World Issues Exam
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
1
New cards
What is an issue?
a complex problem with many sides involving dispute that requires a solution and is a matter of concern to many people
2
New cards
What are the three things an issue must be?
* Complex
* Interrelated
* Controversial
* Interrelated
* Controversial
3
New cards
What is media?
\
\
forms of mass communication like newspapers, television, radio, the internet, etc., as well as the people involved in their production.
4
New cards
What is bias?
prejudice in favor of or against one thing, person, or group compared with another, usually in a way considered to be unfair.
5
New cards
What are ways to *identify* bias?
* Look at who wrote/published the information and why they wrote it; are they pushing a certain agenda?
* Was the author/publisher/organization closely related to the event it is reporting on? How could that impact the way the information is presented/represented?
* Does the argument/information only support one side?
* Is the information overly simplified or generalized to minimize the complexity and even downright misconstrue or misinform?
* Is the language used particularly strong or emotional? Why?
* Is there a use/perpetuation of stereotypes?
* Are the counter arguments, if there are any, fairly and thoroughly developed and presented, just as much as the initial argument is?
* Was the author/publisher/organization closely related to the event it is reporting on? How could that impact the way the information is presented/represented?
* Does the argument/information only support one side?
* Is the information overly simplified or generalized to minimize the complexity and even downright misconstrue or misinform?
* Is the language used particularly strong or emotional? Why?
* Is there a use/perpetuation of stereotypes?
* Are the counter arguments, if there are any, fairly and thoroughly developed and presented, just as much as the initial argument is?
6
New cards
How can you tell if your information may be biased?
Check the credibility of your sources:
* Have more confidence in academic articles, professional journals and most scholarly books due to their editing/peer reviewing process before they can be published
* Have less confidence in magazines and newspapers due to their lack of peer-revision, though they can be held legally responsible for libel (defamation in a written form) if the information is incorrect and/or damaging
* Have the least confidence in sources that are not peer reviewed and cannot be held financially responsible, like many websites
* Have more confidence in academic articles, professional journals and most scholarly books due to their editing/peer reviewing process before they can be published
* Have less confidence in magazines and newspapers due to their lack of peer-revision, though they can be held legally responsible for libel (defamation in a written form) if the information is incorrect and/or damaging
* Have the least confidence in sources that are not peer reviewed and cannot be held financially responsible, like many websites
7
New cards
What is quality of life?
the standard of health, comfort, and happiness experienced by an individual or group
8
New cards
What are some factors impacting/indicating quality of life?
* Population density
* Life expectancy
* Food adequacy
* Food production efficiency
* Trading wealth
* Education
* Health
* Ease of travel
* Crime
* Dependency load
* Housing
* Fertility rate
* Life expectancy
* Food adequacy
* Food production efficiency
* Trading wealth
* Education
* Health
* Ease of travel
* Crime
* Dependency load
* Housing
* Fertility rate
9
New cards
What are some indexes that are used to determine quality of life?
* Freedom Index: measures freedom within a country
\
* GDP per capita: Gross Domestic Product; sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy plus any product taxes (less subsidies) not included in the valuation of output, divided by mid-year population
\
* GINI index: describes distribution of wealth within a country
\
* HPI: Happy Planet Index; measures worldwide environmental progress
\
* HDI; Human Development Index; considers education, wealth and health
\
* Popsicle Index: measures the % of people who feel a young child could safely walk to go buy a popsicle and return safely
\
* GDP per capita: Gross Domestic Product; sum of gross value added by all resident producers in the economy plus any product taxes (less subsidies) not included in the valuation of output, divided by mid-year population
\
* GINI index: describes distribution of wealth within a country
\
* HPI: Happy Planet Index; measures worldwide environmental progress
\
* HDI; Human Development Index; considers education, wealth and health
\
* Popsicle Index: measures the % of people who feel a young child could safely walk to go buy a popsicle and return safely
10
New cards
What is globalization?
a trend towards greater interconnections between systems
11
New cards
What are the six types of globalization?
