Labs 1 & 2: A&PII Lab Practical Study Guide
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
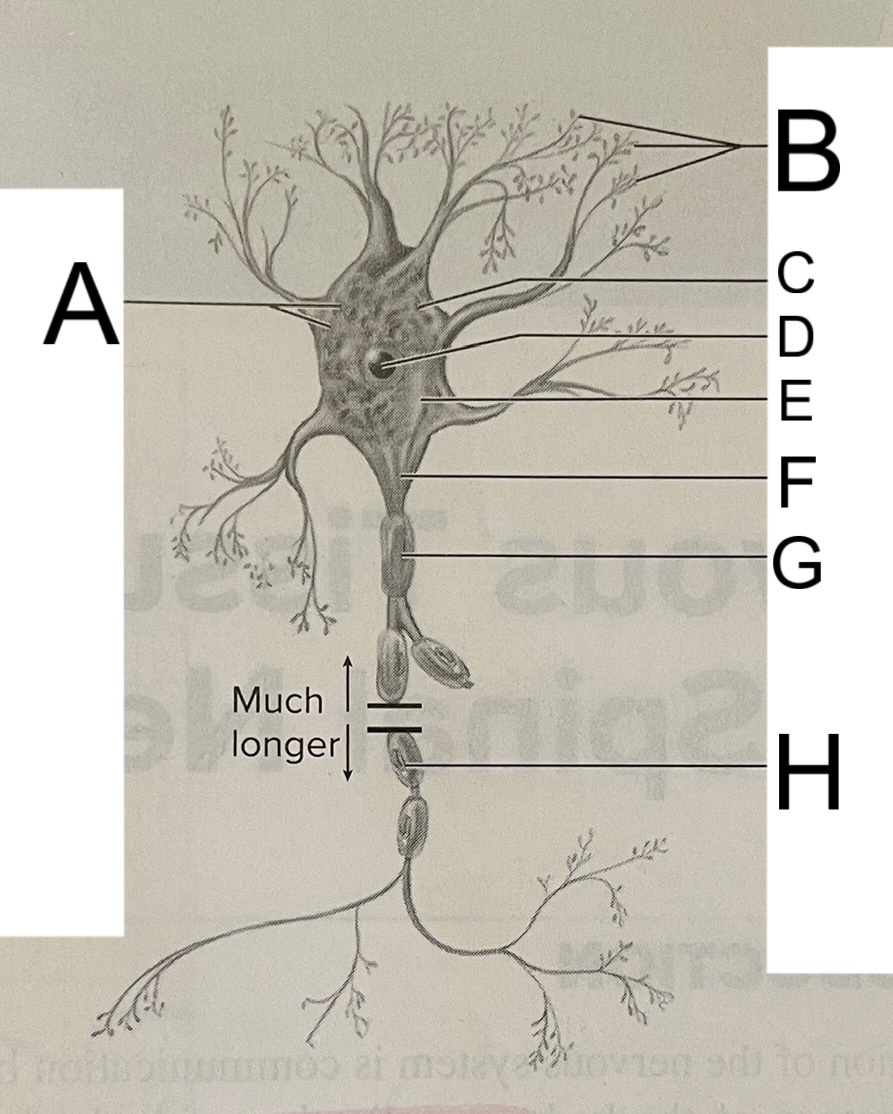
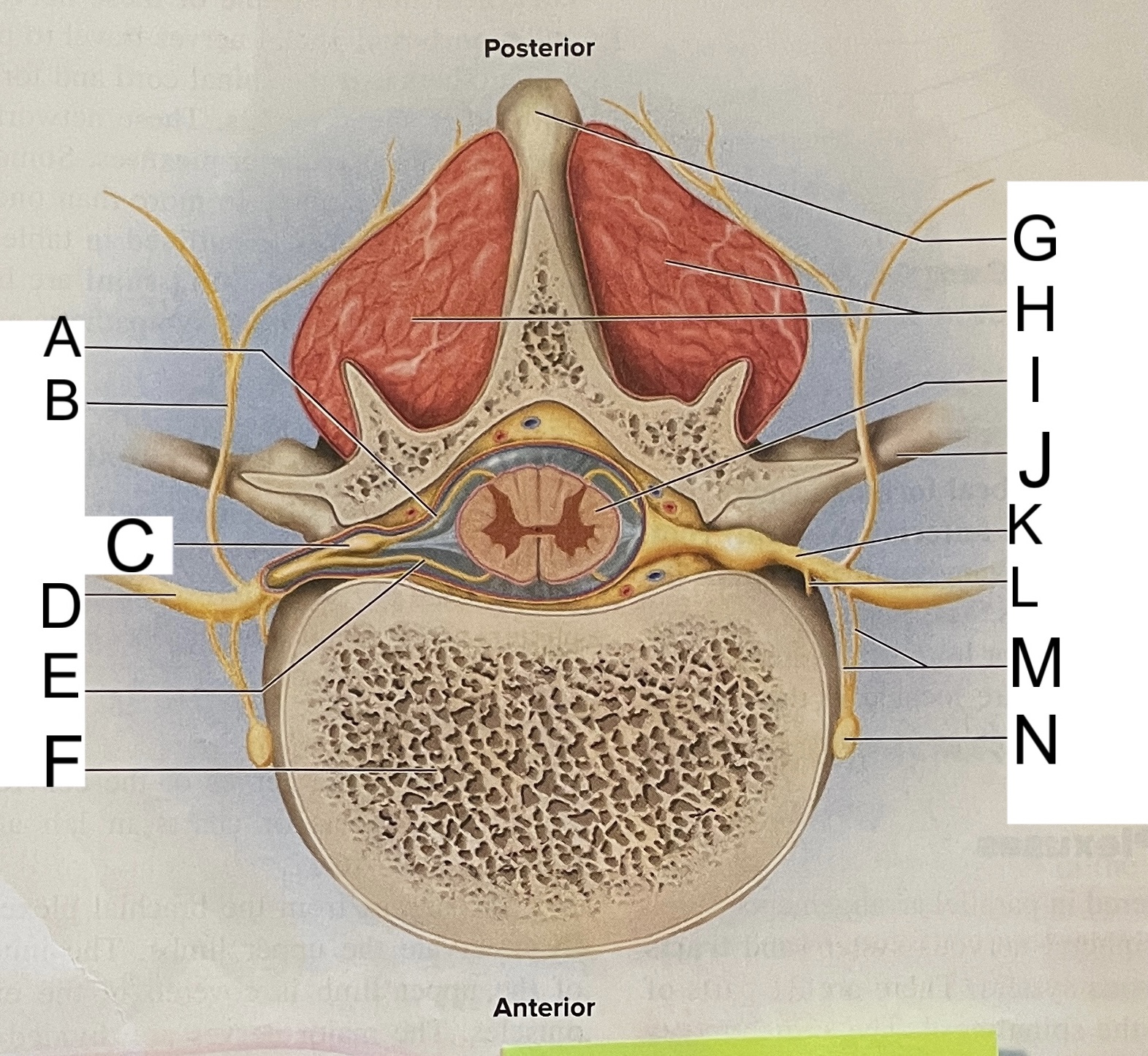
