IOA2 Exam 2 - Retinal Anatomy
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
191 Terms
Between _____, cells in the inner layer of the optic cup (neural retina) proliferate and two zones are evident
4-6 weeks
The outer layer of the optic cup forms the
RPE
What separates the inner from outer neuroblastic layers of the primitive retina at 2.5 months?
Transient layer of Chievitz
What types of cells differentiate from the innermost cells of the neural retina?
-Ganglion cells
-Amacrine cells
-Müller cells
What types of cells differentiate from the outermost cells of the neural retina?
-Photoreceptors
-Horizontal cells
-Bipolar cells
As retinal cells continue developing the transient layer of Chievitz probably becomes a part of the _________.
Inner plexiform layer
At what gestational month is retinal lamination essentially complete?
4.5 months
At 4.5 months of gestation, are photoreceptor outer segments present?
No, only inner segments are present
By 5.5 months of gestation, ganglion cells have thinned out to
1-2 layers (except in macular area)
What cells are included in the completely developed inner nuclear layer by 5.5 months gestation?
-Amacrine cells
-Müller cells
-Bipolar cells
-Horizontal cells
When does the newborn retina achieve adult configuration?
Newborn retina
What is a characteristic of the outer plexiform layer in the newborn retina?
It is thinner, but the line of synapses is established
1)______ and ______ inner and outer segments are fully developed, and tips of the outer segments contact the 2)________.
1) Rods; cone
2) pigment epithelium
Normal retinal vascular development begins at the optic disc at about _______.
16 weeks gestation
By what gestational week does angiogenesis extend the retinal vasculature to the periphery?
40 weeks in utero
What occurs in the 40th week in utero?
Angiogenesis extends the retinal vasculature to the periphery
What happens to retinal vascularization in premature babies?
Completes outside the uterus
How can the macula be differentiated early in gestation?
By an increase in ganglion cells in the macula area
What are the outer plexiform layer of Henle formed by in the macula?
The cone inner fibers elongate and adopt an oblique orientation as synapse with the cells of the inner nuclear layer
Which photoreceptors are present in the macula?
Only cones (taller and thinner); no rods are present
Macular development continues for __________ and may be dependent on a __________.
a few months after birth; light stimulus
Innermost layer of the eye
Retina
The retina is a _______ derived from the _______..
neural layer; neural ectoderm
