shit i need to memorize
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
for chem 202 final
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
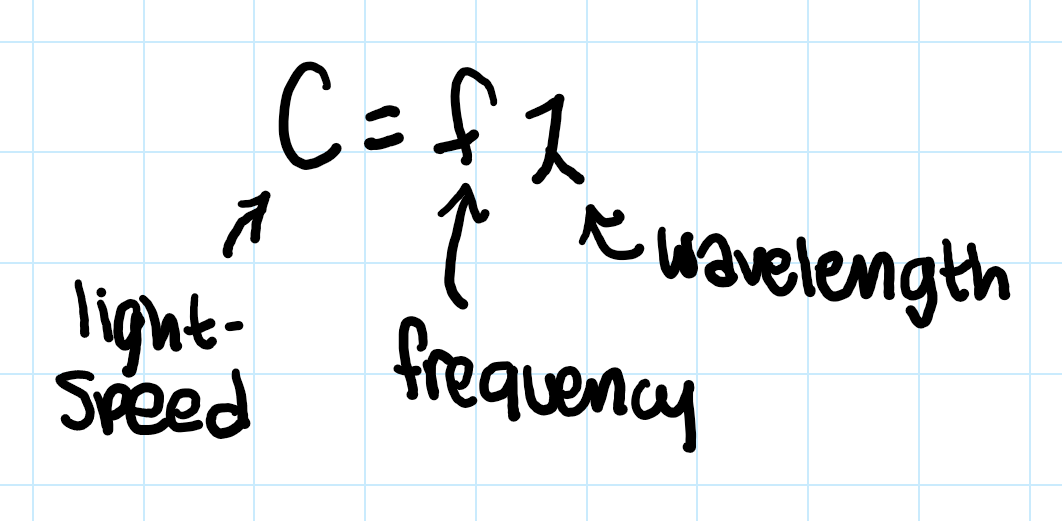
light speed (C) equals what??
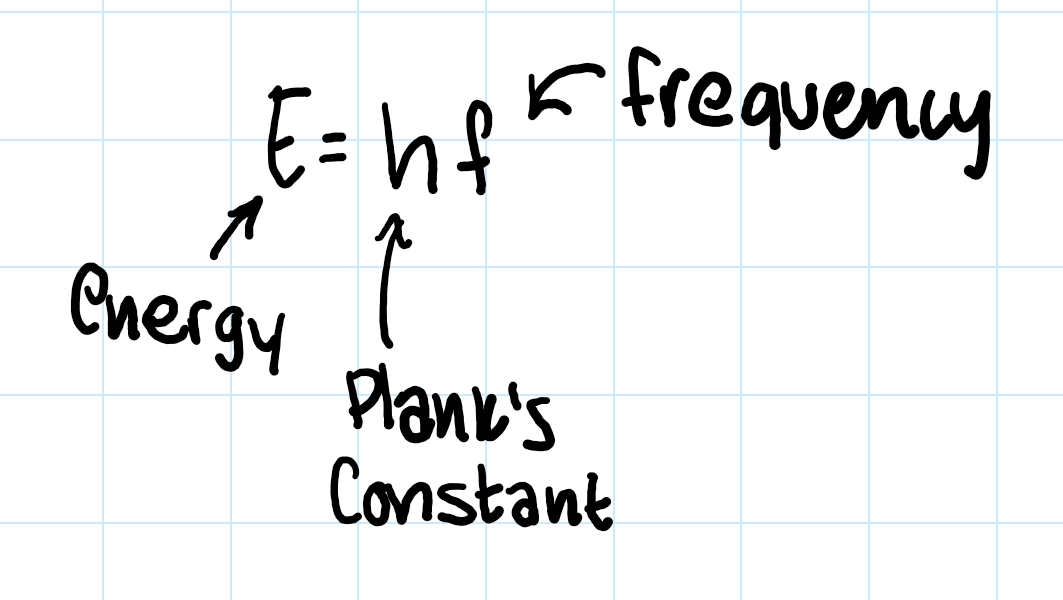
energy (E) equals what??
