plbi 327 midterm
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Charles Darwin
English natural scientist who formulated a theory of evolution by natural selection (1809-1882)
What are the four main points of Darwin
1. Variation is random in a population
2. Traits can be inherited from progenitor to progeny
3. Some traits are better than others
4. More fit traits survive, assumes the existence of competition
Evolution by Natural Selection is the only possible outcome
Thomas Malthus
Eighteenth-century English intellectual who warned that population growth threatened future generations because, in his view, population growth would always outstrip increases in agricultural production.
Carrying Capacity guy
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
Limited resources limits population growth
Macroevolution
large-scale evolutionary changes that take place over long periods of time
Microevolution
Change in allele frequencies in a population over generations.
Speciation
the formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution.
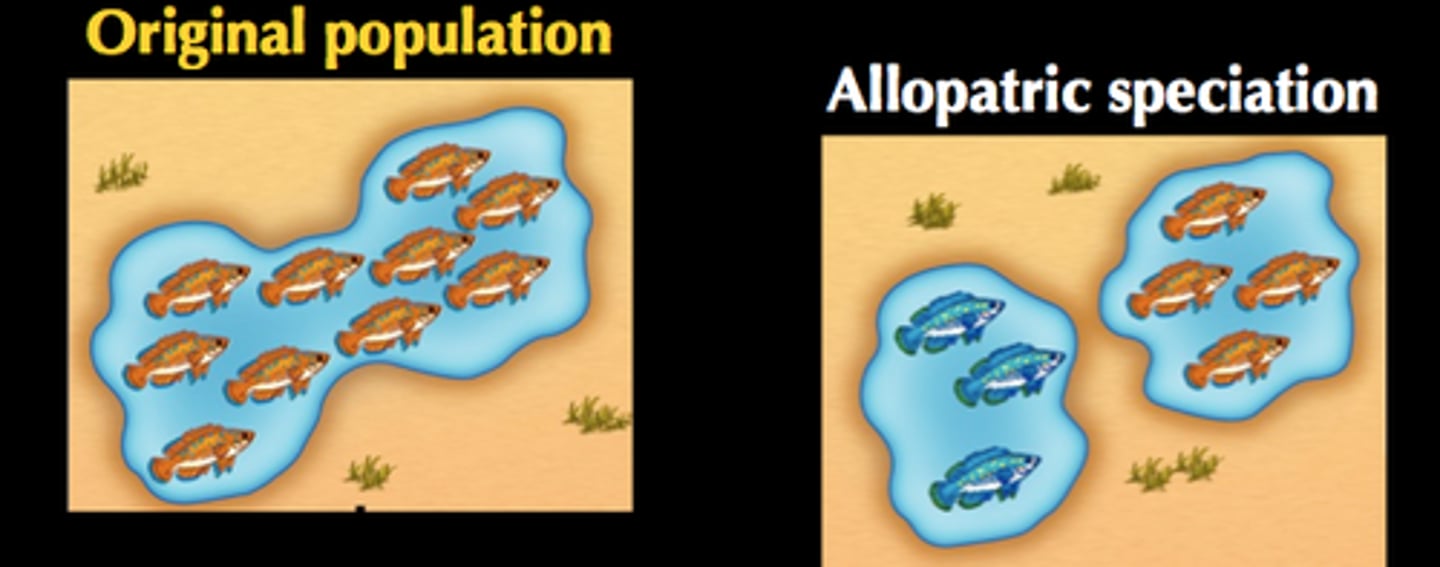
allopatric speciation
The formation of new species in populations that are geographically isolated from one another.
Ex: Seperated by a river
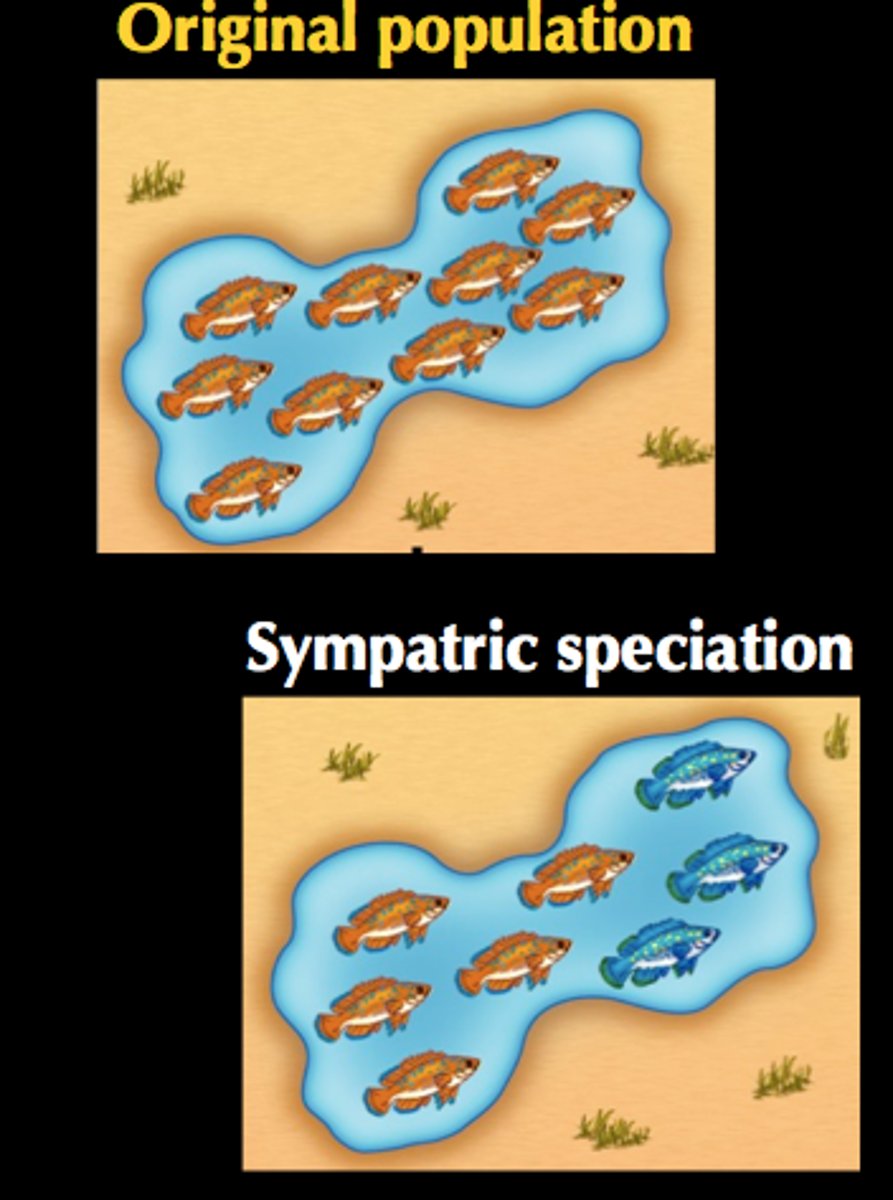
sympatric speciation
The formation of new species in populations that live in the same geographic area
ex: active at different times of day
parapatric speciation
speciation pattern in which populations speciate while in contact along a common border
geographically adjacent, but at the edge of a niche
Ecologically isolated and not reproductively isolated
Polyploidy
A chromosomal alteration in which the organism possesses more than two complete chromosome sets.
Polyploidy in plants
tend to be bigger and stronger than diploid plants
self-fertilization
When pollen fertilizes eggs from the same flower
4n
tetraploid
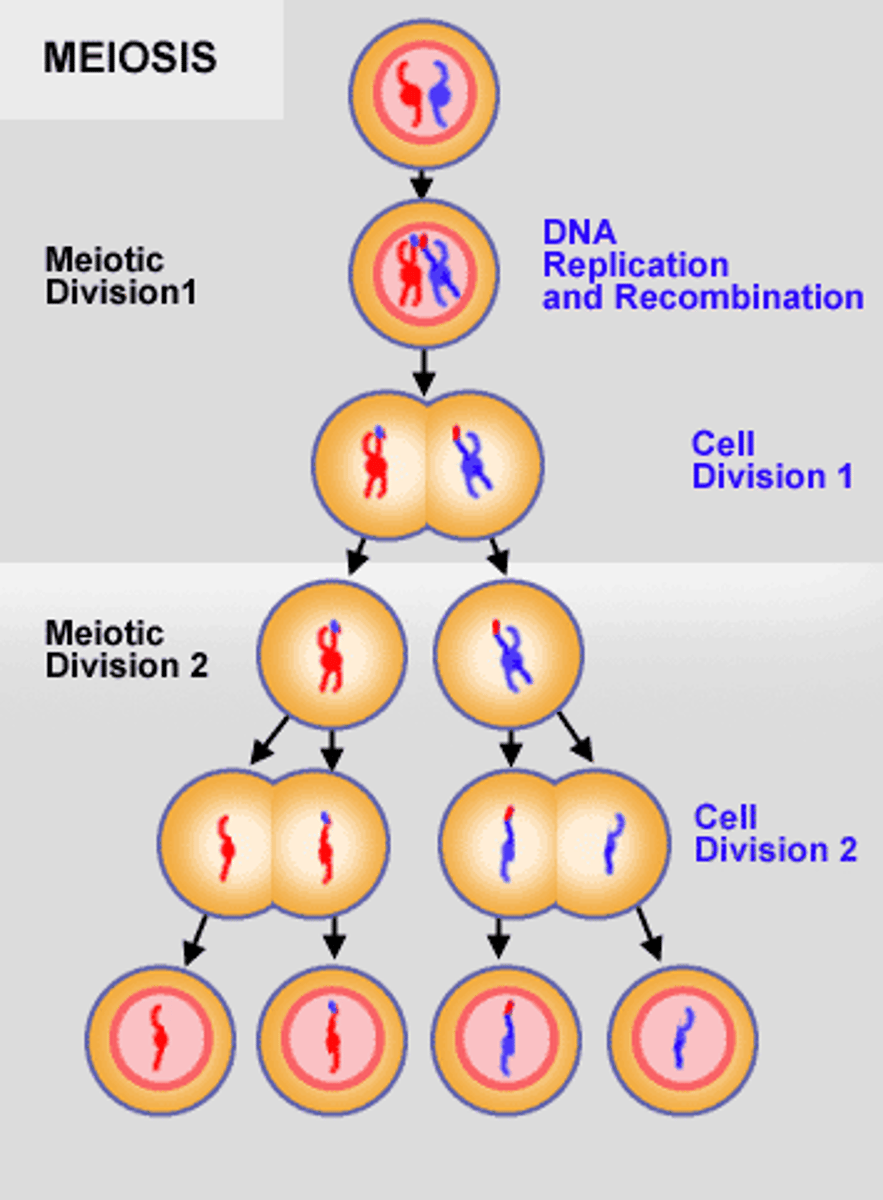
normal meiosis
1 of each chromosome in gamete
Advantages of polyploidy
- More chromosomes so larger cell nuclei → larger cells → larger leaves, stems, fruits, flowers etc.
