Differential Diagnosis
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Non-cavitatated lesions two types
Early Carious Lesions (Decalcification) and Non-carious lesions
Two types of non-carious (non-cavitated) lesions
Fluorosis and Devepmental Defects (hypoplasia and hypocalcificaiton)
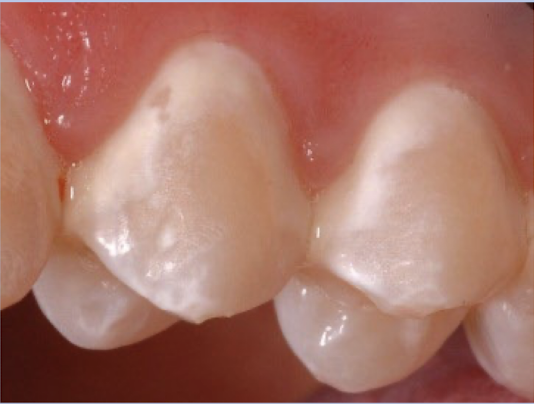
combination/decalcification
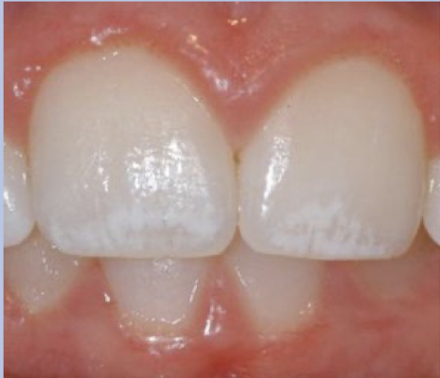
Fluorosis
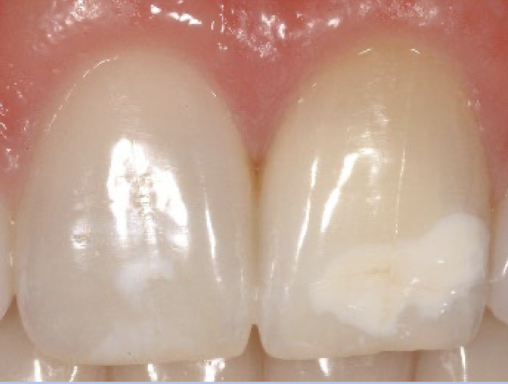
Hypocalcification
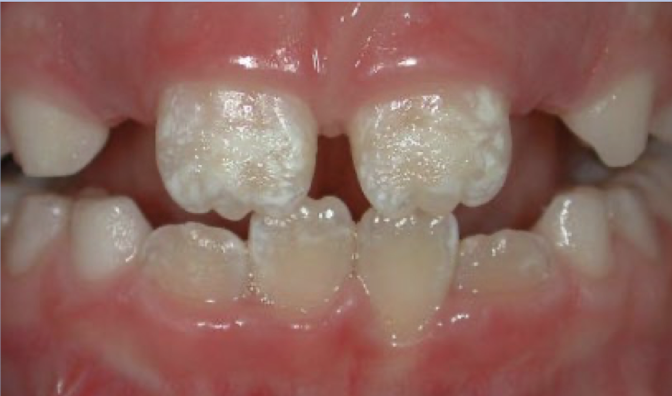
Hypoplasia
Decalcification is caused by ___, fluorosis is caused by __
active caries leison (early), excess fluoride
Fluorosis occurs when? and where?
During development/eruption, incisal edges and cusp tips
Decalcification usually occurs along __ and _. basically in ? areas
gingiva and inter-proximal area, plaque stagnation
Hypocalcification is a condition where ?
ameloblasts cells are affected resulting in hypocalcification
Hypocalcification is caused by __
trauma, fever, malnutrition, hypocalcemia during formation
Fluorosis usually affects ?
incisal edges and cusp tips
Hypocalcification:
front teeth and 6 year molars: occurred when?
bicuspids and second molars: ?
