Sliding filaments theory
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms

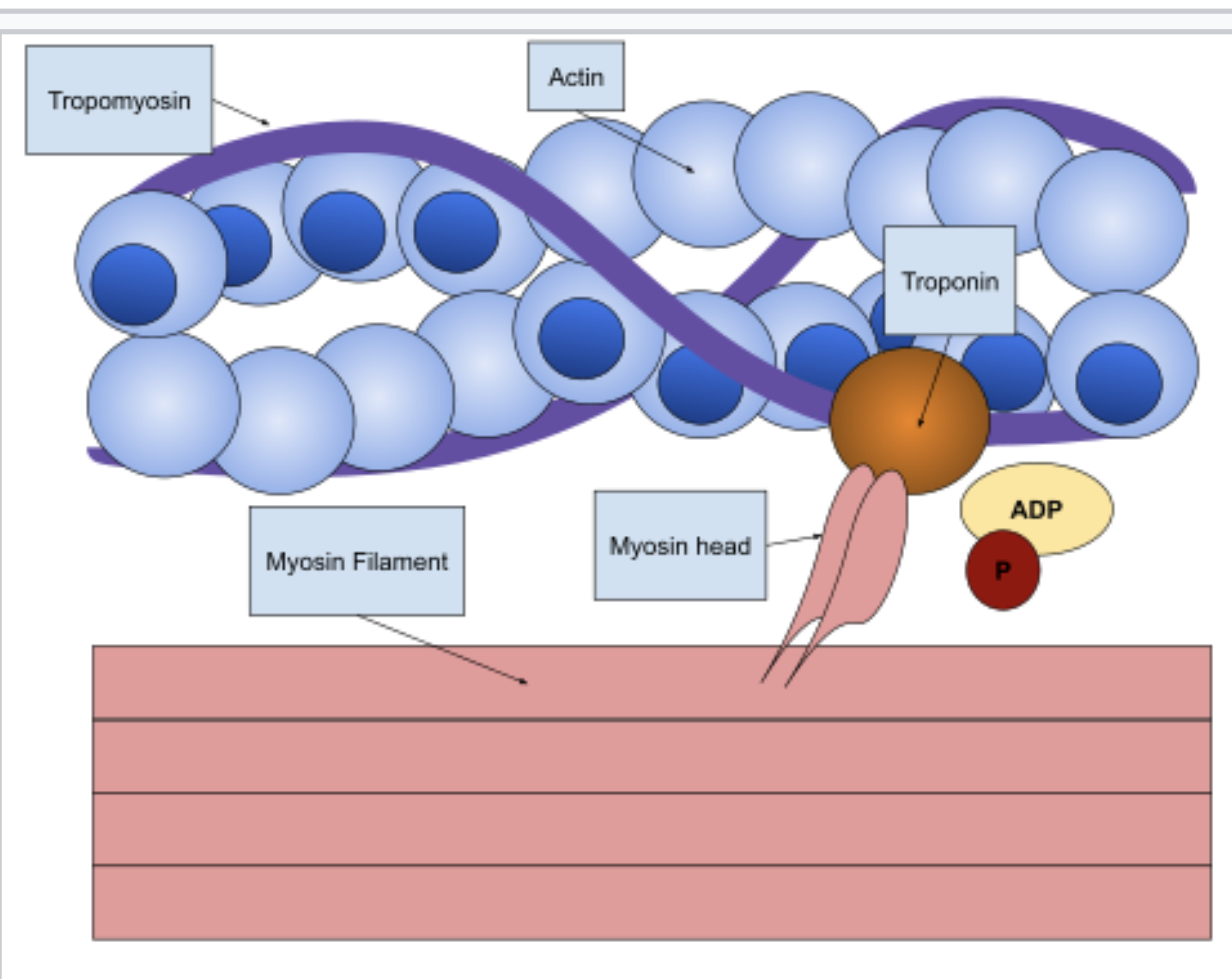
Myofibrils appear striated under microscopes, the striation due to the presence of contractile units called “sarcomeres”.
The sarcomeres have a specific structure.
2.5 um is how long the length of sarcomere at rest
After muscle contractions; shorter
Sliding filaments theory
Myofilaments have globular head units.
The myosin heads can bind to actin filaments.
actin filaments have myosin binding sites. However, the myosin binding sites are covered by protein called tropomyosin. In turn, tropomyosin is bound to another protein called troponin.
When Ca2+ binds to troponin, it induces a conformational change, this pulls tropomyosin to reveal the actomyosin binding sites on the actin filaments.
The myosin heads now form cross bridges, with the actin filaments, and flex in a power stroke.

ATP binds to the myosin head causing it to detach from the actin filaments and return to the previous (cocked) position.
This process continues to contract the muscle it will stop when Ca2+ no longer present and tropomyosin once again block actomyosin binding sites on the actin filaments.