Final Exam
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/641
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
642 Terms
1
New cards
The term “ecology” comes from a word meaning “house.” (True or False)
True
2
New cards
The action of an “ecological filter” is also known as “natural selection.” (True or False)
True
3
New cards
Mineral nutrients can be released from soil particles with the help of secretions by plant roots (True or False)
True
4
New cards
The side of a mountain facing into the prevailing winds from the ocean has less rainfall than the side facing away from the winds (True or False)
False
5
New cards
According to the hypothesis developed in class, marine ray-finned fish are hyposmotic because the MRCA of all extant (alive today) ray finned fishes lived in salt water. (True or False)
False
6
New cards
In C4 photosynthesis, stomates are open at night and CO2 is fixed at night, allowing stomates to be closed during the day. (True or False)
False
7
New cards
Hair on the head helps keep the human brain cool in sunny, hot climates (True or False)
True
8
New cards
If a tadpole metamorphoses into a frog faster in the presence of a predator fish, compared to when it is kept alone, this is an example of phenotypic plasticity (True or False)
True
9
New cards
We do not have any way to estimate what global temperatures were millions of years ago. (True or False)
False
10
New cards
An organism’s life history is the description of its life cycle. (True or False)
False
11
New cards
The shallow edge of a body of water. In the case of the ocean, it is the intertidal zone.
Littoral
12
New cards
Ocean tides enter the mouth of a river, producing a mixture of fresh and salt water and depositing an abundance of nutrient-rich sediments.
Estuary
13
New cards
Vegetation growing on the edge of a stream or river; often including trees that are adapted to more moisture than the trees in the surrounding forest.
Riparian
14
New cards
The bottom floor or sediments of a lake or the ocean
Benthic
15
New cards
In the ocean, the relationships of who eats whom, from plankton to invertebrate larvae to fish, is studied from the perspective of the
A. Organism D. Ecosystem B. Population E. Biosphere C. Community
A. Organism D. Ecosystem B. Population E. Biosphere C. Community
C
16
New cards
In the African savanna, antelopes browse the lower leaves of trees while zebras graze on grasses. This partitioning of resources means that antelopes and zebras have
A. Different habitats
B. Completely different niches
C. Partly different niches
D. The same niche
A. Different habitats
B. Completely different niches
C. Partly different niches
D. The same niche
C
17
New cards
Animals and fungi are both heterotrophs, but animals mostly consume living plants and other animals, while fungi mostly consume dead plants. This means animals and fungi have ______ trophic modes and ______ functional roles.
A. similar; similar
B. similar; different
C. different; similar
D. different; different
A. similar; similar
B. similar; different
C. different; similar
D. different; different
B
18
New cards
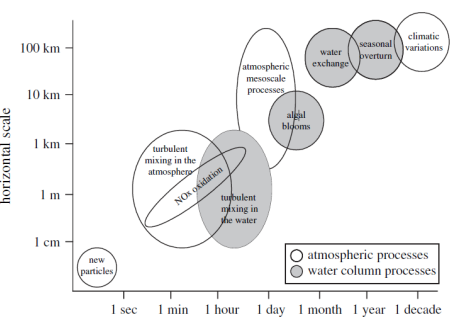
According to the figure (on the right) showing the spatial vs. temporal scale of N deposition into the sea off the coast of Sweden, which water column process affects an area of 100 m and can last several hours?
A. NOx oxidation
B. Turbulent mixing in the water
C. Atmospheric mesoscale processes
D. Algal blooms
E. Water exchange
A. NOx oxidation
B. Turbulent mixing in the water
C. Atmospheric mesoscale processes
D. Algal blooms
E. Water exchange
B
19
New cards
“Alligators adjust the sex of their offspring to favor the rare sex in the population, increasing mating opportunities for the offspring” is an example of a(n) ______ hypothesis, and “The sex of alligators is determined by the temperature of the nest, which affects gene expression in the developing embryo” is an example of a(n) ______ hypothesis.
A. Proximate; proximate
B. Proximate; ultimate
C. Ultimate; proximate
D. Ultimate; ultimate
A. Proximate; proximate
B. Proximate; ultimate
C. Ultimate; proximate
D. Ultimate; ultimate
C
20
New cards
In a study to test the effects of biological control by weevil or psyllid insects on the invasive tree Melaleuca quinquenervia in South Florida, seedlings of the tree were placed in small cages. Each cage contained one tree seedling with either no insect (1 cage), 10 weevils (1 cage), 10 psyllids (1 cage), or 5 of each type of insect (1 cage); 4 cages in total.