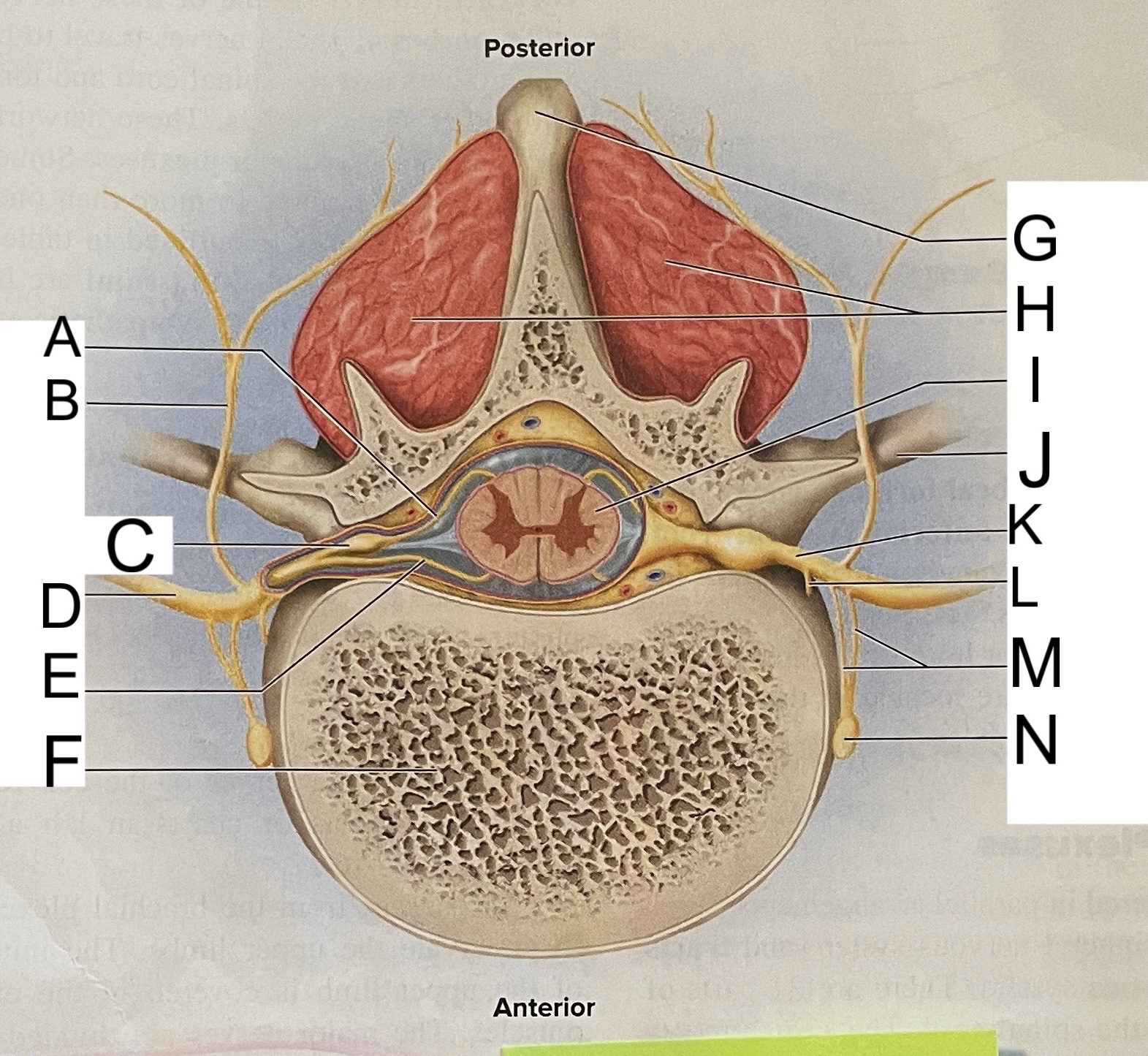
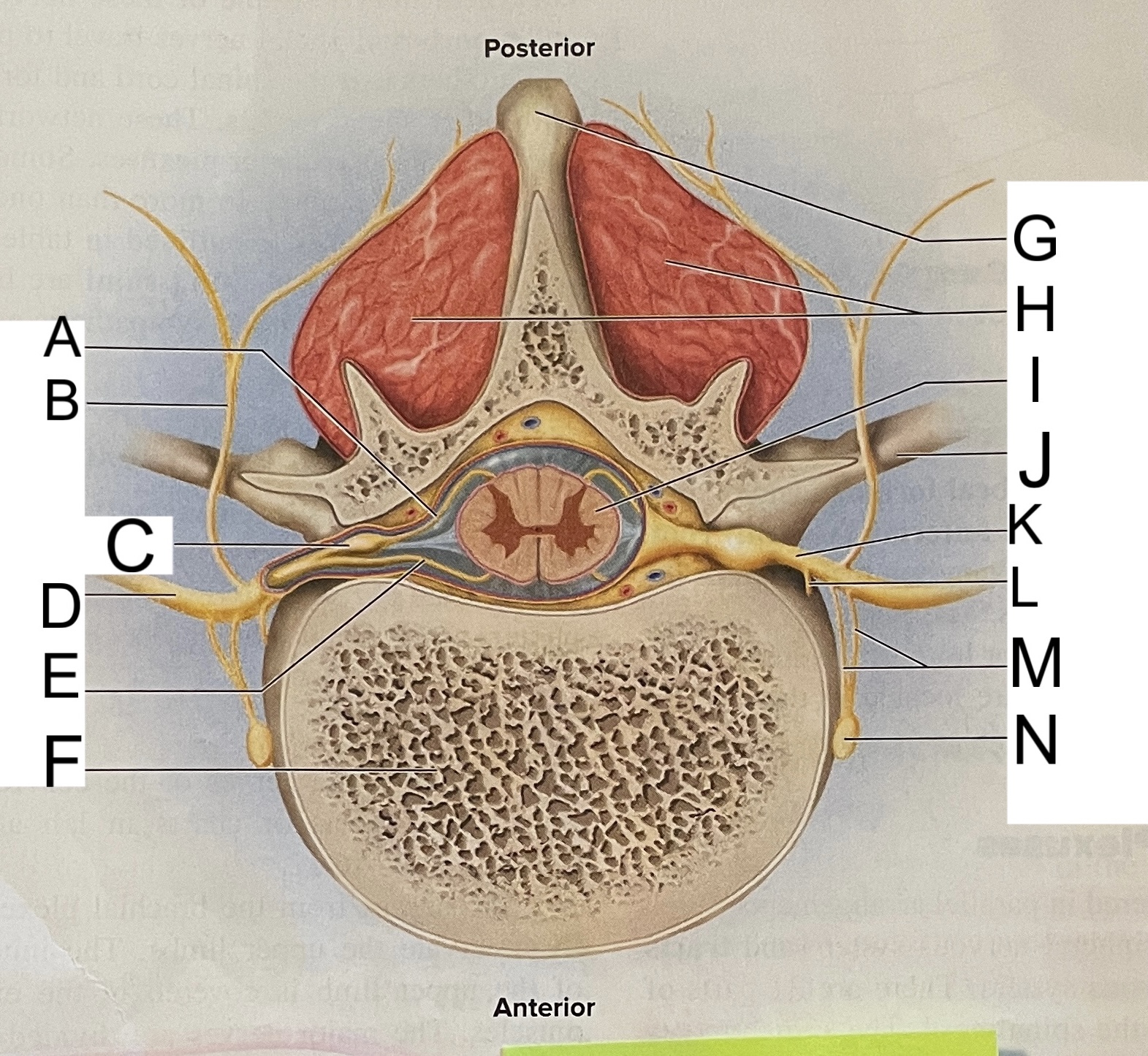
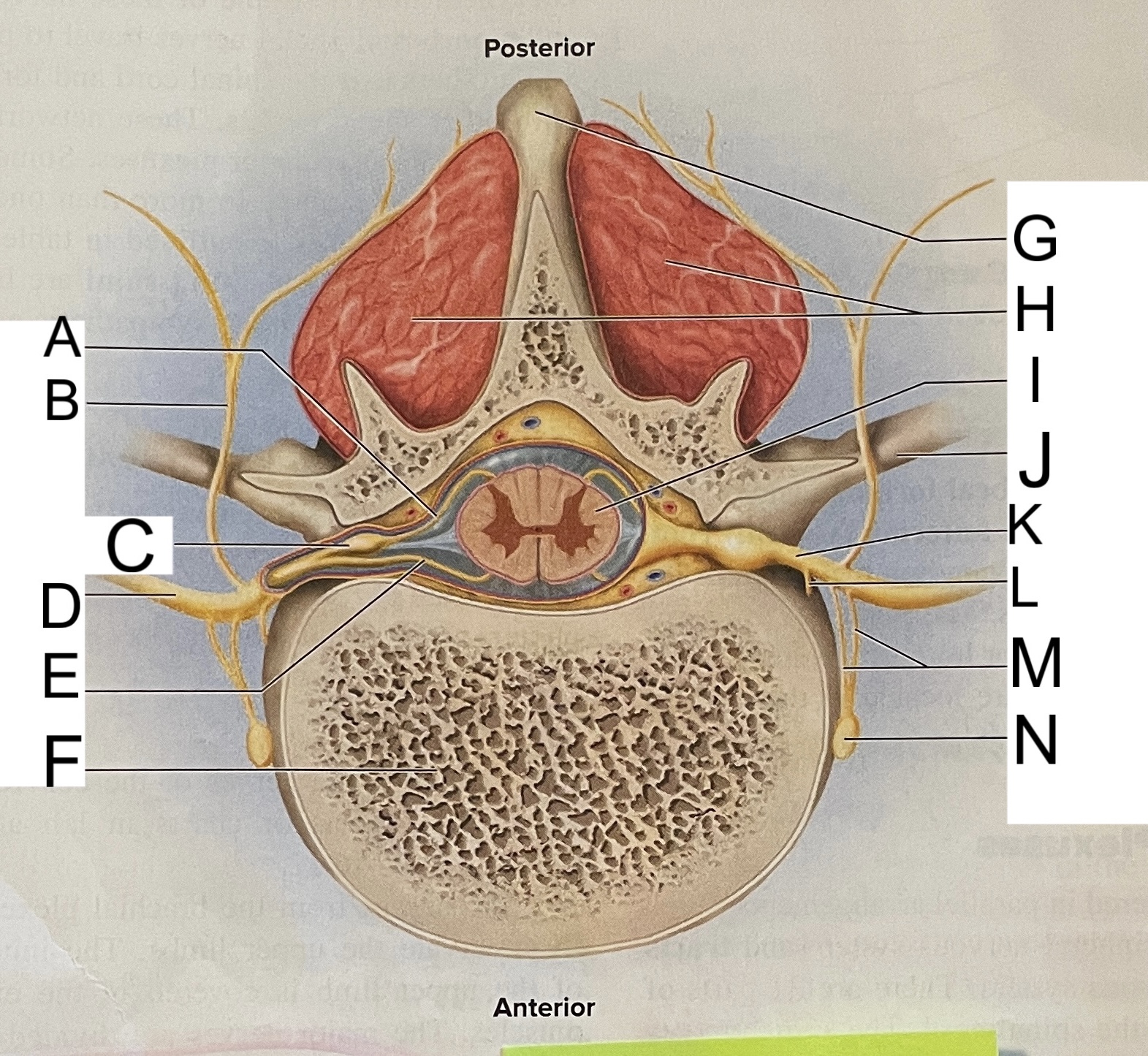
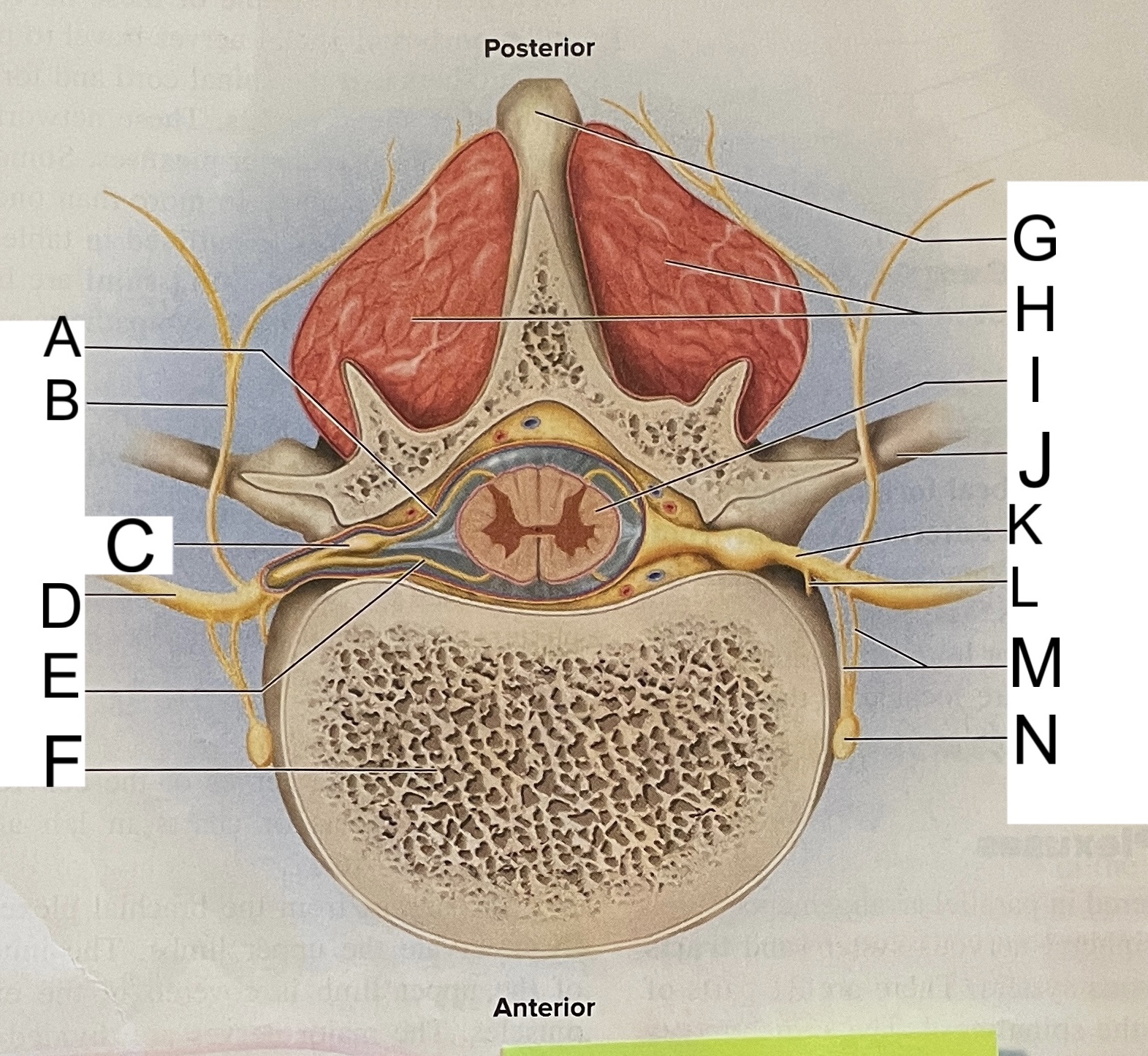
A
nissl bodies
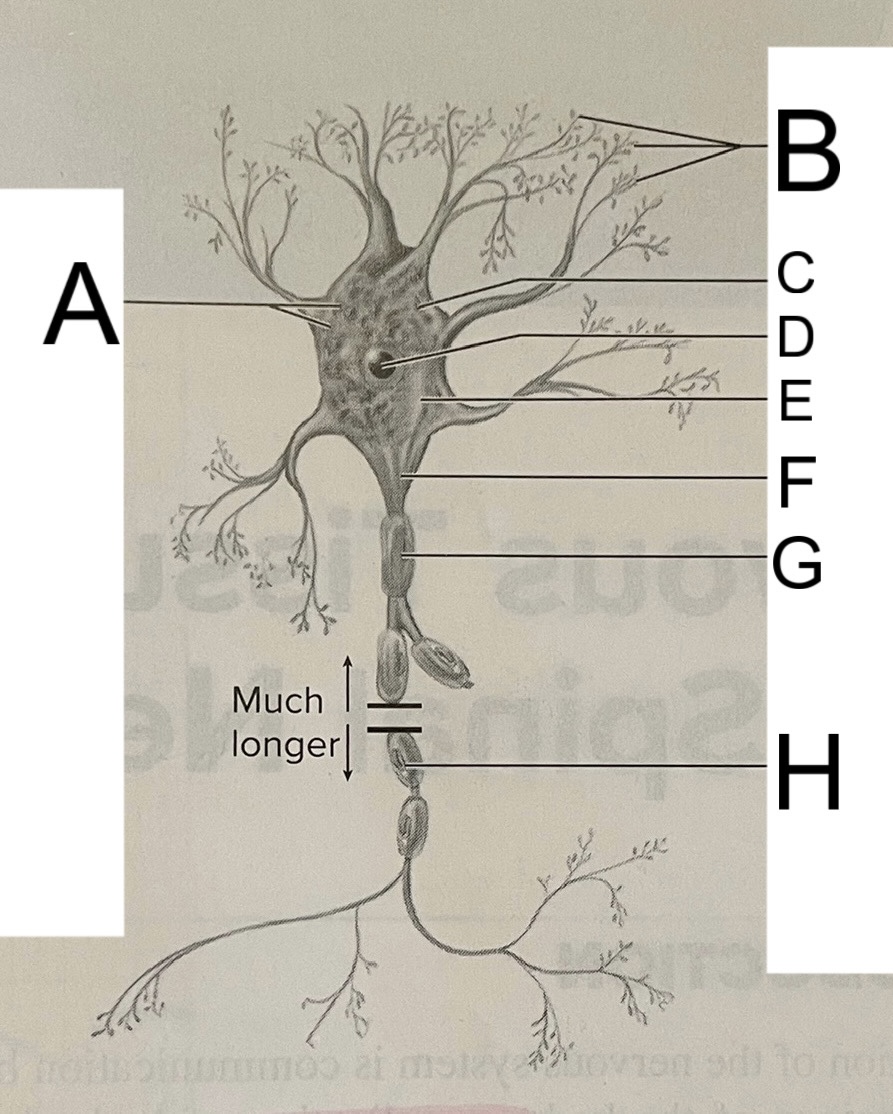