1st year, age 3
Hypoplasia is ?
developmental enamel defect
Which often results in caries due to difficulty in maintaining oral hygiene?
what is this caused by?
hypoplasia, genetic disorders + systemic diseases
Decalcification is __ at eruption
Fluorosis is ___ at eruption
Hypocalcification is __ at eruption
not present, may not show stain, pigmented
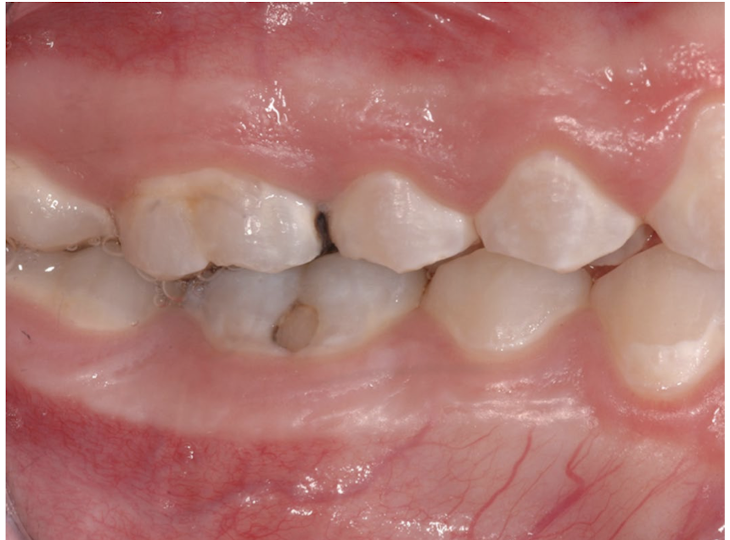
Decalcification teeth affected
canines, pre-molars, molars
Frosted cusp tips?
Fluorosis
Fluorosis and Hypocalcification colors
light white to dark brown
Hypocalcification color
creamy yellow to dark reddish orange, or white/brown spots
Fluorosis is most frequently on ? Often in ?
