GCSE OCR P.E- Applied Anatomy and Physiology
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Everything that you need to know for The Applied Anatomy and Physiology section in Paper 1 of GCSE OCR Physical Education. Bones, joints, muscles, movement, planes, axis, levers, cardiovascular system, respiratory system and effects of exercise. BASED ON SPECIFICATION
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
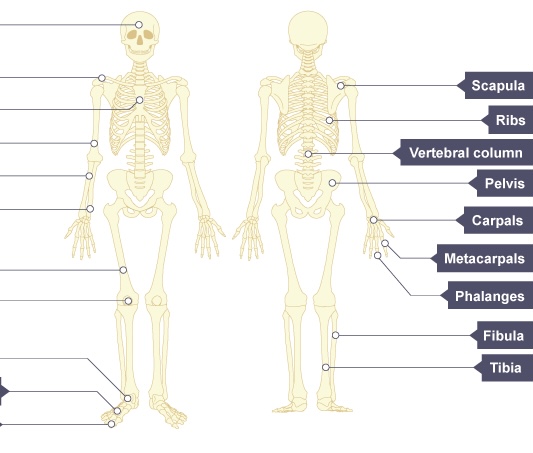
Name the bones on the right from TOP to BOTTOM
Scapula
Ribs
Vertebrae
Pelvis
Carpals
Metacarpals
Phalanges
Fibula
Tibia
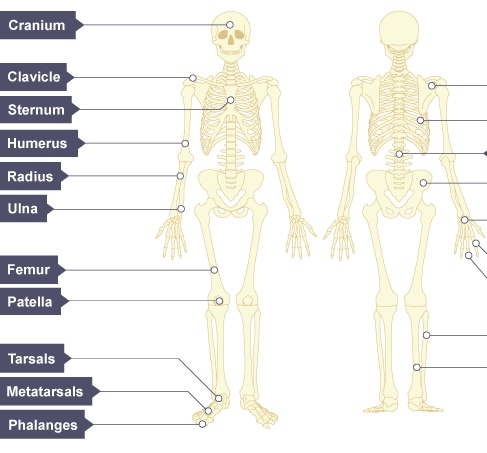
Name the bones on the left from the TOP to BOTTOM
Cranium
Clavicle
Sternum
Humerus
Radius
Ulna
Femur
Patella
Tarsals
Metatarsals
Phalanges
Name the 6 functions of the skeletal system
Blood cell production, posture, support, movement, protection and storage of minerals.
What is a synovial joint?
A freely moveable joint
What are the 2 types of synovial joints?
Hinge, and ball and socket
What are the four structures within a synovial joint?
Cartilage, synovial fluid, ligaments and tendons.
What is the role of cartilage?
To cushion the joint and prevent friction and wear and tear between the bone ends.
What is the role of ligaments?
To connect bone to bone to keep a joint together
To stabilise joints during movement to prevent dislocation
To absorb shock
To maintain correct posture and movement
What is the role of tendons?
To connect muscle to bone
To allow muscle to pull on a bone for movement.
What are the articulating bones at an elbow joint?
Humerus, radius and ulna
What are the articulating bones at a knee joint?
Femur and tibia
What are the articulating bones at a shoulder joint?
Humerus and scapula
What are the articulating bones at a hip joint?
Pelvis and femur
Name the types of movement at a ball and socket joint.
Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation and circumduction
Name the types of movement at a hinge joint
Flexion and extension
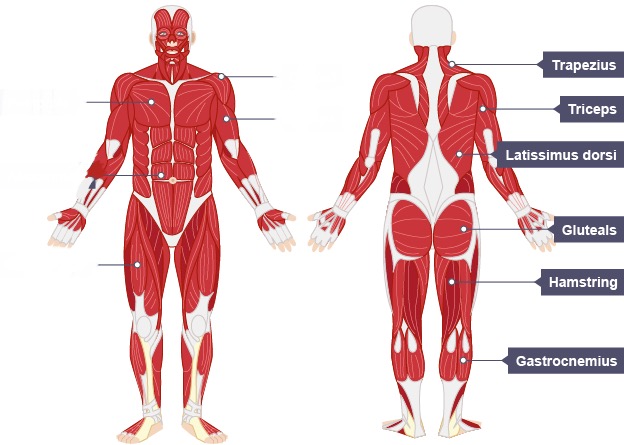
Name the muscles on the right hand side from TOP to BOTTOM
Trapezius
Triceps
Latissimus dorsi
Gluteals
Hamstring
Gastrocnemius
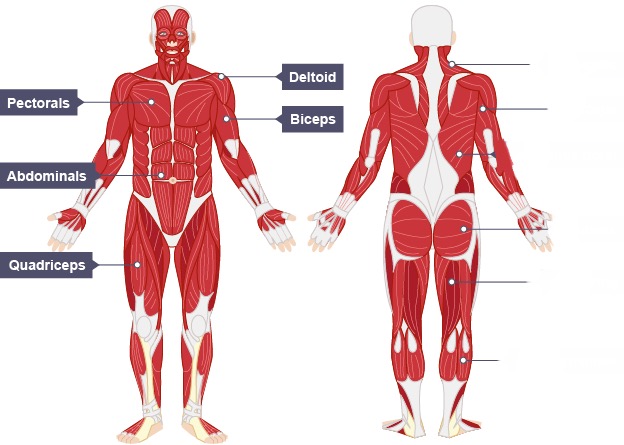
Name the muscles on the left hand side from TOP to BOTTOM
Deltoid
Pectorals
Biceps
Abdominals
Quadriceps
Function of the Tricep
Extends the elbow joint
Function of the Bicep
Flexes the elbow joint
Function of the deltoid
Abducts, flexes and extends the shoulder joint
Function of the pectorals
Helps to addict the arm, and rotate it inwards. Also swings arm across the body.
Function of the trapezius
Helps to rotate the head and bend the neck backwards. Swings arms across and away from the body.
Function of the Gluteals
Extends and rotates the hip joint
Function of the quadriceps
Extends the knee joint
Function of the hamstrings
Flexes the knee joint
Function of the gastrocnemius
Points toes (Plantar flexes the ankle joint)
Function of the Latissimus Dorsi
Addicts the arm at the shoulder joint
Function of the Abdominals
Flexes the trunk and helps to rotate the upper body
Why do muscles work as antagonistic pairs?
As muscles can only contract (pull), they cannot push. Therefore, as one contracts and shortens, another muscle relaxes and lengthens.
Name the three roles a muscle could take
The agonist, the antagonist or the fixator
What is an agonist?
The muscle that works to create the movement.
What is an antagonist?
The muscle that works in the opposite way of the agonist.
What is the fixator?
A muscle that acts as the stabiliser and helps the agonist work effectively of one part of the body during movement of another part.
What are the three components of a lever?
Fulcrum, effort and load
What is the order of a first class lever?
EFL
What is an example of a first class lever?
A header in football
What is the order of a second class lever?
ELF
What is an example of a second class lever?
Going up on point in ballet
What is the order of a third class lever?
FEL
What is an example of a third class lever?
The flexion in a bicep curl.
What is mechanical advantage?
1st and 2nd class levers provide mechanical advantage, this means that a larger load can be moved with a smaller amount of effort.
Name the three types of axis.
Longitudinal axis, transverse axis and frontal axis
Name the three type of planes
Transverse plane, sagittal plane and frontal plane
What pairs with the longitudinal axis?
The transverse plane
What pairs with the Transverse Axis?
The Sagittal Plane
What pairs with the Frontal Axis?
The Frontal Plane
Give an example of the longitudinal axis
A pirouette in dance
Give an example of the transverse axis
A forward roll in gymnastics
Give an example of the frontal axis
A cartwheel in gymnastics
What does the transverse plane divide the body into?
Top and bottom
What does the Sagittal plane divide the body into?
Left and right
What does the frontal plane divide the body into?
Front and Back
What movement happens at the Transverse Plane?
Rotation
What movements happen at the Sagittal Plane?
Flexion and Extension
What movements happen at the Frontal Plane?
Abduction and Adduction
Do the Levers have Mechanical Advantage?
1st- Sometimes
2nd- Always
3rd- Never
What is meant by a double-circulatory system?