B
dendrites
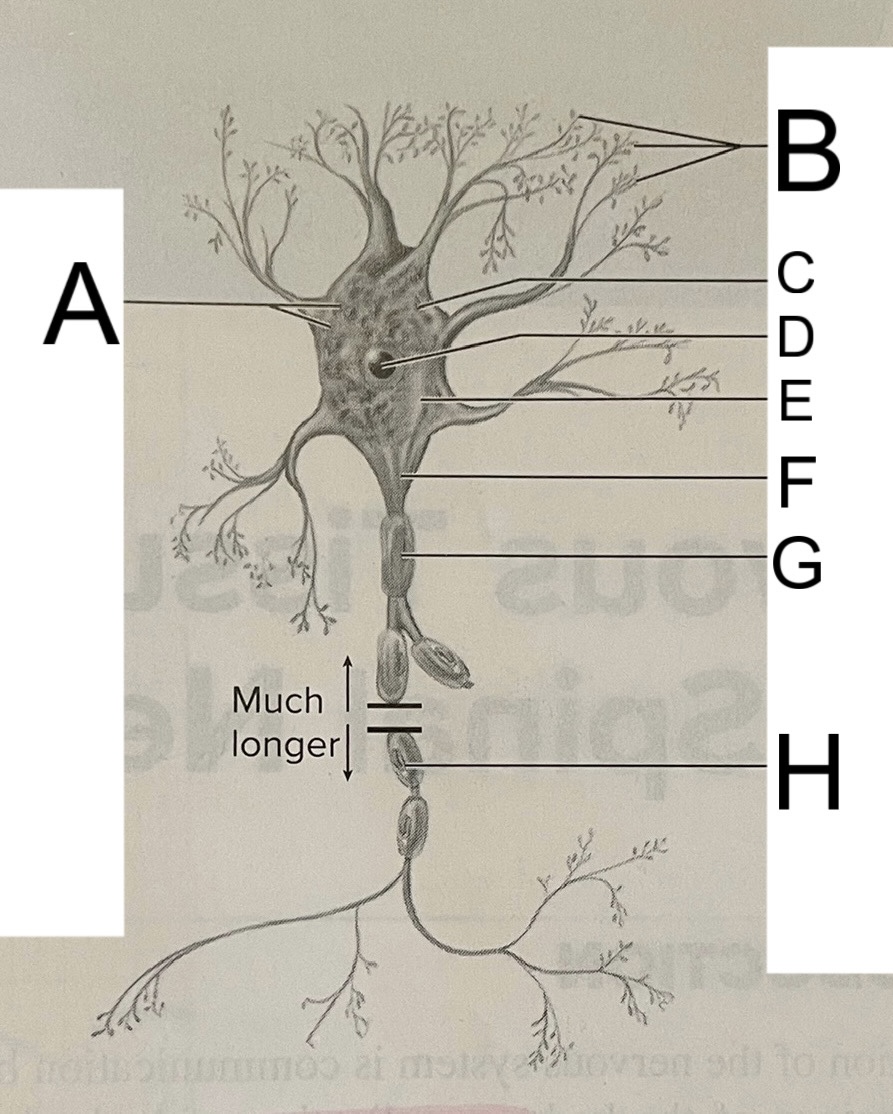
C
soma
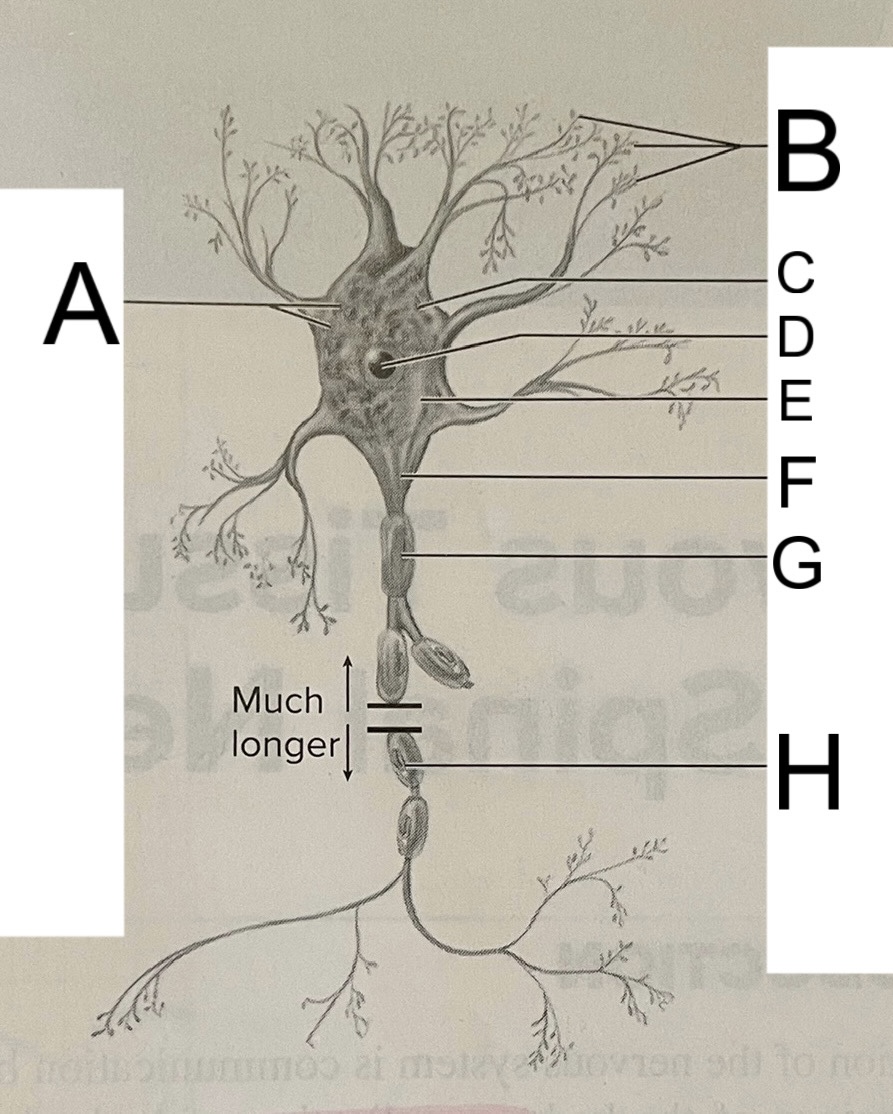
D
nucleus
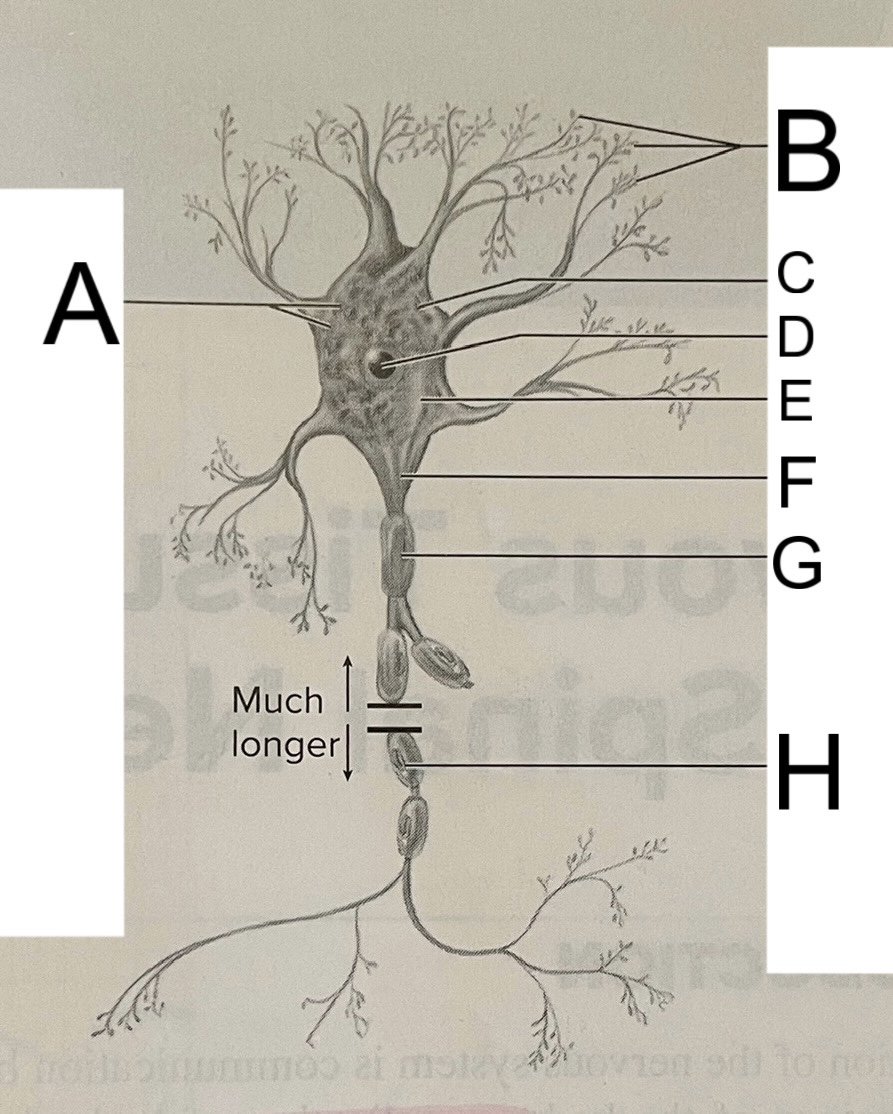
E
neuroplasm