teeth that calcify slowly (canines, premolars, molars), same spot on contra-lateral tooth
What teeth does hypocalcification occur on
any tooth, frequently on labial surfaces of incisors, (often singly)
what color is hypoplasia
white, yellow, brown pitted and rough spot lesions
what teeth for hypoplasia
often contralateral tooth as wel as same tooth on opposing arch (ie all central incisors)
Shape?
Decalcification: well-defined borders
shape?
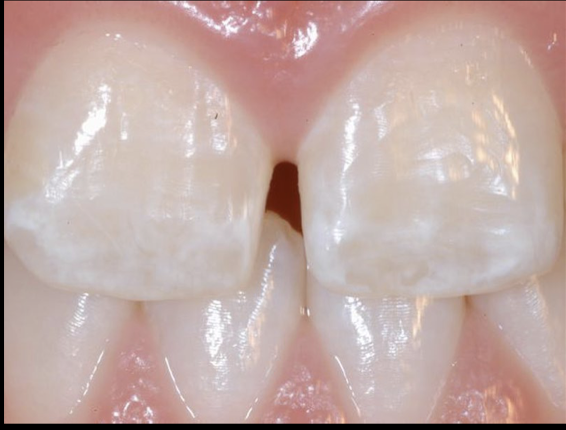
fluorosis: lattice pattern
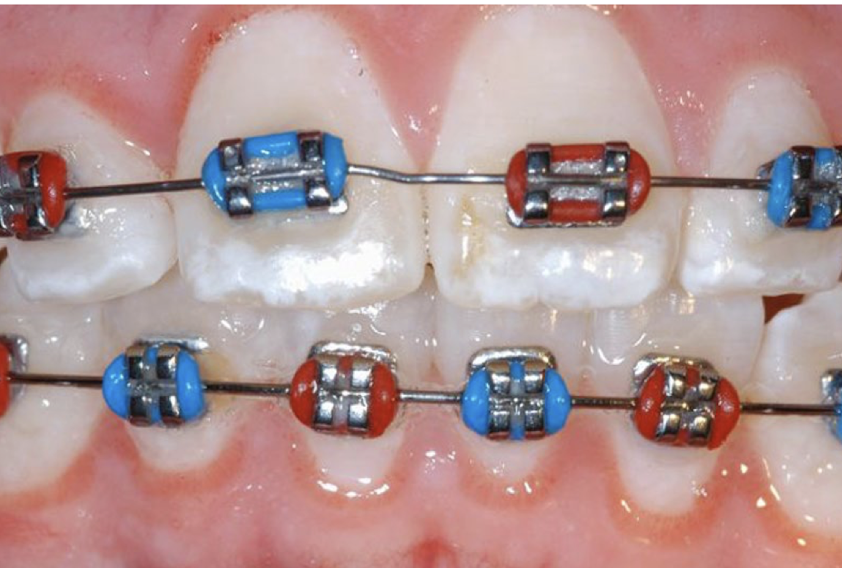
fluorosis
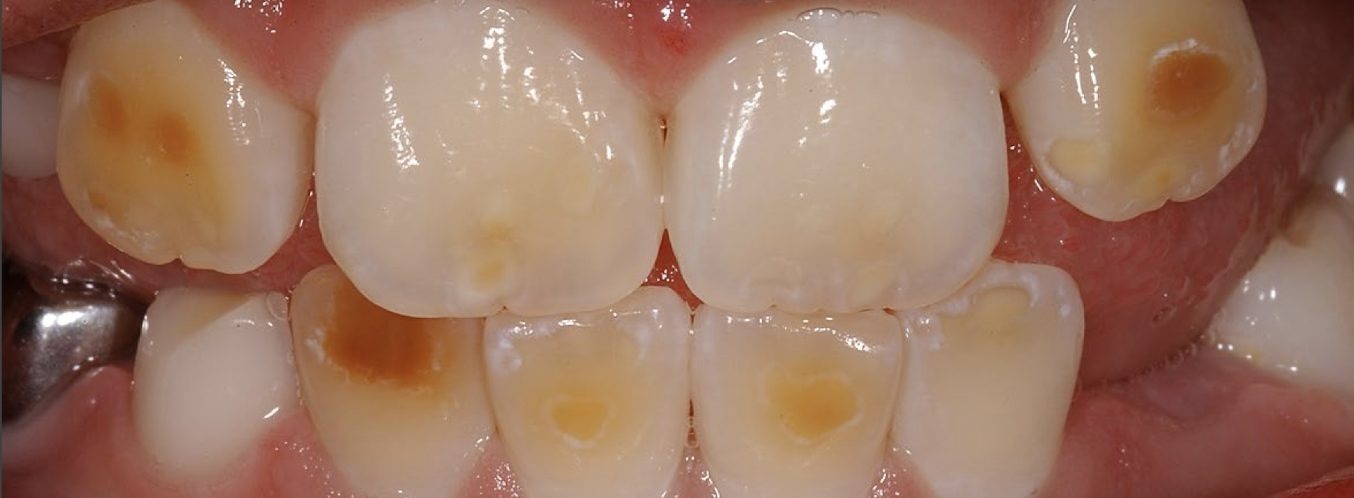
Fluorosis
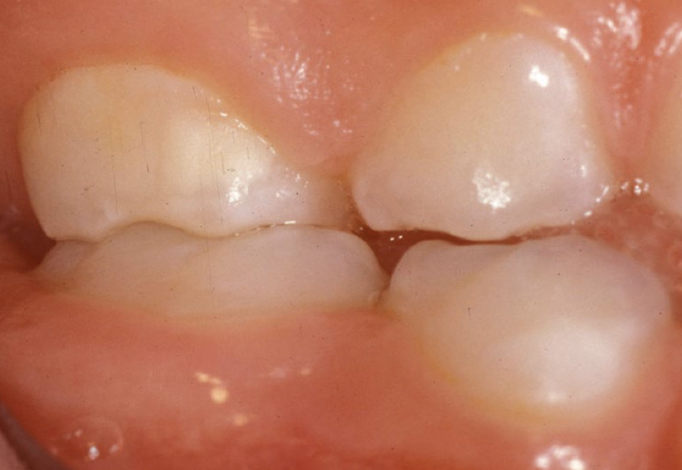
shape?
