CHEMISTRY GCSE paper 1
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
What is a mole?
It is the unit for chemical amounts
What is one mole of a substance equal to in grams?
It's relative formula mass's number in grams (numerically equal)
There is less mass of product than reactant, why?
A product is a gas and escapes from the container
There is less mass of reactant than product, why?
A reactant is a gas (eg air)
Formula for percentage yield?
mass of product actually made/theoretical maximum potential mass
x100
Formula for atom economy
mass of desired product/mass of all reactants (RAM)
x100
Why is a low atom economy bad?
Because it means resources will be used up faster, so it will not be very profitable.
Why is a reaction never 100% efficient?
Not all reactants may make a product
There may be other side reactions
You could lose some product when removing it from the reactant mixture
formula for moles
n=m/Mr
formula for volume of gas
Vgas=molx24
concentration
concentration=amount of substance/volume
Exothermic reaction
Energy transferred to surroundings
Temperature rise
Products have less energy than reactants
Eg Hand warmers
Endothermic reaction
Energy absorbed from surroundings
Temperature decrease
Reactants have less energy than products
Eg Sports injury pack
What kind of reaction is breaking bonds?
Endothermic
What kind of reaction is making bonds?
Exothermic
What does voltage produced by a battery depend on?
Type of electrode (bigger the difference in reactivity of the electrodes the bigger the pd)
Type of electrolyte
Advantages of fuel cells
No moving parts so won't break down
Small and light
Hydrogen has most energy per gram
Water is non-polluting
Phosphate
PO4 3-
Nitrate
NO3 1-
Ammonium
NH4 1+
Sulfate
SO4 2-
Sulfite
SO3 2-
Hydroxide
OH-
Hydrogen carbonate
HCO3 1-
Disadvantages of a ball and stick model
There aren't actually lines connecting the atoms
Sizes aren't relative
No gaps between ions
Other diagram with the charges and square thing disadvantages
You can only see one layer.
Properties of ionic bonds
High mp +bp due to many strong bonds
Solid is not a conductor but molten is, also dissolves in water and conducts electricity because ions are free to move about
Simple covalent molecules properties
Strong forces but weak bonds mean low mp + bp
As size of molecule increases mp + bp increases
Do not conduct electricity as no free e-
Giant covalent properties
Very high bp + mp
Don't conduct electricity
What are the diatomic molecules?
Hydrogen Nitrogen Fluorine Oxygen Iodine Chlorine Bromine (have no fear of ice cold beer)
What are the properties of metallic bonding
Very strong
Mostly high bp + mp
Conducts electricity and heat because of delocalised e-
Layers can slide easily so is malleable
Properties of a solid
Strong forces and regular shape
Don't flow
Vibrate
Properties of a liquid
Weaker forces of attraction than solid
Flow but stick together
Constantly moving
Fills a container
Properties of a gas
Very weak forces
Fill a container
Random movement very fast in straight lines
Uses of nanotubes
Delivery of drugs
Synthetic skin
Computers and tech
Catalysts for fuel cells
Stronger lighter materials
New cosmetics/ deodorants
Fabrics that prevent growth of bacteria
METAL+ACID reaction makes?
SALT+HYDROGEN
METAL+WATER reaction makes?
METAL HYDROXIDE+HYDROGEN
Which metals react vigorously with water and their reaction with acids isn't safe?
Potassium, Sodium, Lithium
Which metals react quickly with acids?
Calcium, Magnesium
Which metals react slowly with water?
Zinc, Iron
Which metal does not react with neither dilute acid nor water?
Copper
ACID+BASE reaction gives what?
SALT+WATER
ACID+METAL OXIDE reaction gives what?
SALT+WATER
ACID+METAL HYDROXIDE reaction gives what?
SALT+WATER
ACID+METAL CARBONATE→
SALT+WATER+CARBON DIOXIDE
In a displacement reaction, which species is oxidized, and which is reduced?
The substance that is being made pure is reduced, and the substance which is adding to the ore is being oxidised
What is made at the cathode in aqueous electrolysis?
If metal is more reactive than hydrogen then it isn't formed, if hydrogen is more reactive then metal is formed.
What is made at the anode in aqueous electrolysis?
Oxygen is produced unless halide is present in which case it is produced.
What model did John Dalton come up with?
Billiard ball model
What model did J J Thomson come up with?
