Body Fluids and Acid-Base Balance in Chemistry
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Intracellular fluid
Fluid located inside cells, 28 L total.
Extracellular fluid
Fluid located outside cells, includes plasma.
Interstitial fluid
Fluid between tissue cells, 10.5 L total.
Plasma
Fluid component of blood, 3.5 L total.
Oxyhemoglobin
Oxygen bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
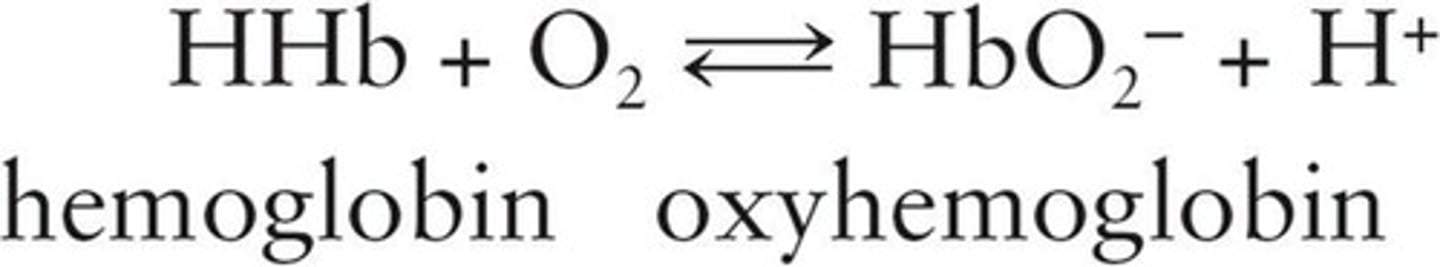
Deoxyhemoglobin
Hemoglobin without oxygen attached.
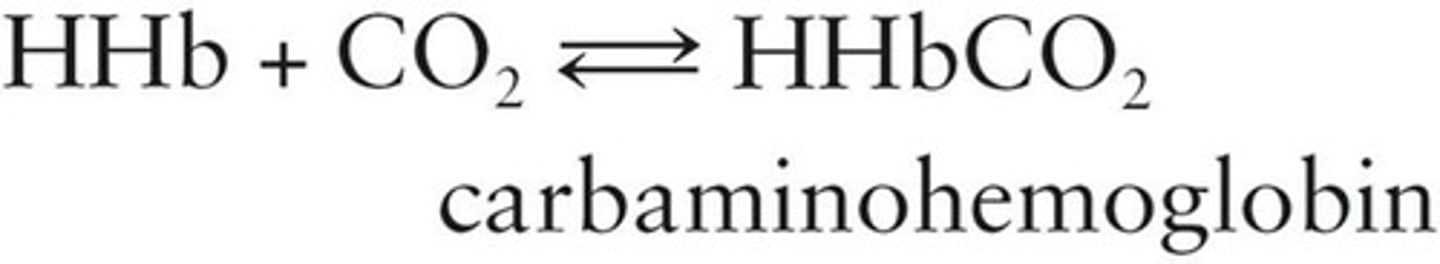
Carbaminohemoglobin
Hemoglobin combined with carbon dioxide.
Chloride shift
Exchange of chloride ions for bicarbonate in red blood cells.
Oxygen transport
Oxygen carried primarily by red blood cells.
Carbon dioxide transport
CO2 transported as bicarbonate ions, carbaminohemoglobin.
Acidosis
Condition of increased acidity in blood.
Alkalosis
Condition of increased alkalinity in blood.
Buffers
Substances that stabilize pH in blood.
Hemoglobin
Protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
Normal urine constituents
Includes urea, creatinine, and amino acids.
Abnormal urine constituents
Presence of glucose or protein indicates issues.
Fluid balance
Maintaining proper levels of body fluids and electrolytes.
Electrolyte balance
Maintaining proper ion concentrations in body fluids.
Blood pressure
Pressure exerted by circulating blood on vessel walls.
Osmotic pressure
Pressure due to solute concentration differences.
Chemical transport
Movement of substances through the bloodstream.
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from high to low concentration.
Capillary walls
Selectively permeable membranes for nutrient exchange.
Respiratory control of pH
Regulation of blood pH via CO2 levels.
Urinary control of pH
Regulation of blood pH via bicarbonate excretion.
Average urine output
Approximately 40-50 g of dissolved solids daily.
Normal urine pH
Ranges from 4.5 to 8.0, average 6.6.
Fluid compartments
Body fluids divided into intracellular and extracellular.
Chemical composition of plasma
Contains proteins, electrolytes, and nutrients.
Extracellular fluid
Fluid outside cells, maintains constant environment.
Oxyhemoglobin
Oxygen-hemoglobin complex in red blood cells.
Deoxyhemoglobin
Hemoglobin without bound oxygen.
Chloride shift
Exchange of bicarbonate and chloride ions.
Carbonic anhydrase
Enzyme that converts carbonic acid to CO2.
Oxygen transport
Oxygen primarily carried by red blood cells.
Carbon dioxide transport
CO2 transported as bicarbonate ions mainly.