This study was a(n):
A. On site field experiment (not a transplant)
B. Microcosm experiment
C. Transplant field experiment
D. Natural experiment
E. Correlational study
This study was a(n):
A. On site field experiment (not a transplant)
B. Microcosm experiment
C. Transplant field experiment
D. Natural experiment
E. Correlational study
B
21
New cards
In a study to test the effects of biological control by weevil or psyllid insects on the invasive tree Melaleuca quinquenervia in South Florida, seedlings of the tree were placed in small cages. Each cage contained one tree seedling with either no insect (1 cage), 10 weevils (1 cage), 10 psyllids (1 cage), or 5 of each type of insect (1 cage); 4 cages in total.
In this study, what is missing from the design, as described?
A. Question
B. Treatments
C. Control(s)
D. Replicates
E. Nothing—it is a fully valid design
In this study, what is missing from the design, as described?
A. Question
B. Treatments
C. Control(s)
D. Replicates
E. Nothing—it is a fully valid design
D
22
New cards
A property of water important to life is that it
A. Does not dissolve minerals in the soil
B. Is denser in the liquid state than in the solid state
C. Is not able to support buoyant organisms
D. Is liquid at only a narrow range of temperatures
E. Is non-polar on the molecular level
A. Does not dissolve minerals in the soil
B. Is denser in the liquid state than in the solid state
C. Is not able to support buoyant organisms
D. Is liquid at only a narrow range of temperatures
E. Is non-polar on the molecular level
B
23
New cards
A pH of 8.0 is _______ more _______ than a pH of 6.0.
A. 2 times; acidic
B. 2 times; basic
C. 10 times; neutral
D. 100 times; acidic
E. 100 times; basic
A. 2 times; acidic
B. 2 times; basic
C. 10 times; neutral
D. 100 times; acidic
E. 100 times; basic
E
24
New cards
Soil structure comprises
A. Mineral particles
B. Air
C. Water
D. Organic matter such as glomalin
E. All of the above
A. Mineral particles
B. Air
C. Water
D. Organic matter such as glomalin
E. All of the above
E
25
New cards
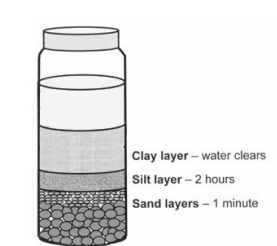
You use the jar method to test the soil at a field site and obtain the result shown on the right. This soil is approximately
A. 60% sand, 20% silt, 20% clay
B. 50% sand, 10% silt, 40% clay
C. 33% sand, 33% silt, 33% clay
D. 30% sand, 10% silt, 60% clay
E. Can’t determine from this result
A. 60% sand, 20% silt, 20% clay
B. 50% sand, 10% silt, 40% clay
C. 33% sand, 33% silt, 33% clay
D. 30% sand, 10% silt, 60% clay
E. Can’t determine from this result
B
26
New cards
A water molecule has just left a soil particle and entered a root cell to begin the process of transpiration. The water entered the root cell because
A. The cell pumped it inside by active transport
B. Its surface tension caused it to adhere to the cell
C. Its cohesion with other water molecules pulled it inside
D. The \[solutes\] outside the cell is greater than the \[solutes\] inside
E. The \[solutes\] inside the cell is greater than the \[solutes\] outside
A. The cell pumped it inside by active transport
B. Its surface tension caused it to adhere to the cell
C. Its cohesion with other water molecules pulled it inside
D. The \[solutes\] outside the cell is greater than the \[solutes\] inside
E. The \[solutes\] inside the cell is greater than the \[solutes\] outside
E
27
New cards
A mangrove acts partly as an osmoconformer when it
A. Grows roots that emerge from the water to obtain oxygen
B. Maintains function despite an increased \[salt\] in its roots
C. Excludes salt from entering the roots
D. Actively transports salt out of the roots
E. Excretes salt from the leaves
A. Grows roots that emerge from the water to obtain oxygen
B. Maintains function despite an increased \[salt\] in its roots
C. Excludes salt from entering the roots
D. Actively transports salt out of the roots
E. Excretes salt from the leaves
B
28
New cards
Overall, plants expend energy to ______ N, and animals expend energy to ______ N.
A. Obtain; obtain
B. Obtain; remove excess
C. Remove excess; obtain
D. Remove excess; remove excess
A. Obtain; obtain
B. Obtain; remove excess
C. Remove excess; obtain
D. Remove excess; remove excess
B
29
New cards
On the right are the absorption spectra of the membranes of purple and green photosynthetic bacteria. According to DasSarma (2006), purple and green bacteria evolved together. This hypothesis is supported by the peak absorption of ______ light by the green bacteria and of ______ light by the purple bacteria.