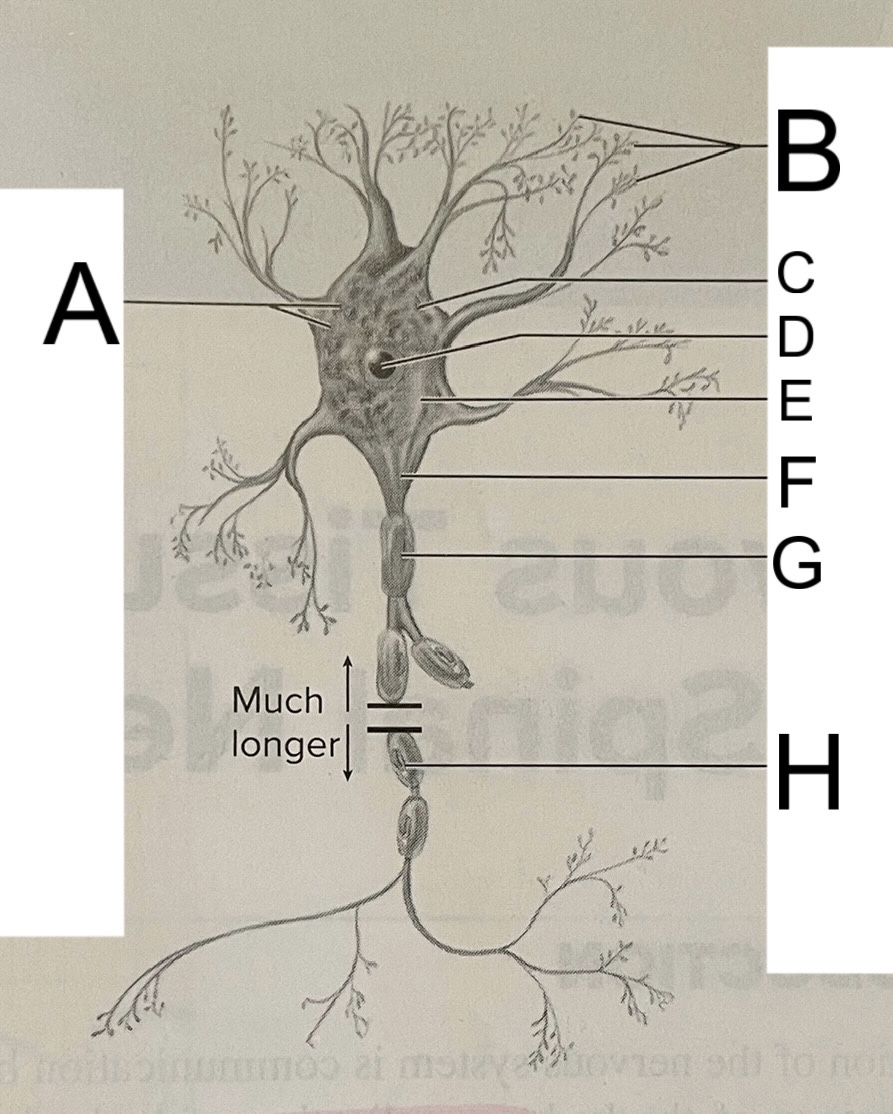
F
axon hillock
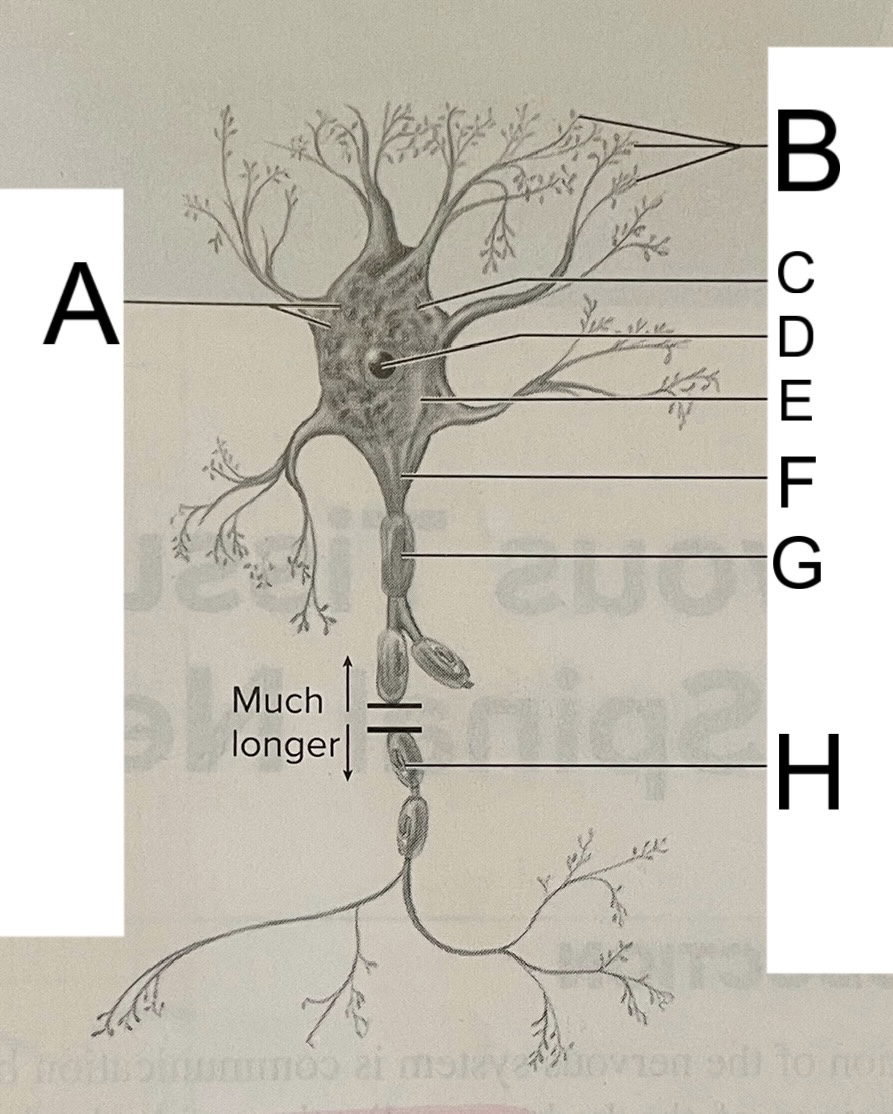
G
axon
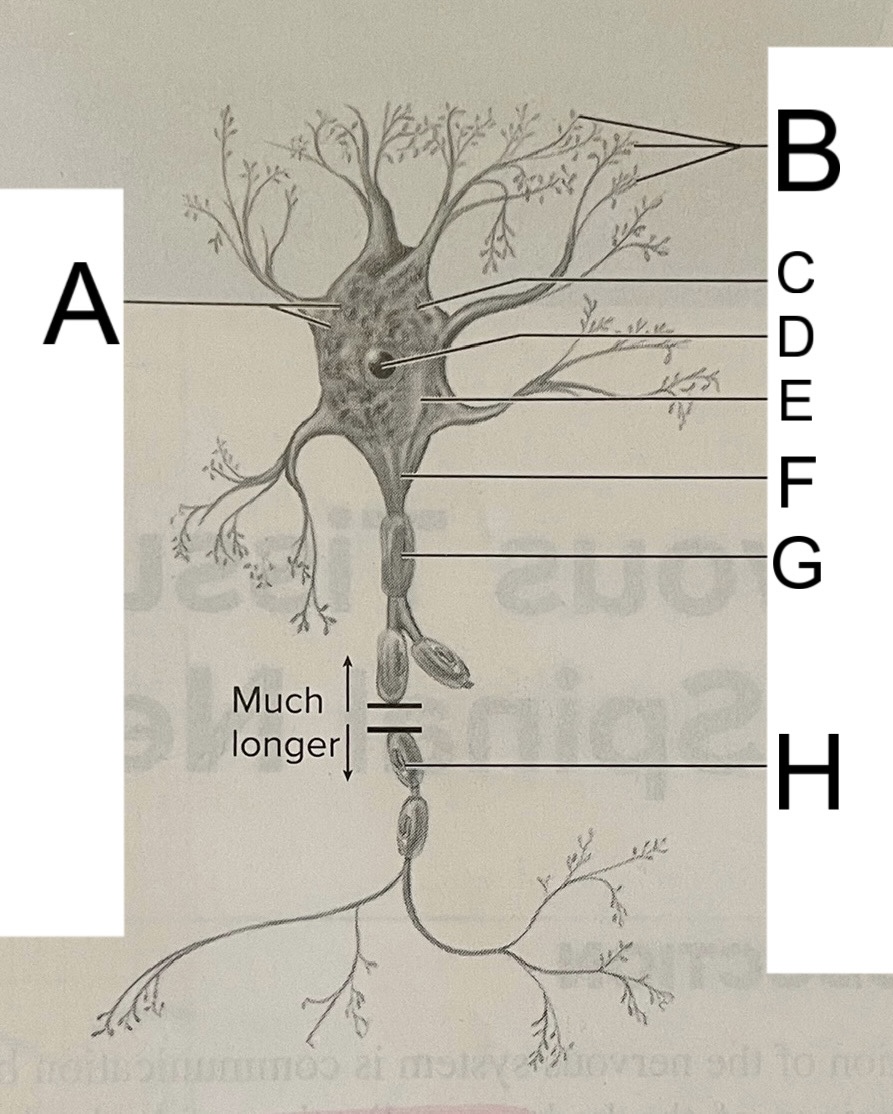
H
schwann cell
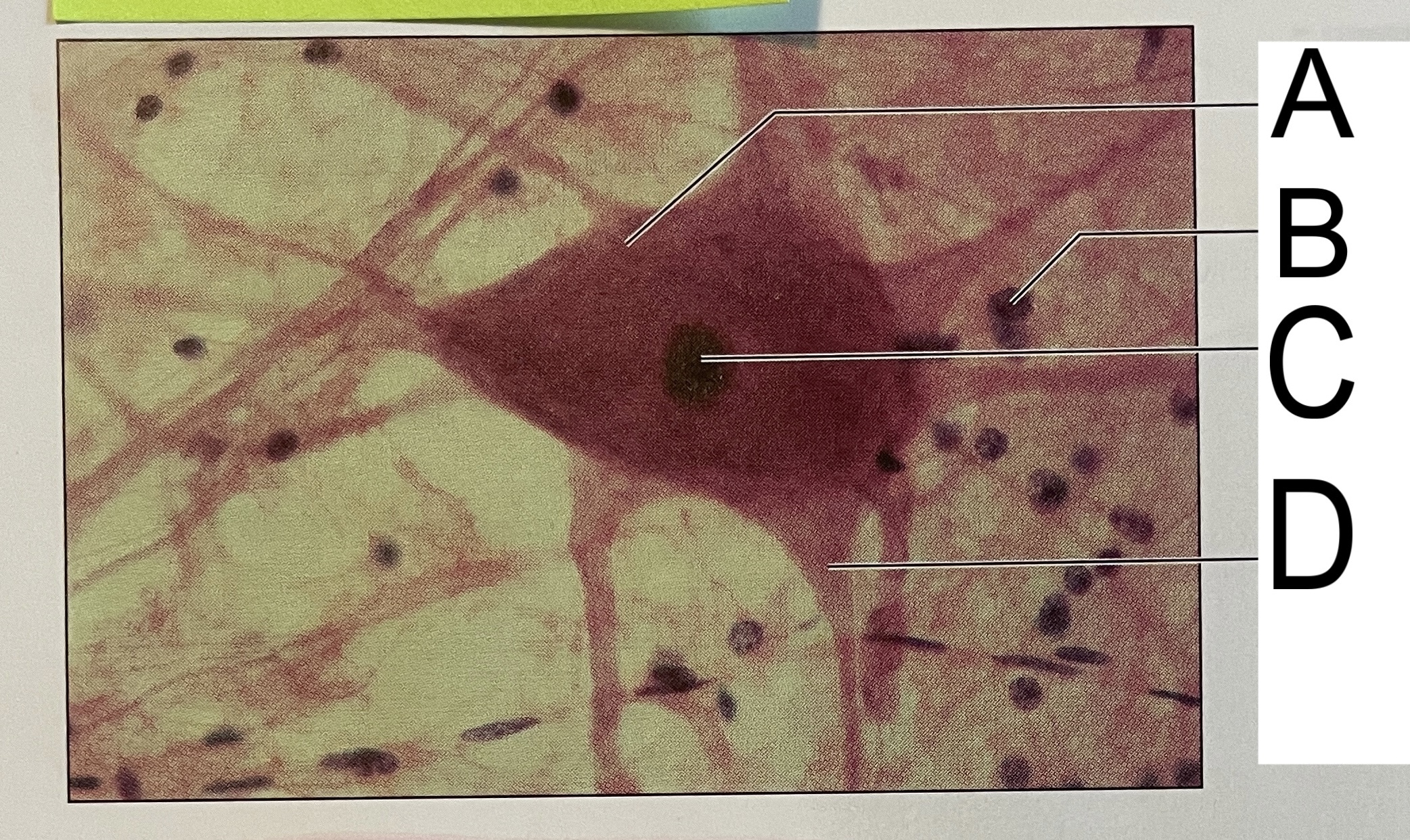
