ESCI 204 midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:29 AM on 2/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
1
New cards
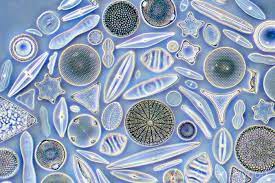
Diatoms
about .1 mm- on the larger side
2 groups- centric and pennate
often form long chains
2 groups- centric and pennate
often form long chains
2
New cards
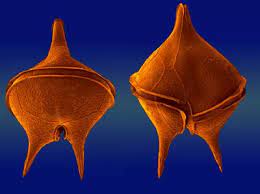
Dinoflagellates
.5 mm- largest phytoplankton
2 flagella for motion
half photosynthetic, half heterotrophic
2 flagella for motion
half photosynthetic, half heterotrophic
3
New cards
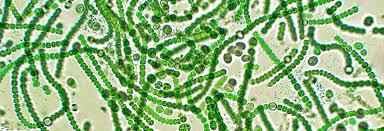
Cyanobacteria
.00005 mm-.04 mm
photosynthetic
3 important genera- synechococcus, trichodesmium, and prochlorococcus
photosynthetic
3 important genera- synechococcus, trichodesmium, and prochlorococcus
4
New cards
Microflagellates
.01 mm
many other groups of flagellated phytoplankton
many other groups of flagellated phytoplankton

5
New cards
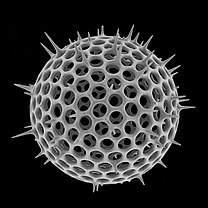
radiolarian
silica shells
6
New cards
foraminifera
calcium carbonate shells
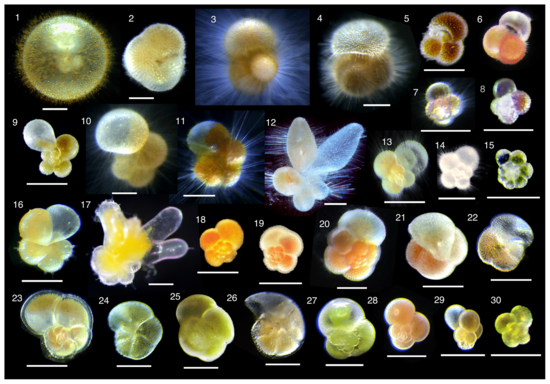
7
New cards
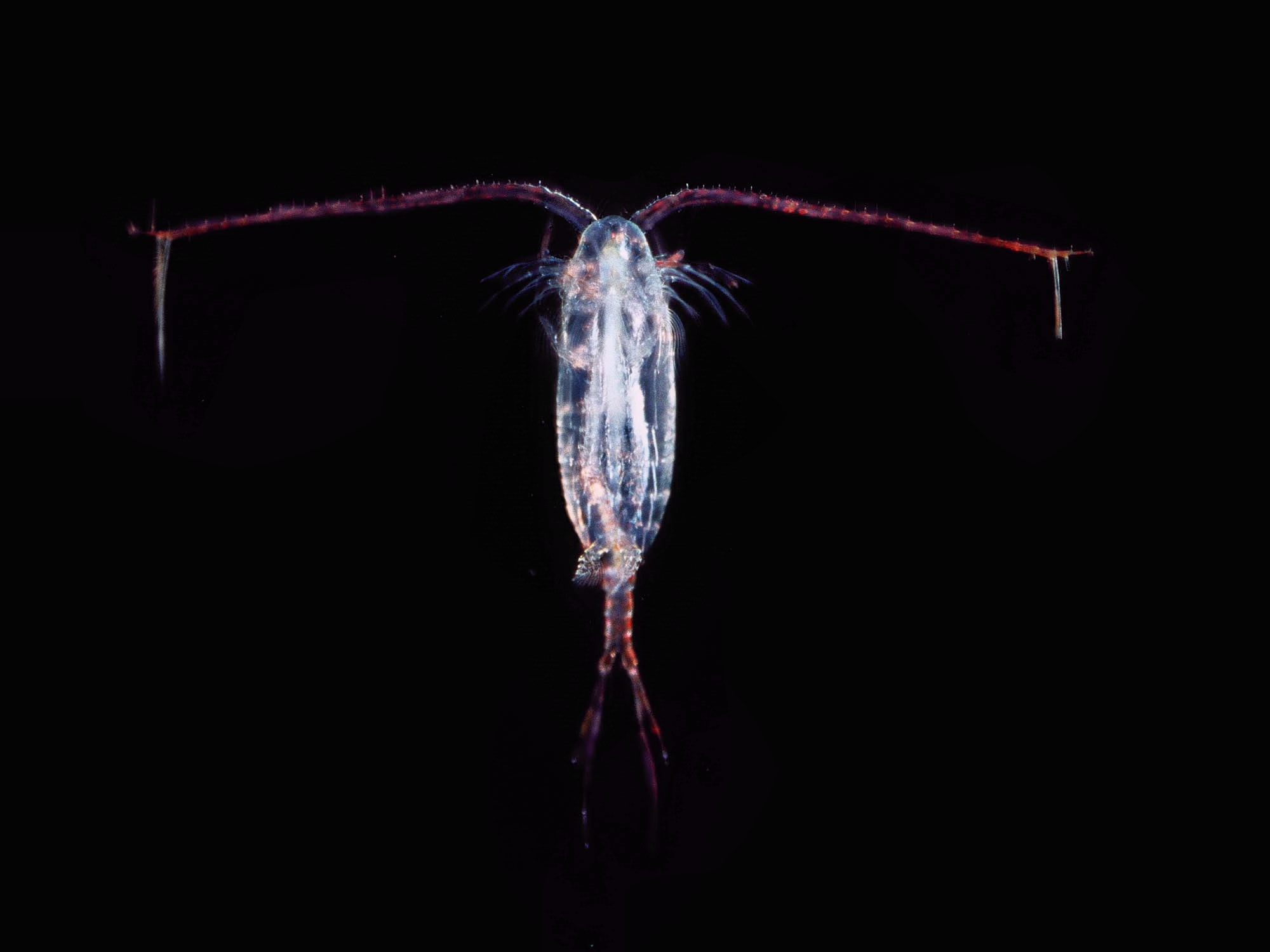
copepods
Grazers of phytoplankton, “smell” chemical plumes

