IB Biology - U1L1 - Introduction to Cells
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
INTRODUCTION TO CELLS Functions of Life 7 Characteristics of Living Things Paramecium Unicellular Organism The Cell Theory (Robert Hooke) Structures Found In All Cells Surface Area: Volume
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
How many characteristics distinguish living things from non-living things?
There are 7 characteristics
When all 7 characteristics are present, what does that make the object/item in question?
When all 7 characteristics are present it is an organism
What are the 7 Characteristics of Living Things?
Metabolism
Reproduction
Sensitivity
Homeostasis
Excretion
Nutrition
Growth
What is metabolism?
The undertaking of essential chemical reactions.
What is reproduction?
Production of offspring (sexually or asexually).
What is Sensitivity?
Responding to internal and external stimuli.
What is homeostasis?
Maintenance of a stable internal environment.
What is excretion?
Removal of waste products.
What is nutrition?
The exchanging of materials/gases with environment.
What is growth?
The movement and changing shape or size.
What mnemonic device could one utilise to remember the 7 Characteristics of Living Things?
MR SHENG.
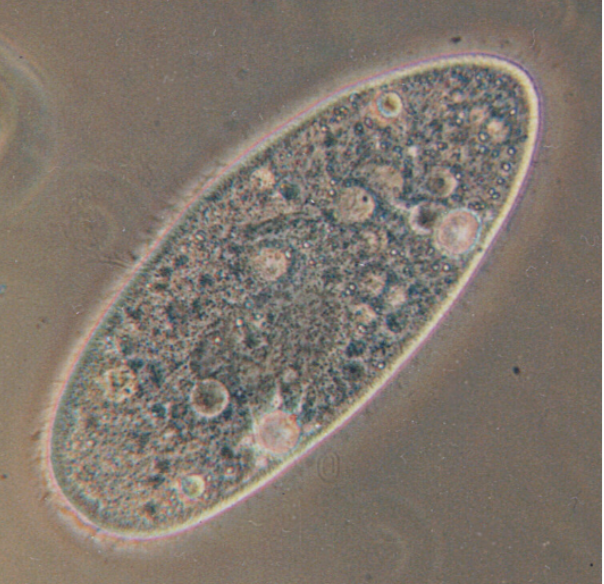
What makes paramecium an organism?
Heterotroph.
Eat plants, animals, or both to get energy.
Cilia.
Small hairs for movement.
Engulf food via feeding grove called a cytostome.
Food particles in vacuoles with digestive enzymes.
Solid waste exit via anal pore, liquid via contractile vacuole.
Gases enter/exit via diffusion.
Divide asexually by fission (divide in half), gene transfer by conjugation.
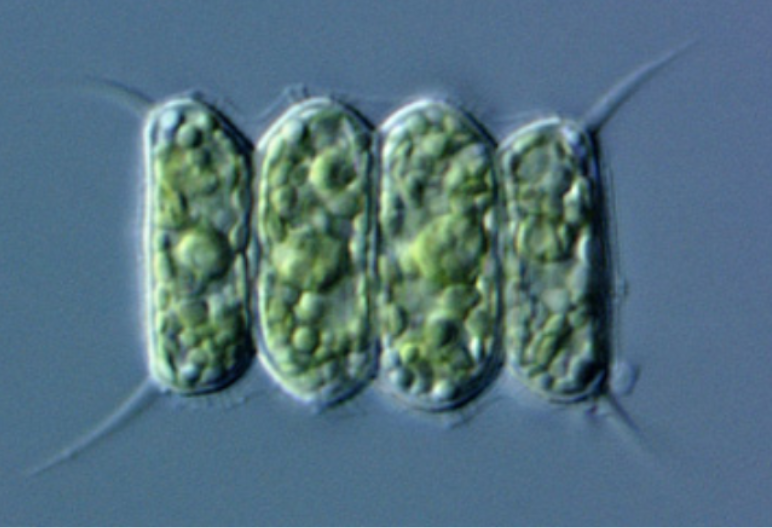
What is a Scenedesmus?
Autotrophic Unicellular Organism.
Gases enter/exit via diffusion.
Produce food via photosynthesis.
Divide via asexual division.
Can form colonies for protection.
The Cell Theory (Robert Hooke)
All things are made of cells.
Cells are the smallest unit of life.
Cells only come from other cells.
First cell must have come from nonliving material.
What are some structures found In all cells?
Plasma membrane.
Genetic material.
Ribosomes.
Cytosol.
What does the plasma membrane do?
It is a barrier that maintains homeostasis.
What does the genetic material do?
It is DNA that controls cell metabolism.
What do Ribosomes do?
They translate proteins (protein synthesis, use info from genetic material).
What does Cytosol do?
It is a fluid for metabolic reactions (cytoplasm).
What makes an organism a caveat to cell structure?
They challenge the idea that cells function individually to accomplish their tasks, because these all work together
What are the caveats to cell structure?
Striated Muscles.
Fungal Hyphae.
Red Blood Cells (RBCs).
Sieve Element.
What are Striated Muscles?
They are long, multi-nucleated cells.
Attached to the Skeleton.
What are Fungal Hyphae?
Some are not partitioned and multi-nucleated.
What constitutes a Sieve Element?
No nuclei.
Few organelles.
Need surrounding cells to survive.
What are Red Blood Cells (RBCs)?
They have no nucleus/mitochondria and can’t replicate.
What is metabolic rate influenced by?
Metabolic rate is influenced by mass/volume.
Larger cells need more energy.
What is rate of exchange influenced by?
Rate of exchange is influenced by surface area.
Larger surface area means more movement can occur.
Volume increase.
Volume increases faster than surface area as cells grow - causing low Surface area/Vol
If it’s too small opposite problem, chemical reactions will occur too quickly
Growing cells.
Growing cells tend to divide
They remain small with high Surface area:Vol.
Cells and Surface Area: Volume.
Cells and tissues specialised or gas/material exchanges will increase surface area to optimise material transfer.