What is the retina's primary function?
To transform light energy into neural signals
The retina extends from the
edge of the optic disc --> ora serrata
Appearance of the retina
Laminar appearance
Name the 10 retinal layers from outermost to innermost
-RPE
-Photoreceptor layer
-Outer limiting membrane
-Outer nuclear layer
-Outer plexiform layer
-Inner nuclear layer
-Inner plexiform layer
-Ganglion cell layer
-Nerve fiber layer
-Internal Limiting membrane
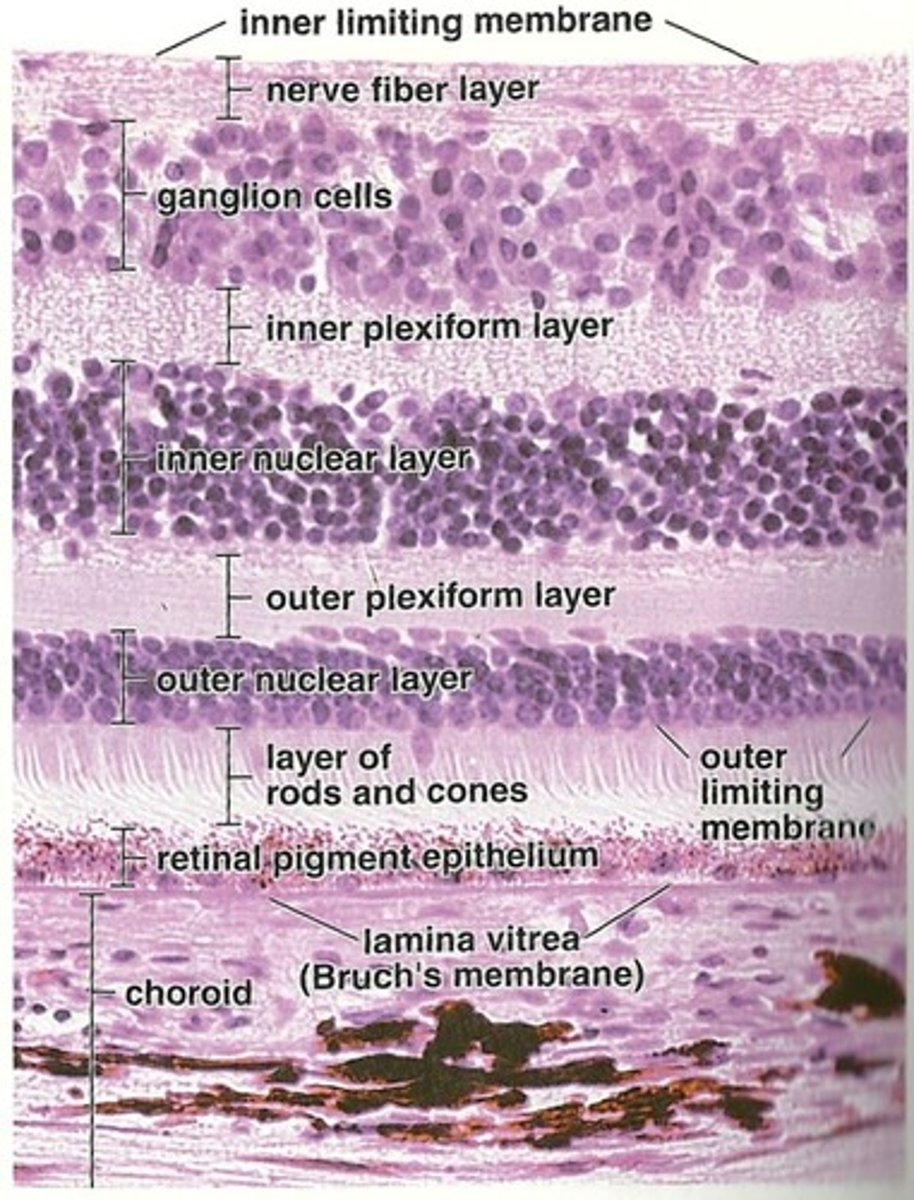
The RPE consists of how many layers?
Single layer of pigmented cells
Where is the apical side of the RPE located?
Faces the retina
What type of membrane is directly adjacent to the basal side of the RPE?
A basal membrane that is shared by Bruch’s membrane
RPE cells contain many organelles, including (6)
-Smooth and rough ER
-Golgi apparatus
-Lysosomes
-Mitochondria
-Phagosomes
-Pigment cells
2 different types of pigment cells contained in the RPE
-Melanosomes
-Lipofuscin (from phagocytosis)
The RPE is embryologically derived from the ________.
outer layer of the optic cup
The RPE contains a basal membrane that fuse to the _________.
Bruch's membrane
Does the RPE have a loose or tight connection with the choroid?
Tight connection
Does the RPE have a loose or tight connection with the neural retina?
Loosely adherent - creates a space between the RPE and neural retina - subretinal space (area of detachments)
2 main functions of the RPE
-Phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer segments
-Transport of ions, water, and metabolites btwn choroid and retina
The photoreceptor layer contains how many rods?
120 million rods
The photoreceptor layer contains how many cones?
6-8 million
The photoreceptor layer contains which type of special sensory cells?
Rods and cones
The photoreceptor layer contains ______, which absorb photons of light
photopigments
Divisions of the Photoreceptor layer (3)
-Outer and inner segment (at photoreceptor layer)
-Outer fiber and Cell body (at the outer nuclear layer)
-Inner fiber and Synaptic terminal (at outer plexiform layer)
The synaptic terminals for rods:
Spherule
The synaptic terminals for cones:
Pedicle
What is the role of the discs in the outer segment of the photoreceptor layer?
surround the photopigment molecules
The outer segment of both rods and cones contains:
hundreds (500-1000) of lipid bilayered discs that are surrounded by a cell membrane
What is the main function of the inner segment of a photoreceptor?
Contains the cell organelles AND AREA OF METABOLIC ACTIVITY AND PHOTOPIGMENT SYNTHESIS
What happens to the new photopigments synthesized by the inner segment?