8
New cards
euphasids
a type of krill, they have eyes- light sensitive

9
New cards
chaetognaths
predatory worms
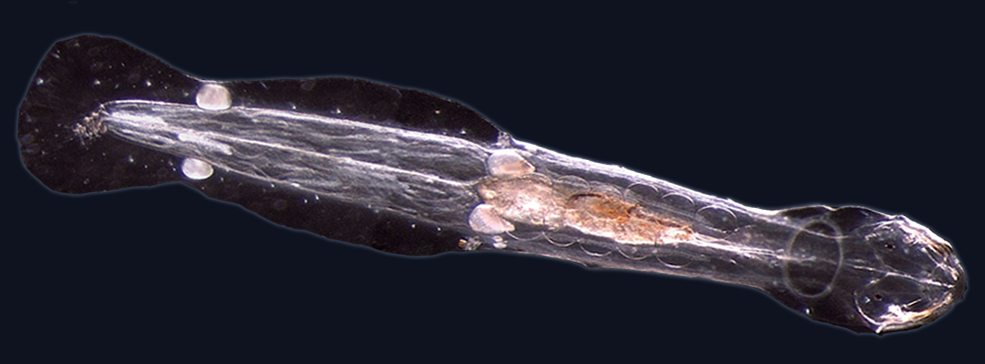
10
New cards
ctenophores
collect prey using their sticky cells or engulf prey
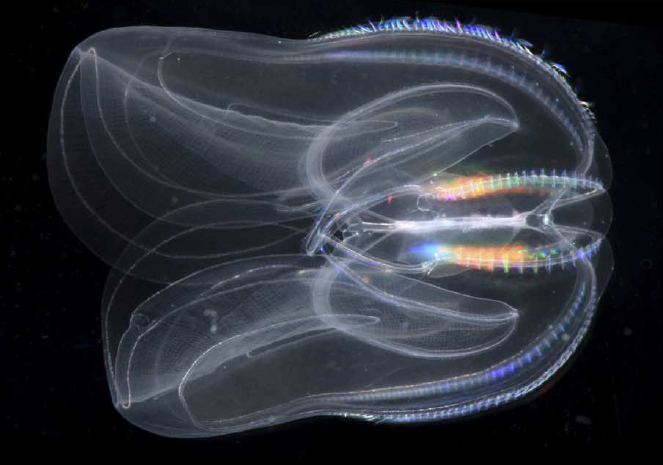
11
New cards
Salps
tunicates- enclosed in a tunic with openings at either end
pump water thru gelatinous bodies
pump water thru gelatinous bodies

12
New cards
Appendicularians (oikopleura)
mucus house builders
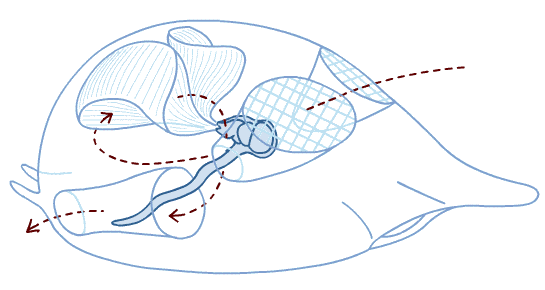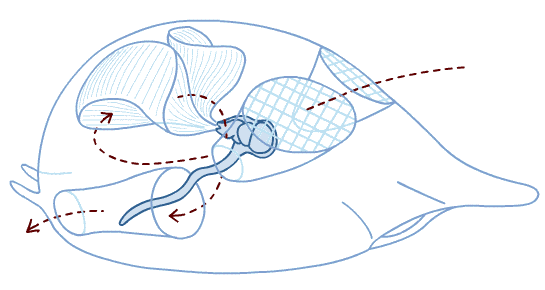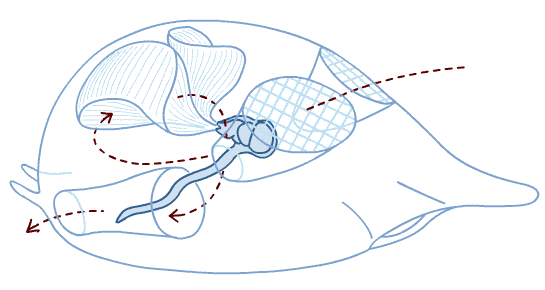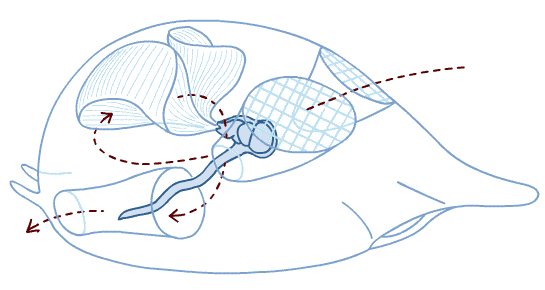
13
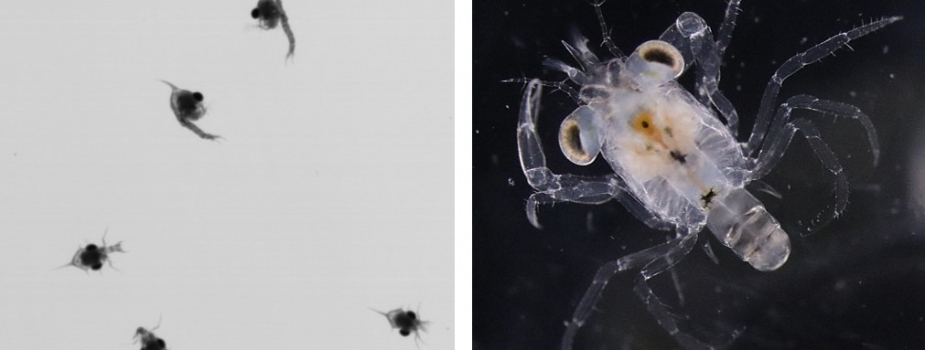
New cards
Crab larvae
14
New cards
polychaete larvae

