STA220- Module 6 Discrete Random Variables
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
What is a random variable?
Variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random phenomenon
outcome varies from observation. to observation according to random variable that can be summarized by probabilities
What is a discrete random variable?
A random variable is discrete if the possible outcomes are a set of separate values
“the number of…” with possible values 0, 1, 2
ordinal scale of measurement: 1 = strongly disagree.. 3 = neutral… 5 = strongly agree
continuous if the possible outcomes are infinite continuum, such as all the real numbers between 0 and 1
What is a probability distribution of a random variable?
A probability distribution lists the possible outcomes and their probabilities
has parameters describing the centre (ex: mean) and the variability (ex: standard deviation)
assigns a probability to each possible value of the variable (between 0 and 1)

What are parameter values?
The values these measures would assume in the long run, if the randomized experiment of the random sample repeatedly took observations on variable y having the probability distribution
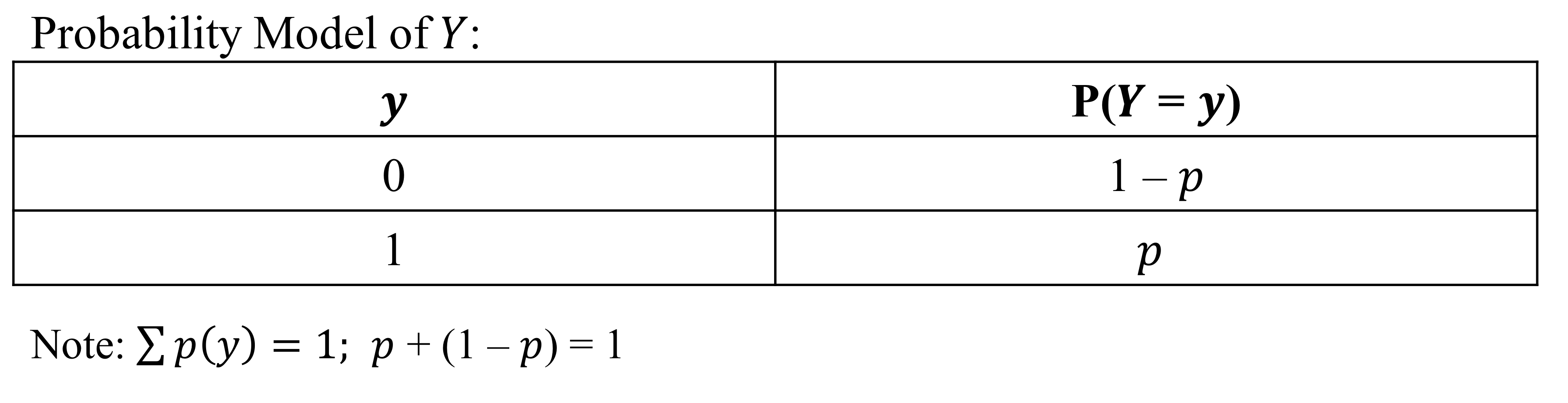
What is the Bernoulli random variable?
Simple random variable with only two outcomes
success or failure, heads or tails
y = 1, y = 0
What is the binomial model?
Model that simply counts the number of successes in a series of n independent Bernoulli trials
makes it easy to find the mean and standar deviation of a Binomial random variable X
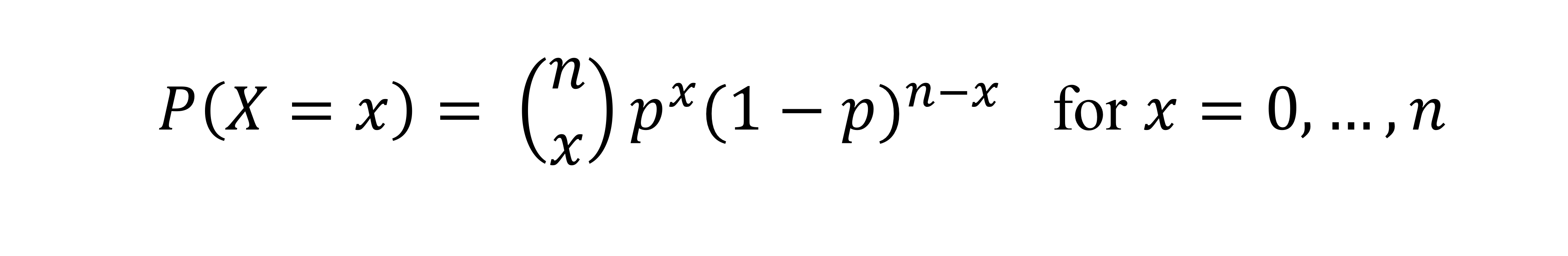
What are the properties of the Binomial model?
There are a fixed number n observations
The n observations are independent
Each observation falls into one of just two categories (successes and failure)
The probability of a success (call it p) is the same for each observation
How does the shape of a binomial distribution depend on p?
When P < 0.5 = skewed right
P > 0.5 = skewed left
P = 0.5 = symmetric