Normal urine constituents
Includes urea, creatinine, and uric acid.
Urine composition
96% water, 4% dissolved waste products.
Acidosis causes
Increased H+ concentration, respiratory issues.
Alkalosis causes
Decreased H+ concentration, hyperventilation.
Blood pH regulation
Maintained by buffers, respiration, and kidneys.
Oxygen partial pressure
Higher in alveoli than in red blood cells.
Fluid balance
Maintained by osmotic and blood pressure differences.
Hemoglobin content
Human blood contains 15 g hemoglobin/100 mL.
Average adult fluid volume
42 L, two-thirds body weight.
Chemical transport
Substances must enter bloodstream for transport.
Urine pH range
Healthy urine pH ranges from 4.5 to 8.0.
Oxygen requirement
Average adult needs 350 mL of oxygen/min.
Protein content in fluids
Intracellular fluid has more protein than plasma.
Fluid compartments
Body fluids are compartmentalized into three regions.
Diffusion in simple organisms
Waste removal occurs by diffusion.
Fluid intake impact
Urine volume varies based on fluid intake.
Respiratory control of pH
Regulates blood pH via CO2 levels.
Urinary control of pH
Regulates blood pH through H+ excretion.
Average urine output
Approximately 1400 mL per day.
Urine Composition
Used for diagnosing pathological conditions.
Paper Test Strip
Checks urine specimen for abnormal constituents.
Glucosuria
Presence of glucose in urine.
Diabetes Mellitus
Condition causing high glucose in urine.
Proteinuria
Excess protein in urine, indicating kidney damage.
Ketonuria
Presence of ketone bodies in urine.
Hemoglobinuria
Hemoglobin in urine due to hemorrhage.
Hematuria
Presence of red blood cells in urine.
Bile Pigments
Indicate liver issues when found in urine.
Fluid Balance
Maintains stable distribution of body fluids.
Thirst Mechanism
Regulates water intake based on fluid loss.
Urine Output
Normal is approximately 1400 mL/day.
Vasopressin
Hormone regulating water reabsorption in kidneys.
Aldosterone
Stimulates sodium reabsorption and water retention.
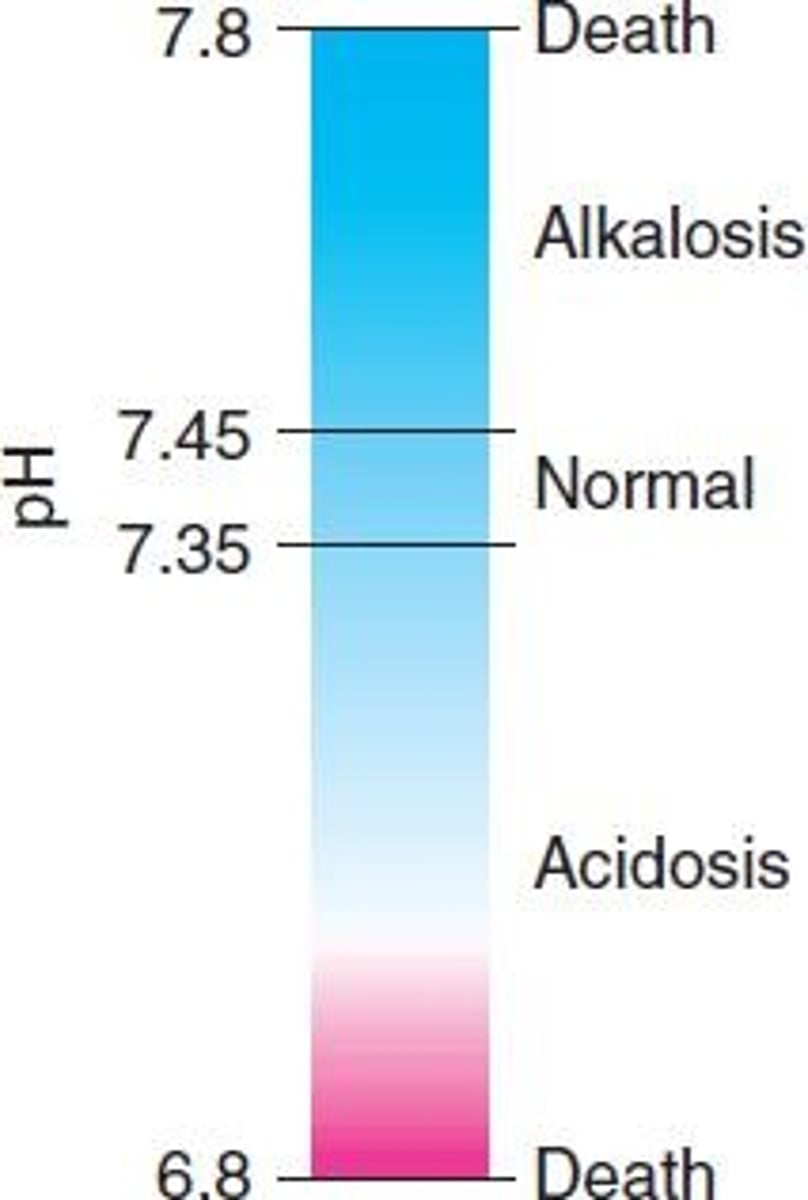
Acid-Base Balance
Maintains blood pH between 7.35 and 7.45.