Plum pudding model
Describe the alpha scattering experiment
Alpha particles were fired at a gold foil, and it was expected that they would all go though the foil or only be partially deflected, instead some were deflected more than expected, and some bounced completely back. This showed that there was a concentrated positive charge in the center of atoms
What did Niels Bohr do?
Energy levels
What did Chadwick do?
Discover neutrons
What order were elements put in in the early periodic table before Mendeleev?
In order of atomic mass, but it was incomplete the table didn't take properties into account
What order did Mendeleev put the atoms into?
In order of atomic mass, but he did take into account properties and left gaps for undiscovered atoms. He predicted the properties of undiscovered elements.
Properties of Transition metals
Good conductors of heat, electricity
Dense, strong, shiny
More than one positive ion
Often form colored ions
Transition metals make good catalysts
Group 8 elements properties
Noble gases
Full outer shell so very unreactive
BP increases down group
Group 1 elements properties
Alkali metals
1 electron in outer shell
mp+bp decrease down group
More reactive as you go down group because electron is more easily lost the further it is away from the nucleus
Low density, float on water
Group 1 metal+oxygen makes what?
metal oxide
Group 1 metal reacted with water gives what?
Metal hydroxide + hydrogen
Group 1 metal + chlorine makes what?
White chlorine salt
Group 7 elements properties
Halogens
Reactivity decreases as you go down the group, because it is harder to gain en electron the further away the outer shell is
Mp + bp increases down group
More reactive halogen displaces a less reactive one
Group 7 element reacted with a metal makes what?
Ionic salt
Reaction of group 7 elements with non metals makes what?
Simple covalent structure
What reactions are almost always exothermic?
Oxidation, displacement, neutralization, combustion
What does temperature change depend on in a reaction?
No of moles of limiting reagent
The different products and reaction
The mass of the thing that gets hot or cold
What is a mixture?
A mixture consists of two or more elements or compounds not
chemically combined together. The chemical properties of each
substance in the mixture are unchanged.
State the reactivity series
Potassium
Sodium
Lithium
Calcium
Magnesium
Carbon
Zinc
Iron
Hydrogen
Copper
What is oxidation in terms of oxygen?
Oxidation is gain of oxygen
What is reduction in terms of oxygen?
Reduction is loss of oxygen
What is the formula for nitric acid?
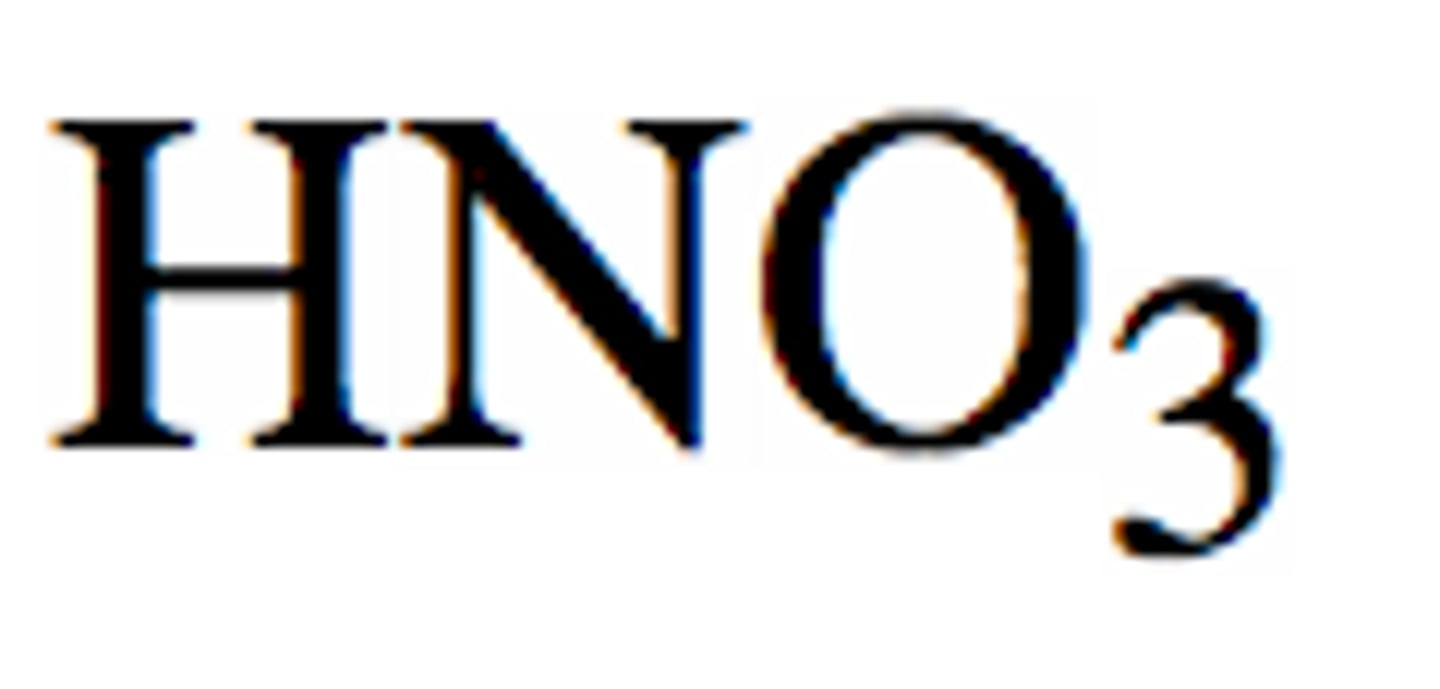
What is electrolysis?