The body has two circulatory loops in which blood circulates; the systemic and the pulmonary.
What are the 3 types of blood vessels?
Arteries, veins and capillaries
Which direction do arteries carry the blood?
AWAY from the heart
Which direction do veins carry the blood?
TOWARDS the heart
What are artery walls like?
They are thick and elastic
What are vein walls like?
Thin
What pressure are the arteries under?
High Pressure
What pressure are the veins under?
Low Pressure
Which type of blood vessel has a larger lumen- arteries or veins?
Veins
What are the two main functions of the blood?
Transportation and temperature control
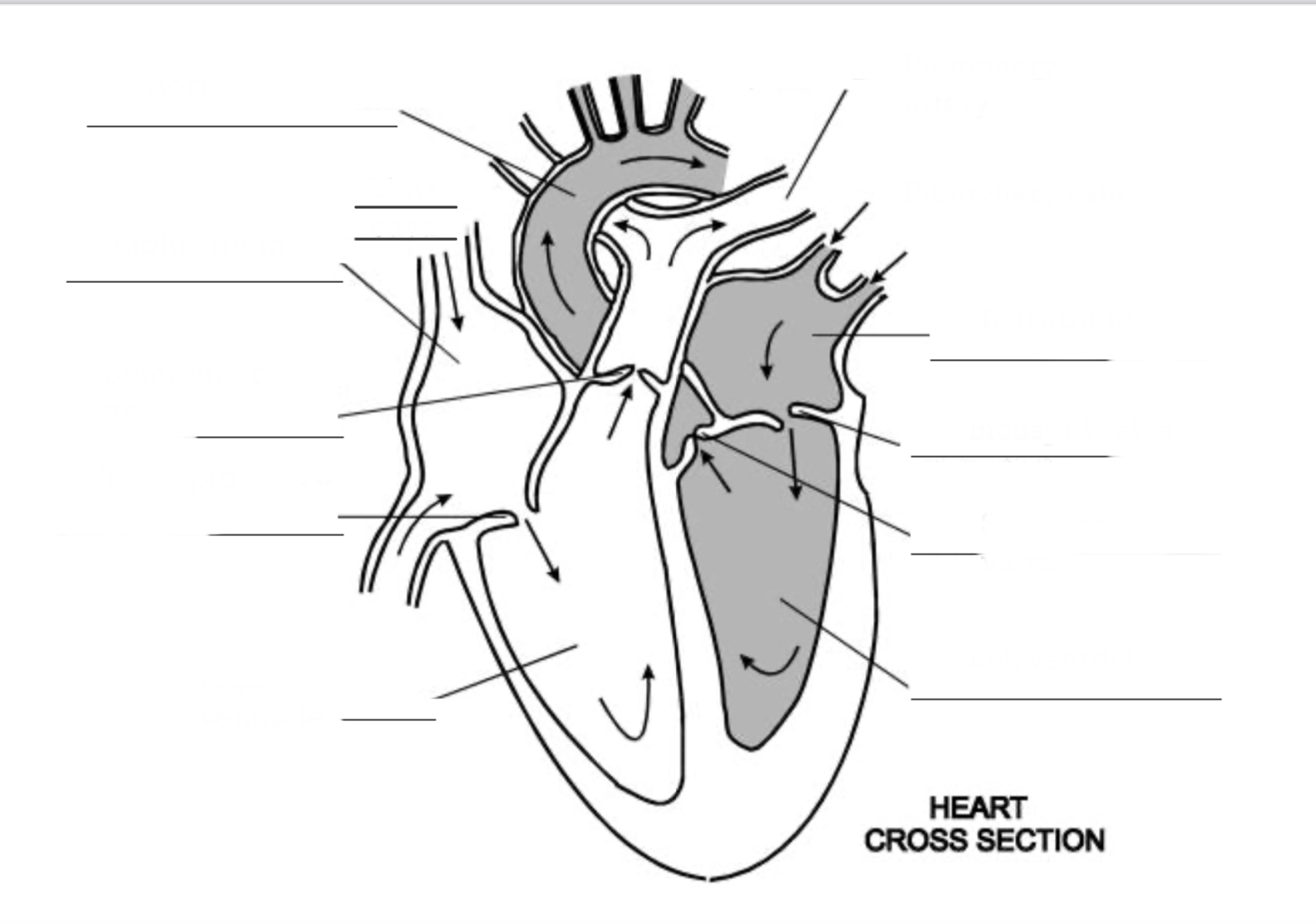
Name the structures the blood would pass through in the heart’s double circulatory system, starting with the Vena Cava.