A. Blue and red; green
B. Blue and red; blue and red
C. Green; blue and red
D. Green; green
E. Green; purple
A. Blue and red; green
B. Blue and red; blue and red
C. Green; blue and red
D. Green; green
E. Green; purple
A
30
New cards
In which lowland environment(s) are C4 grasses expected to be more common than C3 grasses?
A. Cool and dry
B. Cool and wet
C. Hot and dry
D. Hot and wet
E. All of the above
A. Cool and dry
B. Cool and wet
C. Hot and dry
D. Hot and wet
E. All of the above
C
31
New cards
A plant could be kept cool by all of the following mechanisms except
A. Closing its stomata to prevent water loss
B. Folding leaves to shade from the sun
C. Having most of its biomass underground
D. Having silvery hairs on the leaves
E. Having small leaves
A. Closing its stomata to prevent water loss
B. Folding leaves to shade from the sun
C. Having most of its biomass underground
D. Having silvery hairs on the leaves
E. Having small leaves
A
32
New cards
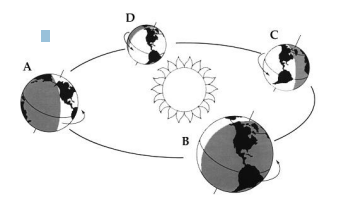
On the diagram on the right, at which point in the Earth’s orbit (A-D) is it winter in the Northern Hemisphere?
C
33
New cards
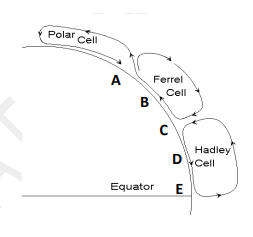
On the diagram of the Earth’s Northern Hemisphere on the right, where (A-E) is dry air sinking and warming, causing low rainfall?
D
34
New cards
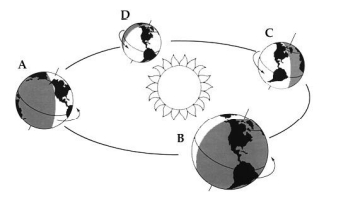
In the Northern Hemisphere, the south-facing slope of a hill will be ______ compared to the north-facing slope. Consider only sun exposure.
A. Shadier and moister
B. Shadier and drier
C. Sunnier and moister
D. Sunnier and dryer
A. Shadier and moister
B. Shadier and drier
C. Sunnier and moister
D. Sunnier and dryer
C
35
New cards
South Florida pine rocklands are generally ______ than hardwood hammocks, and are maintained by ______.
A. Drier; salinity
B. Drier; fire
C. Drier; deep soil
D. Wetter; salinity
E. Wetter; fire
A. Drier; salinity
B. Drier; fire
C. Drier; deep soil
D. Wetter; salinity
E. Wetter; fire
B
36
New cards
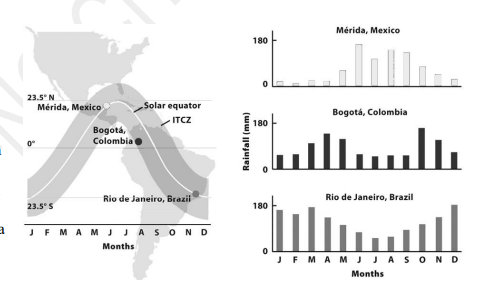
As shown on the right,
A. Bogotá, Mérida, and Rio are at the same latitude
B. Rio has the most pronounced dry season
C. The sun is in the southern sky in June in Rio
D. The sun is in the northern sky in June in Rio
E. It rains the least in Mérida in the months when the sun is overhead at noon
A. Bogotá, Mérida, and Rio are at the same latitude
B. Rio has the most pronounced dry season
C. The sun is in the southern sky in June in Rio
D. The sun is in the northern sky in June in Rio
E. It rains the least in Mérida in the months when the sun is overhead at noon
D
37
New cards
Shrubs and grasses gradually replace trees in the transition from
A. Grassland to savanna to forest
B. Forest to savanna to grassland
C. Evergreen to deciduous forests
D. Tropical to subtropical to temperate
E. Temperate to subtropical to tropical
A. Grassland to savanna to forest
B. Forest to savanna to grassland
C. Evergreen to deciduous forests
D. Tropical to subtropical to temperate
E. Temperate to subtropical to tropical
B
38
New cards
In the tropical rainforest, which layer is formed by plants specialized to climb the tall trees?