* Geographical
* Sociological
* Ecological
* Cultural
* Political
* Sociological
* Ecological
* Cultural
* Political
12
New cards
What is geographical globalization?
networking of world cities and regions rather than separate countries (borderless)
13
New cards
What is sociological globalization?
development of the concept that we are all members of one single society rather than distinct national and cultural societies (common attitudes/standards)
14
New cards
What is ecological globalization?
growing acceptance of the planet as one single ecosystem instead of a collection of ecosystems (ex: World Nations treaty to combat ozone depletion)
15
New cards
What is cultural globalization?
harmony of the world’s cultures (ex: music)
16
New cards
What is political globalization?
adopting uniform policies worldwide from sociological and economic perspectives (ex: United States, Mexico, Canada Free Trade Agreement)
17
New cards
What is technological globalization?
growth of worldwide communication via cellphone, internet, etc.
18
New cards
What is sustainability?
* concern of meeting people’s needs today without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs
* shaped by two ways of looking at the environment and its role in human survival
* shaped by two ways of looking at the environment and its role in human survival
19
New cards
What is *anthropocentric* sustainability?
* the belief that nature is to be used, not preserve
* conservation mustn’t work against societal values
* primary value of natural areas is its value to humanity
* conservation by developing societies is preventing waste for further exploitation
* conservation mustn’t work against societal values
* primary value of natural areas is its value to humanity
* conservation by developing societies is preventing waste for further exploitation
20
New cards
What is *biocentric* sustainability?
* all parts of nature are interconnected
* the environment must be protected and held in greatest value
* natural areas have value in themselves
* all human activities must work within the limits of the planet’s ecosystem
* the environment must be protected and held in greatest value
* natural areas have value in themselves
* all human activities must work within the limits of the planet’s ecosystem
21
New cards
What is demography?
the study of human populations and the implications of changes in population size and composition
22
New cards
What is the Demographic Transition Model?
a chart that tracks the phenomenon of high birth and death rates changing to low birth and death rates over time as a population fluctuates
23
New cards
Which theorist is most commonly associated with the Demographic Transition Model?
Warren Thompson
24
New cards
What are population pyramids?
a graph used to make comparisons between men and women in the same age group or between young people and older people
25
New cards
What are the defining factors of stage 1 of the Demographic Transition Model?
* High birth rates
* High death rates
* Stable but small population, slow natural increase
* Wide, thin bottom that curves upwards to a narrow peak
* High fertility rate
* Low life expectancy
* Poor access to medicine
Ex: Canada in 1750 or Chad today
* High death rates
* Stable but small population, slow natural increase
* Wide, thin bottom that curves upwards to a narrow peak
* High fertility rate
* Low life expectancy
* Poor access to medicine
Ex: Canada in 1750 or Chad today
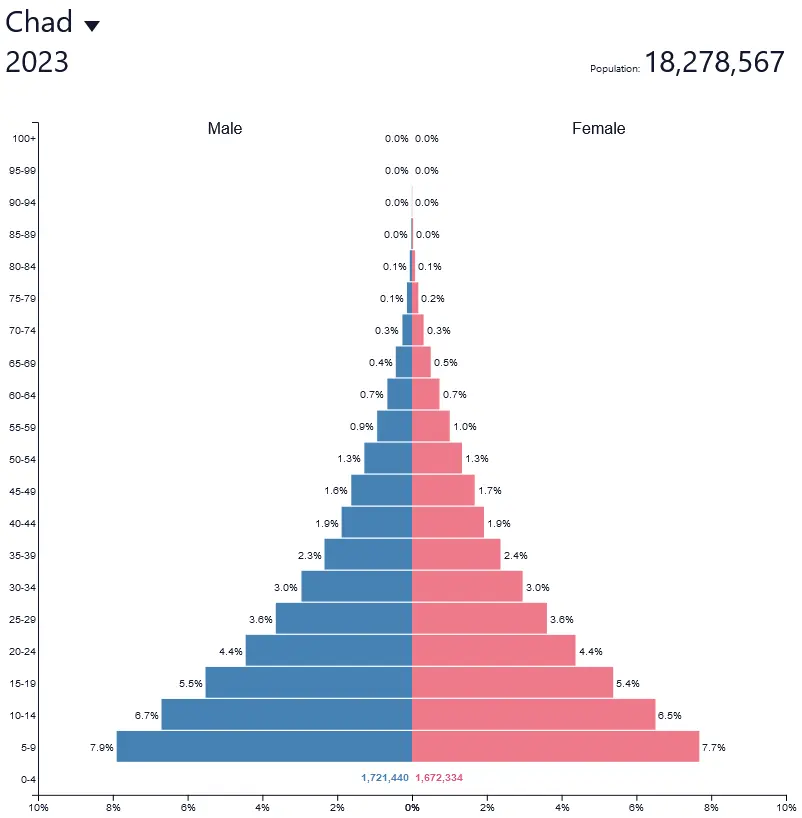
26
New cards
What are the defining factors of stage 2 of the Demographic Transition Model?