hypocalcification: oval or round
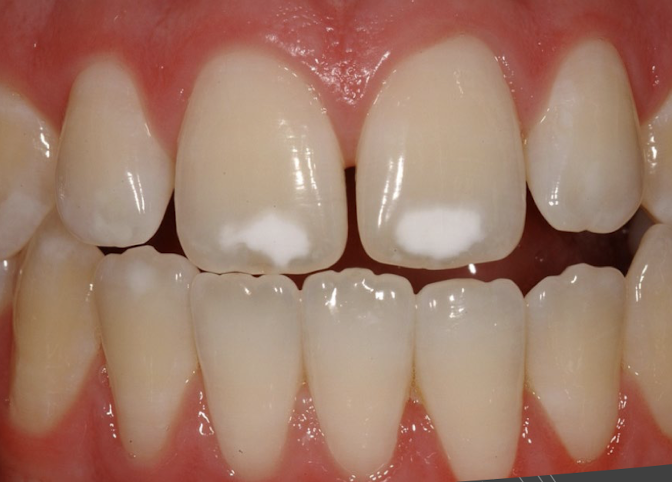
hypocalcification
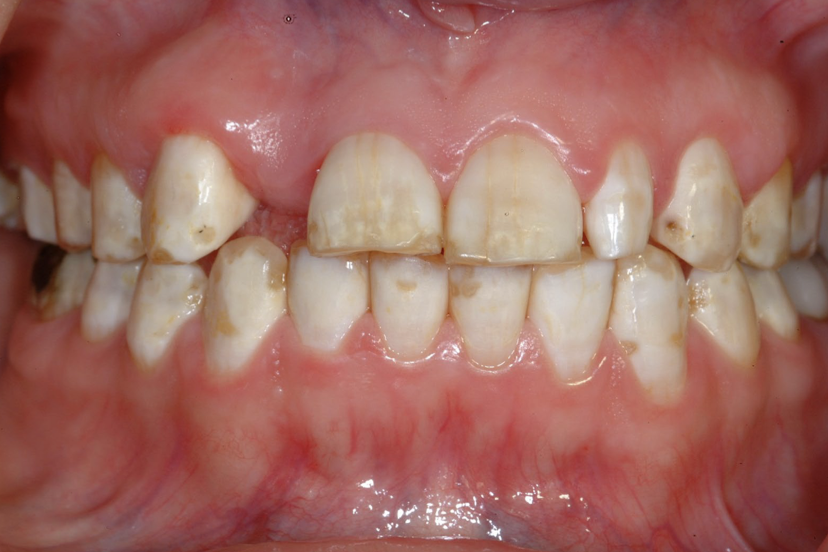
Hypoplasia
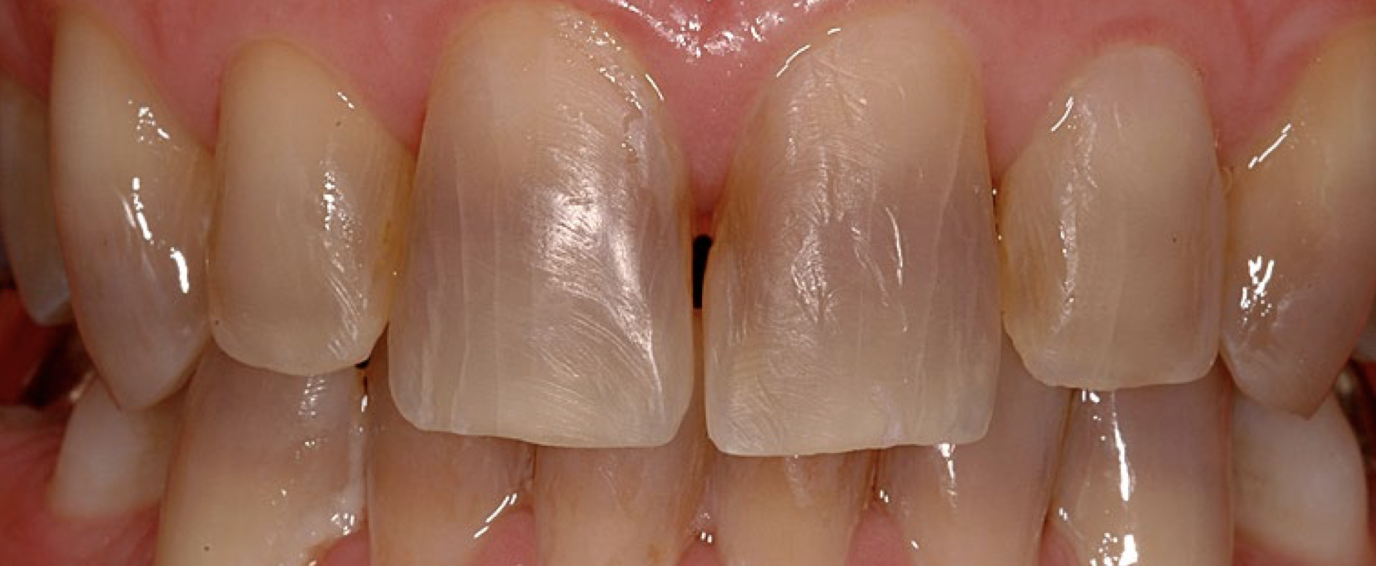
does it respond to bleaching?
Tetracycline: no
Can non carious lesions progress into a caries lesion?
yes if not cleansable
Tooth wear: 3 A’s
2 other
Abrasion, erosion, attrition
physiological (age), pathological