paramagnetic
unpaired electrons
diamagnetic
paired electrons
atomic radius periodic trend
atomic radius increases as you go down a column
atomic radius decreases as you go across a period
ionization energy periodic trend
ionization energy decreases as you go down a column
ionization energy increases as you go across a period
electronegativity periodic trend
electronegativity decreases as you go down a column
electronegativity increases as you go across a period
metallic character periodic trend
metallic character increases as you go diagonally down left on the periodic table
away from flourine
metallic character decreases as you go diagonally up right on the periodic table
towards flourine
quantum numbers (n)
principal quantum number
s and p block??? literally just your row number
d block?? row number - 1
f block?? row number - 2
quantum numbers (l)
azimuthal quantum number
n-1
or more if your n is higher
quantum numbers (ml)
orientation quantum number
± l
quantum numbers (ms)
spin quantum number
± ½
no right or wrong answer
soluble ionic compounds and exceptions
NO3- : always soluble, no exceptions
C2H3O2- : always soluble, no exceptions
Cl-, Br-, I- (group 17’s) : not soluble with Ag+, Hg22+, and Pb2+
SO42- (sulfate) : not soluble with Sr2+, Ba2+, Hg22+, and Pb2+
NH4+
alkali metals (group 1)
alkali earth metals (group 2)
insoluble ionic compounds and exceptions
S2- : soluble with NH4+, alkali metals, Ca2+, Sr2+, and Ba2+