\
\
* High birth rates
* Rapidly falling death rate
* Very rapid natural increase
* Dramatic decline in the death rate due to better sanitary conditions, access to medicine or better food supply.
* Life expectancy increases so the population pyramid gets wider in the lower half
* Straight sides, pyramid shape
Ex: Palestine
* Rapidly falling death rate
* Very rapid natural increase
* Dramatic decline in the death rate due to better sanitary conditions, access to medicine or better food supply.
* Life expectancy increases so the population pyramid gets wider in the lower half
* Straight sides, pyramid shape
Ex: Palestine
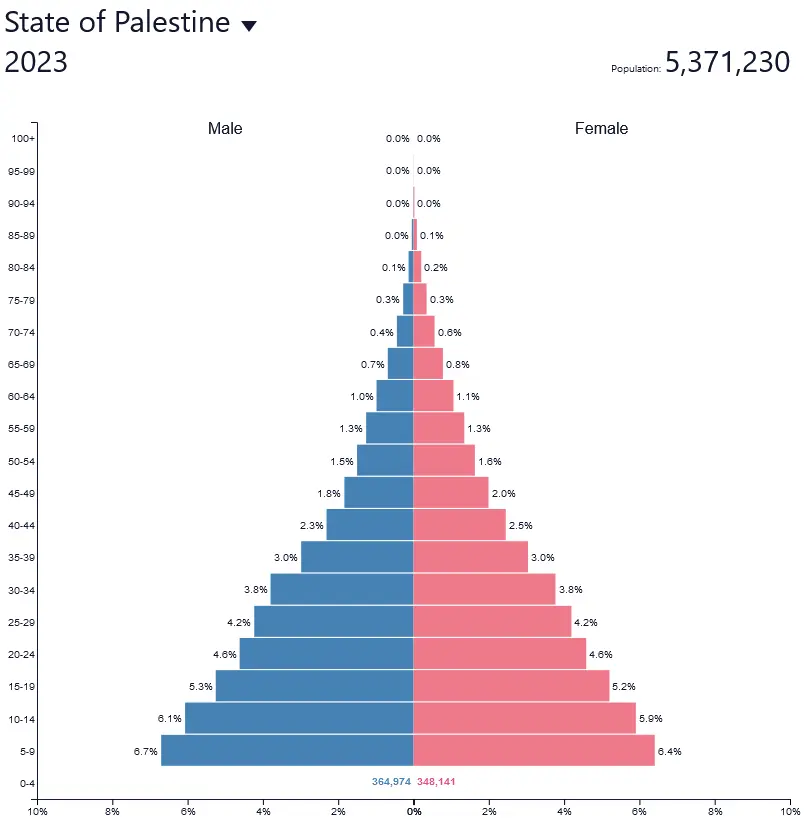
27
New cards
What are the defining factors of stage 3 of the Demographic Transition Model?