15
New cards
Barnacle cyprid

16
New cards
ichthyoplankton
17
New cards
barnacles

18
New cards
mussel

19
New cards
sea stars

20
New cards
anemones

21
New cards
sea urchin

22
New cards
chitons

23
New cards
hydrothermal vent giant tubeworms

24
New cards
pompeii worms

25
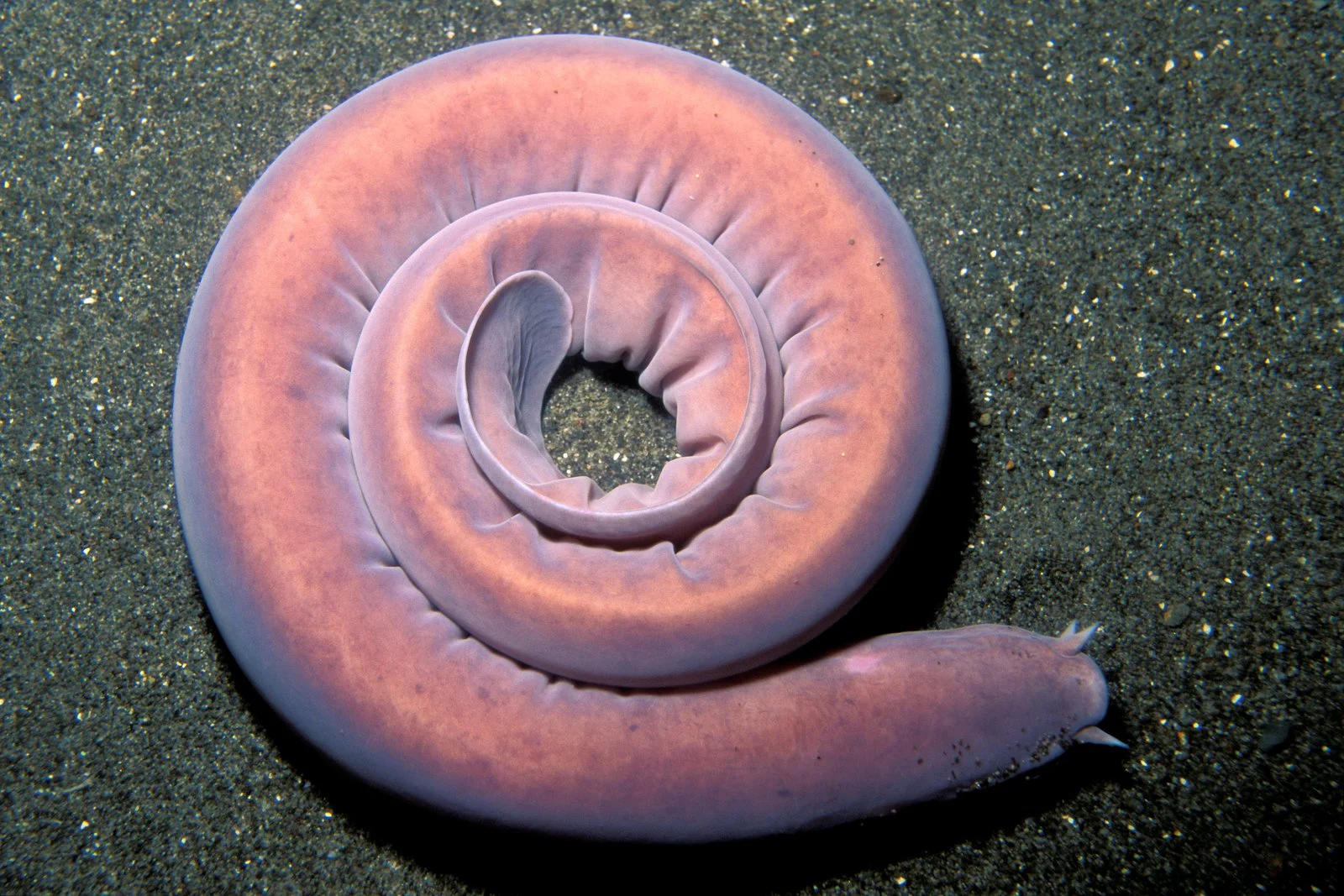