CO32- and PO43- : soluble with NH4+ and alkali metals
OH- : alkali metals, Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+
breaking bonds
REQUIRES ENERGY
endothermic
(+) delta H
on the “reactants” side of the reaction
building bonds
RELEASES ENERGY
exothermic
(-) delta H
on the “products” side of the reaction
nonpolar
0-0.5
polar covalent
0.5-1.6
ionic
1.6-2
linear
electron geometry: linear
molecular geometry: linear
2 electron binding sites
2 bonds
0 lone pairs
180 degrees bond angles
ex: CO2
trigonal planar
electron geometry: trigonal planar
molecular geometry: trigonal planar
electron binding sites: 3
3 bonds
0 lone pairs
120 degree bond angles
ex: BCl3
bent (trigonal planar)
electron geometry: trigonal planar
molecular geometry: bent
electron binding sites: 3
2 bonds
1 lone pair
less than 120 degree bond angles
ex: SO2
tetrahedral
electron geometry: tetrahedral
molecular geometry: tetrahedral
electron binding sites: 4
4 bonds
0 lone pairs
109.5 degree bond angles
ex: CH4
trigonal pyramidal
electron geometry: tetrahedral
molecular geometry: trigonal pyramidal
electron binding sites: 4
3 bonds
1 lone pair
107.5 degree bond angles
ex: PH3
bent (tetrahedral)
electron geometry: tetrahedral
molecular geometry: bent
electron binding sites: 4
2 bonds
2 lone pairs
104.5 degree bond angles
ex: H2O
trigonal bipyramidal
electron geometry: trigonal bipyramidal
molecular geometry: trigonal bipyramidal