A
nissl bodies
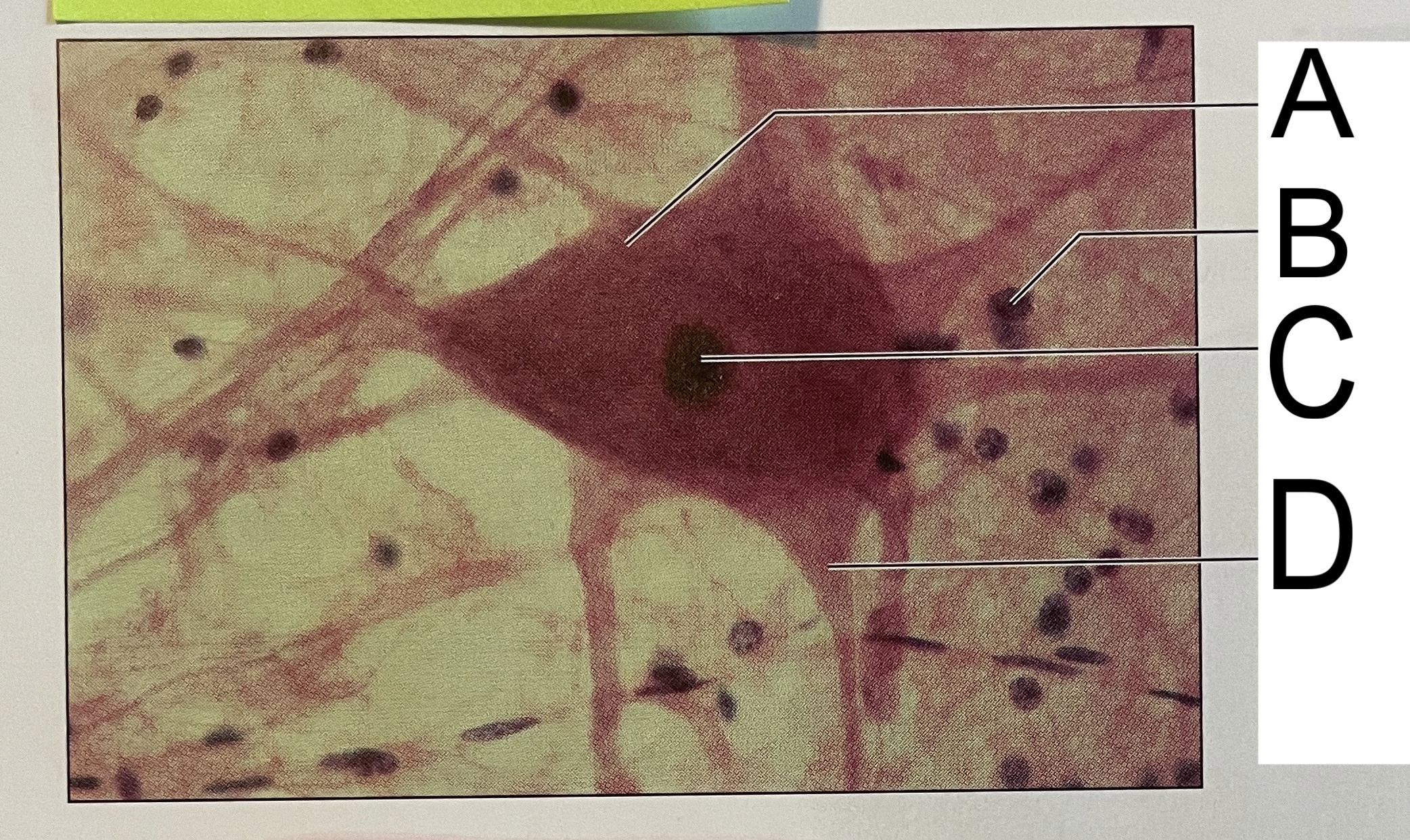
B
neuroglia
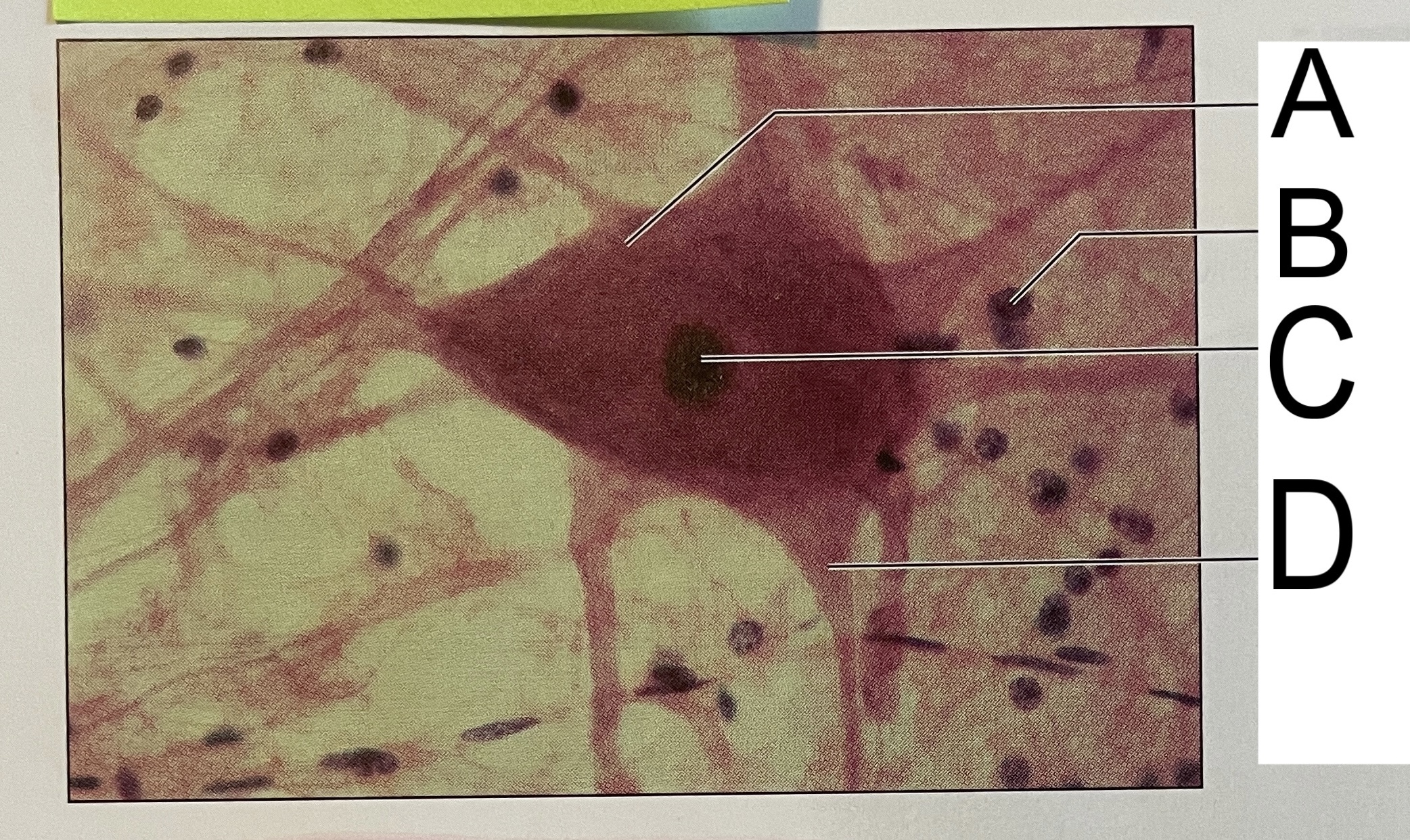
C
nucleus
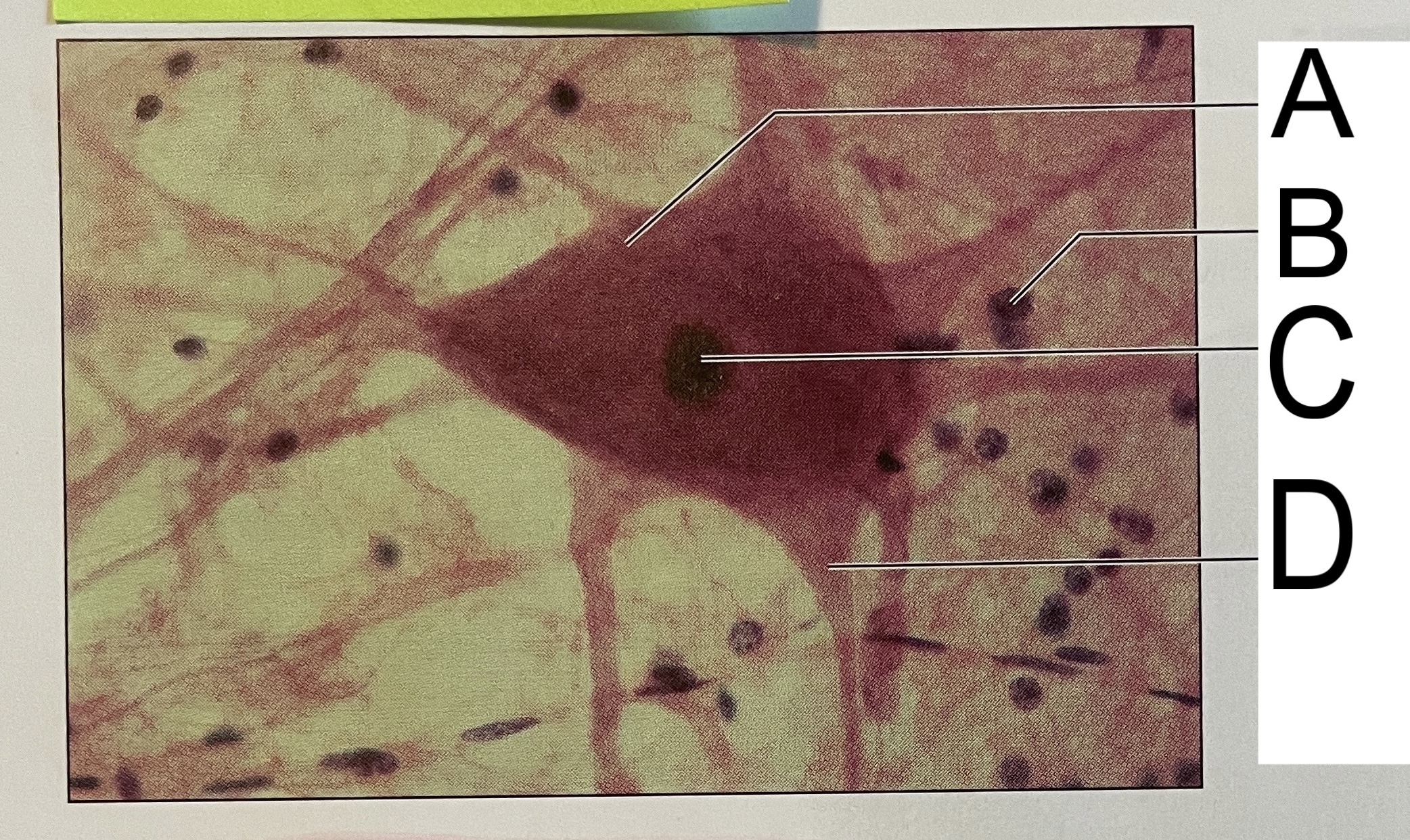
D
axon hillock