Mechanical forces by foreign element:
Chemical reduction:
Tooth to tooth wear:
abrasion, erosion, attrition
Abfraction causes tension and compression → ?
cervical tooth breakdown wedge: shape cerivical lesions
Abfraction is caused by?
bruxism (grinding), occlusal function mastication, parafunction
occlusal and incisal surfaces: shiny well defined facets, myofacial pain disfunction and stiff jaw, often due to bruxism
attrition
Glazed, smooth, round and edged surfaces, looks scooped out. No well defined facets, sensitivity, often due to bulimia and GERD
erosion
Pitted, scratched surface, if extreme will have facet or scooped out dentin. Patient usually does not have sensitivity, most often due to tooth brush and tooth paste
abrasion
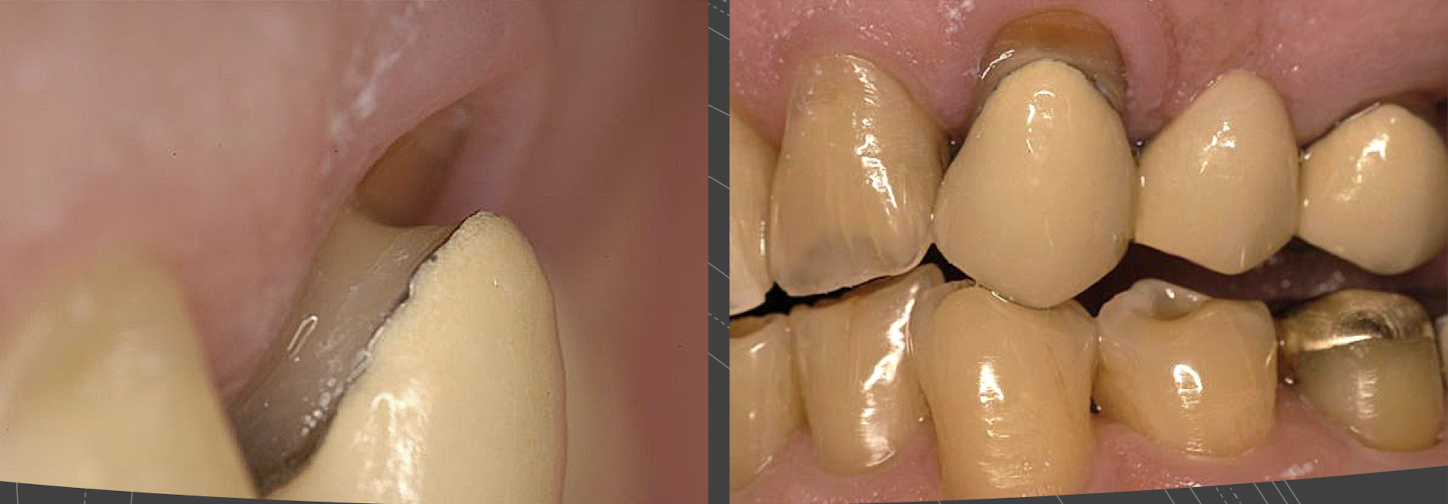
most often occurs on ? Where most common?