New cards
hagfish

26
New cards
Osedax
bone boring worm
27
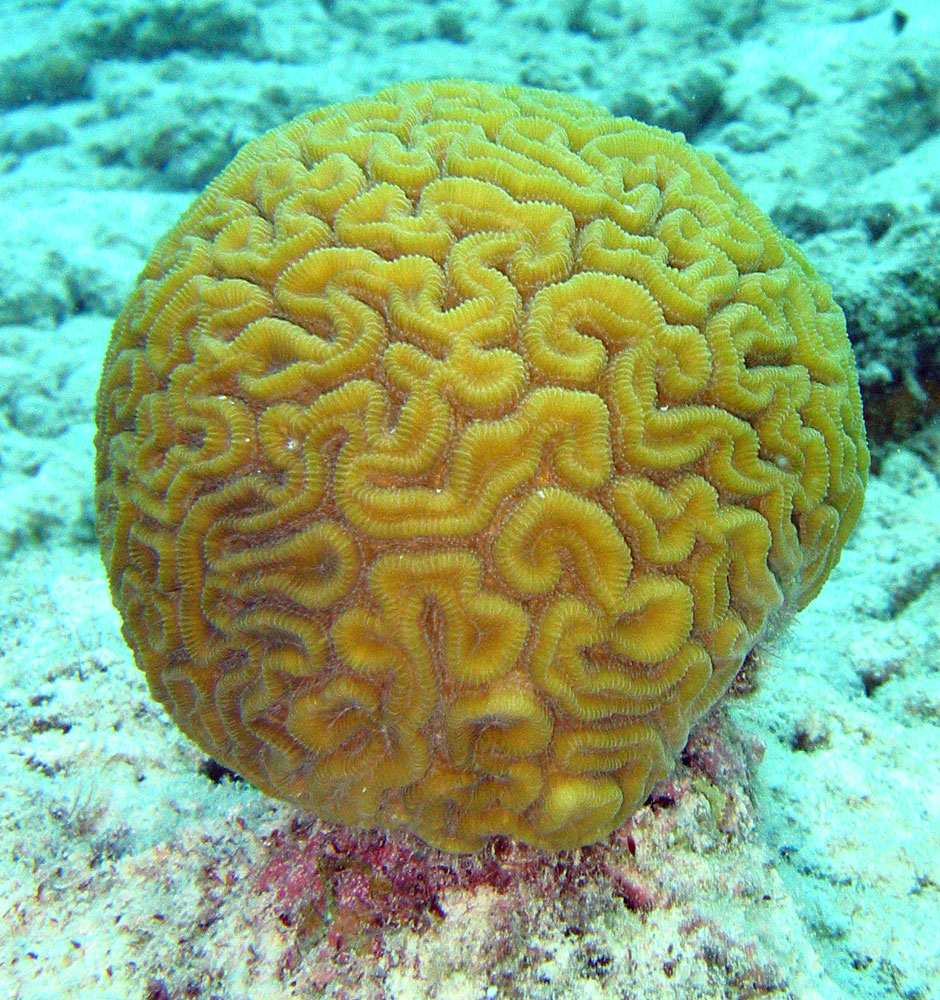
New cards
brain coral

28
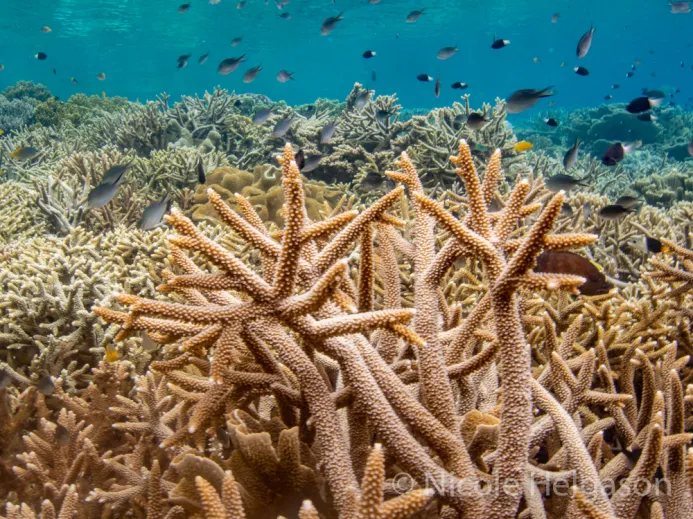
New cards
branching coral

29
New cards
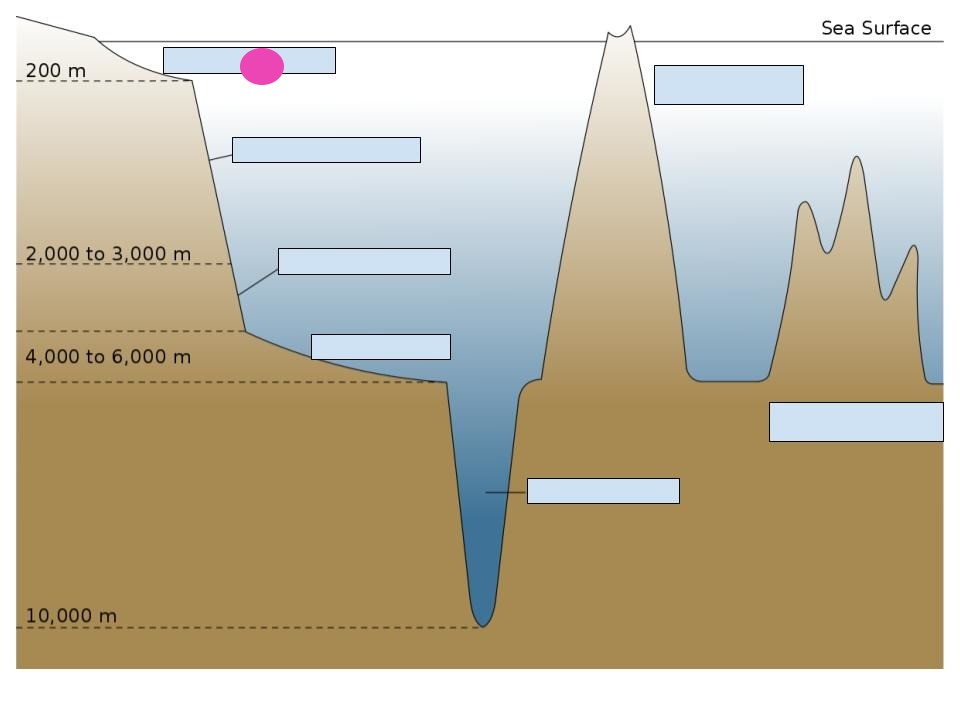
continental shelf
30
New cards
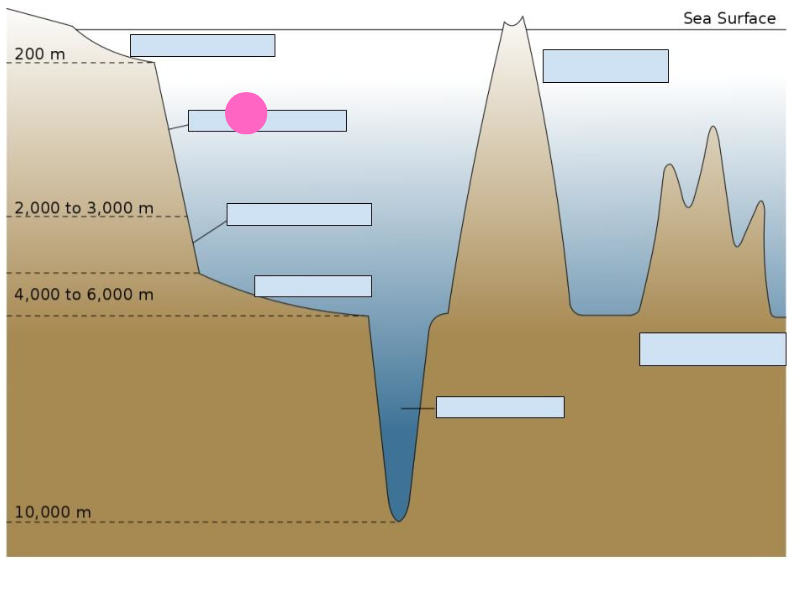