A. Emergent D. Liana B. Canopy E. Epiphyte C. Understory
A. Emergent D. Liana B. Canopy E. Epiphyte C. Understory
D
39
New cards
About how many months out of the year is there sufficient precipitation for plant growth in Hong Kong? Do not consider the length of the growing season.
A. 0
B. 3
C. 9
D. 12
E. Need more data to estimate
A. 0
B. 3
C. 9
D. 12
E. Need more data to estimate
C
40
New cards
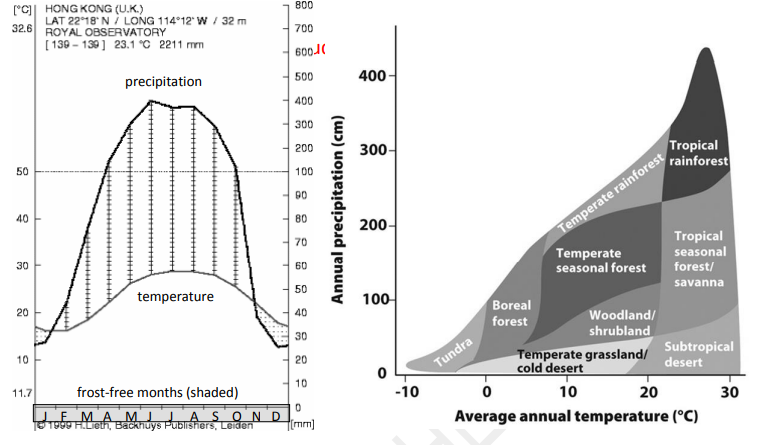
Please use the Walter diagram for Hong Kong and the Whitaker biome diagram above to answer these questions. On the Walter diagram, temperature is shown by the gray curve and precipitation by the black curve. Frost-free months are shown by the shaded box on the x-axis. The x-axis represents a year and is divided into 12 months, starting with January. Hong Kong has 23.1°C average annual temperature and 2211 mm average annual precipitation.
The warmest month in Hong Kong has an average temperature of about _____.
A. 17°C
B. 23°C
C. 28°C
D. 57°C
E. 65°C
The warmest month in Hong Kong has an average temperature of about _____.
A. 17°C
B. 23°C
C. 28°C
D. 57°C
E. 65°C
C
41
New cards
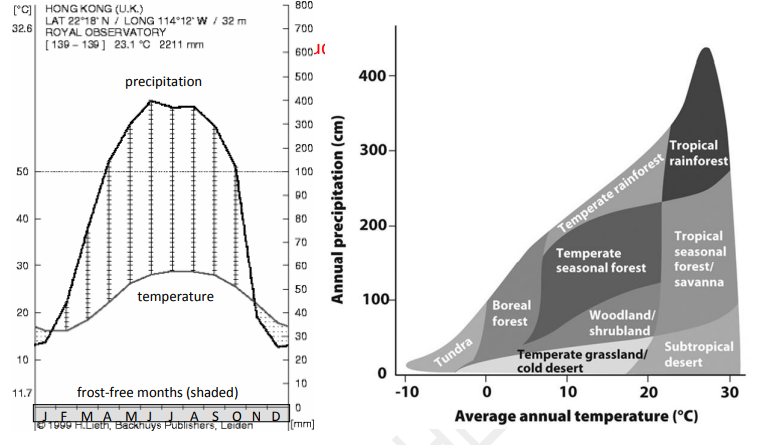
Please use the Walter diagram for Hong Kong and the Whitaker biome diagram above to answer these questions. On the Walter diagram, temperature is shown by the gray curve and precipitation by the black curve. Frost-free months are shown by the shaded box on the x-axis. The x-axis represents a year and is divided into 12 months, starting with January. Hong Kong has 23.1°C average annual temperature and 2211 mm average annual precipitation.
According to the relevant data and the Whitaker diagram only, which biome is Hong Kong in?
A. Temperate grassland
B. Woodland/ shrubland
C. Temperate seasonal forest
D. Tropical seasonal forest/ savanna
E. Tropical rainforest
According to the relevant data and the Whitaker diagram only, which biome is Hong Kong in?