Chemical decomposition produced by passing an electric current through a liquid or solution
How do cells produce electricity?
There are chemicals that react to produce electricity
What is the overall product of hydrogen fuel cells?
Oxidation of hydrogen to produce water
What is diamond?
It is a giant covalent carbon allotrope, each atom makes 4 bonds and this makes diamond really hard. Does not conduct as no free electrons
Tetrahedral lattice
What is graphite?
Three (giant) covalent bonds creating sheets of carbon arranged in hexagons.
Soft and slippery
High melting point
Conducts electricity
Layers can slide over each other as no bonds
What is graphene?
A single layer of graphite which is very strong and light. Can conduct
What are fullerenes?
Molecules of carbon shaped like closed tubes or hollow balls, can cage other molecules to deliver a drug
What colours does litmus paper turn to?
Red in acid
Blue in alkali
What colours does methyl orange turn?
Red in acid
Yellow in alkali
What colours does phenolphalein turn?
Clear in acid
Pink in alkali
What is pH a measure of?
Hydrogen ion concentration, for every decrease of 1 on pH scale, concentration of hydrogen ions increases by 10
What is the half equation at the anode in a hydrogen fuel cell?
4H+(aq) + O2(g) + 4e- → 2H2O(g)
Why can substances conduct heat?
Because the electrons can transfer energy
Disadvantages of rechargeable batteries?
Made from highly toxic chemicals
Batteries need replacing
Lose energy when you recharge them
Disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells?
Hydrogen is a gas and needs lots of space to contain it
It is also explosive, so difficult to store
Why do bulk materials and nano-particles have different properties?
Because nano-particles have a much higher surface area to volume ratio
What is the equation for relative atomic mass of isotopes?
E sign is sum of, so add the different values
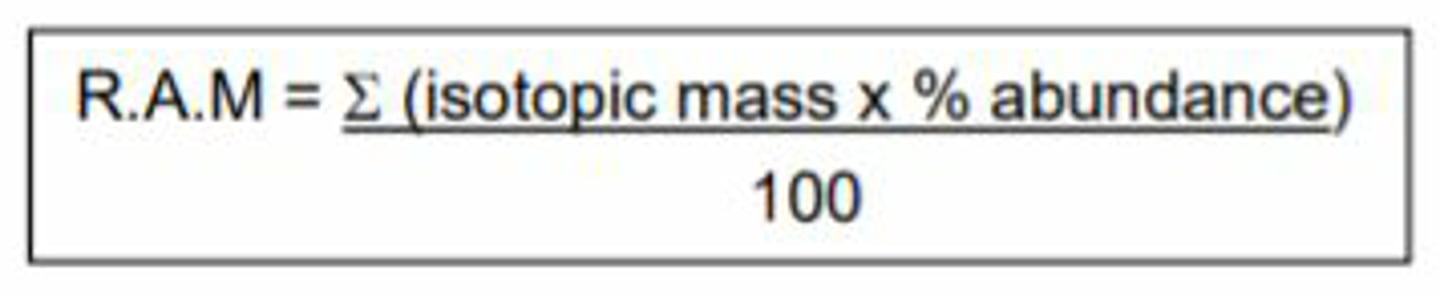
What are examples of physical properties?
mp and bp
conductivity
color
density
If the overall energy change is negative, then is the reaction exothermic or endothermic?
Exothermic
Is a fuel cell exothermic or endothermic?