Continental slope
31
New cards
continental rise
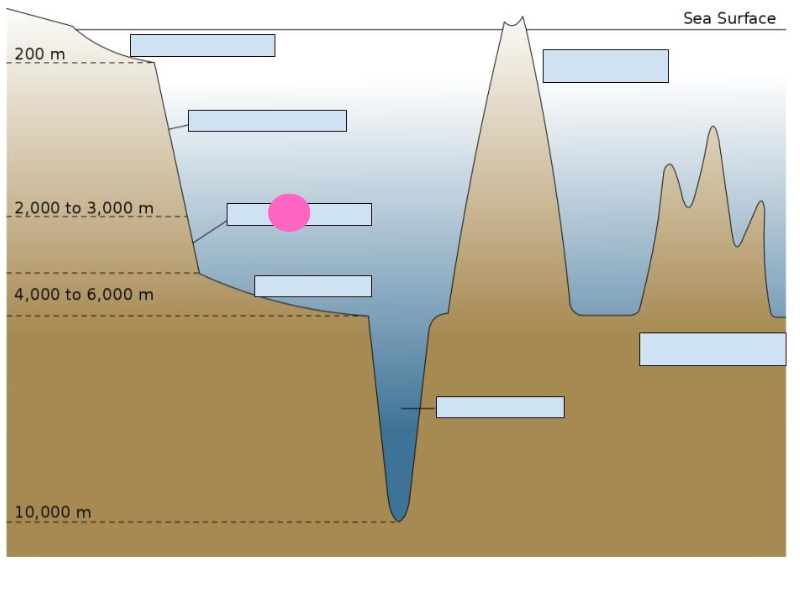
32
New cards
submarine canyon
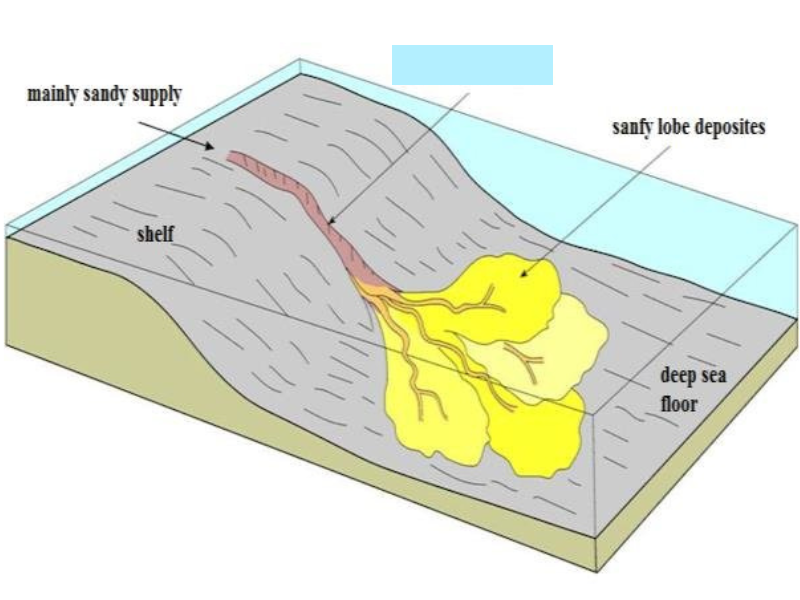
33
New cards
abyssal plain
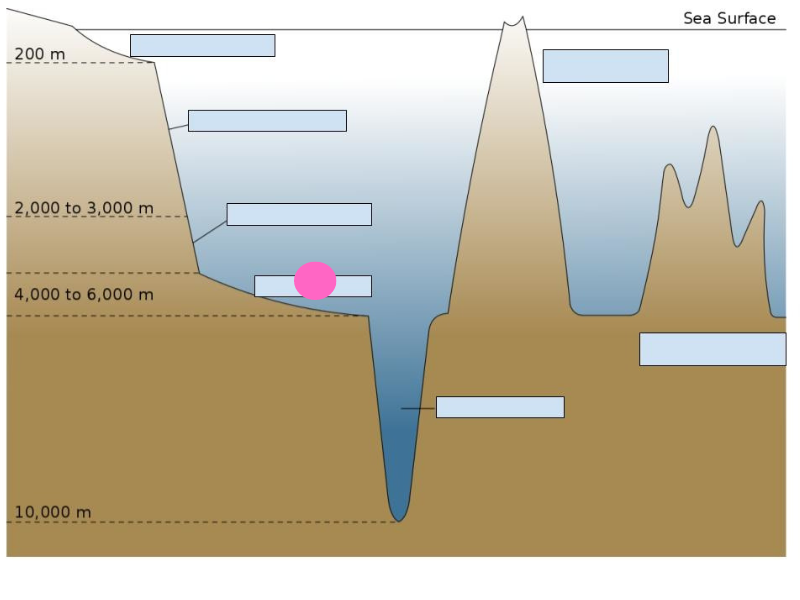
34
New cards
mid-ocean ridge
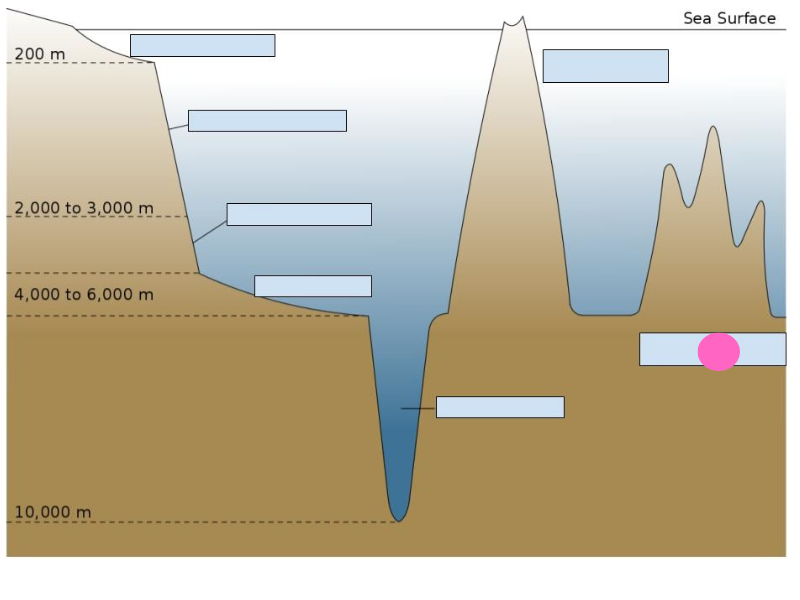
35
New cards