* Falling birth rate (people may choose to have fewer children due to low infant mortality rates and access to birth control)
* Falling death rate, more slowly
* Natural increase slows down
* Typically women are entering the work force in larger numbers
* Pyramid shape lifted onto a rectangular base
Ex: Mexico
* Falling death rate, more slowly
* Natural increase slows down
* Typically women are entering the work force in larger numbers
* Pyramid shape lifted onto a rectangular base
Ex: Mexico
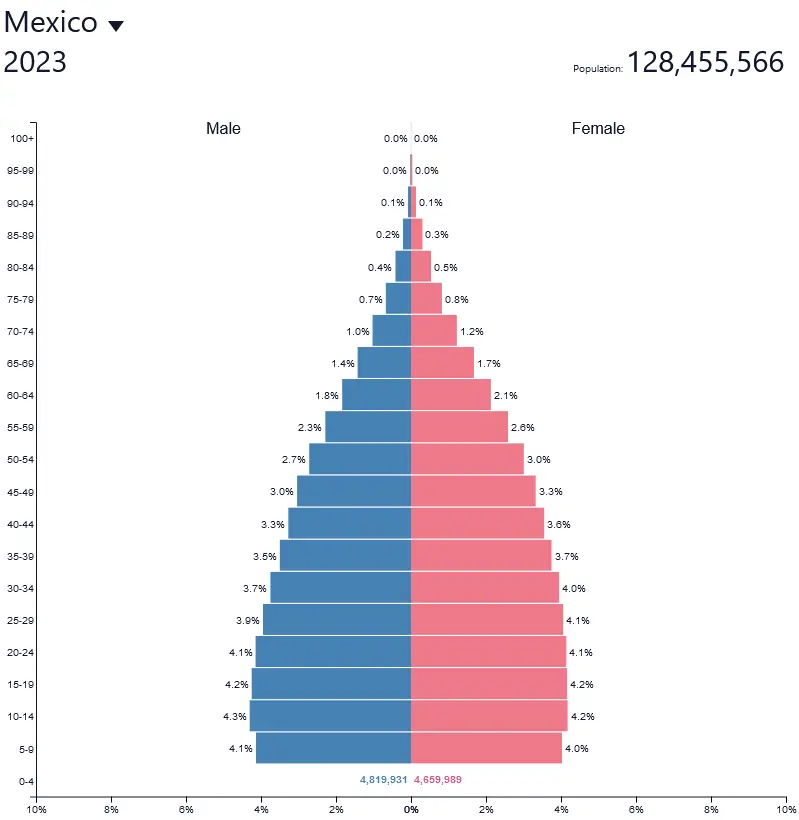
28
New cards
What are the defining factors of stage 4 of the Demographic Transition Model?
* Low birth rate
* Low death rate
* Falling natural increase that eventually stabilizes
* Highly urbanized societies
* High life expectancy rate
* Population growth typically happens due to immigration instead of natural increase
* Curved shape, arching at a rounded top
Ex: Australia
* Low death rate
* Falling natural increase that eventually stabilizes
* Highly urbanized societies
* High life expectancy rate
* Population growth typically happens due to immigration instead of natural increase
* Curved shape, arching at a rounded top
Ex: Australia
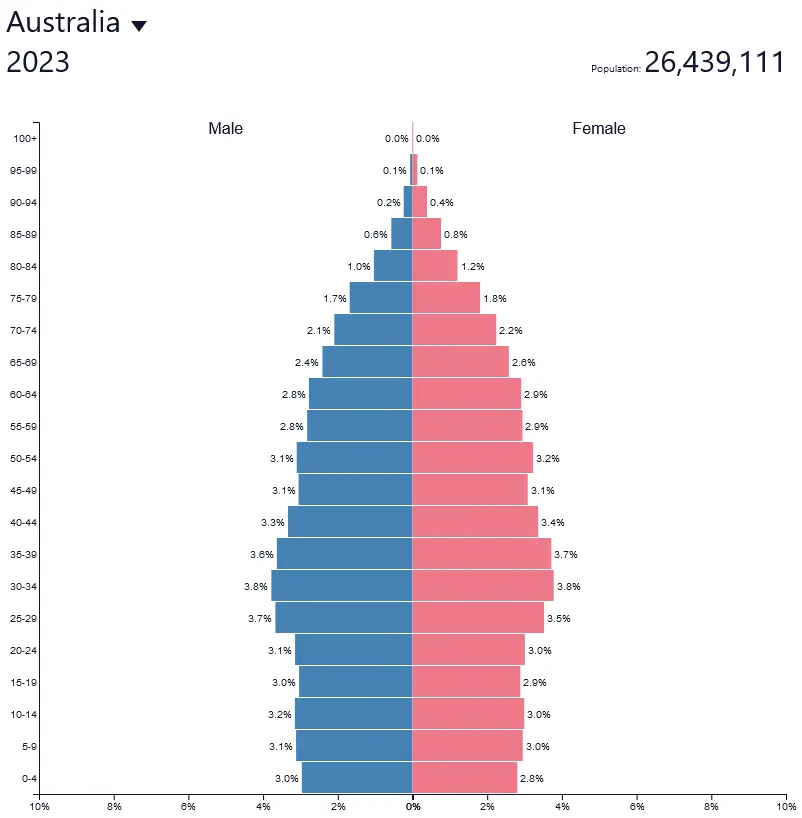
29
New cards
What are the defining factors of stage 5 of the Demographic Transition Model?