- May allow plants to grow in a wider array of habitats and be more resistant to pests and diseases

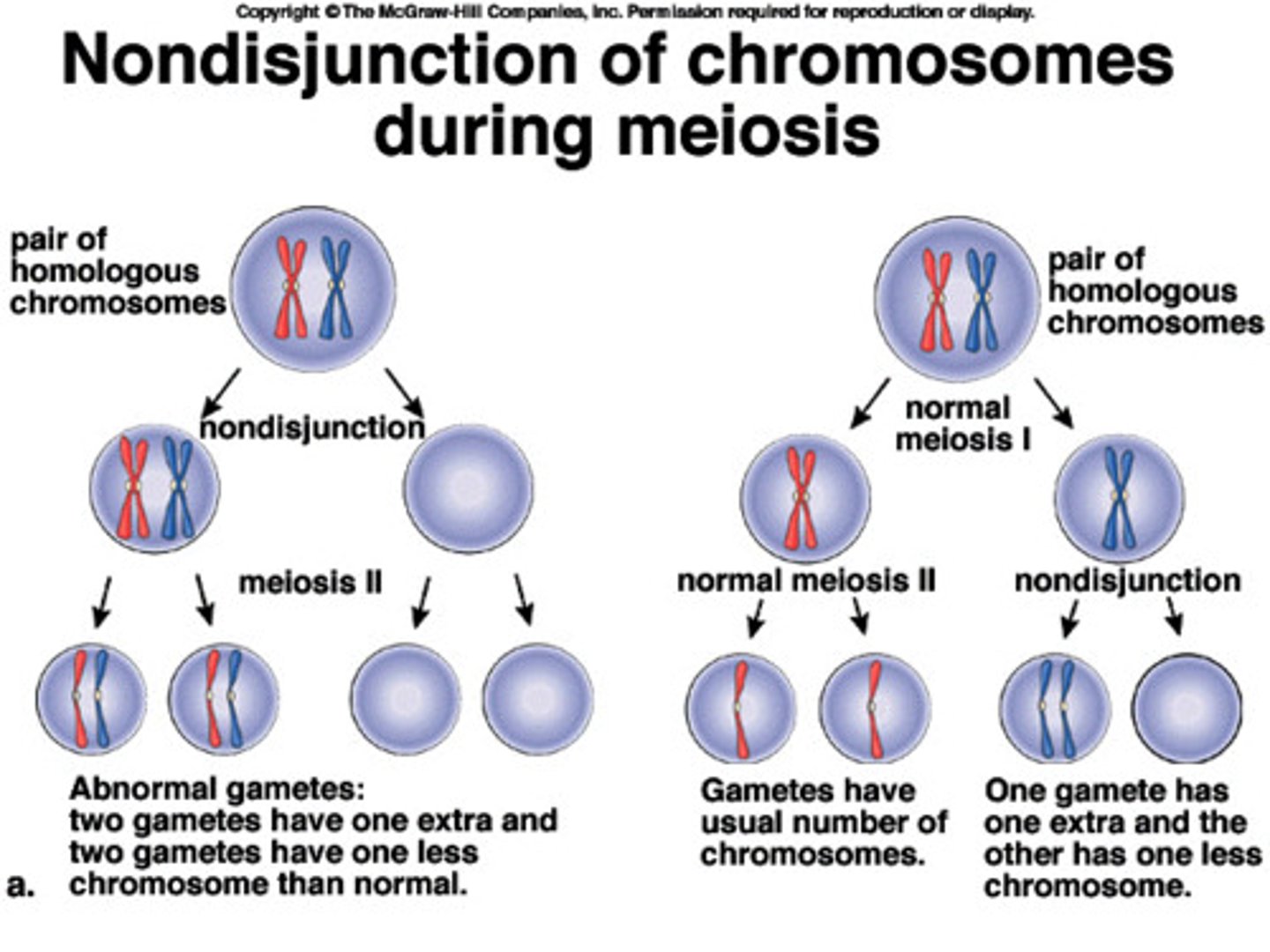
Non-disjunction in Meiosis I
Homologous chromosomes fail to separate
only meiosis 2 occurs normally
-result in 2n + 2n
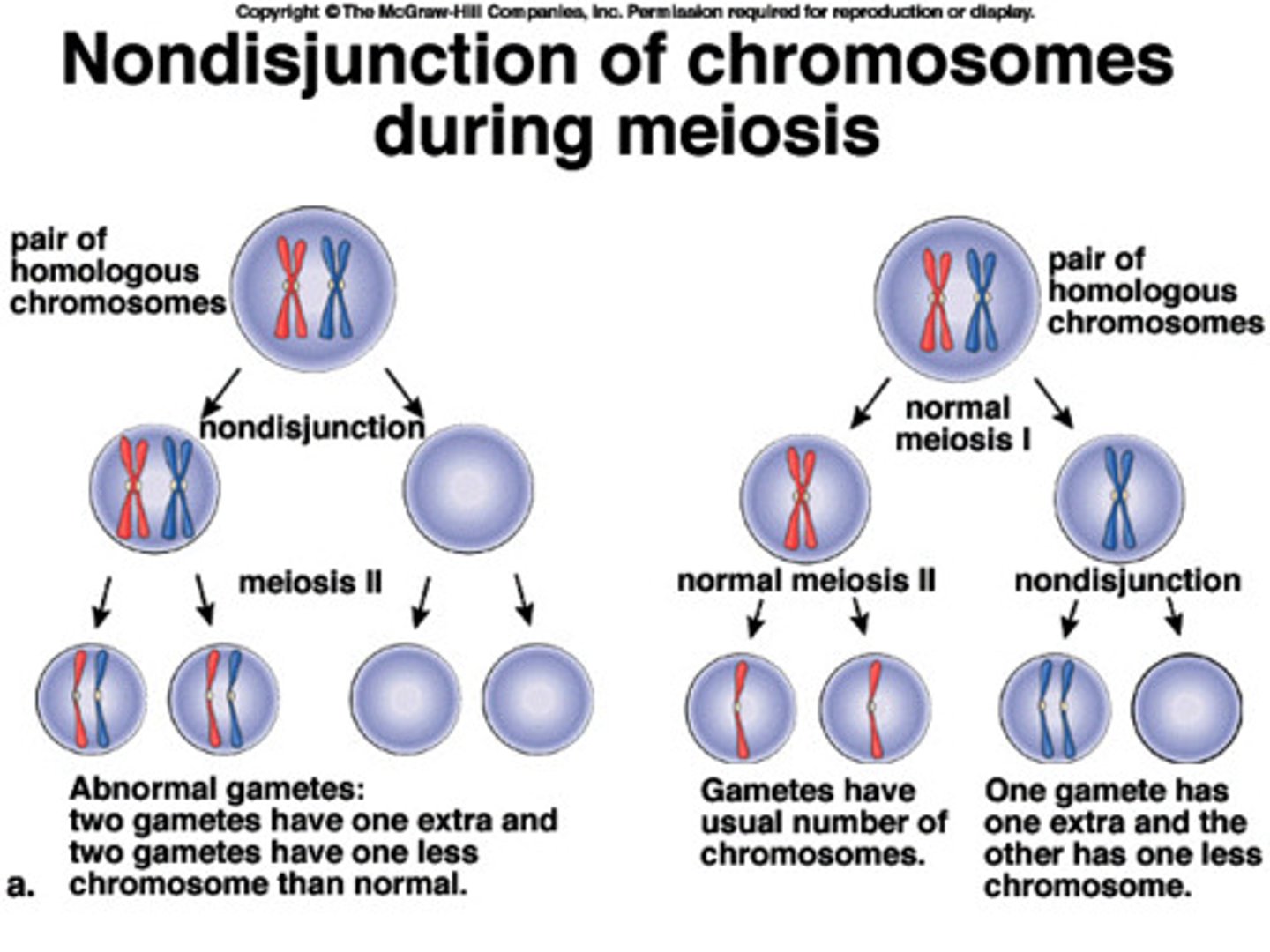
Non-disjunction in Meiosis II
Sister chromatids fail to separate
meiosis 1 occurs as normal but
-result in 1 2n and 2 1n
Heterosis (hybrid vigor)
ability of offspring to out perform the average of the parents breed
2x the dna with polyploidy
Negatives of polyploidy
issues with meiosis and mitosis
extra dna takes up a ton of space
Autopolyploidy
an individual that has more than two chromosome sets that are all derived from a single species
multiplication of the genome within ONE SPECIES
auto = same
allopolyploidy
polyploidy resulting from contribution of chromosomes from two or more species
Hybridization between two or more DIFFERENT SPECIES
allo = different
Carl Linnaeus