Vena Cava, Right Atrium, Tricuspid Valve, Right Ventricle, Pulmonary Artery, LUNGS
Pulmonary vein, Left Atrium, Bicuspid Valve, Left Ventricle, Semi- lunar valve, Aorta, BODY
What is heart rate?
Number of beats per minute (bpm)
What is stroke volume?
The amount of blood pumped out of the left ventricle per beat
What is cardiac output?
Heart Rate x Stroke volume
What is the four components of blood?
Red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma and platelets.
What is the role of red blood cells?
Containing haemoglobin, they transport oxygen around the body.
What is the pathway of air through the respiratory system?
Mouth/Nose, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli
What is the role of the diaphragm in breathing?
During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and moves downwards. During expiration, the diaphragm relaxes and moves back to its domed shape.
What is the role of the intercostal muscles in breathing?
During inspiration, the intercostal muscles contract and move the ribs upwards and outwards. During expiration, the intercostal muscles relax so the ribs move inwards and downwards.
What is breathing rate?
The number of breaths taken in a minute.
What is tidal volume?
The amount of air which enters the lungs during normal inhalation at rest.
What is minute ventilation?
The volume of gas inhaled or exhaled from the lungs per minute.
Where does gas exchange take place, and by what process?
Gas exchange occurs at the alveoli by diffusion.
How are alveoli adapted to increase the rate of diffusion?
A large blood supply
A high surface area to volume ratio
A short diffusion distance- one cell thick
During gas exchange, the blood travelling into the capillaries is deoxygenated. What is diffusing into the alveoli, and what is diffusing out, into the red blood cells?
Carbon dioxide diffuses into the alveoli.
Oxygen diffuses into the red blood cells in the blood forming oxyhaemoglobin.
Define anaerobic exercise.
Exercise which does not allow for the predominant use of oxygen. Usually very high intensity for a short period of time.
Define aerobic exercise.
Use of oxygen for the duration of the exercise. Usually moderate intensity at a continuous rate.
Give two examples of anaerobic exercise.
Weight lifting and sprinting.
Give an example of aerobic exercise.
Long distance running.
What is the short term effects of exercise on muscle temperature?
The temperature of the muscles increases.
What is the short term effect of exercise on heart rate?
The heart rate increases.
What is the short term effect of exercise on stroke volume?
Stroke volume increases.
What is the short term effect of exercise on cardiac output?
Cardiac output increases.
What is the short term effect of exercise on blood flow?
Oxygenated blood is redistributed to the working muscles through vascular shunting.
What is the short term effect of exercise on respiratory rate?
Respiratory rate increases.
What is the short term effect of exercise on tidal volume?
Tidal volume increases.
What is the short term effect of exercise on minute ventilation?
Minute ventilation increases.
What is produced due to anaerobic exercise? Why?
Lactic acid is produced as oxygen cannot be delivered to the working muscles quickly enough, meaning glucose is not fully broken down to carbon dioxide and water.
What are the long term effects of exercise on bone density?
Bone density is increased, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
What is the long term effect of exercise on hypertrophy of the heart?
Cardiac hypertrophy occurs, meaning that the size of the heart will increase, meaning that the heart will contract with greater force and become more efficient.
What is the long term effect of exercise on muscular strength? Why?
Muscular strength is increased due to muscular hypertrophy, where micro-tears in the muscle fibres grow back stronger
What is the long term effect of exercise on muscular endurance? Why?
Muscular endurance increases as slow twitch fibres will get larger.
What is the long term effect of exercise on resistance to fatigue? Why?
Increased resistance to fatigue due to increased oxygen capacity and a higher anaerobic threshold, delaying lactic acid onset.
What is the long term effect of exercise on resting heart rate and resting stroke volume?
Stroke volume is increased, making resting heart rate decrease.