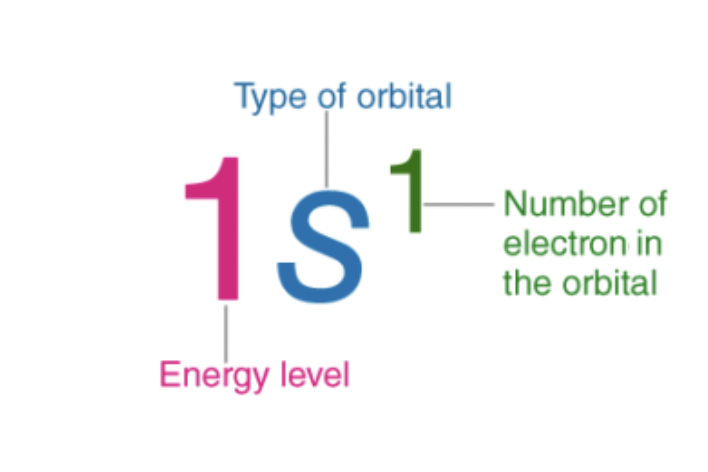
orbital filling diagram
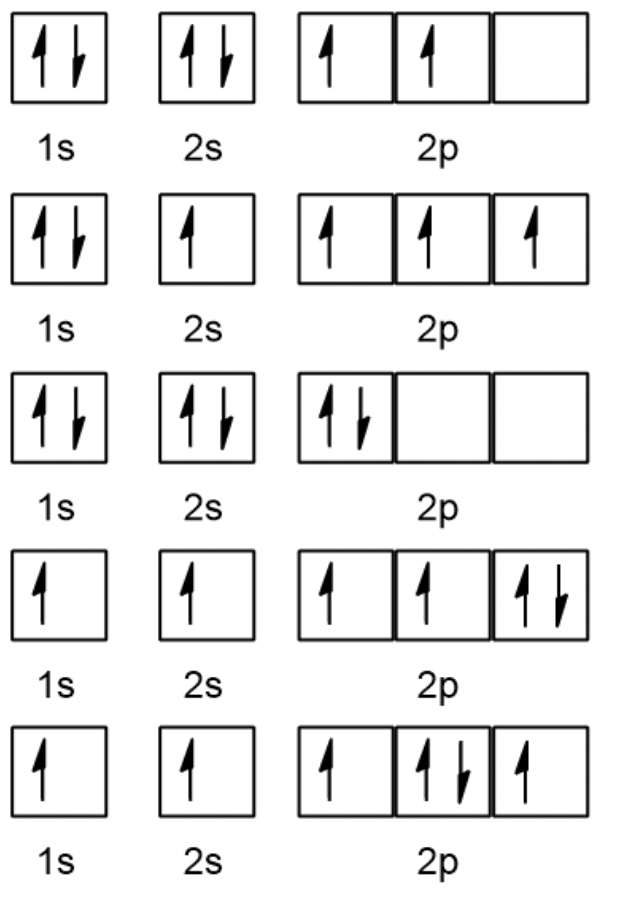
The Aufbau Principle
electrons enter orbitals of lowest energy first
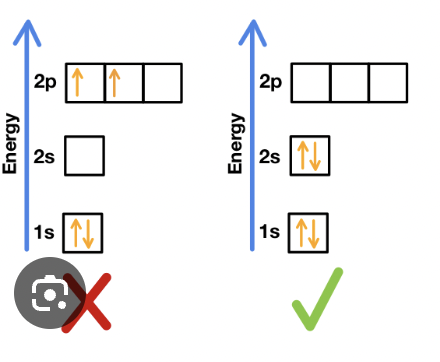
Pauli Exclusion Principle
no 2 electrons have the exact same energy state
electrons have a quantum property called spin
max of 2 electrons in an orbital, must have opposite spin
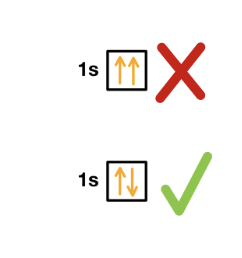
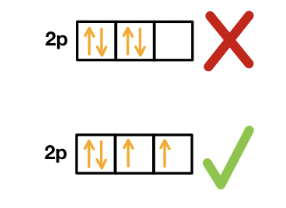
Hund’s Rule
when electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, they do so to maximize the overall spin
weighted average formula
avg=(mass1 x percentage1) + (mass2 x percentage2)
higher energy transitions are associated with high frequency, shorter wavelength light
higher energy transitions are associated with high frequency, shorter wavelength light
define atom
building blocks of matter
excited state
when n increases
spin
rotation of electrons