"Father of Taxonomy"; established his classification of living things; famous for animal naming system of binomial nomenclature
binomial system
Identifying organisms by their genus and species names
Taxa
group or level of organization into which organisms are classified
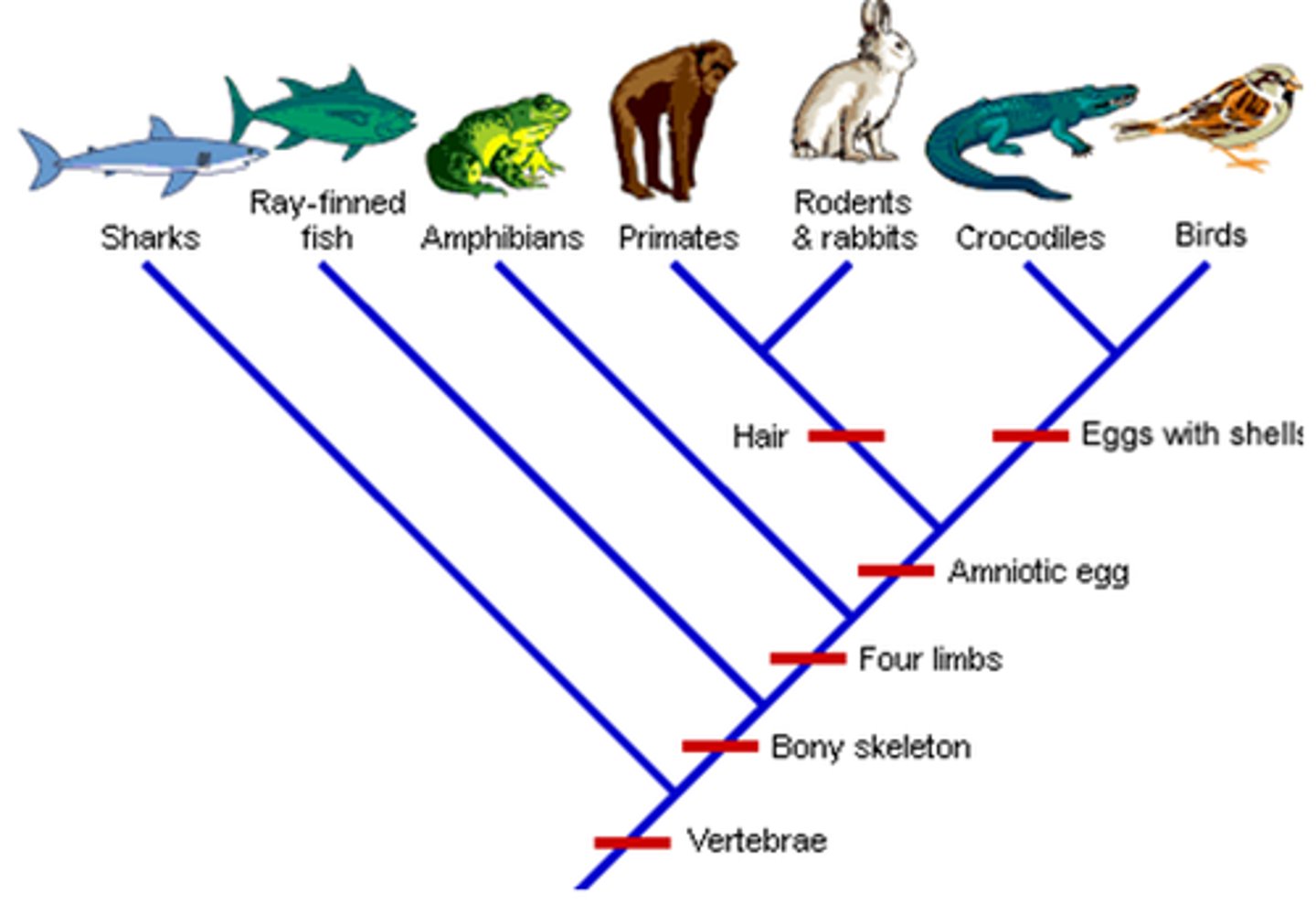
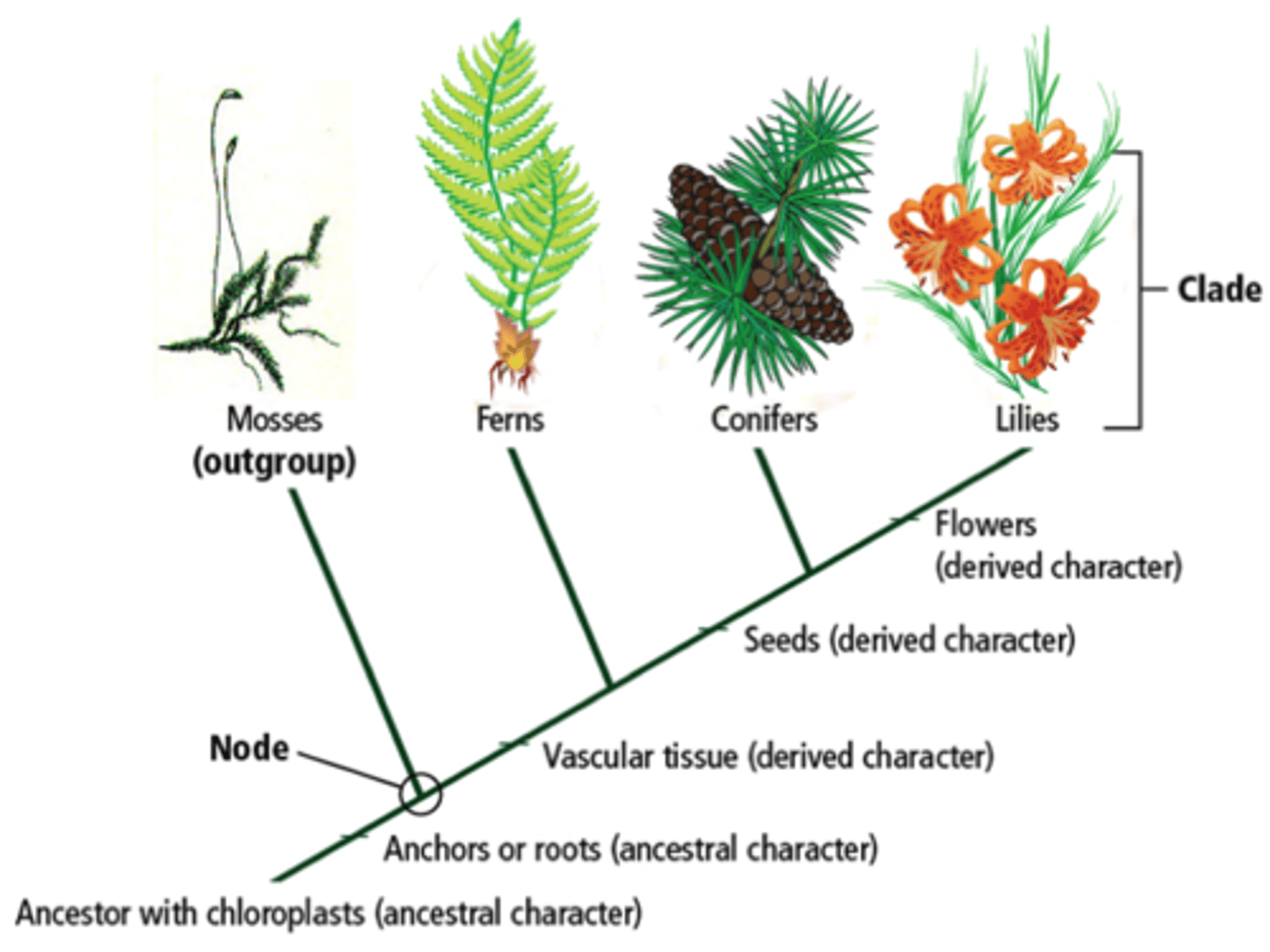
phylogeny tree
branching diagram showing relationships among different species or groups
Clade (monophyletic group)
A group of species that includes an ancestral species and all its descendants. -> CLADE
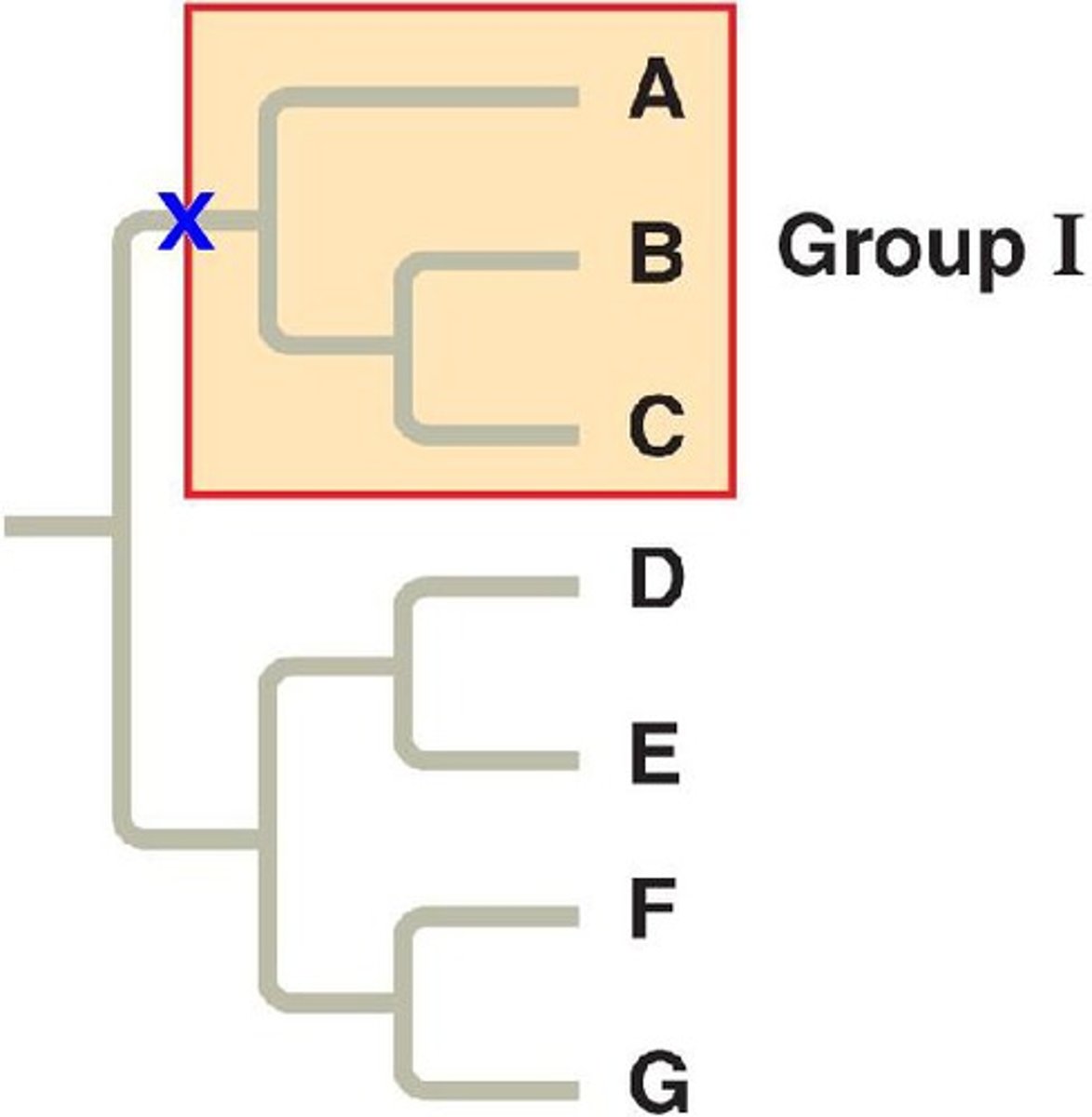
terminal taxa
The species being investigated
monophyletic
ALL descendants came from one common ancestor
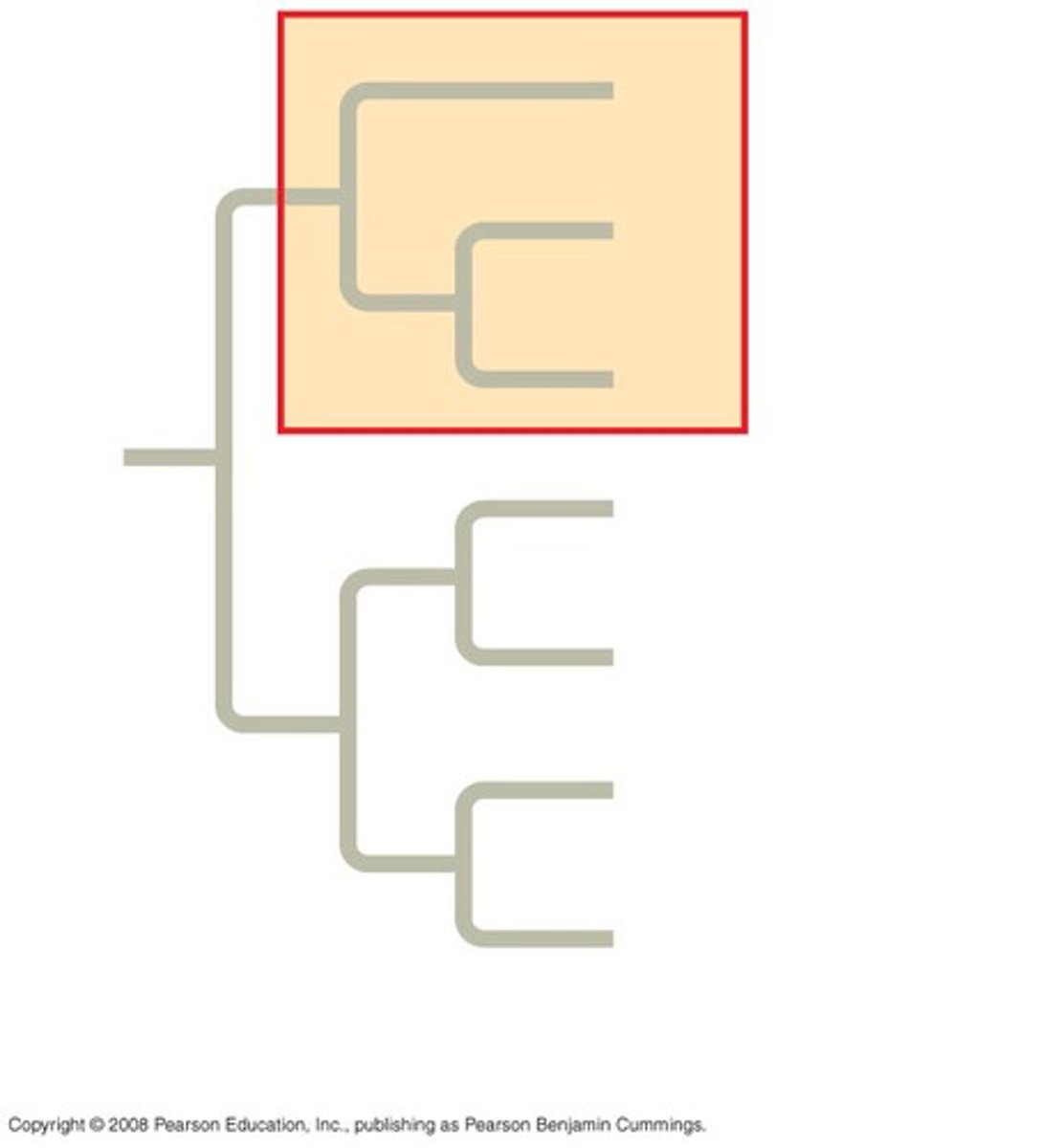
paraphyletic
Pertaining to a group of taxa that consists of a common ancestor and some, but not all, of its descendants.
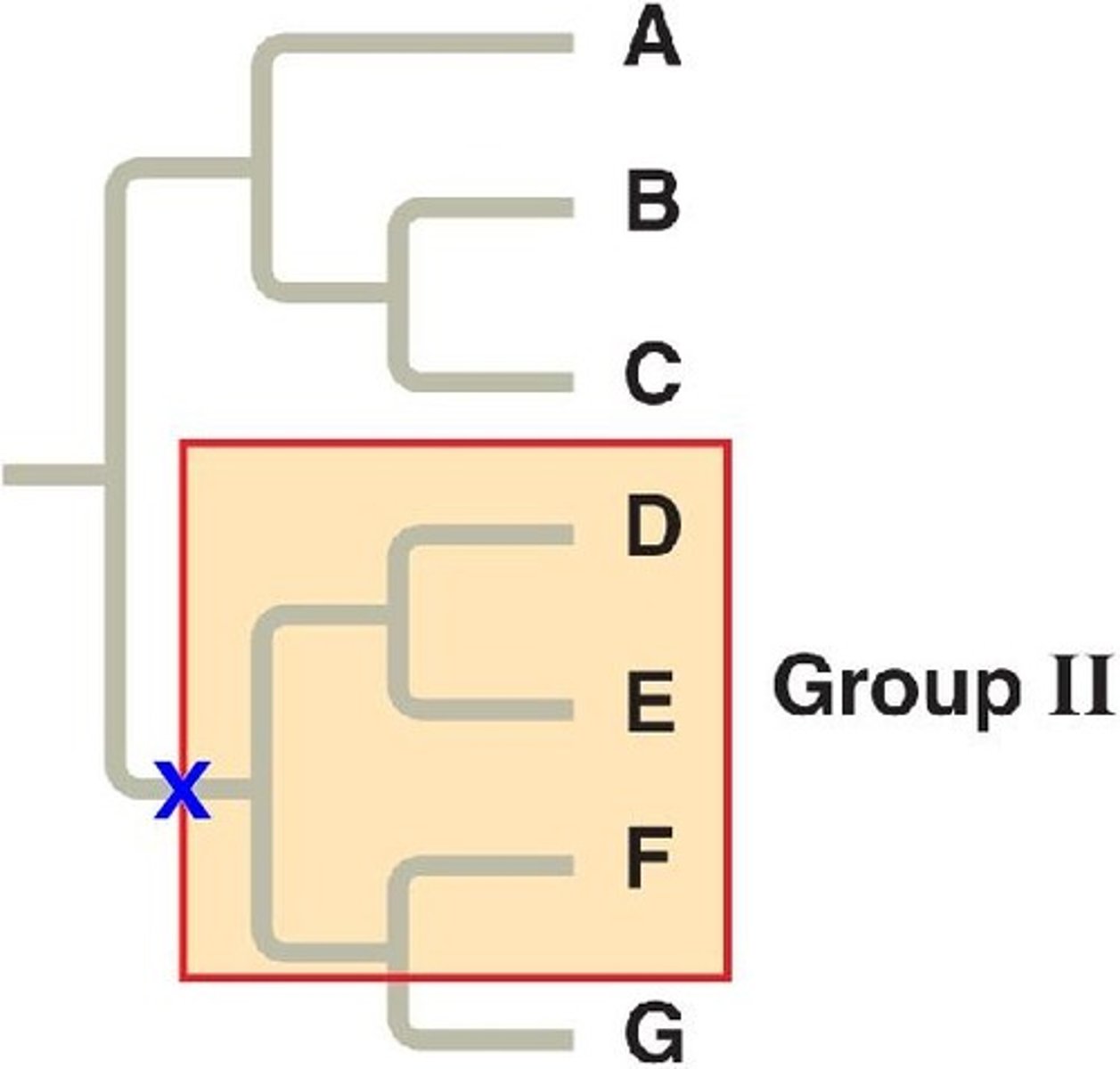
polyphyletic
pertaining to a group of taxa derived from two or more different ancestors
algae is a good example of this. primarily a human classification issue.