Exothermic
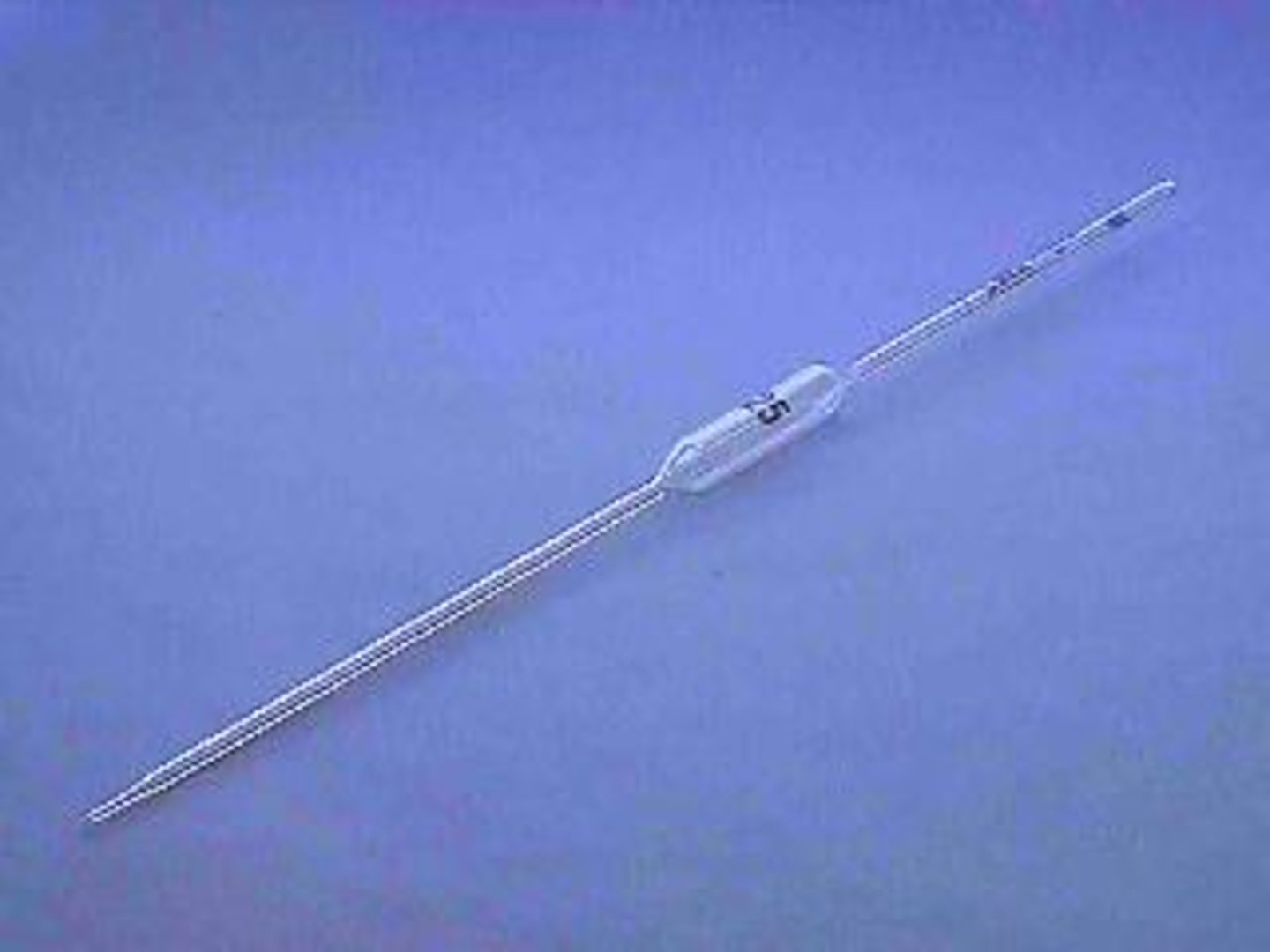
What is the substance of unknown concentration in titration measured with?