abfraction: single tooth (abrasion is multiple), most common on buccal of canines and posterior teeth
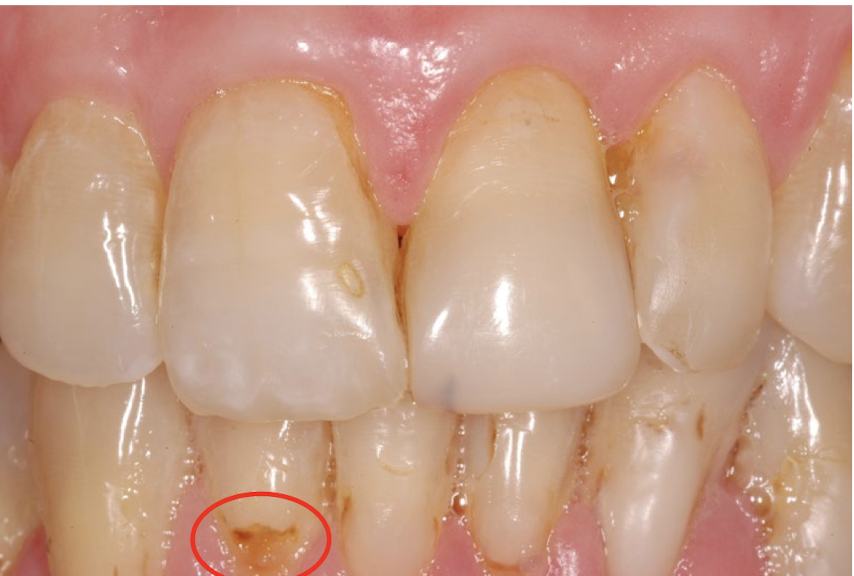
abrasion resulting in caries lesion
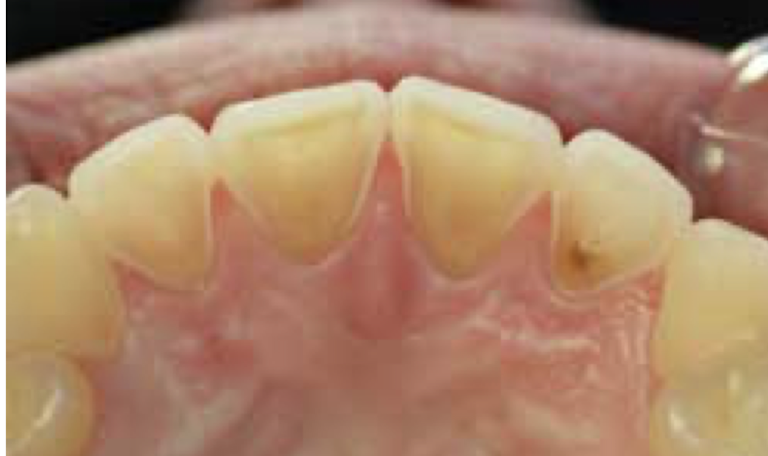
erosion
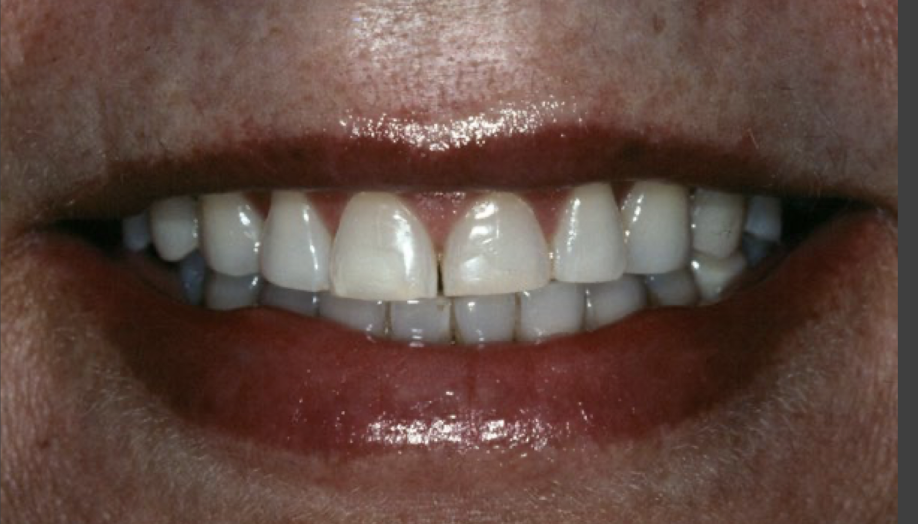
Bruxism and Attrition
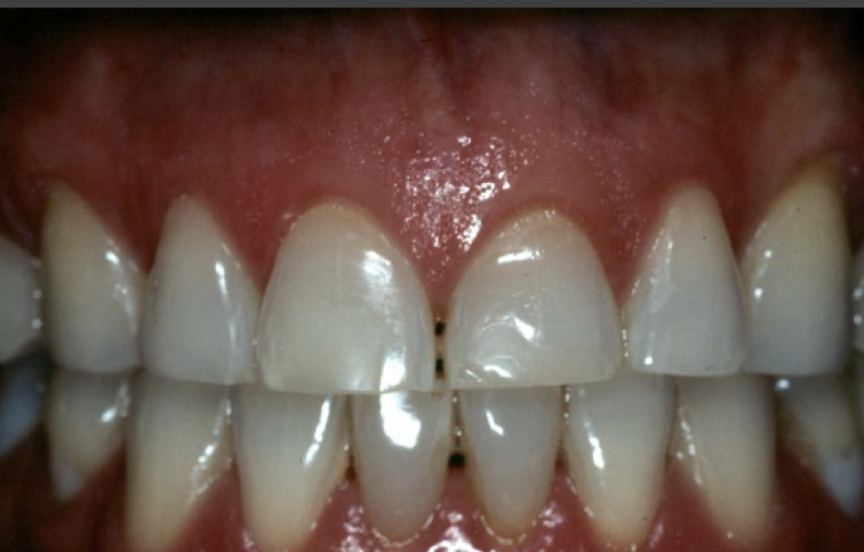
Bruxism and Attrition
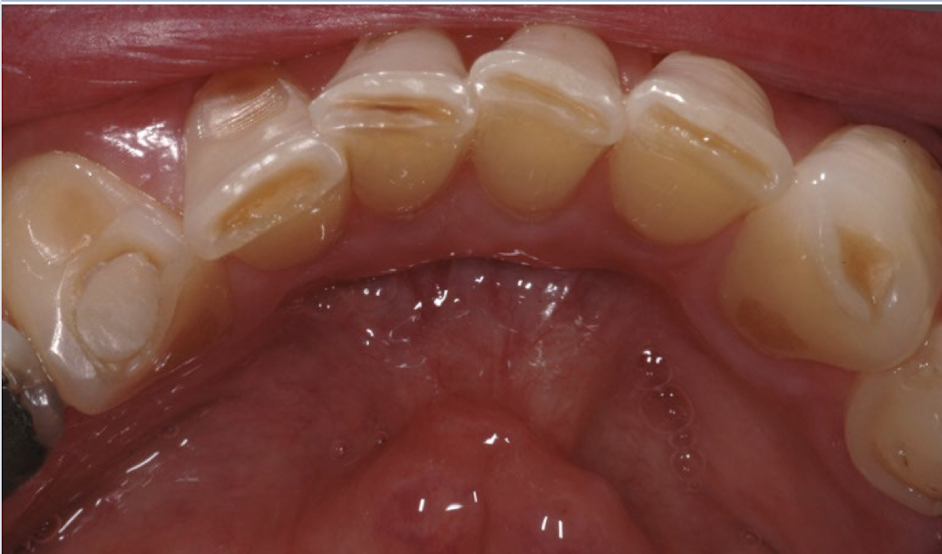