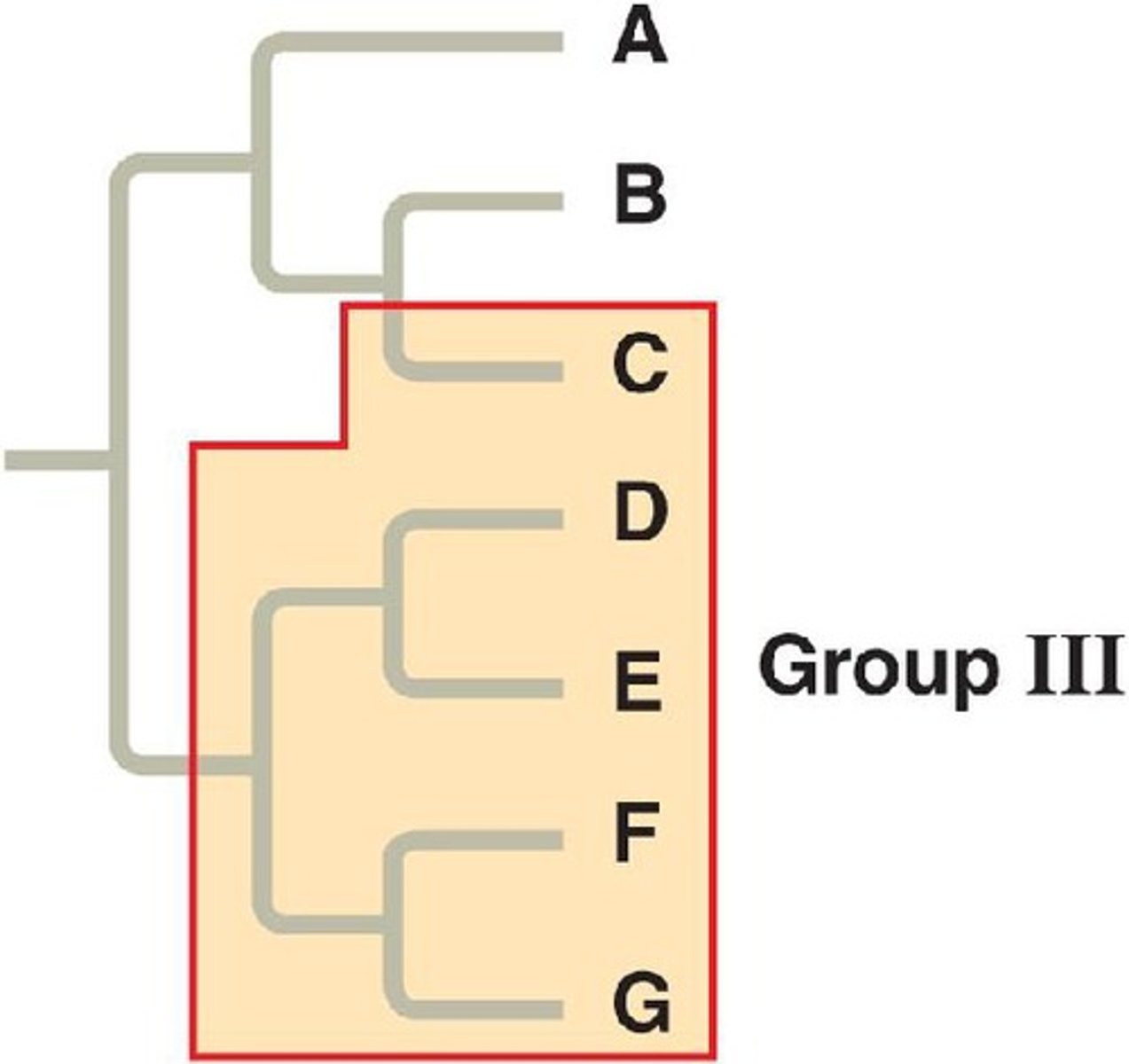
LUCA
Last Universal Common Ancestor. The shared ancestor that multiple organisms diverged from
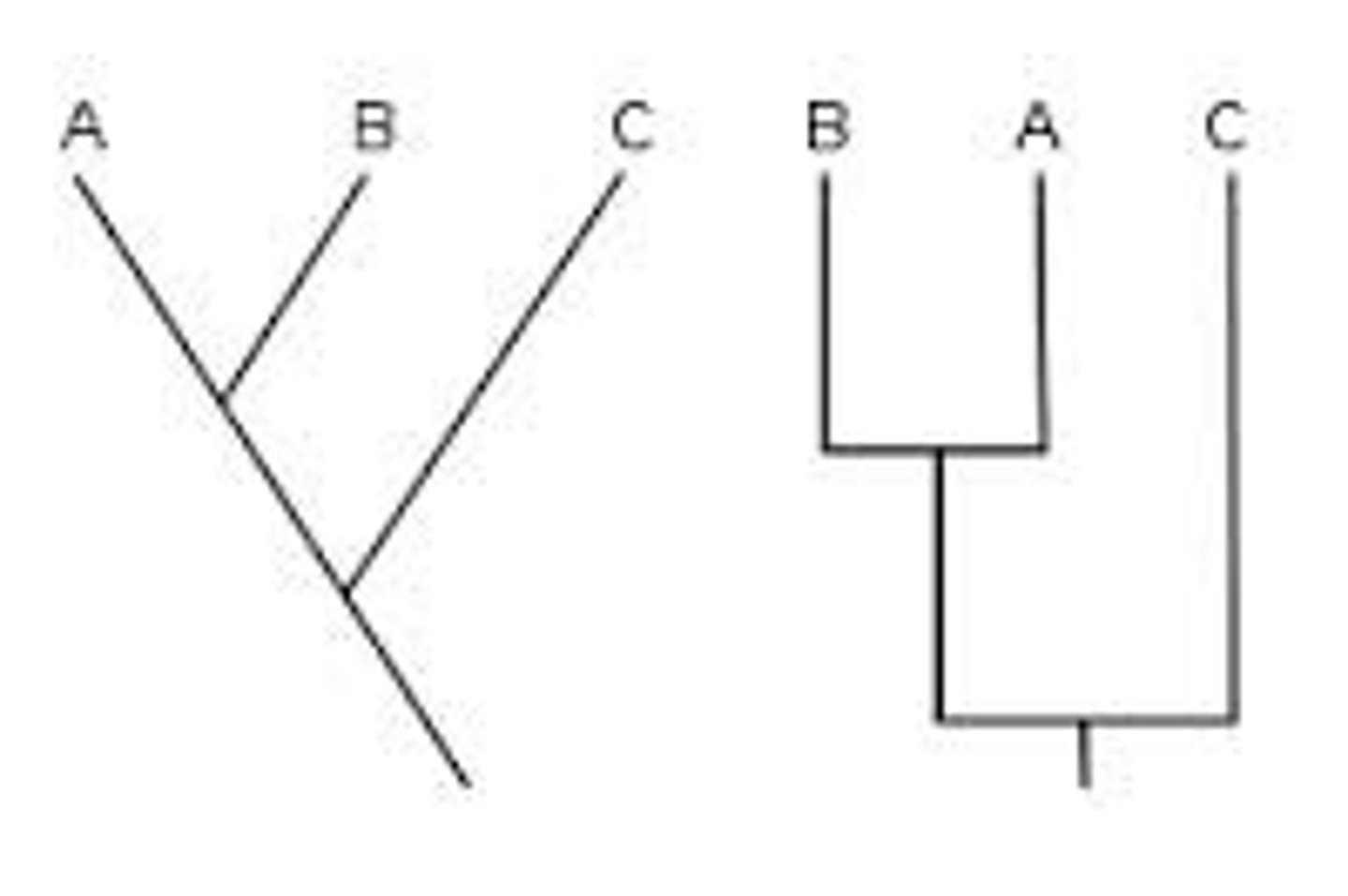
cladograms KNOW HOW TO MAKE THESE.
a branching diagram showing the cladistic relationship between a number of species.
LOWEST NUMBER OF CHANGES
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
hadean
Pre Cambrian. Before Archezoic. Rockless, formation of Earth, solidifying crust
hell. The first life.
anaerobic enviorment
First life
3.5 bya. it was Archea and Bacteria
cyanobacteria
Bacteria that can carry out photosynthesis
hadean extinction event
exterminated anaerobic bacteria and ended up raising O2 levels, this was bad for them and they couldn't handle it and they died.
banded iron formations
alternating bands of iron oxide and chert some of which date to as early as 2.5 bya (used as evidence for an oxygenated atmosphere during Precambrian time)
Chloroflexus
green nonsulfur bacteria
Anoxygenic photosynthesis - no O2 production
principle of parsimony
the belief that explanations of phenomena and events should remain simple until the simple explanations are no longer valid
what did mosses develop taxonomically (bryophyte)
embryos
what did ferns develop after moss (Tracheophyta)
xylem and phloem
what did pines develop after ferns (gymnosperm)
wood and seeds
what did oaks develop after pines (angiosperm)
flowers
make a simple cladogram of land plant taxonomy
ez
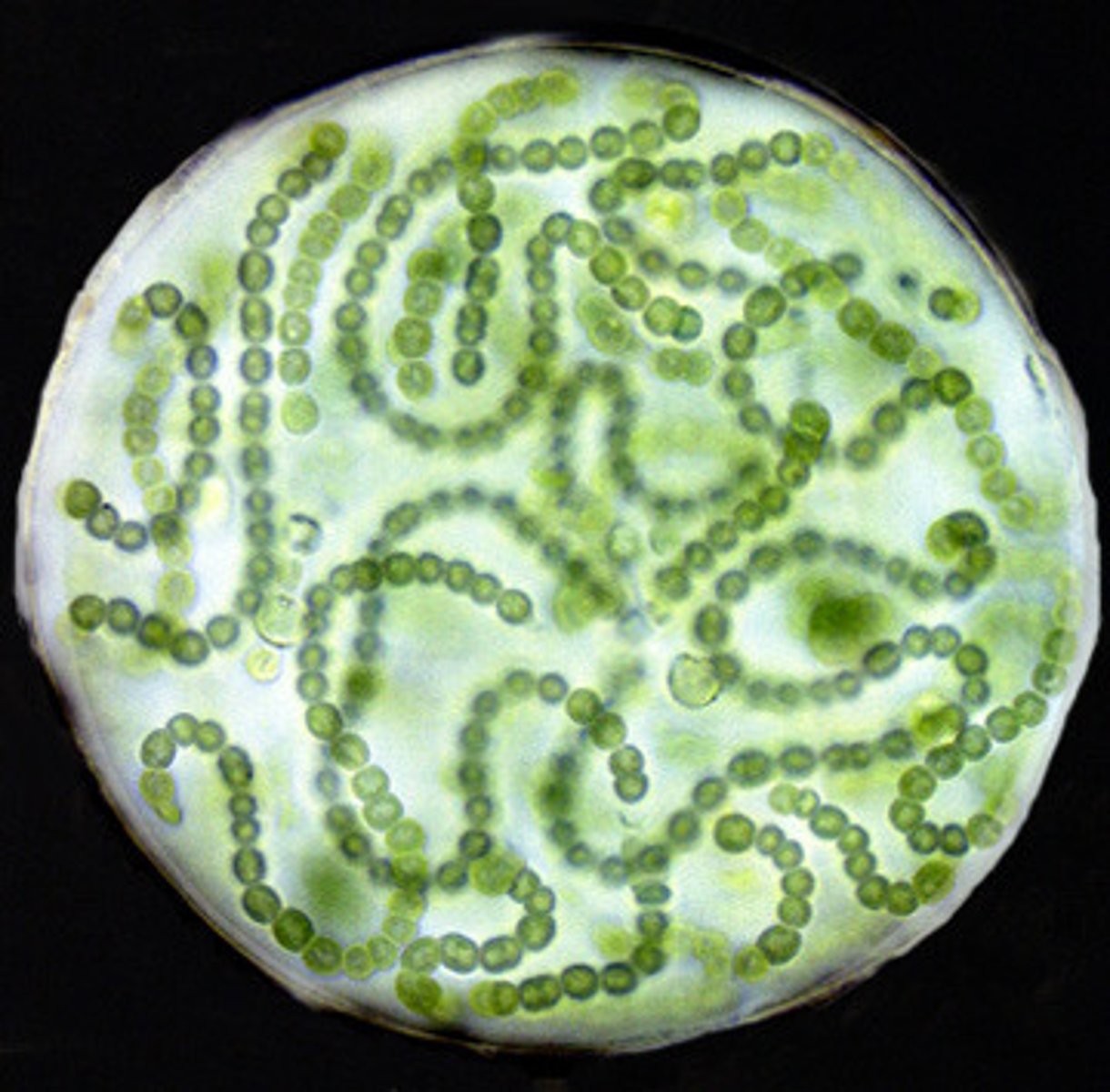
Cyanobacteria dna transfer
Cyanobacteria share a lot of dna between each other and they have easy transformation. (encorporate floating pieces of dna they find)
Cyanobacteria morphology
-filaments, spheres, spirals
-individual cells, chains or colonies
Unicellular. Binary fission. No sexual stage. Mucilaginous.