* Birth rate begins to rise again
* Low death rate
* Stable or slow natural increase
* Maintains its rounded tip but begins to expand outward at the base
Ex: Ukraine
* Low death rate
* Stable or slow natural increase
* Maintains its rounded tip but begins to expand outward at the base
Ex: Ukraine
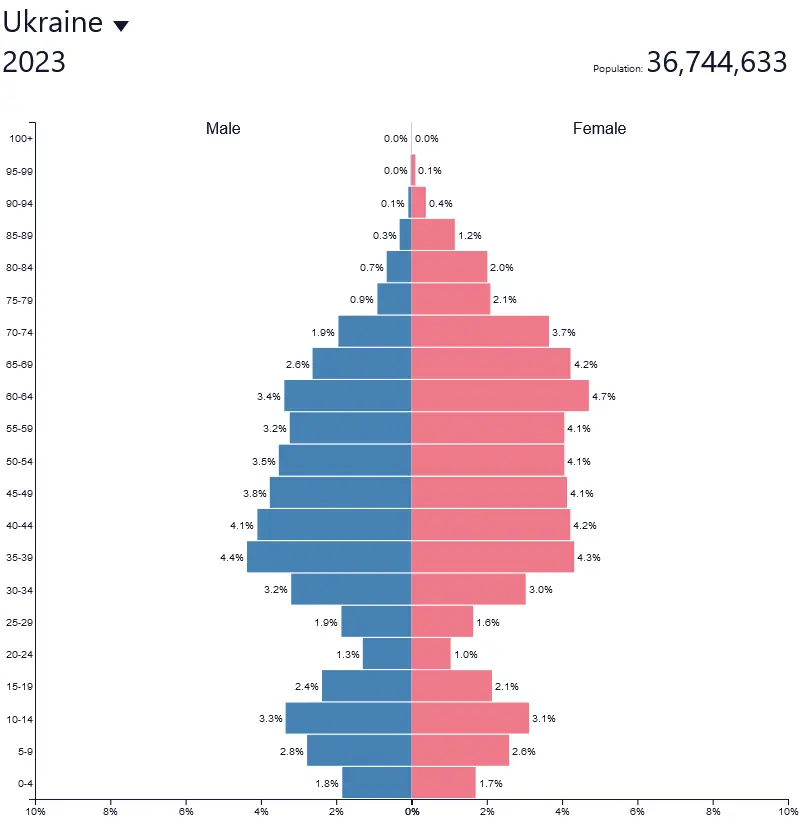
30
New cards
Why is the status of women a critical factor in demographic transition?
Discrimination against women appears to be the root cause of much of the high fertility and female disadvantage in survival, with regional variations reflecting differences in cultural systems.
(via encyclopedia.com)
(via encyclopedia.com)
31
New cards
What is a push factor?
certain conditions cause people to leave the places where they live.
These may include:
* High crime rates
* Lack of economic opportunity
* Shortages of food
* Wartime conditions
* Low wages, underemployment and unemployment
* Persecution
These may include:
* High crime rates
* Lack of economic opportunity
* Shortages of food
* Wartime conditions
* Low wages, underemployment and unemployment
* Persecution
32
New cards
What is a pull factor?
other conditions attract people to new places to live
These may include:
* Educational opportunities
* High standards of living
* Safe from religious and political persecution
* Plentiful resources such as fresh water, forests, wildlife or agricultural land
These may include:
* Educational opportunities
* High standards of living
* Safe from religious and political persecution
* Plentiful resources such as fresh water, forests, wildlife or agricultural land
33
New cards
What is a refugee?
involuntary migrants who move to other countries to seek safety and/or protection
34
New cards
What are internally displaced persons (IDPs?)
people who have to move *within* a country
35
New cards
What is an asylum seeker?
a person who has left their country and is seeking protection from persecution and serious human rights violations in another country, but who hasn’t yet been legally recognized as a refugee and is waiting to receive a decision on their asylum claim
(via amnesty.org)
(via amnesty.org)
36
New cards
What are some ways that developing countries have tried to tackle overpopulation?