transform fault
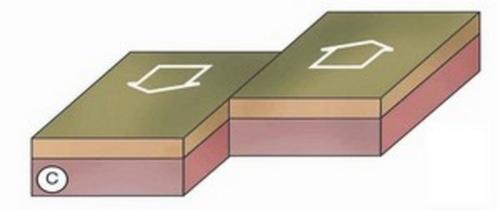
36
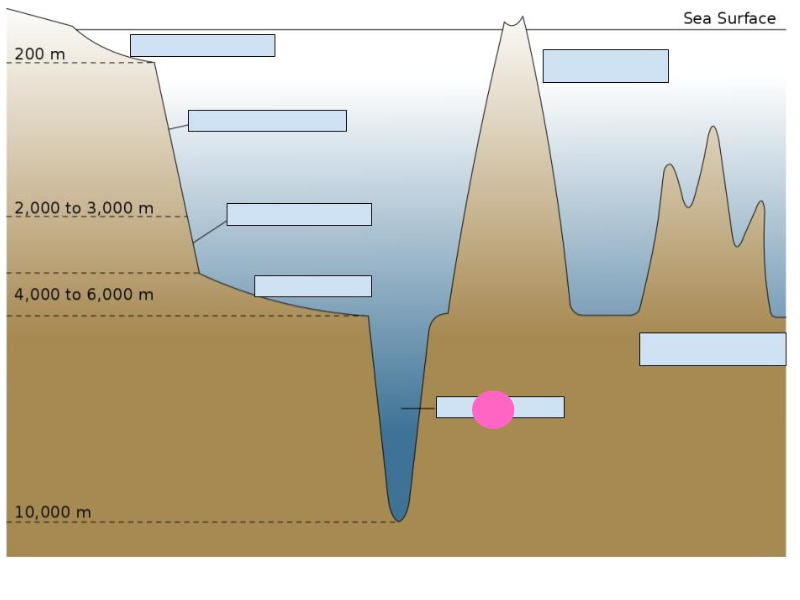
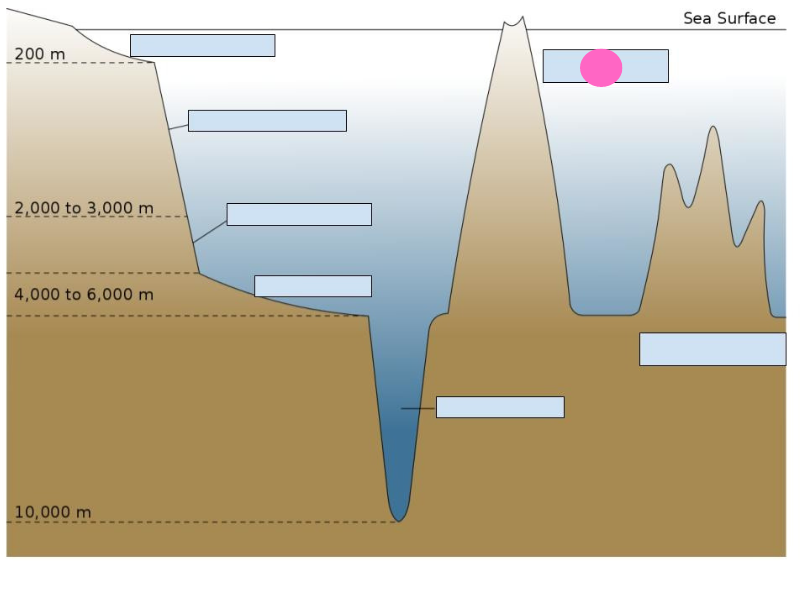
New cards
deep-sea trench
37
New cards
seamount
38
New cards
guyot
39
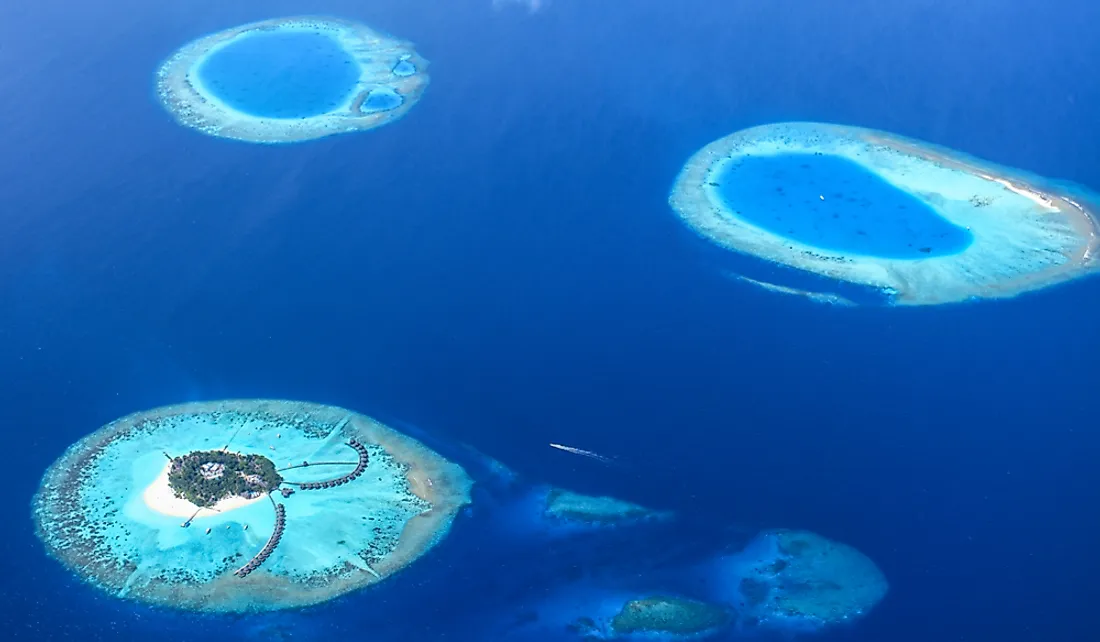
New cards
atoll
ring of coral left behind after island sinks