mucilagenous sheath
jellylike layer often surrounding cyanobacteria
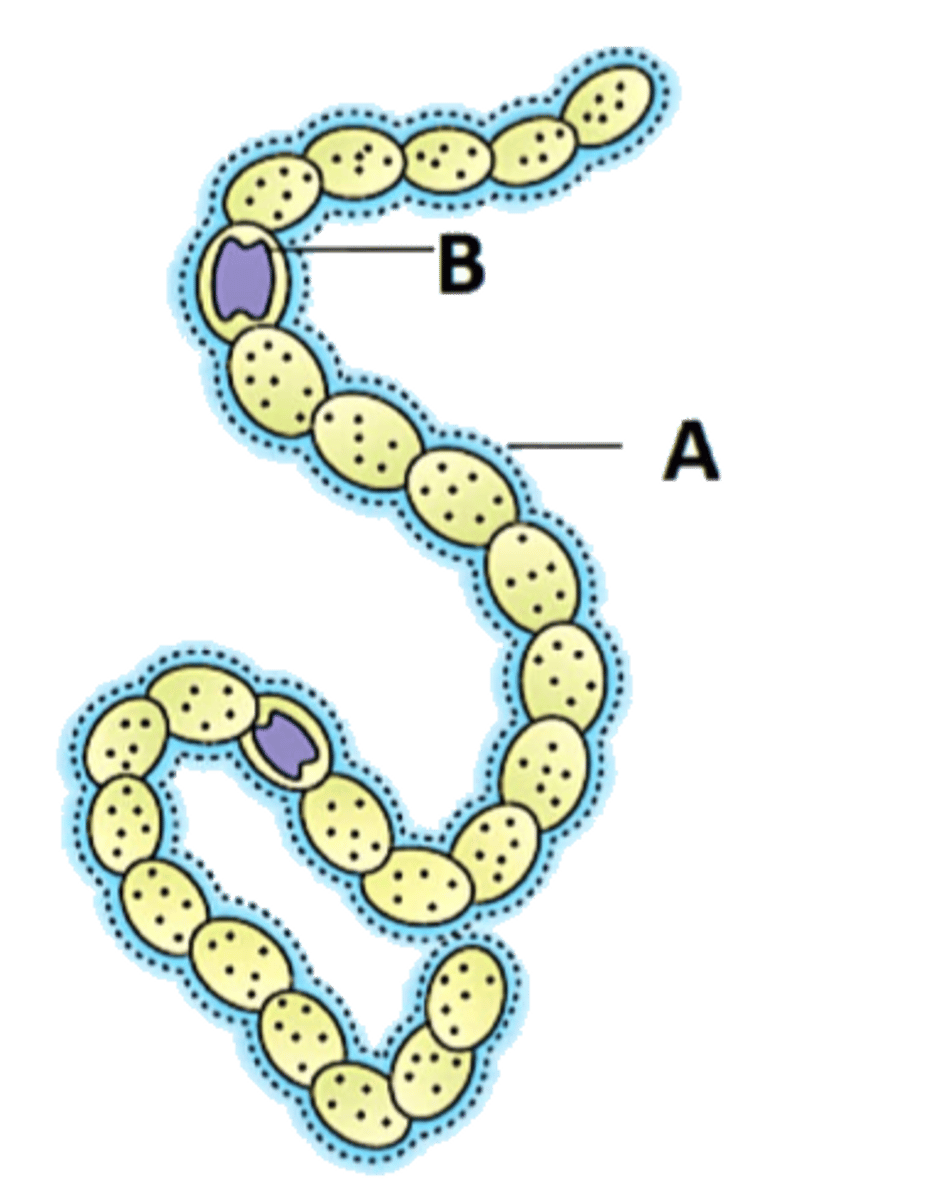
what is the mucilaginous sheath made of
glyoaminoglycans, otherwise known as mucopolysaccharides
glyoaminoglycans
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are a group of polysaccharides that are found in the body's tissues and cells.Also known as mucopolysaccharides.
What is the function of the Mucilagneous Sheath
It helps the cell not dry out.
important for water retention.
can also help with buoyancy.
can help to deter herbivores. (covered in gel is not appetizing)
They can provide UV protection (Important because there was no ozone layer at the time!)
Nostoc (cyanobacteria)
Genus and type of bacteria
Very large balls
chained organism
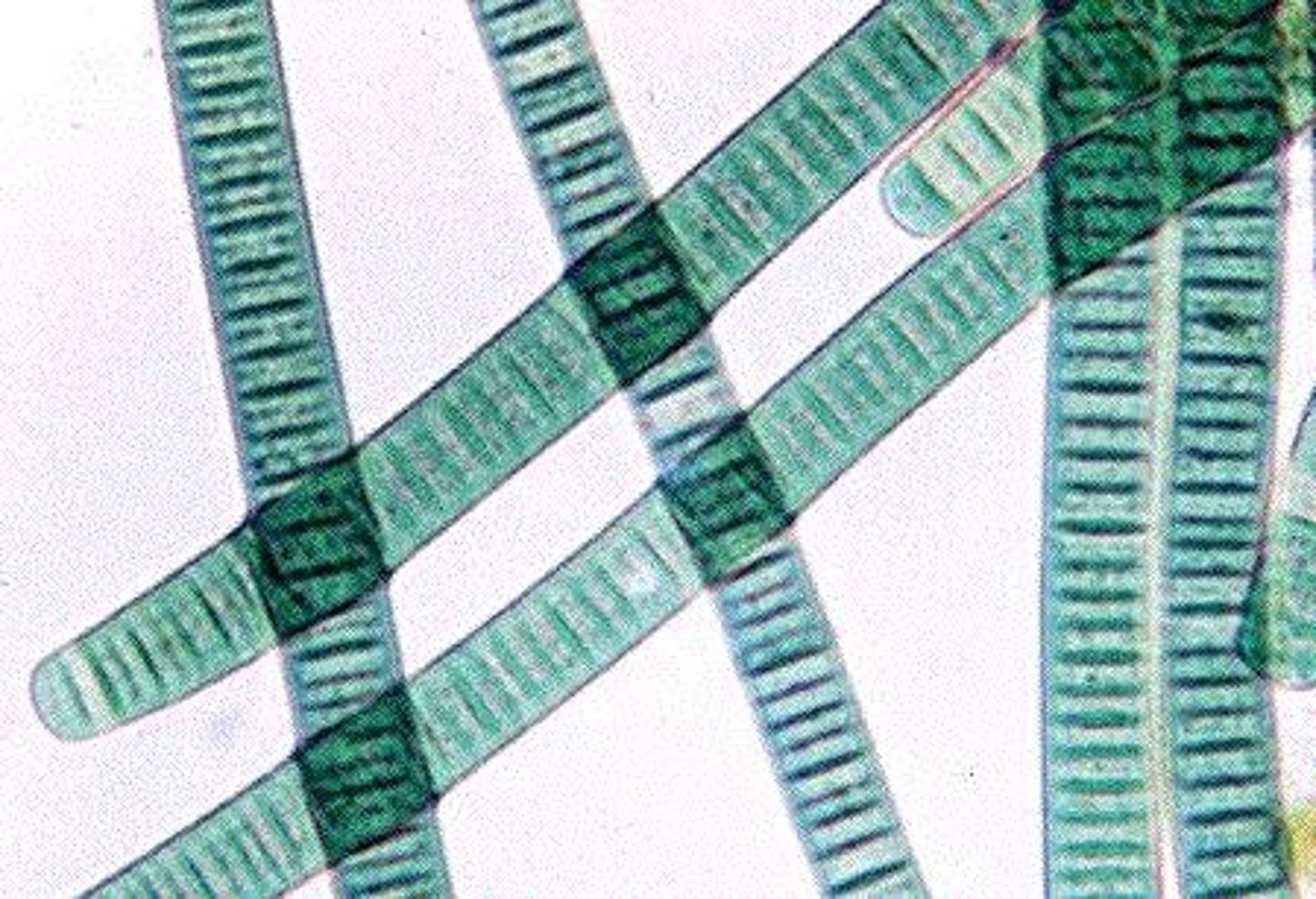
filaments of cyanobacteria are called
trichomes
filaments of cyanobacteria exists because
error in mitosis kept them fused together after binary fission
it was an error at first but it's not STILL an error, it's intentional now.
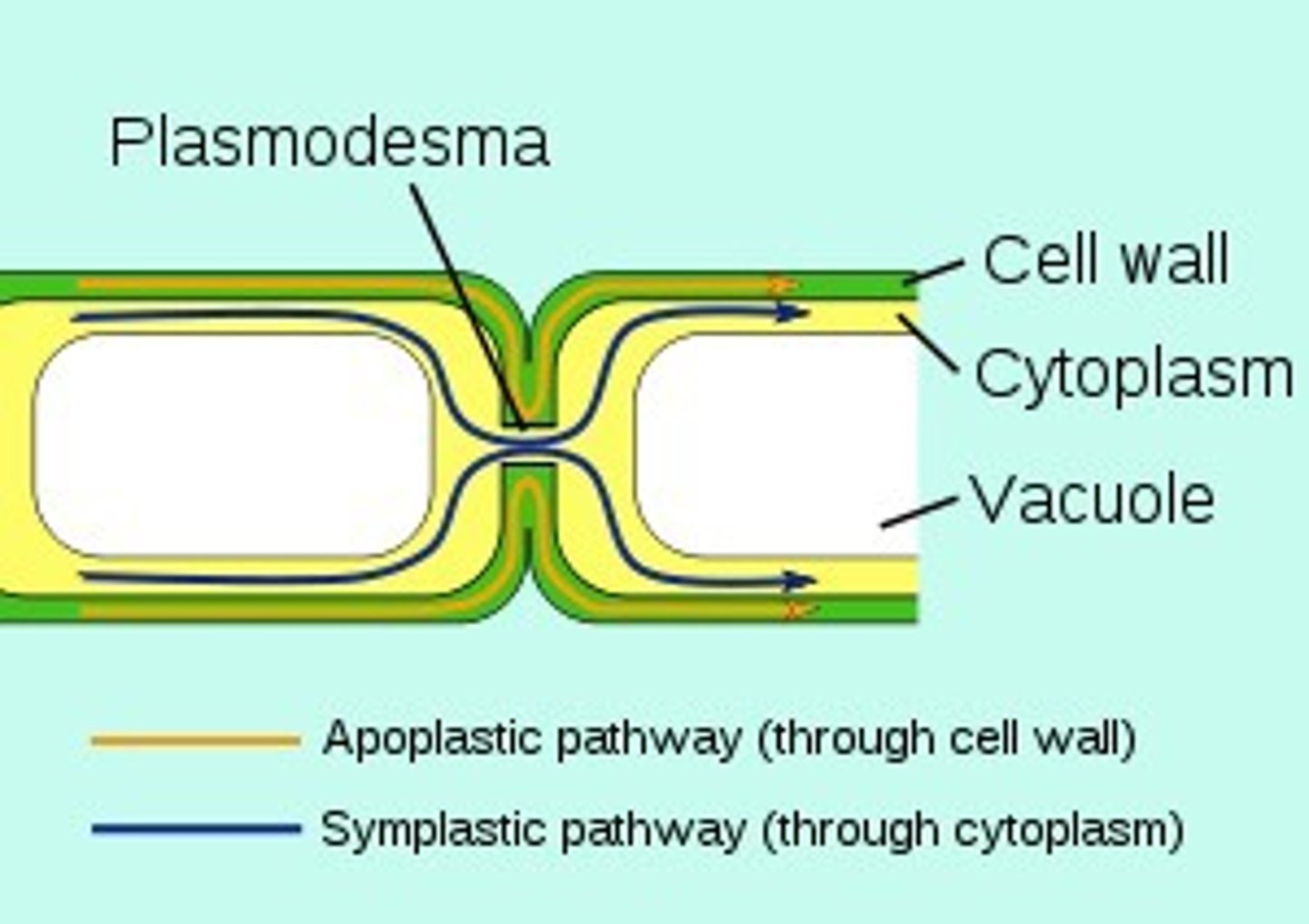
filaments in cyanobaxteria are primative ___________
plasmodesmata
Plasmodesmata
An open channel in the cell wall of plants through which strands of cytosol connect from adjacent cells
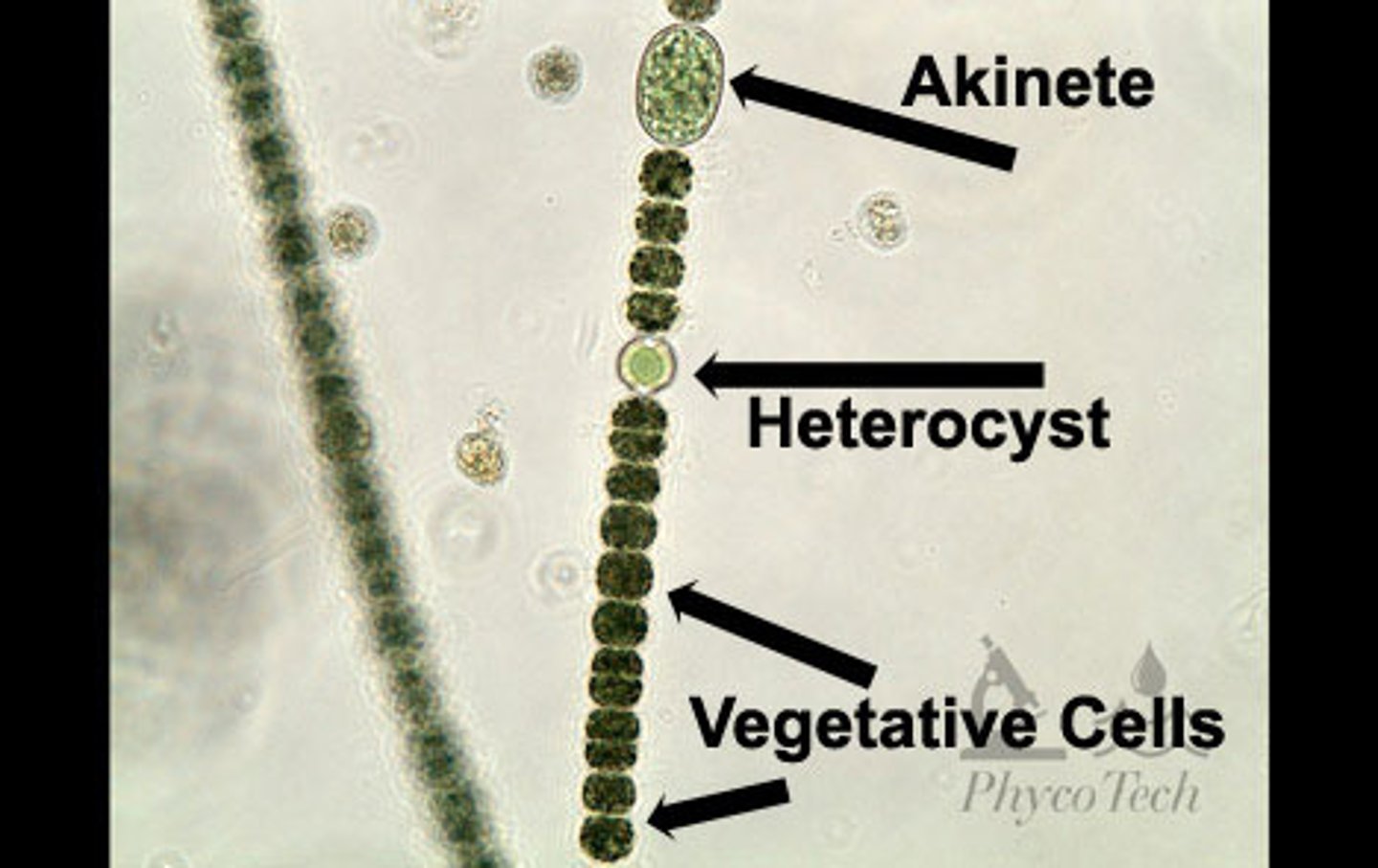
Resting spores
Spores with a thick wall that protects the contents during adverse conditions. The spores only germinate after a period of dormancy, when the conditions have improved.
