L22: acids, bases and buffers
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
biophysics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
what is the water equilibrium equation: Kw? why is this different from the Keq of water?
Kw = [H+][OH-]
[H2O] is constant in almost all aqueous solutions so it can be emitted from the equation
![<p>Kw = [H+][OH-]</p><p>[H2O] is constant in almost all aqueous solutions so it can be emitted from the equation</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9a1e6fe0-429c-4085-abb0-b8faa802ddc3.jpg)
what can Kw of pure water be simplified to? why?
Kw = [H+]2
because in pure water [H+] = [OH-]
what is the definition of an acid?
proton doner - produces H+ ions by dissociation
what is the definition of a base?
substance that releases OH- ions
what is the equation for PH?
PH = -log10 [H+]
what are the 2 methods of preparing a base?
mixing a (large volume of) WEAK acid with its conjugate base
mixing a (large volume of) WEAK base with its conjugate acid
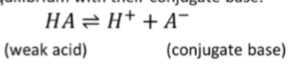
what is the acid dissociation constant? equation?
the equilibrium constant for a weak acid
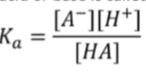
at what PH do buffers stabilise at?
their pKa
what does pKa tell us?
how strong an acid is

pKa equation?
pKa = -log10 Ka
what equation do we use to calculate the PH of a buffer?
henderson-hasselbalch equation:
PH = pKa + log [A-]/[HA]
![<p>henderson-hasselbalch equation:</p><p>PH = pKa + log [A-]/[HA]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d68e7767-5886-420a-b641-ce03a9544a21.jpg)
what happens if we add a strong acid near a buffers pKa?
adding [H+]
soaked up by the conjugate base A- to form more weak acid
what will happen if we add strong base near the pKa?
adding [OH-]
soaked up by the weak acid to form more conjugate base and water
what does a PH of a molecule bigger than, smaller than and the same as its pKa tell us about the state of the molecule?
PH<pKa = mainly weak acid form
PH>pKa = mainly conjugate base form
PH = pKa: half half
amino acids exist as zwitterions at neutral PH, at what PH are they anions/cations?
anion (-): Ph above pka (high PH) - donate H+
cation (+): PH below pKa (low PH) - accept H+