Attrition
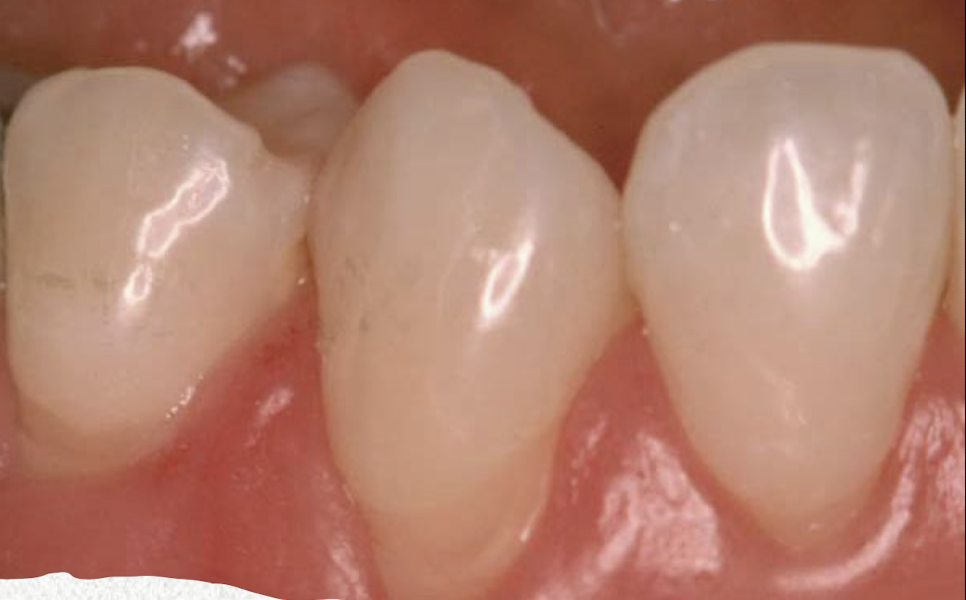
Abfraction
Clinical factors to consider (6)
Age
Diet
Oral Hygiene
Occlusion
Habits
Bruxism and Parafunction
2 kinds of cavitated lesions
non carious lesions or carious lesions
3 kinds of non carious cavitated lesions
tooth wear (E,A,A,A), enamel and dentin dysplasia, trauma
3 kinds of carious lesions
cavitation in enamel, in dentin, rampant caries