* tax incentives
* enforcing policies that limit the number of children a family can have (ex: India and China)
* enforcing policies that limit the number of children a family can have (ex: India and China)
37
New cards
What natural and human factors would influence the magnitude of the Earth’s carrying capacity?
* food and water supply
* habitat space
* competition with other species
* sanitation
* diseases
* medical care
* habitat space
* competition with other species
* sanitation
* diseases
* medical care
38
New cards
What is population overshoot?
a concern that human populations may become too large to be sustained by their environment or resources in the long term
39
New cards
What theorist is most closely associated with the notion of carrying capacity and overshoot?
Thomas Malthus
40
New cards
What are some major priorities to improve urban life in the future?
**NOTE: Know any four of these for the exam.**
**NOTE: Know any four of these for the exam.**
* increase transportation throughout cities
* create more community spaces
* limit carbon emissions and other types of pollution
* create more affordable housing
* preserve the environment and green spaces
* create more community spaces
* limit carbon emissions and other types of pollution
* create more affordable housing
* preserve the environment and green spaces
41
New cards
What are some examples of why “the effects of colonial empires endure today” is a true statement?
* Environmental degradation, leading to climate change
* Plantations (Indigenous people became cheap labour, died, or left their native area)
* Loss of culture
* Trade and manufacturing restrictions imposed on colonies delayed the growth of, or destroyed, local customs, farming practices, manufacturing and business
* New political systems overrode previous ways of living, disregarding preexisting cultures and customs
* Plantations (Indigenous people became cheap labour, died, or left their native area)
* Loss of culture
* Trade and manufacturing restrictions imposed on colonies delayed the growth of, or destroyed, local customs, farming practices, manufacturing and business
* New political systems overrode previous ways of living, disregarding preexisting cultures and customs
42
New cards
Why have some countries experienced “economic takeoff,” while others have not?
* Lack of access to resources (more desirable goods to trade for = more countries in pursuit of trade)
* Lack of globalizing and making economic connections to other countries
* Lack of globalizing and making economic connections to other countries
43
New cards
How useful are Walter Rostow’s five stages of economic development as a blueprint for LEDCs to follow?
**Hardly; extremely biased and Westernized, cannot be translated to other cultures with same degree of accuracy.**
Criticisms/Weaknesses:
1: Rostow is 'historical in the sense that the end result is known in the outset and is derived from the historical geographyof developed society.
2: Rostow is mechanical in the sense the underlying motor of change is not disclosed and therefore the stages become little more than a classificatory system based on data from developed countries.
3: His model is based on American and European history and aspiring to American norm of high mass consumption.
4: His model represents a “non-communist manifesto” or we can say a “capitalist manifesto”
Criticisms/Weaknesses:
1: Rostow is 'historical in the sense that the end result is known in the outset and is derived from the historical geographyof developed society.
2: Rostow is mechanical in the sense the underlying motor of change is not disclosed and therefore the stages become little more than a classificatory system based on data from developed countries.
3: His model is based on American and European history and aspiring to American norm of high mass consumption.
4: His model represents a “non-communist manifesto” or we can say a “capitalist manifesto”
44
New cards
What three countries are affiliated with the CUSMA?
* Canada
* United States
* Mexico
* United States
* Mexico
45
New cards
Do you believe that transnational companies exploit LEDCs? Or, do you believe that transnational companies are important to economic growth of those countries?
**NOTE: This is entirely subjective. I’ve attached my paragraph response from the Unit 3 test as an example.**
**NOTE: This is entirely subjective. I’ve attached my paragraph response from the Unit 3 test as an example.**
Objectivity is a matter that can exist completely separately from opinion, which can be said about the idea of transnational companies taking advantage of LEDCs, whilst still, undeniably, being important for a country’s economic development - these two concepts are not mutually exclusive. On one hand, transnational companies can introduce new technology and foreign resources, but it can also open doors for MEDCs to exploit LEDCs, prioritizing their own growth and prosperity. Both of these ideas can be true at once - especially considering that standards of development are often viewed through a Westernized lens.