electron binding sites: 5
5 bonds
0 lone pairs
120 degree equatorial bond angles
90 degree axial bond angles
ex: PCl5
seesaw
electron geometry: trigonal bipyramidal
molecular geometry: seesaw
electron binding sites: 5
4 bonds
1 lone pair
less than 120 degree equatorial bond angles
less than 90 degree axial bond angles
ex: SF4
t-shaped
electron geometry: trigonal bipyramidal
molecular geometry: t-shaped
electron binding sites: 5
3 bonds
2 lone pairs
less than 90 degree bond angles
ex: ClF3
linear (trigonal bipyramidal)
electron geometry: trigonal bipyramidal
molecular geometry: linear
electron binding sites: 5
2 bonds
3 lone pairs
180 degree bond angles
ex: XeF2
octahedral
electron geometry: octahedral
molecular geometry: octahedral
electron binding sites: 6
6 bonds
0 lone pairs
90 degree bond angles
ex: SF6
square pyramidal
electron geometry: octahedral
molecular geometry: square pyramidal
electron binding sites: 6
5 bonds
1 lone pair
less than 90 degree bond angles
ex: BrF5
square planar
electron geometry: octahedral
molecular geometry: square planar
electron binding sites: 6
4 bonds
2 lone pairs
90 degree bond angles
ex: XeF4
solution is what
solute and solvent mixed together
molarity (M)

molality (m)

mole fraction (X)

mol percent (mol %)

parts by mass (%)
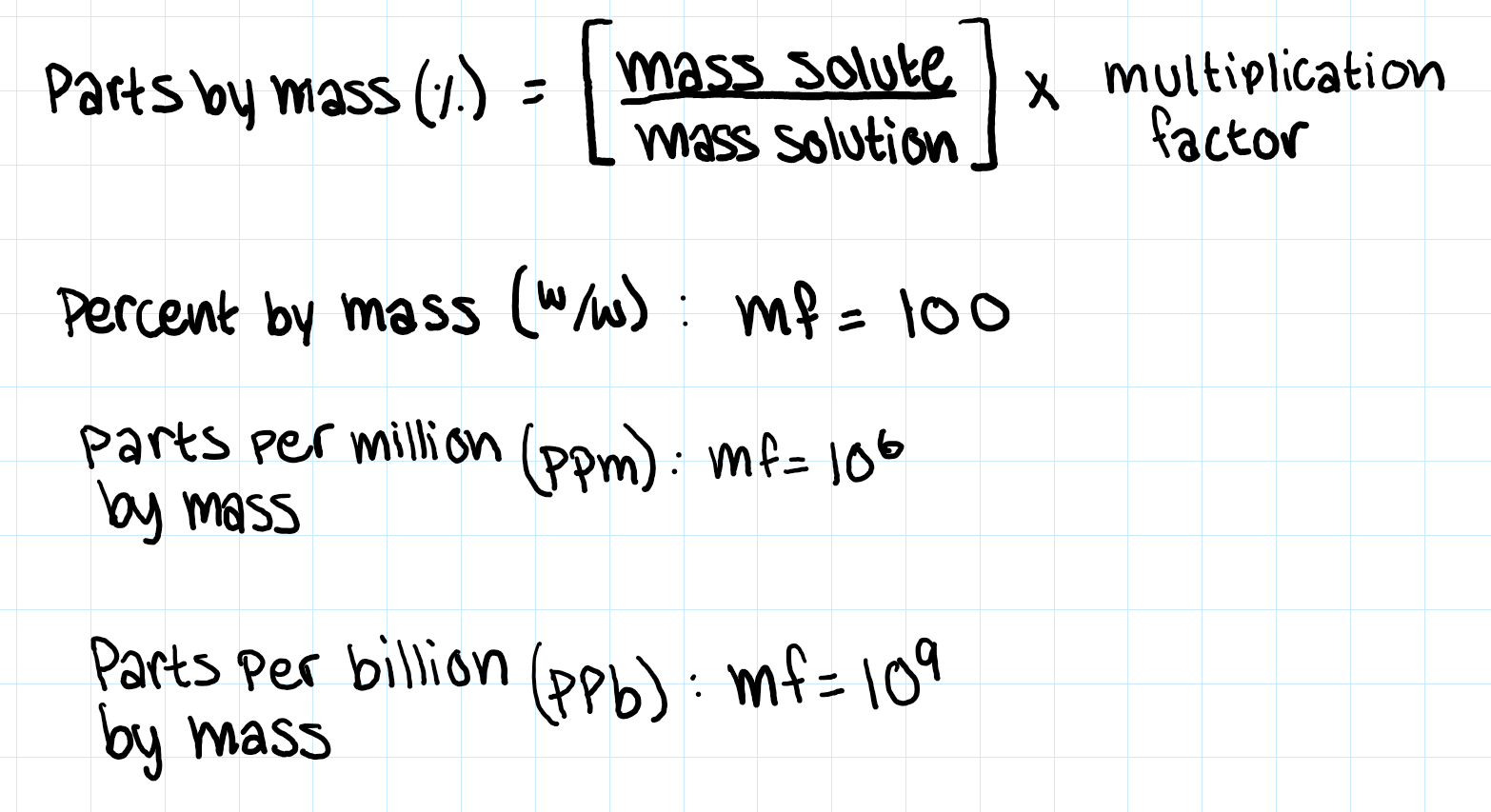
raoult’s law (non-volatile, non-electrolyte)
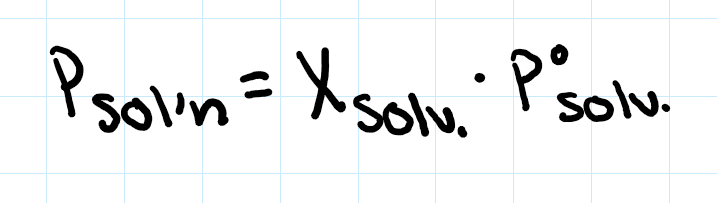