A. Temperate grassland
B. Woodland/ shrubland
C. Temperate seasonal forest
D. Tropical seasonal forest/ savanna
E. Tropical rainforest
D
42
New cards
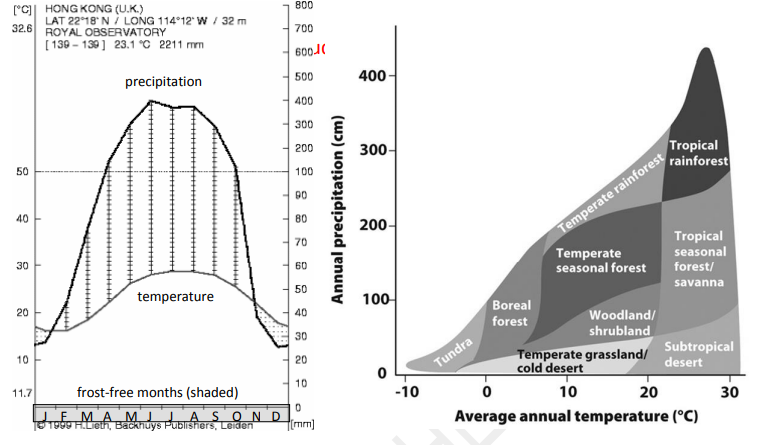
Please use the Walter diagram for Hong Kong and the Whitaker biome diagram above to answer these questions. On the Walter diagram, temperature is shown by the gray curve and precipitation by the black curve. Frost-free months are shown by the shaded box on the x-axis. The x-axis represents a year and is divided into 12 months, starting with January. Hong Kong has 23.1°C average annual temperature and 2211 mm average annual precipitation.
European magpies fledge the maximum number of offspring if they lay 7 eggs. If they lay fewer than 7 eggs, they get fewer offspring. If they lay more than 7 eggs, the parents cannot feed all of the chicks well, so they are undernourished and have lower survival. Egg number is thus under which type of selection?
A. Directional selection
B. Stabilizing selection
C. Disruptive selection
D. Selection for phenotypic plasticity
E. Genetic drift
European magpies fledge the maximum number of offspring if they lay 7 eggs. If they lay fewer than 7 eggs, they get fewer offspring. If they lay more than 7 eggs, the parents cannot feed all of the chicks well, so they are undernourished and have lower survival. Egg number is thus under which type of selection?
A. Directional selection
B. Stabilizing selection
C. Disruptive selection
D. Selection for phenotypic plasticity
E. Genetic drift
B
43
New cards
If their food supply is dwindling when desert locusts mature, they change color to become conspicuous (black and yellow), group together, and forage in a swarm. This is an example of which kind(s) of phenotypic plasticity?
A. Morphological
B. Behavioral
C. Physiological
D. (A) and (B)
E. (B) and (C)
A. Morphological
B. Behavioral
C. Physiological
D. (A) and (B)
E. (B) and (C)
D
44
New cards
On a temperate forest tree such as a maple or oak, a sun leaf has ______ surface area than/as a shade leaf, and is ______ than/as a shade leaf.
A. More; thicker
B. More; thinner
C. Less; thicker
D. Less; thinner
E. The same; the same thickness
A. More; thicker
B. More; thinner
C. Less; thicker
D. Less; thinner
E. The same; the same thickness
C
45
New cards
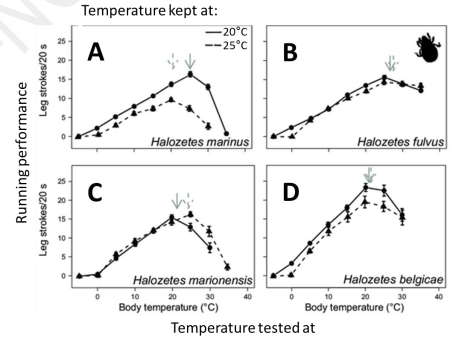
Here are results (on the right) modified from Deere & Chown (2006) showing the running performance of 4 species of mites kept at cool (solid line) and warm (dotted line) temperatures and then tested at temperatures from 0-40°C. Which species of mite (A-D) acclimated best to the two temperatures they were kept at?
C
46
New cards
Which has the longest digestive system, a leaf-eating herbivore (vegetarian), omnivore, or carnivore mammal?