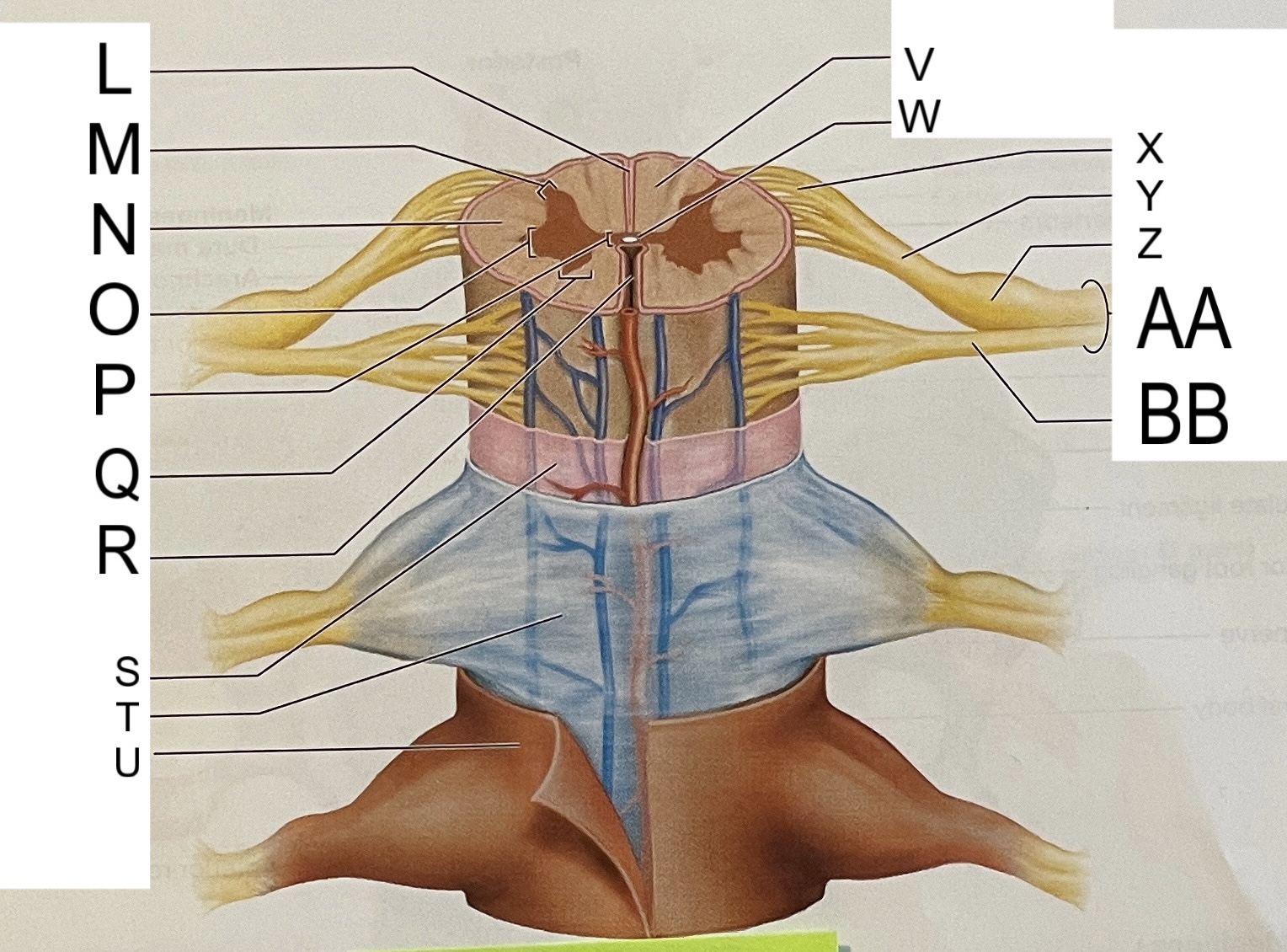
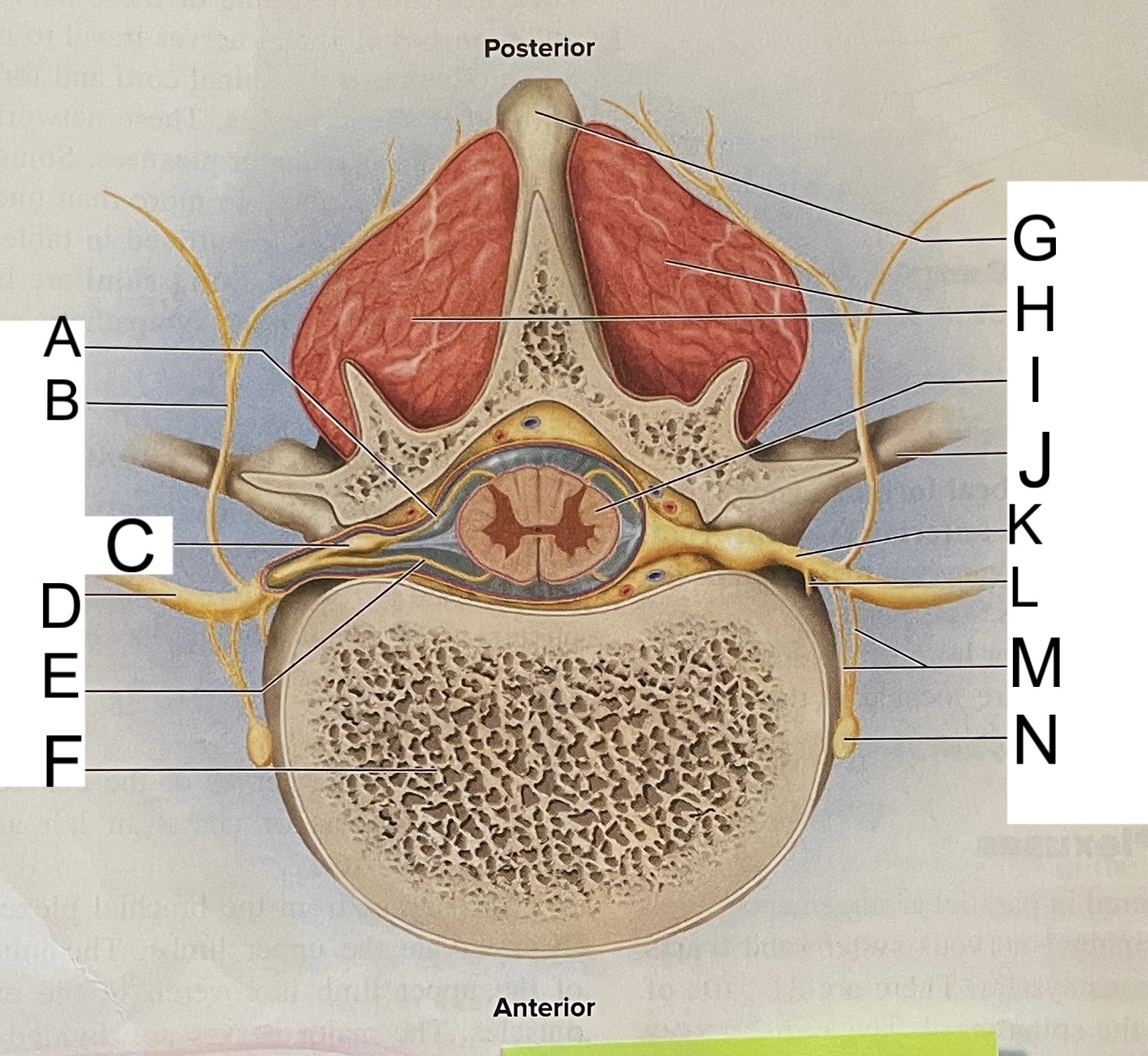
L
posterior median sulcus
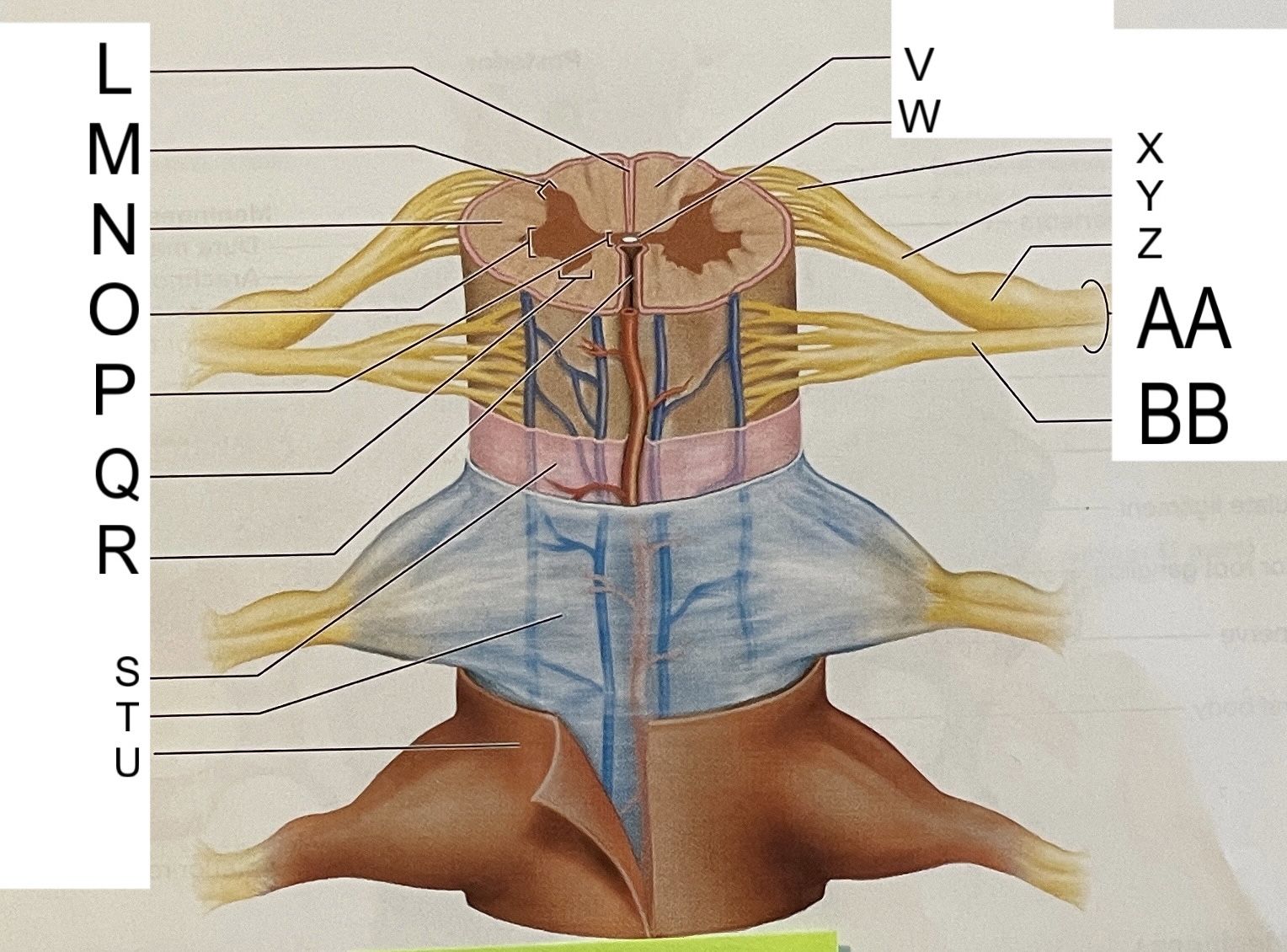
M
posterior/dorsal horn
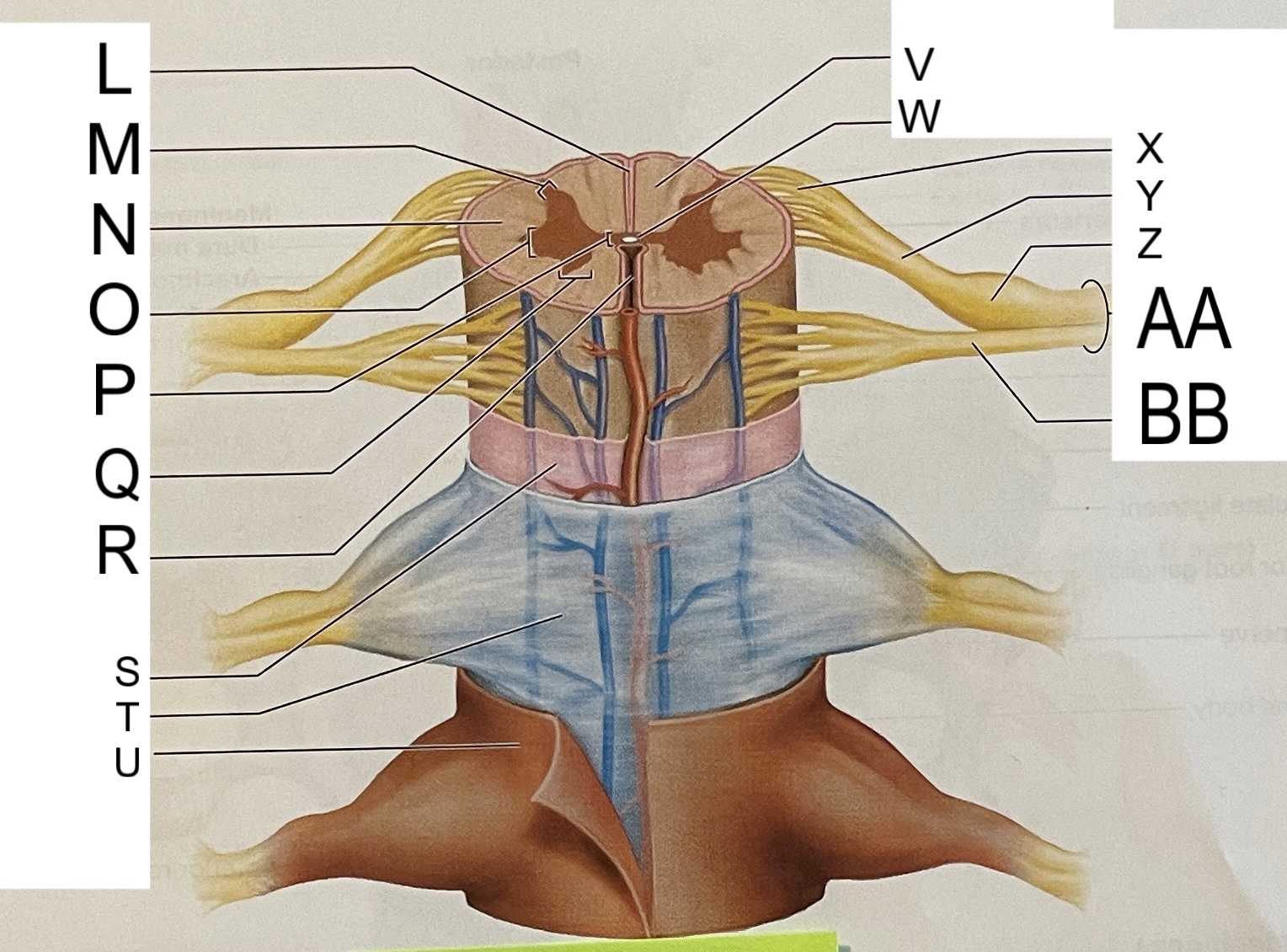