40
New cards
geological forces that drive plate tectonics and seafloor spreading
pieces of the lithosphere are constantly in motion because of heating/gravity, they move the asthenosphere along with them but gravity is the main force that drives tectonics
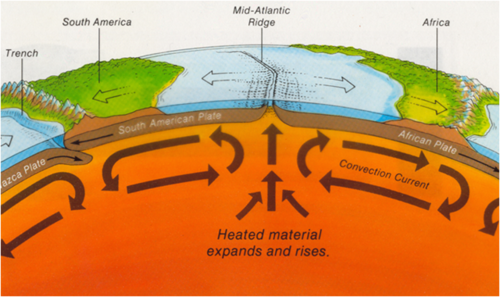
41
New cards
pressure gradients
caused by sea slope (barotropic) or difference in density (baroclinic)
42
New cards
Coriolis effect
objects in motion appearing to be thrown off course because of Earth’s rotation, North=right and South=left
43
New cards
wind
net average flow is 90 degrees to the right of the wind in the North, left in the South
44
New cards
friction
180 degrees to the direction of motion, slows things down and prevents them from going too fast
45
New cards
gyres
tend to circulate around mounds- indicate high pressure
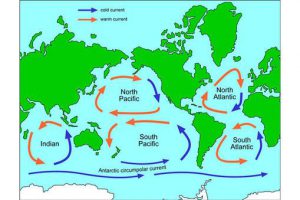
46
New cards
equatorial currents
north and south equatorial gyres
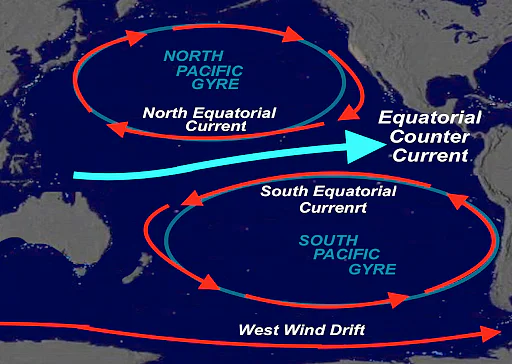
47
New cards
equatorial counter currents
goes right through the middle
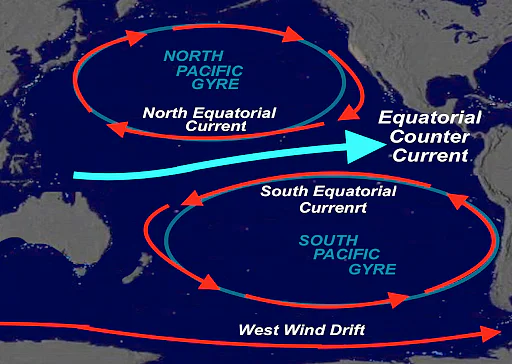
48
New cards
Antarctic circumpolar current
\
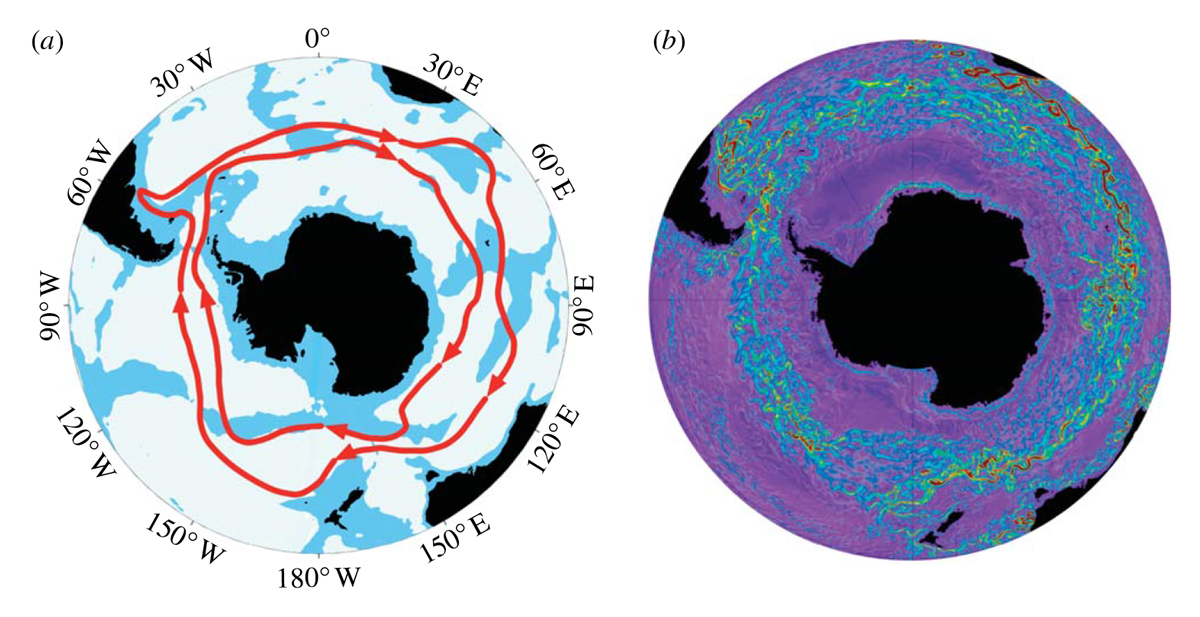
49
New cards
upwelling
caused by 2 currents crashing into each other, mixes all layers of the ocean and brings nutrients + cold water to the surface
50
New cards
generation of great ocean conveyor belt
caused by temperature and salinity in deep ocean, and wind driven currents on the surface, helps mix the water so there are nutrients at the top and phytoplankton to feed the deep
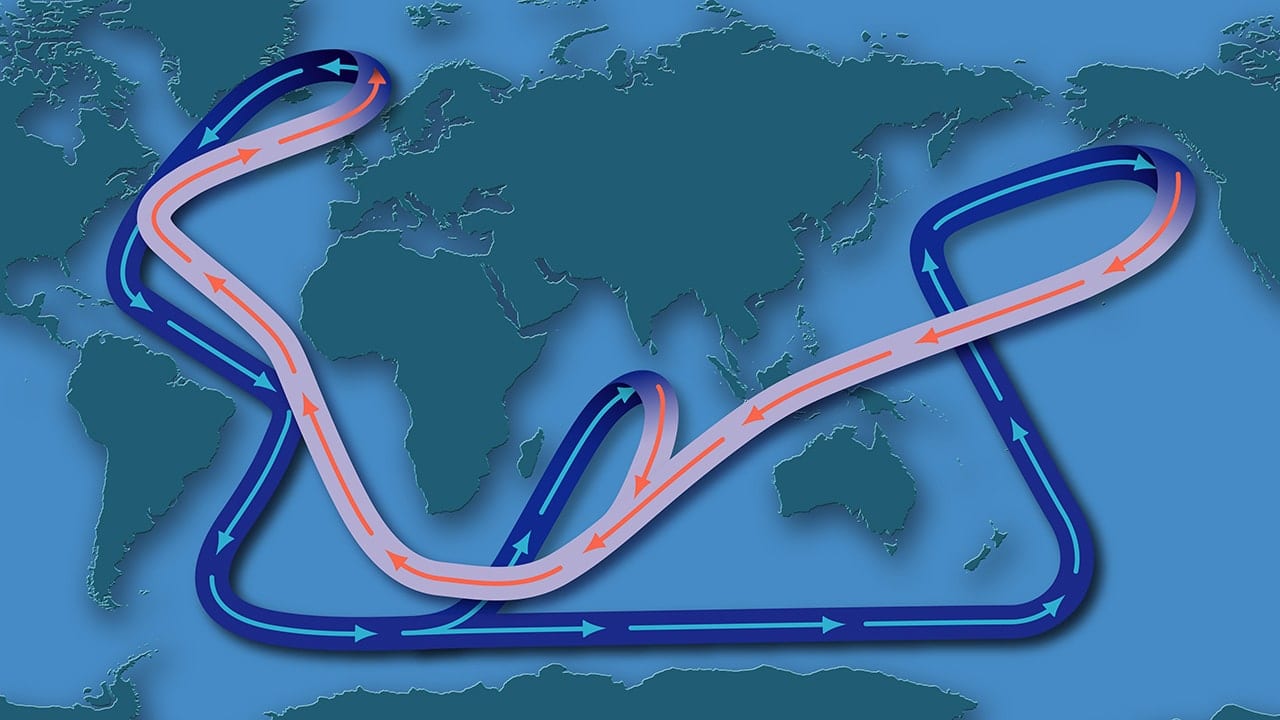
51
New cards
deep water chemistry changes in the conveyor
they lose salinity and gain temperature and sometimes the reverse, and nutrients get pushed up to the surface for phytoplankton
52
New cards
average salinity
35%
53
New cards
average temp
20 degrees C
54
New cards
average density
1\.03 g/cm^3
55
New cards
thermocline
steep temperature gradient in water, usually has a layer where the temperature is different above/below it
56
New cards
halocline
steep salinity gradient in water, has a layer where the salinity sharply increases
57
New cards
pycnocline
steep density gradient in water, density goes up with depth- there’s a layer where there’s a sharp decrease
58
New cards
nutricline
a sharp decrease in nutrients as the depth increases
59
New cards
stratification
separation of things into different groups/layers- reduces mixing, traps phytoplankton at the top with light
60
New cards
limiting factor of productivity in open ocean ecosystems
light is highest at the top, nutrients are highest at the bottom, phytoplankton (the base of the food web) need both to thrive
61
New cards
Redfield ratio
C:N:P=106:16:1
62
New cards
diatom life cycle
asexual or sexual repro possible
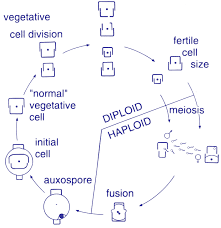
63
New cards
dinoflagellate life cycle
usually asexual reproduction w mitosis
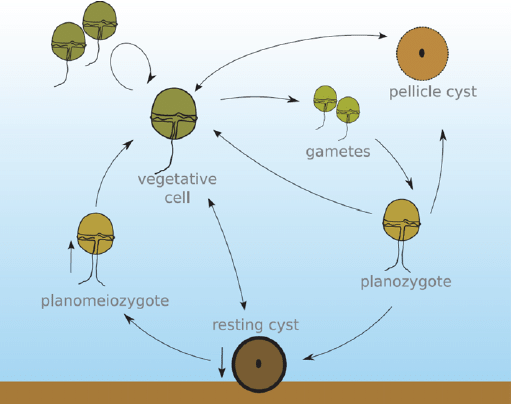
64
New cards
gross production
overall production of phytoplankton
65
New cards
net production
production of phytoplankton minus the energy it takes for them to be able to produce
66
New cards
respiration
opposite of photosynthesis
67
New cards
phytoplankton diversity
different phytoplankton thrive in different conditions- small ones use energy more efficiently but large ones are harder to eat
68
New cards
small phytoplankton are better