A. The herbivore
B. The omnivore
C. The carnivore
D. No difference would be expected
A. The herbivore
B. The omnivore
C. The carnivore
D. No difference would be expected
A
47
New cards
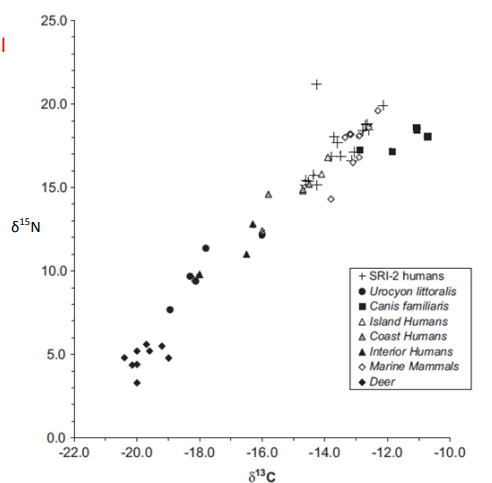
Please use the figure on the right, showing δ 15N (‰; y-axis) vs. δ 13C (‰; x-axis) for Late Holocene humans and associated fauna in Southern California.
Which humans most likely domesticated dogs (Canis familiaris) and shared their food (which included fish) with the dogs?
A. SRI-2
B. Island
C. Coast
D. Interior
E. Can’t tell
Which humans most likely domesticated dogs (Canis familiaris) and shared their food (which included fish) with the dogs?
A. SRI-2
B. Island
C. Coast
D. Interior
E. Can’t tell
A
48
New cards
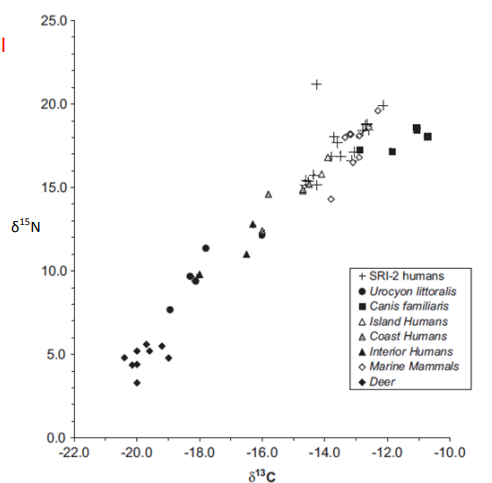
Please use the figure on the right, showing δ 15N (‰; y-axis) vs. δ 13C (‰; x-axis) for Late Holocene humans and associated fauna in Southern California.
Use relative δ 15N values to infer trophic level. Deer are herbivores, foxes (Urocyon) are omnivores, and dogs (Canis) are carnivores. Interior Humans thus were probably
A. Vegetarian
B. Omnivorous
C. Carnivorous
D. Can’t tell
Use relative δ 15N values to infer trophic level. Deer are herbivores, foxes (Urocyon) are omnivores, and dogs (Canis) are carnivores. Interior Humans thus were probably
A. Vegetarian
B. Omnivorous
C. Carnivorous
D. Can’t tell
B
49
New cards
All of the following are life history trade-offs except:
A. Allocation of energy to growth vs. reproduction
B. Few large offspring vs. many small offspring
C. Mating with a superior male vs. mating with an inferior male
D. Reproducing later at a larger size vs. reproducing earlier at a smaller size
E. Several small bouts of reproduction vs. one large bout of reproduction
A. Allocation of energy to growth vs. reproduction
B. Few large offspring vs. many small offspring
C. Mating with a superior male vs. mating with an inferior male
D. Reproducing later at a larger size vs. reproducing earlier at a smaller size
E. Several small bouts of reproduction vs. one large bout of reproduction
C
50
New cards
The sycomore fig (Ficus sycomorus) is a tree of tropical southern Africa. An aspect of the sycomore fig’s life history that is the most like r-selection is that it