Some cyanobacteria make these
heterocyte
A specialized cell that engages in nitrogen fixation in some filamentous cyanobacteria; formerly called heterocyst.
Thick walls. Nitrogenase doesn't like water.
look like glass balls
Oscillatoria (Cyanobacteria)
long filament of cells; photoautotrophs; cyanobacteria
form structures called hormogonium
how Oscillatoria change their morphology based on programmed cell death
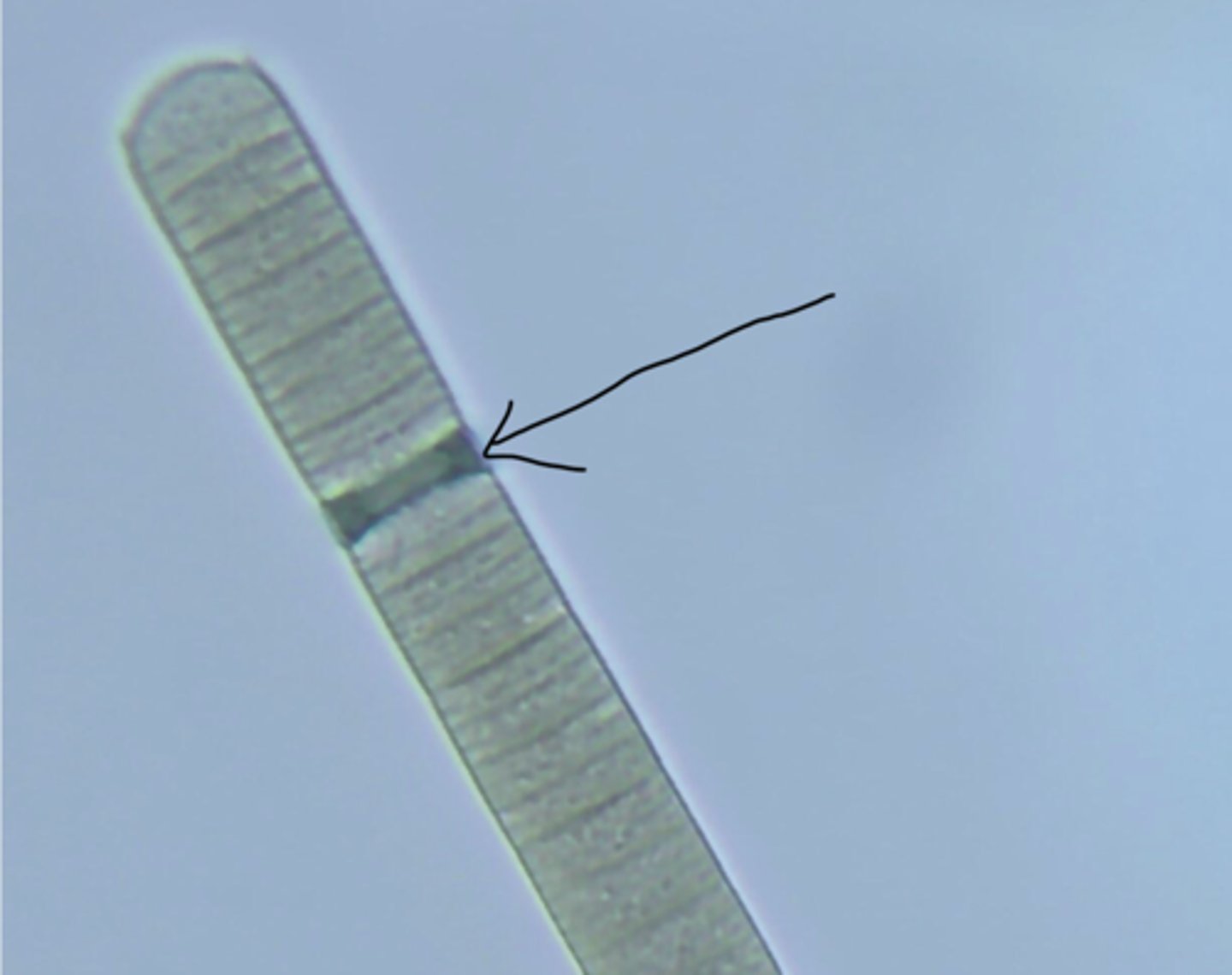
Hormogonium
A short motile chain of three to five cells produced by filamentous cyanobacteria to disseminate their cells.
important for asexual reproduction.
cell-cell adhesion
binds cells into tissues/organs
cell specialization/differentiation
The process by which cells change as they grow and develop to become specialized with different functions.
how does cyanobacteria reproduce
Totally asexually. Binary fission. They have circular chromosomes
what kind of chromosomes do cyanobacteria have?
circular chromosomes
Cyanobacteria reproduction
binary fission, budding, fragmentation, multiple fission
what does the hormogonium do
The trichomes (filaments) of cyanobacteria break into hormogonia at regular intervals.
Each hormogonium is a short piece of filament that contains 5-15 cells.
The hormogonia glide and develop into new filaments.
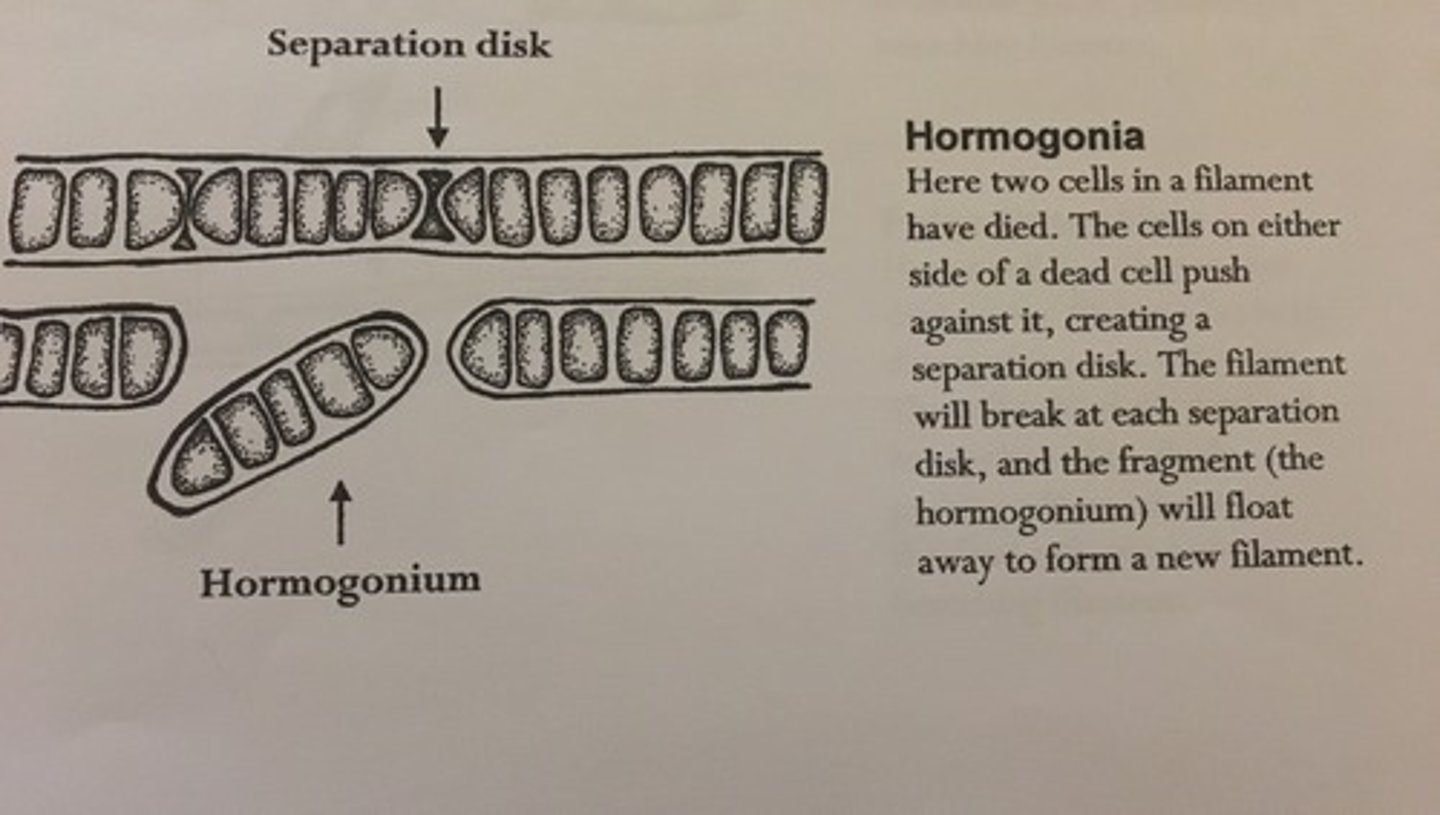
separation disk
Note the separation discs in the uppermost filament: these are formed by the death of cells at intervals along a filament, the dead cells filling with mucilage. Filaments will eventually fragment at these separation discs into separate segments called hormogonia or hormogones, a form of asexual reproduction
algal bloom
The rapid growth of a population of algae
Stromalites
layered rocks that form when certain prokaryotes bind thin films of sediment together
USED TO BE CYANOBACTERIA
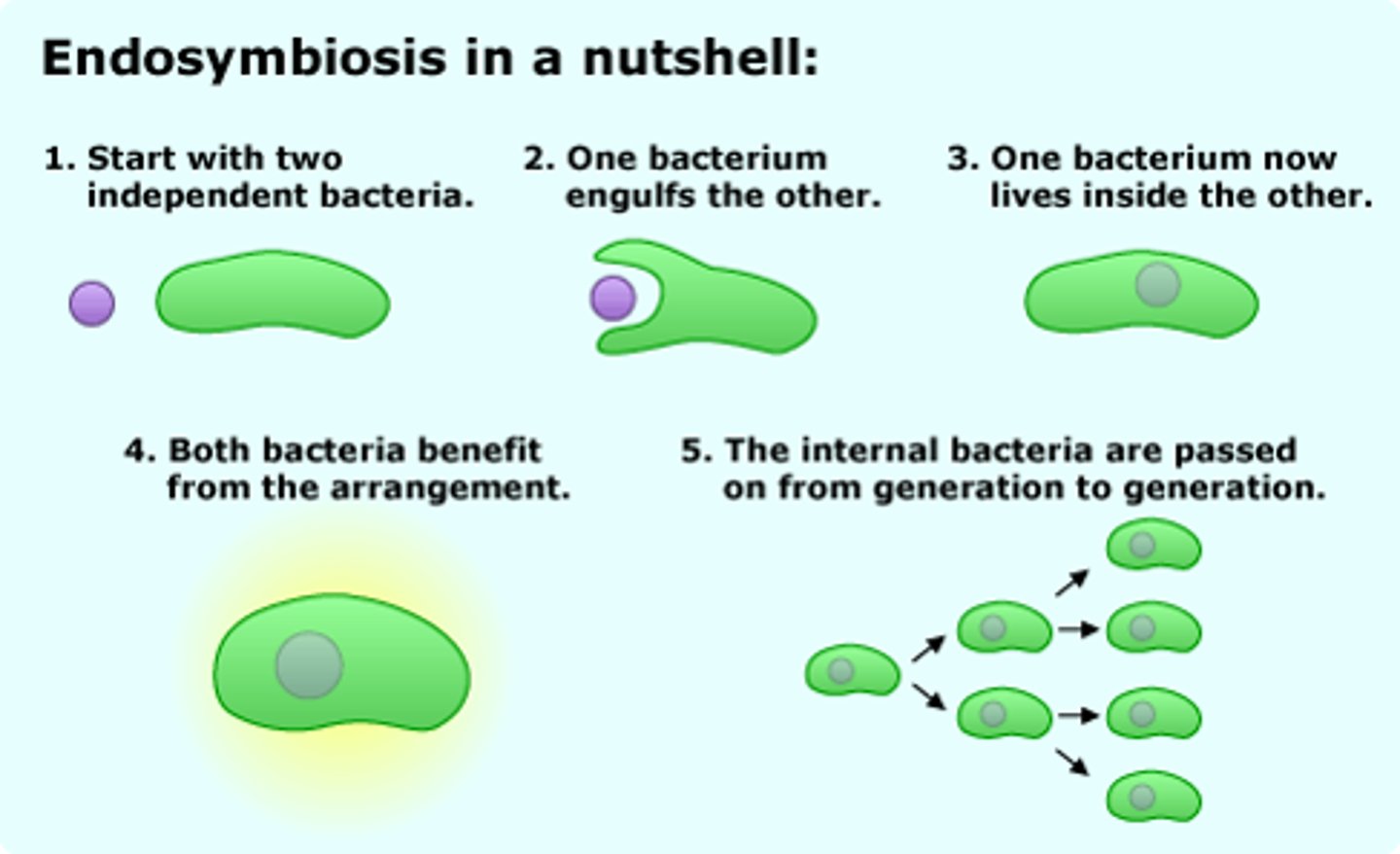
Endosymbiosis
A theorized process in which early eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes.