46
New cards
What is the Human Development Index (HDI)?
a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education, and per capita income indicators, which is used to rank countries into four tiers of human development
47
New cards
What is the Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI)?
an index that captures the percentage of households in a country deprived along three dimensions of well-being – monetary poverty, education, and basic infrastructure services – to provide a more complete picture of poverty.
48
New cards
How does the Global Multidimensional Poverty Index way of measuring poverty compare to the UN Human Development Index approach?
While both the HDI and the MPI use the three broad dimensions health, education and standard of living, the HDI uses indicators at the **aggregate*** level while MPI uses micro data and all indicators must come from the same survey.
\
***aggregate**: a mass or body of units or parts somewhat loosely associated with one another
\
***aggregate**: a mass or body of units or parts somewhat loosely associated with one another
49
New cards
How does income inequality affect the world on an international scale?
excessive inequality could erode social cohesion, lead to political polarization, and ultimately lower economic growth
(via imf.org)
(via imf.org)
50
New cards
Which two forms of chemical deterioration are most common?
acidification: when acidic compounds like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides are released into the atmosphere in concentrations high enough to be toxic to plants, animals, and microorganisms. This usually occurs through burning fossil fuels or other industrial processes. (some wording stolen from Casper, some other stolen from e.campusontario.pressbooks.pub)
eutrophication: occurs when a body of water receives an excessive nutrient load, particularly phosphorus and nitrogen. This often results in an overgrowth of algae. As the algae die and decompose, oxygen is depleted from the water, and this lack of oxygen in the water causes the death of aquatic animals, like fish. (via usgs.gov) sources: runoff, sewage, industrial discharge (via Casper’s notes)
eutrophication: occurs when a body of water receives an excessive nutrient load, particularly phosphorus and nitrogen. This often results in an overgrowth of algae. As the algae die and decompose, oxygen is depleted from the water, and this lack of oxygen in the water causes the death of aquatic animals, like fish. (via usgs.gov) sources: runoff, sewage, industrial discharge (via Casper’s notes)
51
New cards
What is soil erosion?
when the impact of water or wind detaches and removes soil particles, causing the soil to deteriorate
(via iastate.edu)
(via iastate.edu)
52
New cards
What is degradation?
caused by multiple forces, including extreme weather conditions, particularly drought. It is also caused by human activities that pollute or degrade the quality of soils and land utility (via who.int)
53
New cards
How serious is the challenge of land degradation in the world?
very serious; destroys habitats and depletes resources
54
New cards
How are increases in land degradation and world population connected?
“as more people are born more resources are used, contributing to land degradation through, land clearance, poor farming practices, overgrazing and overdrafting, urban sprawl and urban development, car emissions”
(credit to Sasha !!)
(credit to Sasha !!)
55
New cards
What are the environmental consequences of deforestation?
* “Trees absorb and store carbon dioxide. If forests are cleared, or even disturbed, they release carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. Forest loss and damage is the cause of around 10% of global warming” -WWF
* Desertification and soil erosion
* Resource depletion and habitat disturbance/destruction
* Desertification and soil erosion
* Resource depletion and habitat disturbance/destruction
56
New cards
What is desertification?
the process by which fertile land becomes desert, typically as a result of drought, deforestation, or inappropriate agriculture.
57
New cards
Which type of society is most responsible for degradation of lands and forests, MEDCs or LEDCs?
MEDCs due to industrial activities, large-scale and unsustainable agriculture practice, resource extraction and higher consumption patterns, technological advancements and global trade, which adds pressure to make less environmentally conscious decisions.
(Partially stolen from Casper)
(Partially stolen from Casper)
58
New cards
What are common-pool resources (lakes, rivers, aquifers)?
* a shared resource not owned by private or public entities
* natural or manufactured resource systems in which the amount of the resource stock made accessible to each user is not based on any criteria.
(via wallstreetmojo.com)
* natural or manufactured resource systems in which the amount of the resource stock made accessible to each user is not based on any criteria.
(via wallstreetmojo.com)
59
New cards
What is the tragedy of the commons?
* A tragedy of the commons occurs when a group of people in a community use a shared resource for their self-interest, which leads to the depletion of the resource for the whole community
(via wallstreetmojo.com)
* Ex: overfishing
(via wallstreetmojo.com)
* Ex: overfishing