they use energy more efficiently, sink slower, grow/divide faster
69
New cards
why are large phytoplankton common in Puget Sound?
there are 2 different areas for stratification and mixing so it’s easier to grow larger
70
New cards
primary basins in Puget Sound
Hood Canal, whidbey basin, south sound, main basin
71
New cards
sills in Puget Sound
admiralty inlet sill, hood canal sill, tacoma narrows sill
72
New cards
why is puget sound so productive?
highly nutritious environment due to many mixing areas and various rivers flowing into the sound
73
New cards
paralytic shellfish poisoning
humans eat mussels and clams that have consumed dinoflagellates that produce neurotoxins
74
New cards
how do oceanographers create maps of phytoplankton from space?
they measure color/certain wavelengths that indicate phytoplankton
75
New cards
Limiting nutrients
N, P, Fe
76
New cards
holoplankton
spend their entire lives as plankton
77
New cards
meroplankton
spend part of their lives as plankton- usually a larval stage for a larger fish/invertebrate
78
New cards
Reynold’s number
The ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces (predicts whether flow is laminar or turbulent), copepods need low numbers to graze effectively
79
New cards
how to estimate phytoplankton and zooplankton grazing per capita with the dilution method
increased dilution of the seawater spreads out the phytoplankton and zooplankton so that it’s harder for the zooplankton to graze on phytoplankton.
80
New cards
Why do zooplankton perform diel vertical migration?
they go to the surface at night so they can eat, and they go to the bottom during the day to avoid predation by seeing predators
81
New cards
what causes vertical zonation patterns- intertidal rocky benthos
as you go down the layers, physical stress decreases due to proximity to the water but biological stress goes up due to more predators
82
New cards
competition between chthamalus, balanus, and mytilus
chthamalus grows first/fastest, then balanus arrives and begins to take over the lower areas of chthamalus. then mytilus arrives and overgrows both of them as high as it can go.
83
New cards
where are hydrothermal vents found?
spreading centers
84
New cards
energy source for hydrothermal vents
mantle heats fluid and reduces their density
85
New cards
4 stages of whale falls
1-mobile scavenger phase
2-enrichment opportunist phase- bone worms
3- sulphophilic phase
4- reef stage
2-enrichment opportunist phase- bone worms
3- sulphophilic phase
4- reef stage
86
New cards
food source during sulphophilic stage
anaerobic respiration in bones produces sulfide
87
New cards
how do whale falls serve as stepping stones for dispersal of hydrothermal vent species?
hydrothermal vent species shoot out larvae, they find a whale fall to attach to so they can shoot out more larvae to look for a new hydrothermal vent
88
New cards
stages of coral reef succession
fringing reef- reef surrounding an island
barrier reef- the reef forms a barrier far out from the island
atoll- the island is below the water but there’s still a ring of reef
barrier reef- the reef forms a barrier far out from the island
atoll- the island is below the water but there’s still a ring of reef
89
New cards
high diversity in deep sea benthic communities
long lived, stable habitats, large habitat area, high levels of food production/energy, intermediate predation, highly complex habitat, heterogeneous food resources