Pipette

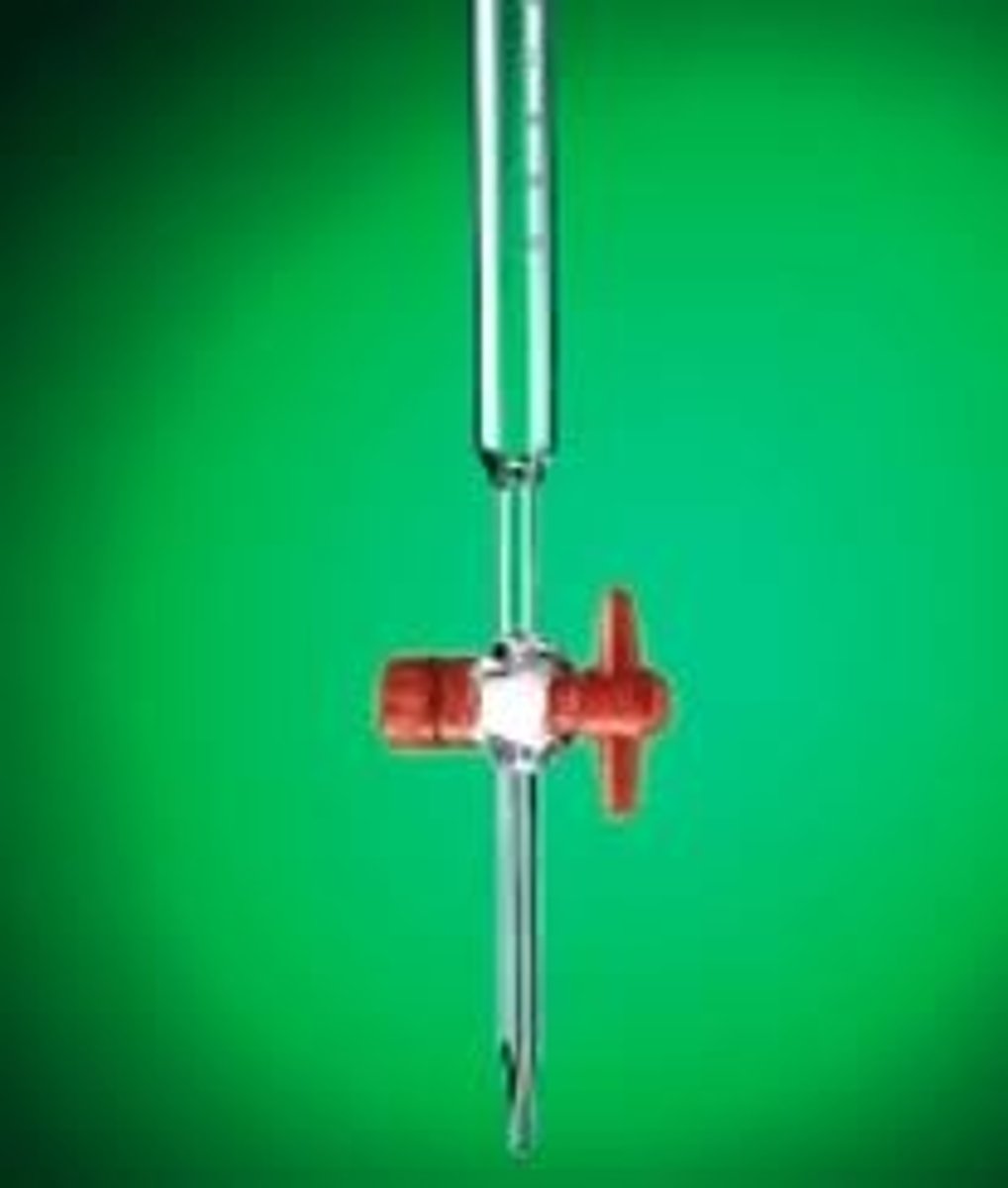
What is the substance of known concentration measured with in titration and dropped into the other substance?
Burette

What is the equation of ethanoic acid? Is it a strong or weak acid?
CH3COOH
Weak acid
What is formed at the cathode in molten electrolysis?
Metal in it's pure form
At anode what is formed in molten electrolysis?
Non-metal in it's pure form
If the overall energy change is positive, is the reaction exothermic or endothermic?
Endothermic
What is the half equation at the cathode in a hydrogen fuel cell?
H2(g) - 2e- → 2H+(aq)
What is the half equation at the anode in aqueous electrolysis if no halide present?
4OH- = 2H2O+O2+4e-
Why does the anode in aqueous electrolysis need to be constantly replaced?
Oxygen forms at the positive electrodes. This oxygen reacts with the carbon of the positive electrodes, forming carbon dioxide, and they gradually burn away. As a result, the positive electrodes have to be replaced frequently. This adds to the cost of the process.