Bio ch. 10 and 11
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What is the transforming factor? Who discovered it?
Proved that DNA was the hereditary material and it was discovered by Frederick Griffith
What are DNA and RNA made of?
Nucleic acids made by long chains of chemical units called nucleotides
What are the four nitrogen-containing bases in a nucleotide
adenine, cytosine, thymine, and guanine
What is a nucleotide made up of?
a nitrogenous base, a 5 carbon sugar, and a phosphate group
How is RNA different than DNA?
it uses the sugar ribose, it has uracil instead of thymine
What is a purine?
Double rings, remember Pure As Gold (Adenine and Guanine)
What is a pyrimidine?
Single ring, C, T, and U
What is the 3D structure of DNA? Who worked it out?
Two polynucleotide strands wrapped around each other in a double helix. Watson and Crick found this out.
Where is the sugar-phosphate found on dna?
On the outside, this was found out from an xray crystallography image taken by Rosalind Franklin. This led watson to find the shape as helical.
What is Chargaff’s rule?
A always pairs with T and C always pairs with G
Why is DNA replication said to be semiconservative?
Because each new DNA helix has one old strand with one new strand
What does helicase do?
Unwinds DNA
What does DNA Polymerase do?
Brings free floating bases to connect and make a new strand of dna
What does ligase do?
It glues all of the Okazaki fragments together on the lagging strand when replicating dna
What is a translation regarding dna synthesis?
RNA is used to make proteins
What is transcription?
The synthesis of mRNA created from dna
What is a gene?
A region of DNA that can be expressed to produce a functional product
What did archibald Garrod suggest about genes and proteins?
Genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes
Who came up with the one gene one polypeptide hypothesis?
George Beadle and Edward Tatum (1940’s)
What is a codon?
A triplet code where 3 bases code for an amino acid
How does translation occur?
mRNA is read 3 bases at a time and tRNA has an anticodon that is complementary to the codon which brings in the appropriate amino acid coded for the mRNA information
What is the start codon?
AUG, methionine (Remember: school starts in AUGust)
What are the three stop codons?
UAA, UAG, and UGA
What bond holds the bases together?
Hydrogen Bonds
What links RNA nucleotides?
RNA polymerase
How does mRNA exit the nucleus?
Through nuclear pores
What happens during RNA splicing?
RNA transcripts splice out introns introns and the exons are spliced together.
What happens to the mRNA before it leaves the nucleus?
A cap is added to one end and a tail is added to the other end. These protect the mRNA from cellular enzymes and assist in attaching the mRNA to the ribosomes.
What are the two subunits of ribosomes?
Big and small
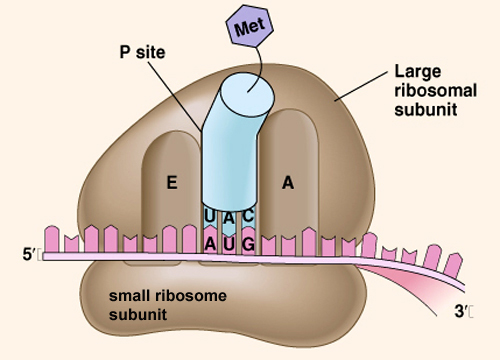
In what order does the movement of a codon in a ribosome take place?
A site, to P site, to E site. (Remember: APE)
What is peptide bond formation?
The polypeptide separates from the tRNA where it was bound (P site) and attaches by a peptide bond to the amino acid of the tRNA (A site)
What is the flow of genetic information in a cell?
DNA to RNA to protein
What is a mutation?
Changes in the genetic information of a cell or virus, caused by errors in DNA replication or recombination, or by physical or chemical agents called mutagens
What is substitution?
The replacement of one nucleotide with another
What happens to a codon because of an insertion or deletion?
It shifts the frame that mRNA is being read by, it is disastrous and results in the codons further down being read in the wrong order.
What is mutegenesis?
The production of mutations.
What is a virus?
An infectious particle consisting of a bit of nucleic acid wrapped in a protein coat called a capsid
What happens when phage DNA enters a lytic cycle?
It is replicated, transcribed, and translated and the new viral DNA and protein molecules are assembled into new phages which burst from the host cell.
What happens in the lysogenic cycle?
Phage DNA inserts into the host chromosome and is passed on to generations of daughter cells.
What are the possible sources of emerging viruses?
Mutations from an existing virus, a virus moving from one species to another, and the spread of a virus from an isolated population
What is a retrovirus? Give an example.
A retrovirus uses RNA as a template to make DNA. They carry an enzyme called reverse transcriptase (RNA to DNA). HIV is a retrovirus
What is a prion?
Infectious proteins (they are misshapen) that can cause brain diseases in animals
What are the three ways bacteria move genes from cell to cell?
Transformation, transduction, and conjugation
What is a plasmid?
A small, circular DNA molecule separate from the bacterial chromosome
What is gene expression?
How genetic information flows from genes to proteins (genotype to phenotype)
What is gene regulation?
the turning on and off of genes can help organisms respond to environmental changes
What is differentiation? Give an example
cells become specialized in structure and function, as a zygote develops into a multicellular organism, it undergoes differentiation
What is a histone?
Found in a chromosome, small proteins that have DNA wrapped around it.
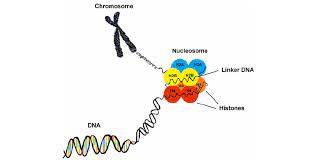
What happens as a result of DNA packing?
It tends to block gene expression by preventing access of transcription proteins to DNA
What is alternative RNA splicing?
Happens after transcription, it generates two or more types of mRNA from the same transcript.
What is a homeotic gene?
A control gene that regulates groups of other genes that determine which body part will be made where
What is nuclear transplantation?
DNA from a donor cell is inserted into a nucleus-free host egg which results in a clone of the DNA donor
What is reproductive cloning?
A blastocyst is implanted into the uterus of a surrogate mother, it results in the birth of a new living individual
What is therapeutic cloning?
Produces stem cells which can have great medical potential
What causes cancer?
Mutations in genes that control cell division
How can a mutation affect a proto-oncogene?
It can turn it into an ocogene which causes cells to divide excessively
What can reduce the risk of cancer?
Lifestyle choices