N
lateral column
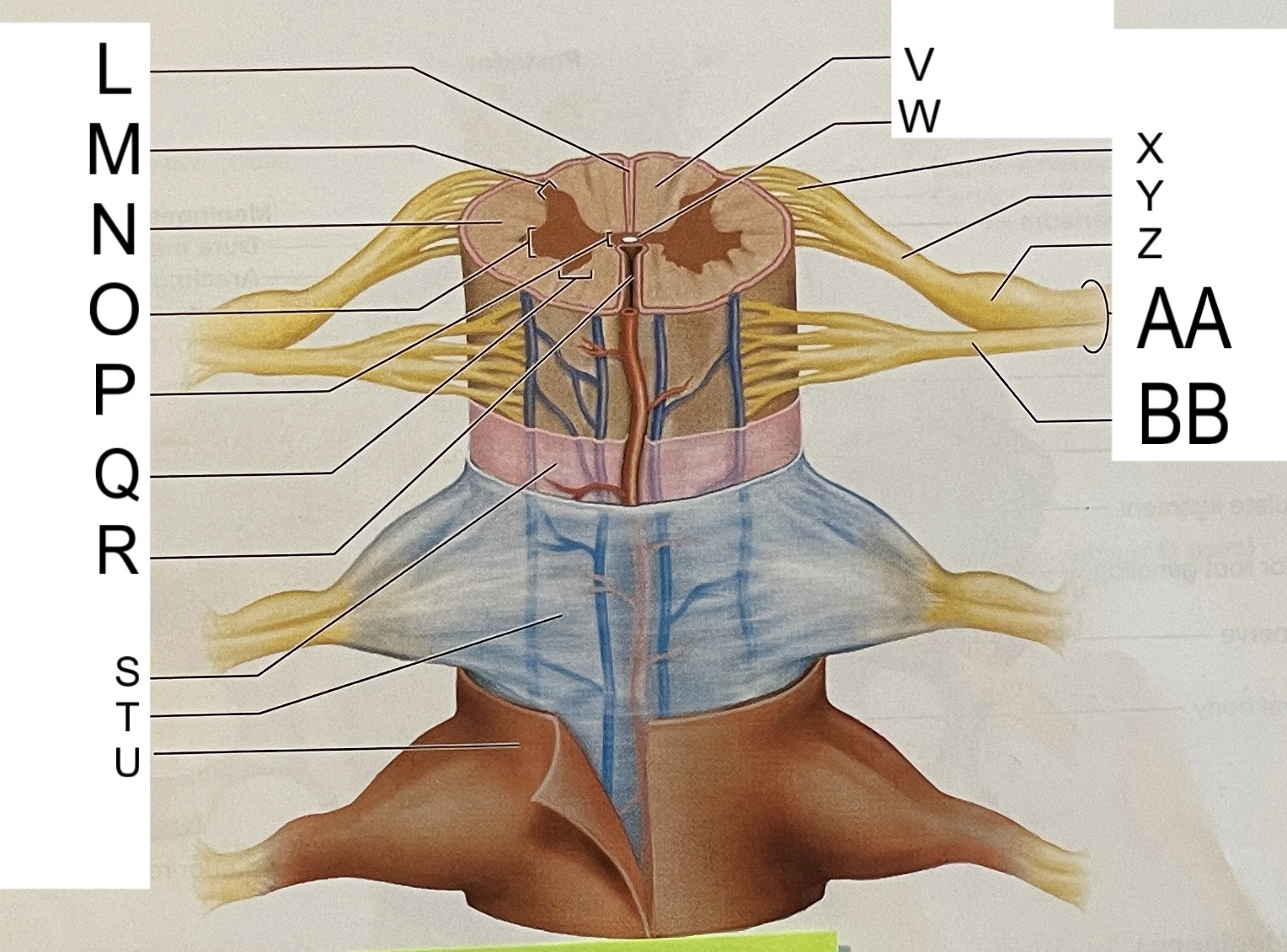
O
lateral horn
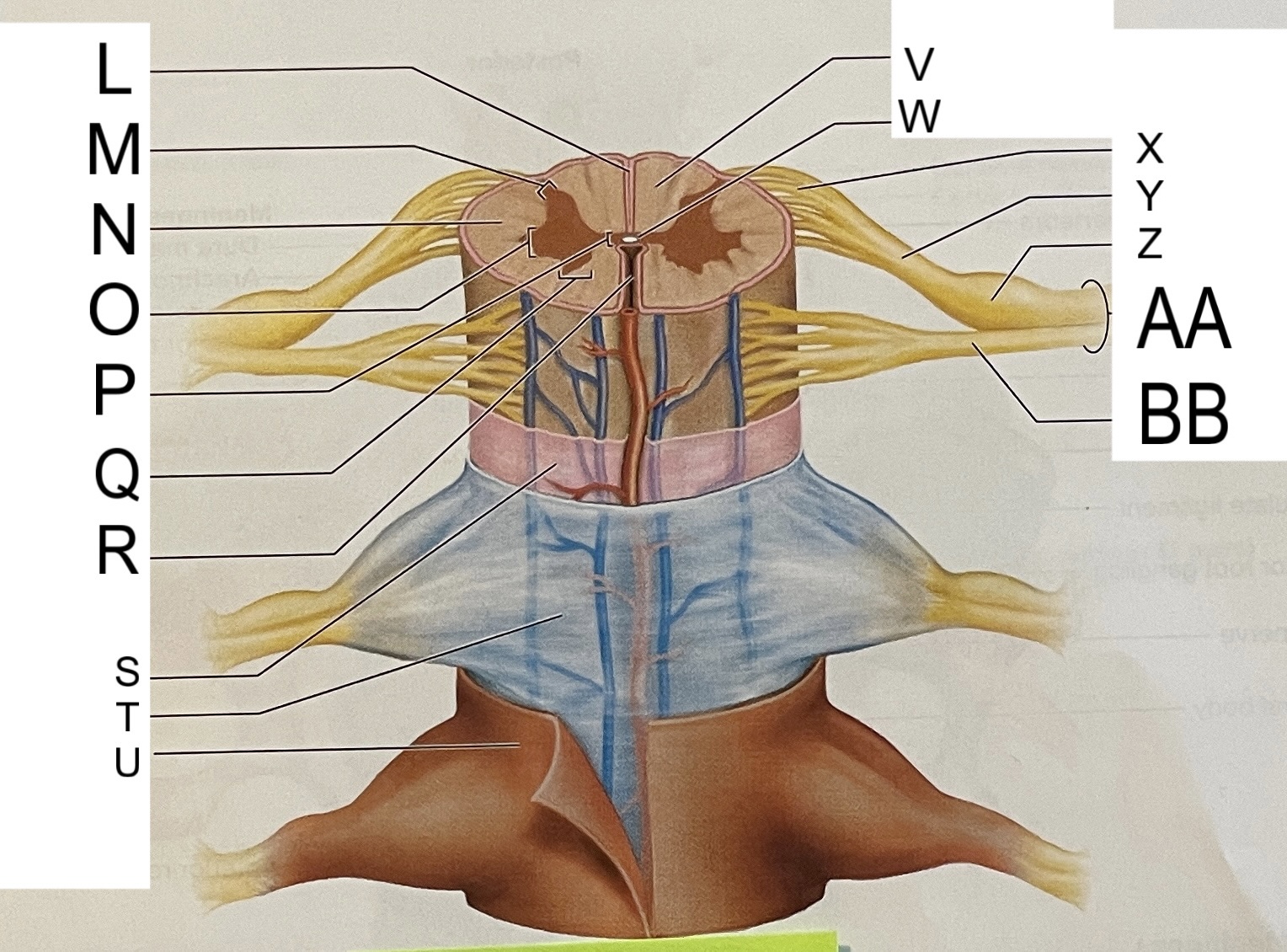
P
gray commissure
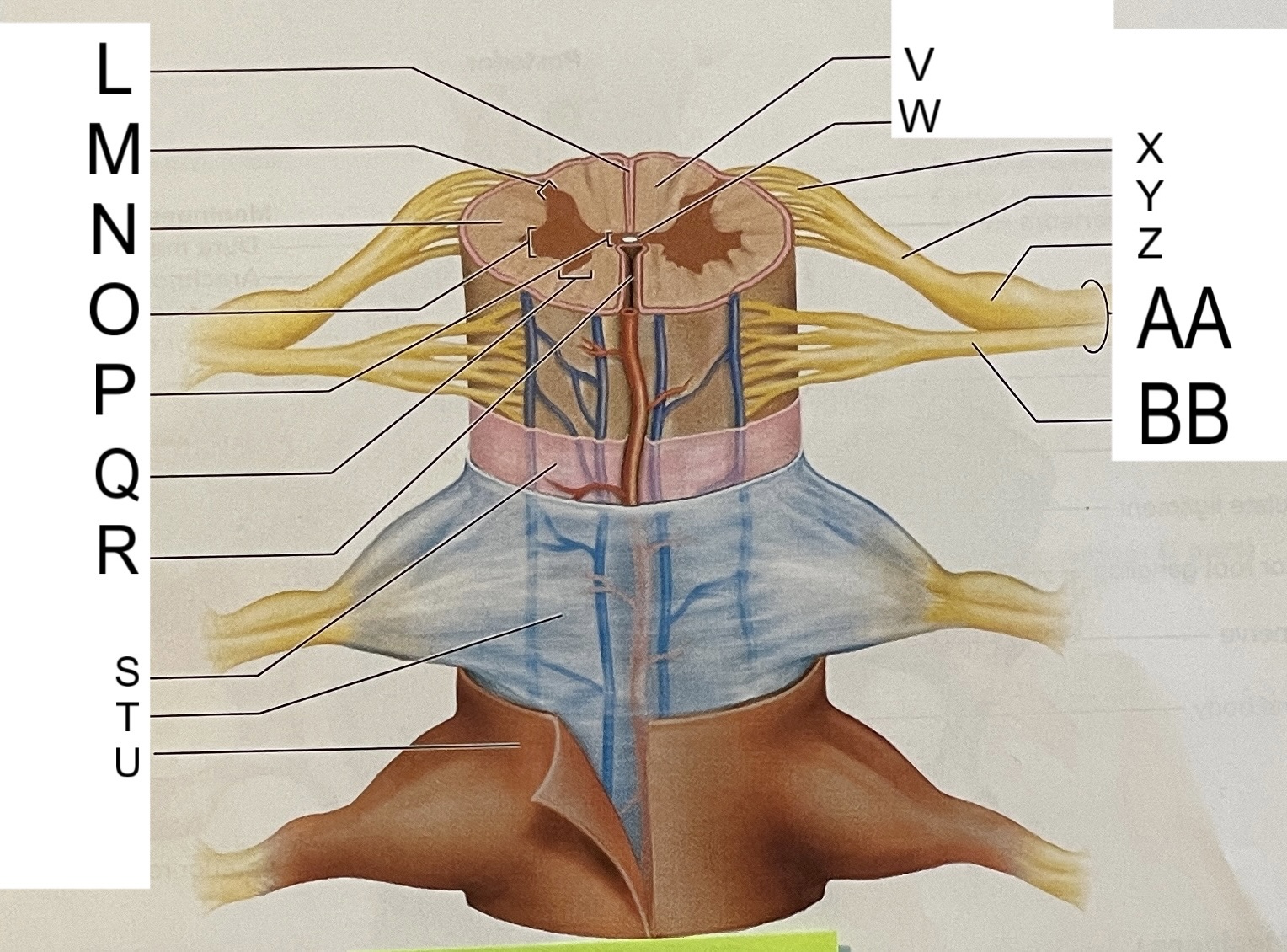
Q