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells
origin of chloroplasts
Cyanobacteria (photosynthetic prokaryotes) contain chlorophyll and enzymes similar to chloroplasts
Theory of Endosymbiosis Chloroplasts are the descendants of cyanobacteria that were engulfed by eukaryotic cells about 2 billion years ago
They lived in symbiotic relationship within the cells that had engulfed
Over time, the cyanobacteria became permanent residents of the cells and progressively changed
secondary endosymbiosis
a process in eukaryotic evolution in which a heterotrophic eukaryotic cell engulfed a photosynthetic eukaryotic cell which survived in a symbiotic relationship inside the heterotrophic cell
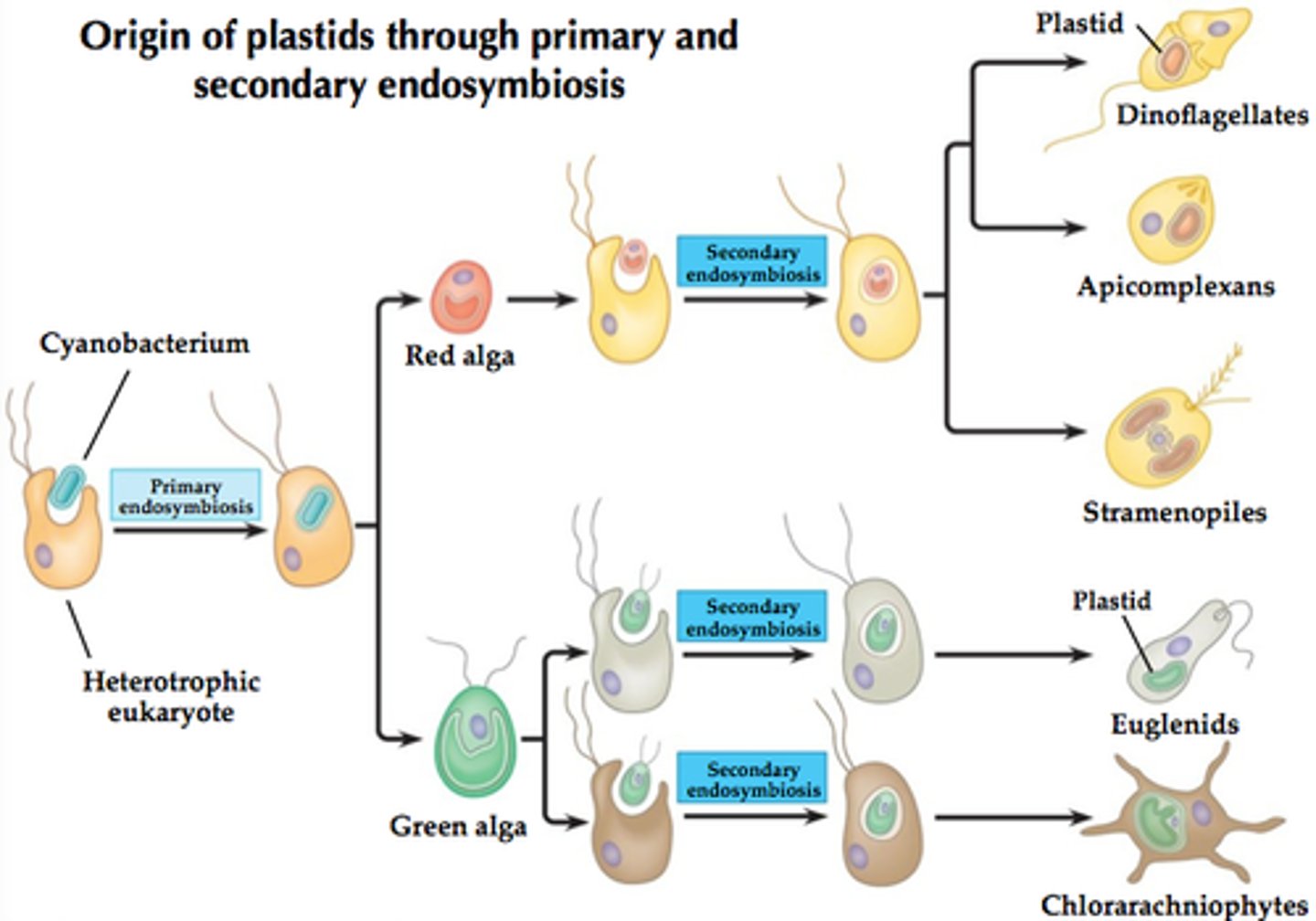
membrane counts
Green Algae have 2 membranes
Red Algae have 2 membranes
Brown Algae have 4 membranes
Diatoms have 4 membranes
Euglenoids have 3 membranes
Draw primary and secondary endosymbiosis
yes yes do this (primary and secondaru endodymb)
Misconceptions: In a 3 domain tree, all 3 are equally related
NOT TRUE: Archaea and eukarya are more closely related
Misconception: Not all eukarya are related to archaea
NOT TRUE: All eukarya are related to the common ancestor of archaea
Are cyanobacteria considered algae?
NOPE! Algae are protists.
protista is a ______________ group
polyphyletic
what are some examples of protists
algae, protozoa, slime molds, water molds
What trophy are protists?
they can be photosynthetic autotrophs, or heterotrophs or a mic between them.
Glaucophytes
Unicellular freshwater algae with chloroplasts containing traces of peptidoglycan, the characteristic cell wall material of bacteria.
RETAIN BACTERIAL CELL WALL (in the chloroplast)
Discoba
Protist supergroup of unicellular flagellates; often with feeding groove and uses phagocytosis to ingest food; disc-shaped mitochondrial cristae
Stramenopila
A diverse protistan clade that includes several heterotrophic groups and a variety of photosynthetic protists.

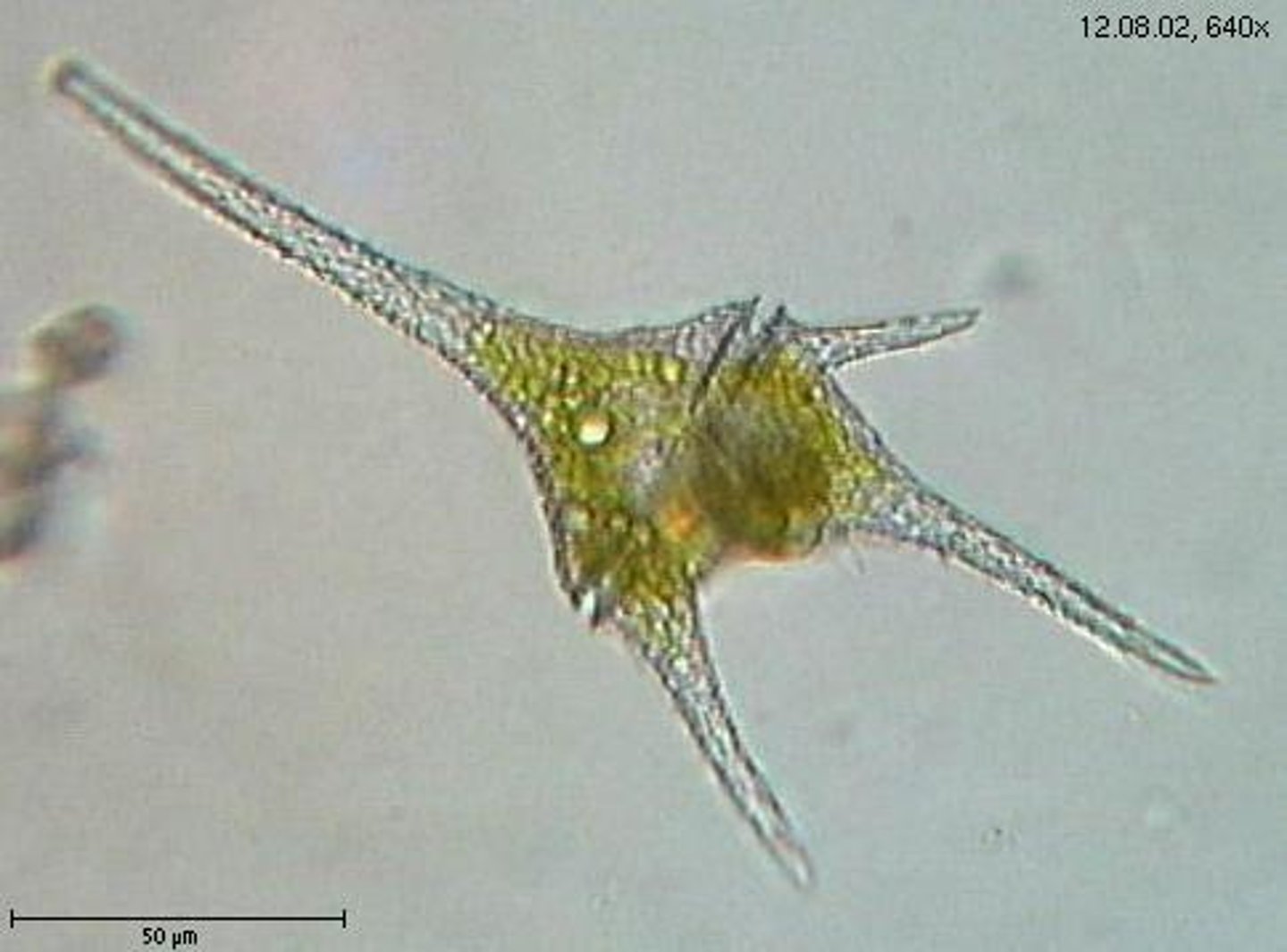
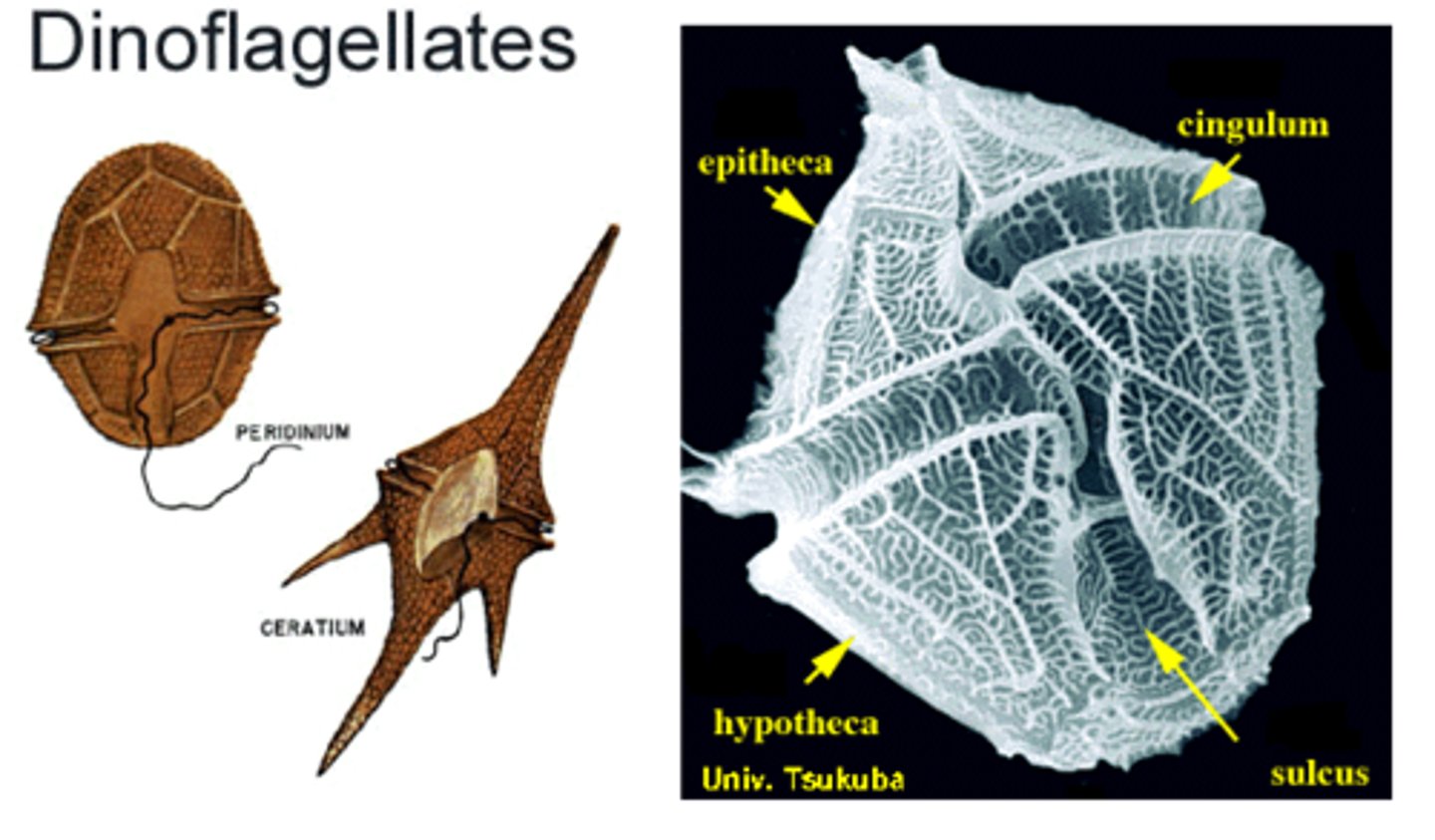
Dinoflagellates