A. Lives hundreds of years and becomes very large
B. Lives in rich soils deposited over many years on riverbanks
C. Produces hundreds of fruits at a time, each containing about 100 seeds.
D. Produces only a few offspring that survive to maturity
E. Requires a specialized pollinator to produce seeds
A. Lives hundreds of years and becomes very large
B. Lives in rich soils deposited over many years on riverbanks
C. Produces hundreds of fruits at a time, each containing about 100 seeds.
D. Produces only a few offspring that survive to maturity
E. Requires a specialized pollinator to produce seeds
C
51
New cards
Iteroparity might most likely be favored over semelparity when
A. Adults eventually become crowded and compete strongly
B. Adults spend only a small fraction of their energy budget on reproduction
C. Good conditions for offspring survival occur only rarely
D. In a plant, a gigantic flower display attracts more pollinators than a modest one
E. Production of huge numbers of offspring at one time is needed to survive predators
A. Adults eventually become crowded and compete strongly
B. Adults spend only a small fraction of their energy budget on reproduction
C. Good conditions for offspring survival occur only rarely
D. In a plant, a gigantic flower display attracts more pollinators than a modest one
E. Production of huge numbers of offspring at one time is needed to survive predators
B
52
New cards
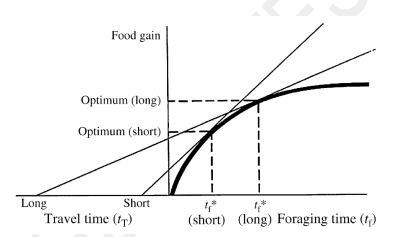
According to optimal foraging (Charnov’s marginal value theorem as shown on the right), an alligator would be most likely to leave its present gator hole if
A. The next hole is large
B. The next hole is nearby
C. Food quality is decreasing in the present hole
D. (A) and (B)
E. (B) and (C)
A. The next hole is large
B. The next hole is nearby
C. Food quality is decreasing in the present hole
D. (A) and (B)
E. (B) and (C)
E
53
New cards
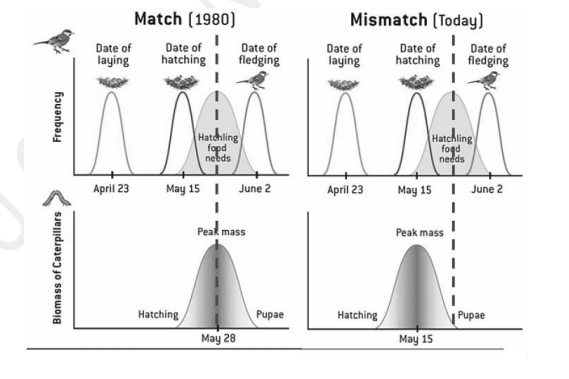
The recent mismatch (as shown below) between the hatching of songbird eggs in the Eastern USA and Europe and the availability of food (caterpillars) for the hatchlings has been caused by
A. birds laying eggs sooner due to climate change
B. birds laying eggs later due to climate change
C. trees leafing out sooner and insect eggs hatching sooner due to climate change
D. trees leafing out later and insect eggs hatching later due to climate change
E. fewer insects on the trees due to agricultural pesticide use
A. birds laying eggs sooner due to climate change
B. birds laying eggs later due to climate change
C. trees leafing out sooner and insect eggs hatching sooner due to climate change
D. trees leafing out later and insect eggs hatching later due to climate change
E. fewer insects on the trees due to agricultural pesticide use
C
54
New cards
According to the websites you were invited to visit, some (but not many) species of plants have purple leaves because
A. The plants lack chlorophyll and are parasites
B. The purple pigment protects leaves from light that is too intense.
C. Herbivores are attracted by the color purple
D. The purple color is a mutation that people liked the look of and selected for
E. The purple pigment protects the leaves from fungal disease
A. The plants lack chlorophyll and are parasites
B. The purple pigment protects leaves from light that is too intense.
C. Herbivores are attracted by the color purple
D. The purple color is a mutation that people liked the look of and selected for
E. The purple pigment protects the leaves from fungal disease
D
55
New cards
According to the NYT article on climate change questions and answers that you were invited to read, climate change _____ threaten our civilization, and _____ solvable by individual choices (e.g. transportation, energy use, diet) alone.
A. Does; is
B. Does; is not
C. Does not; is
D. Does not, is not
E. May; may be
A. Does; is
B. Does; is not
C. Does not; is
D. Does not, is not
E. May; may be
B
56
New cards
According to the article on Nepenthes pitcher plants that you were invited to read
A. Nepenthes don’t need photosynthesis because they consume prey
B. A thirsty hiker cannot safely drink the fluid in a Nepenthes pitcher
C. Stable isotopes are not useful for determining the “diet” of Nepenthes
D. Nepenthes grow in desert soils that are very low in nutrients
E. Nepenthes make both aerial and ground pitchers that capture different prey
A. Nepenthes don’t need photosynthesis because they consume prey
B. A thirsty hiker cannot safely drink the fluid in a Nepenthes pitcher
C. Stable isotopes are not useful for determining the “diet” of Nepenthes
D. Nepenthes grow in desert soils that are very low in nutrients
E. Nepenthes make both aerial and ground pitchers that capture different prey
E
57
New cards
Viscosity
is the thickness of a fluid that causes objects to encounter resistance as they move through it.
58
New cards
Ions
are atoms or molecules with an electric charge.
59
New cards
Saturation
is the upper limit of solubility in water for a given mineral.
60
New cards
Acidity
is the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution.
61
New cards
pH
is a measure of its acidity and is defined as the negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration.