Alkalosis
Abnormally high blood pH.
Acidosis
Abnormally low blood pH.
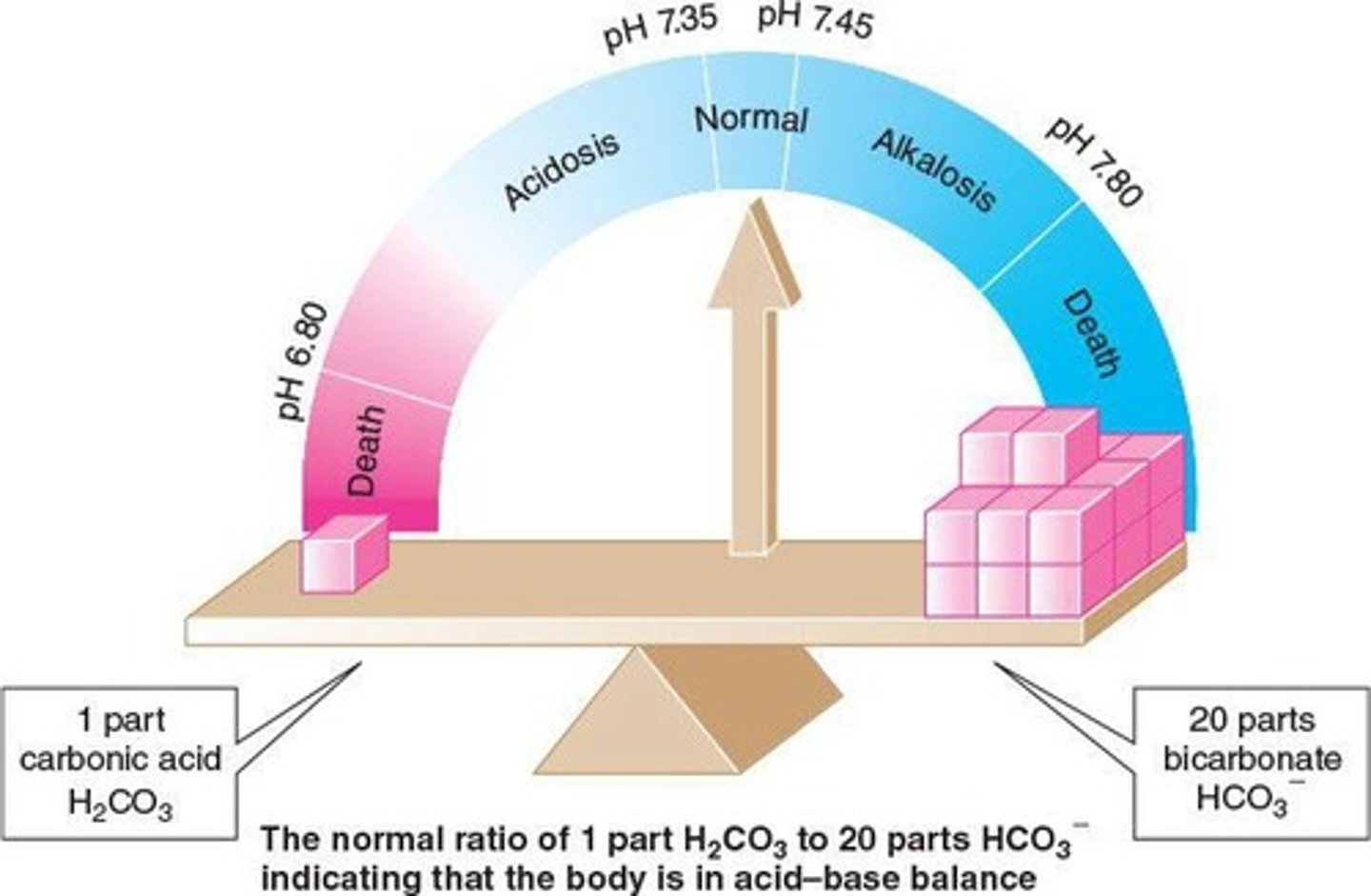
Buffer Systems
Maintain constant blood pH via chemical reactions.
Bicarbonate Buffer
Regulates pH with bicarbonate and carbonic acid.
Respiratory Control
Regulates blood acidity through CO2 elimination.
Hyperventilation
Rapid breathing causing decreased CO2 levels.
Hypoventilation
Slow breathing leading to increased CO2 levels.
Metabolic Acidosis
Caused by increase in H+ ions in blood.
Metabolic Alkalosis
Caused by loss of acids or excess bases.
Symptoms of Acidosis
Includes hyperventilation and disorientation.
Symptoms of Alkalosis
Includes numbness and tingling.
Treatment for Acidosis
May involve bicarbonate administration or dialysis.
Treatment for Alkalosis
Rebreathing exhaled air or treating underlying causes.