raoult’s law (volatile, non-electrolyte)
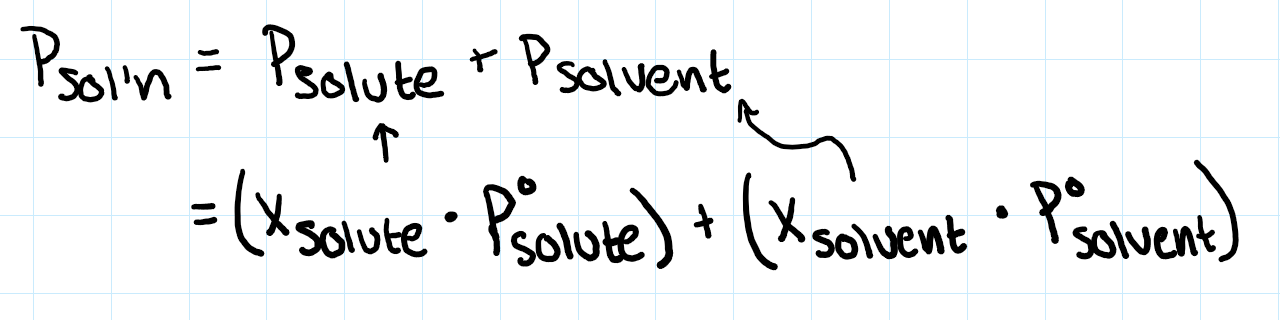
raoult’s law (volatile?, electrolyte)
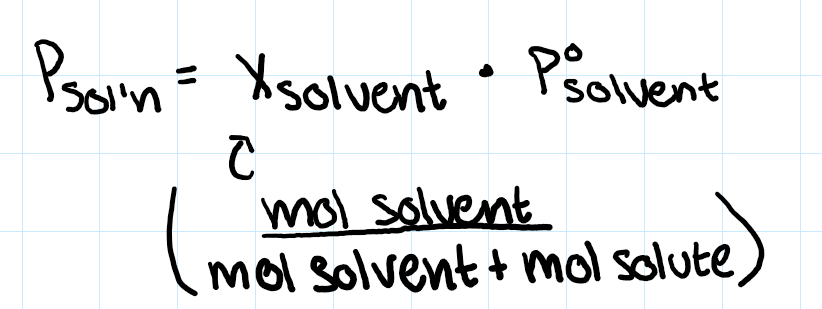
calculating change in freezing/boiling point
b/c of electrolytes (raoult’s law sorta)
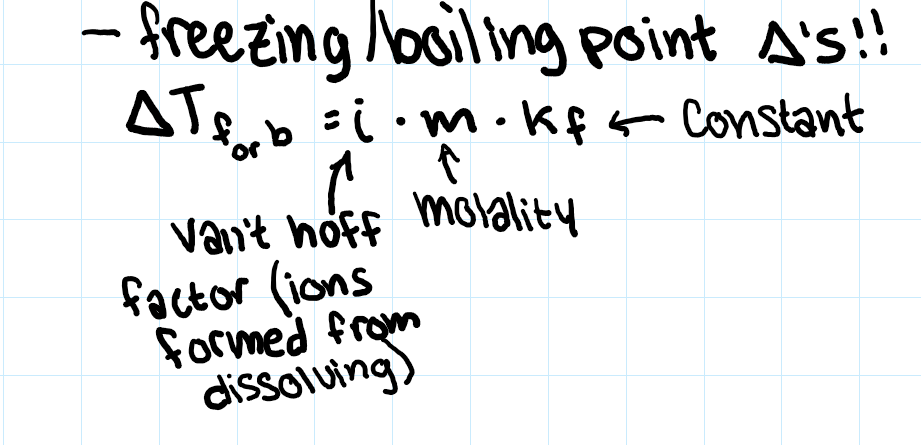
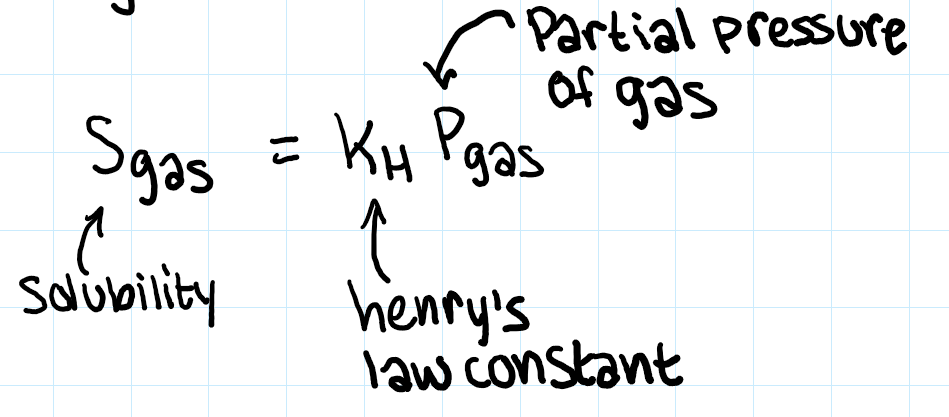
henry’s law
converts atm to molarity basically
osmotic pressure equation
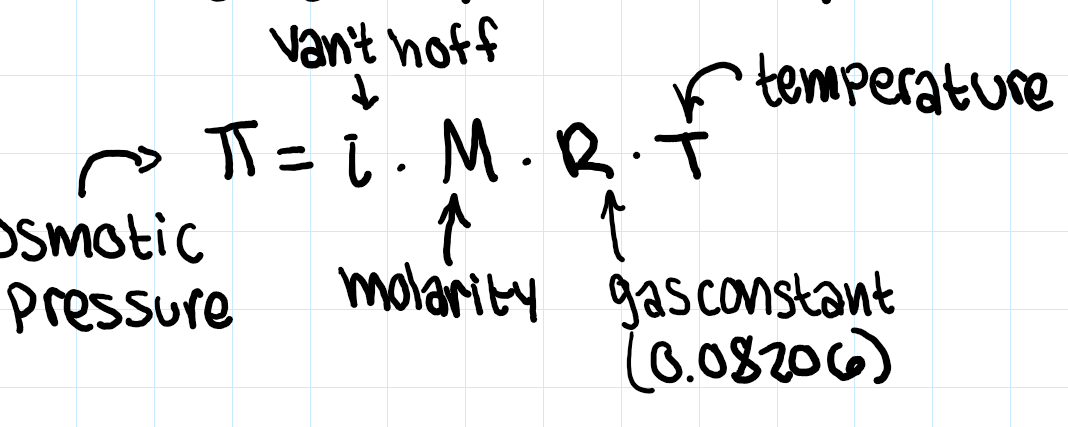
all those extra Ecell and delta G equations for electrochem and delta G

alpha decay particle
highest ionization power
lowest penetrating power
always released

beta decay particle
literally an electron
mid ionization power and penetrating power
BETA DECAY IS RELEASED OF ELECTRON
a neutron converts into a proton and an electron basically
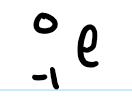
gamma emission
literally just light
no mass or charge
lowest ionization power
highest penetrating power
releases light (gamma radiation) b/c an element(?) is “meta stable” and needs to chill out
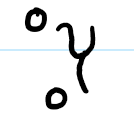
meta stable
element is too excited and needs to release gamma radiation in order to stabilize/chill out
positron particle and emission
literally an “anti-electron”
they get released
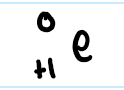
electron capture
literally beta decay just in reverse
an electron is CAPTURED
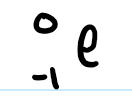
subatomic particles notation