Group of protists that form "blooms", can be toxic. make up phytoplankton and can be bioluminescent. They generally have two flagella, half are heterotrophic and the other half are photosynthetic, many species are luminescent

Dinoflagellates (Alveolates)
photosynthetic unicellular alveolate protist with two flagella, one that it uses to spin itself for locomotion and one that it uses to steer; many of them are luminous in water and they are the cause of toxic red tides in oceans that can be deadly for marine life
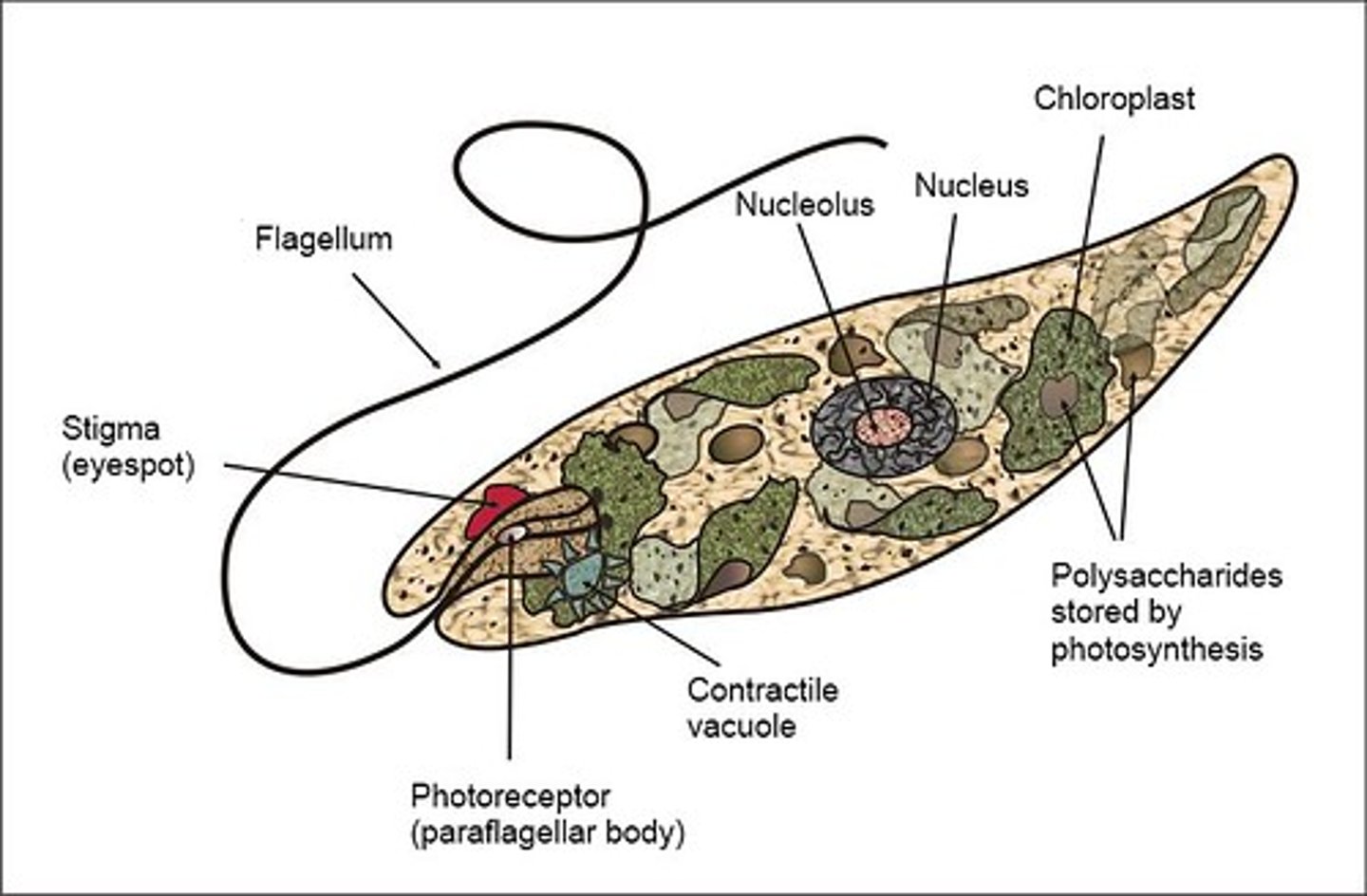
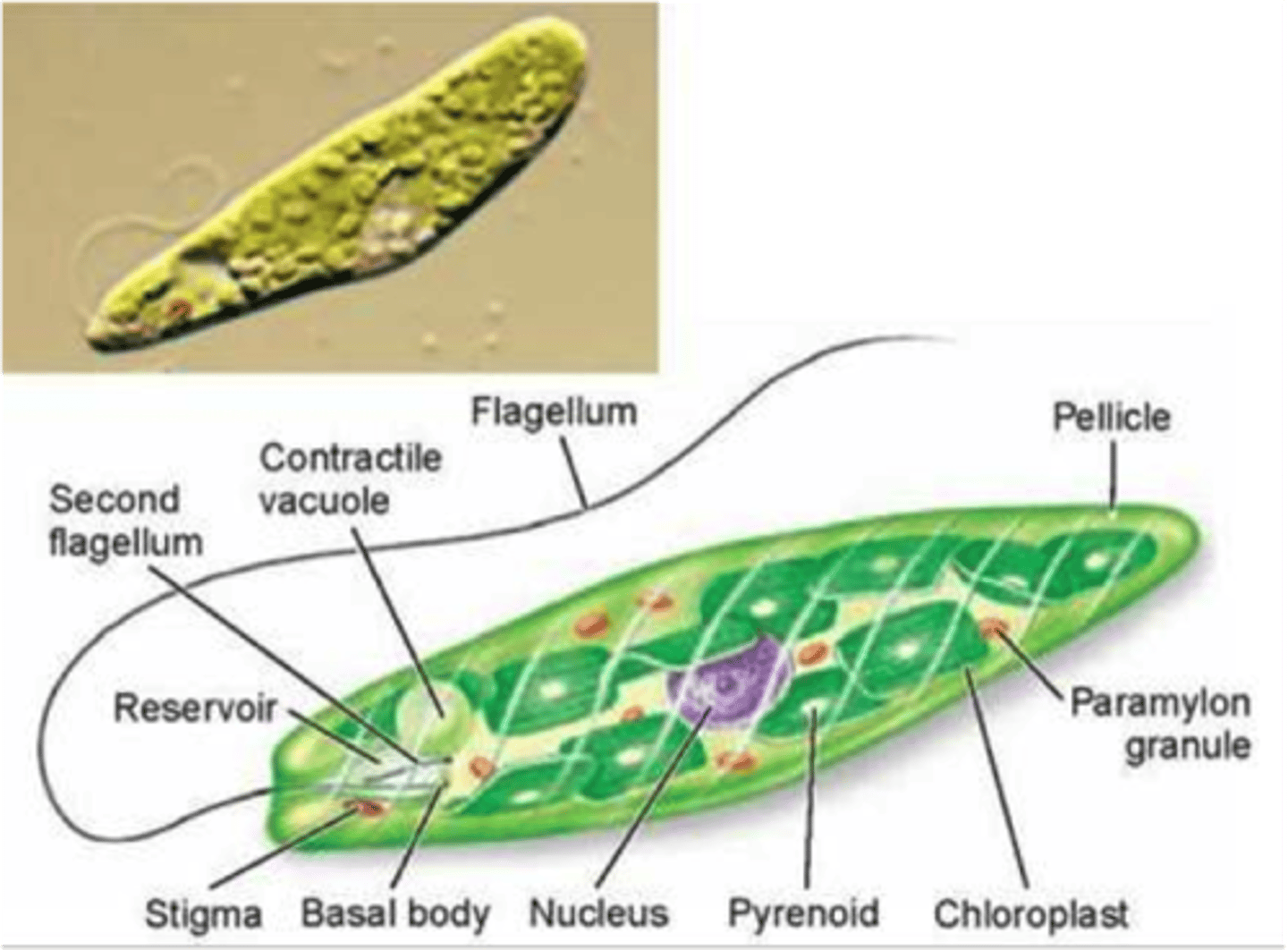
Eugelnoids
unicellular
terminal flagellum
no cell wall
contain chloroplasts with chlorophyll
eyespot can receive light
contractile vacuole to regulate water
do euglenoids have a sexual stage?
No. they do not have a sexual stage.
Longitudinal division
the cell never divide in a transverse manner, always longitudinal (always down the long end of the cell)
metaboly
the change in shape of euglena when it can't swim freely due to the flexibility of the euglena pellicle
Biological process that describes the abillity of a cell to change shape
To catch prey.
Relationship between metaboly and heterotophic
More metaboly = more heterotrophic
paramylon
The storage molecule of euglenoids
Plastids
A group of membrane‐bound organelles commonly found in photosynthetic organisms and mainly responsible for the synthesis and storage of food.
nucleomorph
tiny vestigial nucleus.
this happens in some secondary and tertiary endosymbiosis cases but most of the time you lose the mitochondria and nucleus.
sometimes you even lose a membrane
Normal outcome of secondary endosymbiosis
4 membranes
1. original cyanobacteria membrane
2. primary endosymbiosis membrane (from host cell 1)
3. New phagosome from ancestral host cell #2
4. ancestral host cell outer membrane
Pellicle
A firm, flexible coating outside the plasma membrane
proteinaceous plates
made of proteins called articulans - non-polar amino acids
articulans
connected via microtubules, they can get longer and shorter. LIKE A SUIT OF ARMOR.
An Endo exoskeleton