62
New cards
Acid Deposition
the deposition of acids from the atmosphere as rain, snow, or other forms of precipitation. It is a result of emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide, which are converted to sulfuric acid and nitric acid in the atmosphere and transported downwind.
63
New cards
Solute
A solute is a substance that is dissolved in a solution, typically a liquid, such as water.
64
New cards
Semipermeable membrane
is a membrane that allows certain molecules and ions to pass through it, while blocking the passage of other molecules and ions.
65
New cards
Passive transport
is the process by which molecules move through a membrane without the need for energy.
66
New cards
Active transport
is the process by which molecules move against a concentration gradient, from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration, with the help of energy.
67
New cards
Osmosis
is the process by which molecules move across a semi-permeable membrane in order to equalize the concentrations of the solution on either side.
68
New cards
Osmotic potential
is the measure of the ability of a solution to cause water to move across a semi-permeable membrane.
69
New cards
Osmoregulation
is the process by which an organism maintains the concentration of its internal fluids, such as blood and intracellular fluids, within a normal range.
70
New cards
Hyperosmotic
solutions are solutions that have a higher solute concentration than the solution they are being compared with.
71
New cards
Hyposmotic
solutions are solutions that have a lower solute concentration than the solution they are being compared with.
72
New cards
Sample standard deviation
is a measure of the variation of a sample of data from the mean.
73
New cards
Standard error of the mean
is a measure of the variability of the mean of a sample of data from the true mean of the population.
74
New cards
Bicarbonate ion (HCO3 − )
A negatively charged ion composed of one hydrogen atom, one carbon atom, and three oxygen atoms.
75
New cards
Carbonate ion (CO3 2−)
A negatively charged ion composed of one carbon atom and three oxygen atoms.
76
New cards
Boundary layer
A thin layer of air that is in contact with the surface of the Earth and that affects the exchange of energy and momentum between the atmosphere and surface.
77
New cards
Countercurrent circulation
A type of circulation where two fluids with different properties flow in opposite directions to each other.
78
New cards
Concurrent circulation
A type of circulation where two fluids with different properties flow in the same direction. Anaerobic
79
New cards
Q10
is a measure of its rate of change in response to a 10°C increase in temperature.
80
New cards
Thermophilic
organisms are organisms that thrive in high temperatures.
81
New cards
Thermal pollution
is the introduction of heat into a body of water, resulting in an increase in the water temperature that can adversely affect aquatic life.
82
New cards
Glycerol
is a type of alcohol that is used in many different biological processes. It is a key component in the formation of lipids and is also used in the formation of glycoproteins.
83
New cards
Glycoproteins
are proteins that contain carbohydrates (sugars). They are important components of cell membranes and are involved in many cellular processes.
84
New cards
Supercooling
is the process by which a liquid can remain liquid at temperatures below its freezing point.
85
New cards
Optimum
is the point at which a particular environmental factor is most favorable for an organism or process.
86
New cards
Thermal Optimum
is the point at which the temperature is most favorable for an organism or process. Isozymes
87
New cards
Coral Bleaching
is a phenomenon in which corals lose their color due to environmental stress. This can be caused by increased temperatures, pollution, and other factors.
88
New cards
Water Potential
The potential energy generated by the attractive forces between water molecules and the environment, including gravity, pressure, osmotic potential, and matric potential.
89
New cards
Matric Potential
The potential energy generated by the attractive forces between water molecules and soil particles.
90
New cards
Field Capacity
The maximum amount of water that soil can hold against the force of gravity.
91
New cards
Wilting Point
The lowest water potential at which most plants can obtain water from the soil.
92
New cards
Salinization
The process of increasing the salt content of soil and ground water.
93
New cards
Cohesion
The strong attractive forces between molecules of the same type, such as water molecules.
94
New cards
Root Pressure
The pressure generated by osmotic potential in the roots of a plant that draws in water from the soil and forces it into the xylem elements.
95
New cards
Transpiration
The process of water loss from a plant leaf to the atmosphere.
96
New cards
Cohesion–Tension Theory
The mechanism of water movement from roots to leaves due to water cohesion and water tension.
97
New cards
Stomata
Specialized cells found on the surface of a leaf that regulate the exchange of gases between the leaf and the atmosphere.
98
New cards
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a type of energy that is made up of electric and magnetic fields and travels in waves.
99
New cards
Visible light
Visible light is a type of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye.
100
New cards
Photosynthetically active region
The photosynthetically active region is the range of wavelengths of light that can be used for photosynthesis.