They are transported to the outer segment via cilium, where they are incorporated into discs
Name the two regions of the inner segment
Myoid
Elipsoid
Inner layer of the inner segment where protein synthesis occurs
Myoid
What cellular organelles are located in the Myoid region?
RER and Golgi
Outer layer of the inner segment paced with mitochondria for ATP production
Elipsoid
Photoreceptors contain hundreds of _______.
discs
Each disc in the photoreceptors contains thousands of ________.
photopigment molecules (Rhodopsin and lodupsin)
The photoreceptor layer is resposible for
light absorption
What type of vision are rods responsible for?
scoptopic vision (detect objects at low illumination)
Where is the density of rods greatest in the retina?
About 5 mm concentrically from the fovea in an area known as the rod ring
What photopigment do rod discs contain?
Rhodopsin
At what wavelength does rhodopsin maximally absorb photons?
507nm
Can rods detect color?
NO
What type of vision are cones responsible for?
Photopic (color) vision and high visual acuity
What are the three different pigment molecules found in cones, and what wavelengths do they absorb maximally?
Blue (420nm)
Green (531nm)
Red (588nm)
Is the outer (external) limiting membrane a true membrane?
no
These are not present in the outer (external) limiting membrane
cells
The outer (external) limiting membrane is a band of desmosomal attachments known as
zonula adherents
The outer (external) limiting membrane is a band of desmosomal attachments (zonula adherents) between ________ and _______.
Muller cells and inner segments of photoreceptors
Function of outer (external) limiting membrane
Provides structure and acts as a barrier for large metabolites
The outer nuclear layer contains:
cell bodies of rods and cones
What cell processes synapse in the outer plexiform layer?
Rod spherules and cone pedicles synapse with the dendrites of bipolar and horizontal cells
At the macular area, the outer plexiform layer is known as:
Henle's fiber layer
The Outer Plexiform Layer is the only layer that receives blood supply from the ________ and _________.
choroid and retina (CRA)
Where does the first synapse in the visual pathway occur?
Outer plexiform layer, between first and second order neurons
What forms the wide external band of the OPL?
Inner fibers of rods and cones
What forms the narrower inner band of the OPL?
Synapses between photoreceptor cells and cells from the inner nuclear layer (horizontal and bipolar cells)
Rods spherules and cone pedicles synapse with
bipolar cell dendrites
Each rod spherule can synapse with how many bipolar cells?
1-4 bipolar cells
Rods use how many types of bipolar cells?
one type
Cone pedicles are smaller or larger than the rod spherule?
larger
Horizontal cell processes synapse with bipolar dendrites and contact other horizontal processes via
gap junctions
The Inner Nuclear Layer contains what cell bodies (5)?
-Horizontal cells
-Bipolar cells
-Amacrine cells
-Müller cells
-Interplexiform cells
What type of cells do the Horizontal cells synapse with?
-Photoreceptors
-Bipolar cells
Horizontal cells
Horizontal cells synapse with photoreceptors in a _______.
triad form
What is the function of the horizontal cells?
Modify the info that reaches the bipolar cells by providing lateral inhibition
Inner Nuclear Layer plays a role in the process of ________.
visual integration
The location of synapse in the inner plexiform layer is between the
second and third order neurons in visual pathway
Which cells form connections in the Inner Plexiform Layer?
-Bipolar cells
-Amacrine cells
-Ganglion cells
Ganglion dendrites synapse with ________.
bipolar axons
Synapses between ganglion dendrites and bipolar axons are modified by
amacrine cells
What occurs in the inner plexiform layer?
Processing of motion detection and changes in brightness, as recogntion of contrast and hue
Bipolar cells ________ stimulation of ganglion cells
increase
Amacrine cells _______ stimulation of ganglion cells
decrease
Layer where ganglion cell bodies are located
Ganglion Cell Layer
How many layers thick is the ganglion cell layer?
1-2 layers thick
In the macular area, the ganglion cell layer increases to _________ layers thick.
4-7 layers thick
Every ganglion cell has a _______.
single axon
Each axon terminates in the ______.
LGN
How many types of ganglion cells exist?
18 different types
2 categories of ganglion cells
P-cells (parvocellular)
M-cells (magnocellular)
Are P-cells small or large diameter axons?
small diameter axons
What are P-cells sensitive to?
color and fine detail