anterior horn
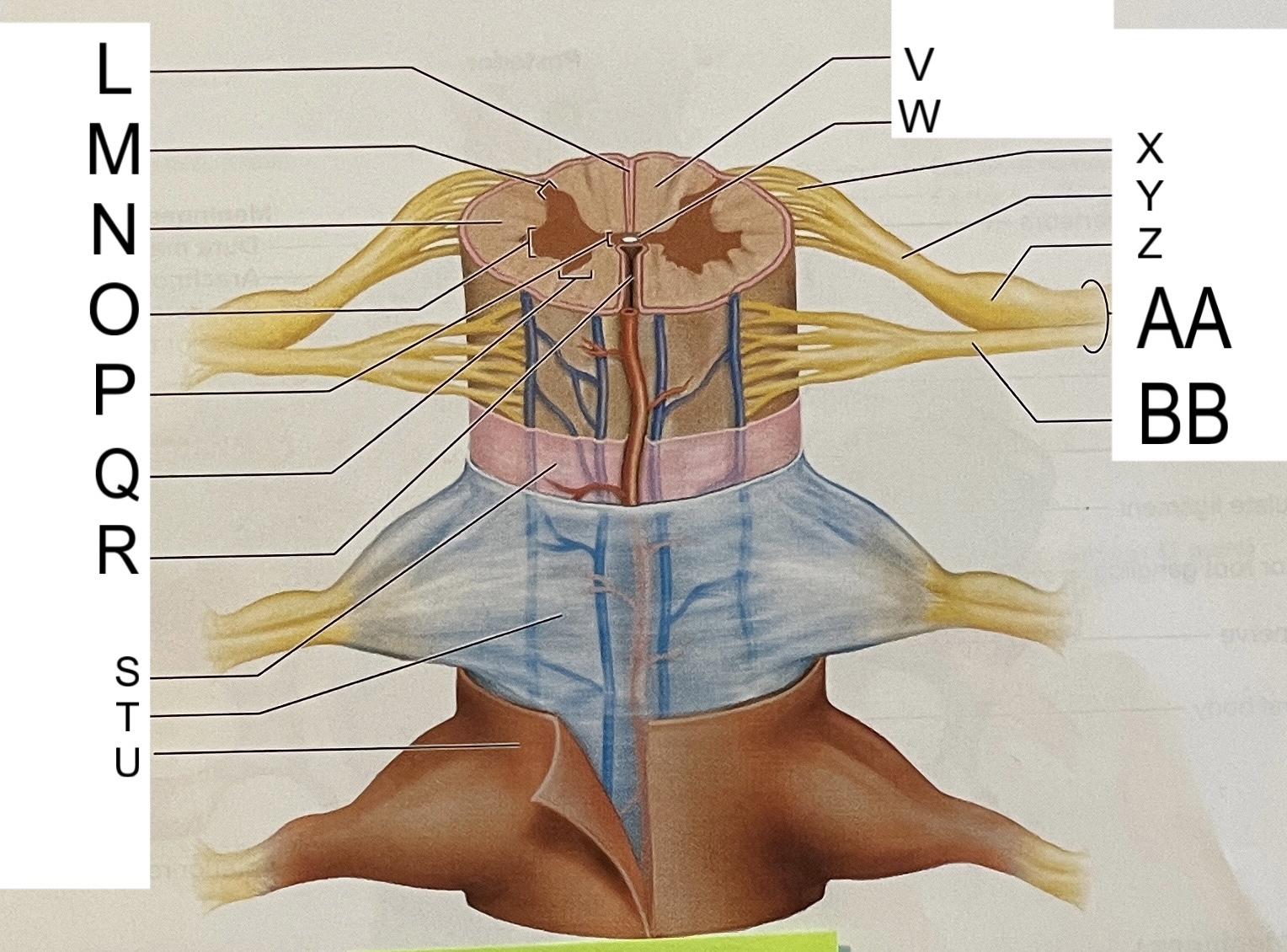
R
anterior median fissure
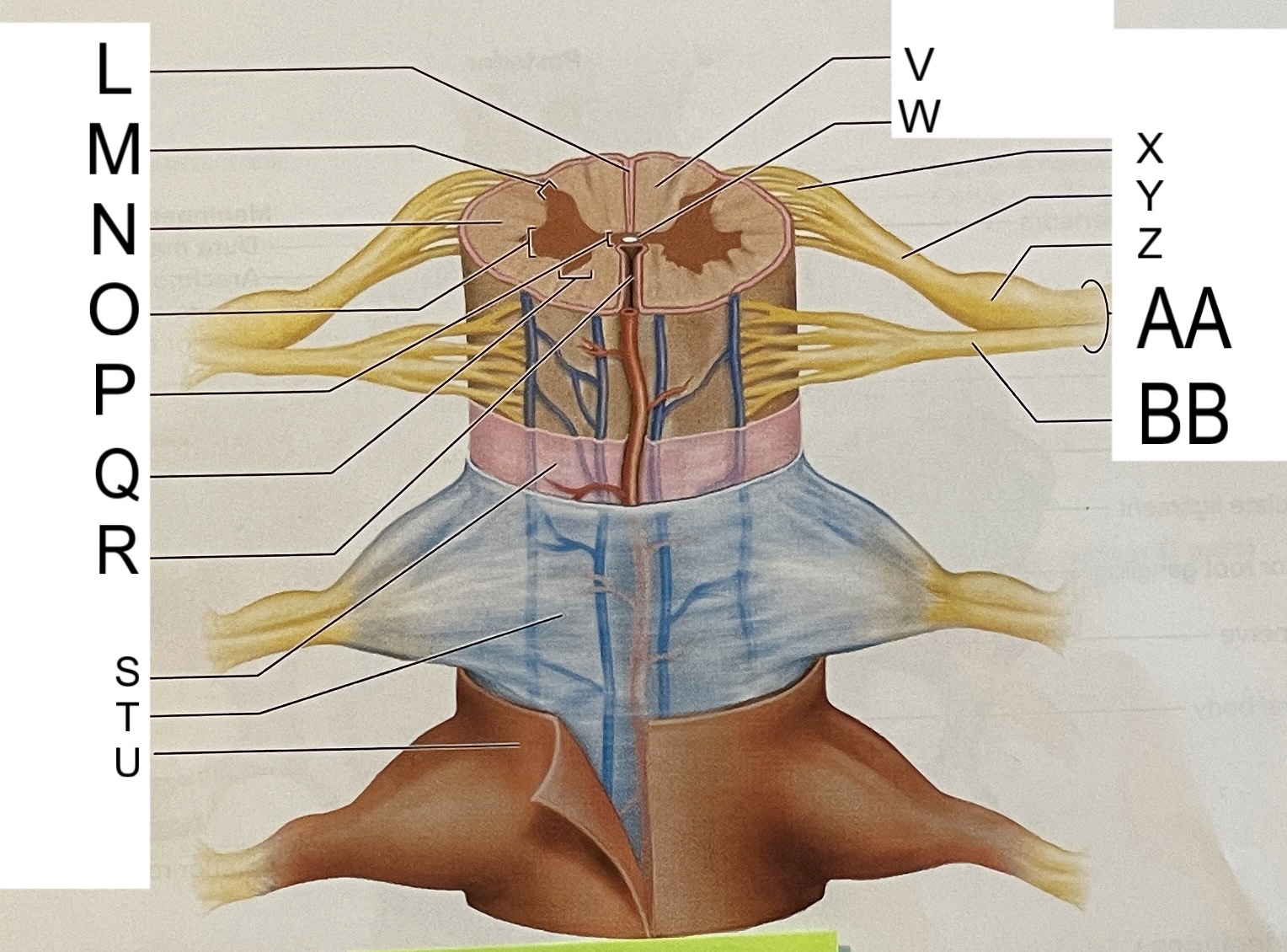
S
pia mater
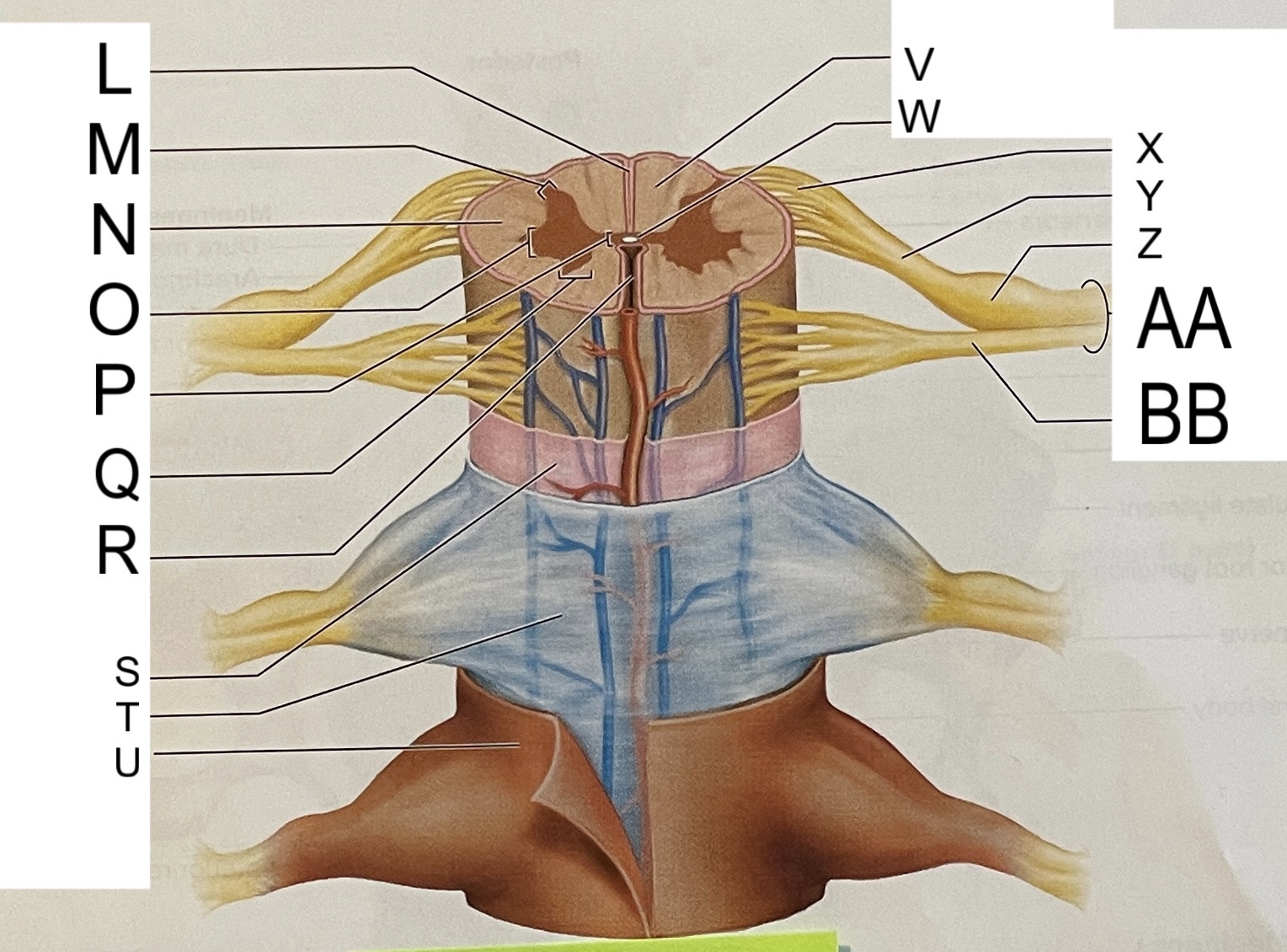
T
arachnoid mater
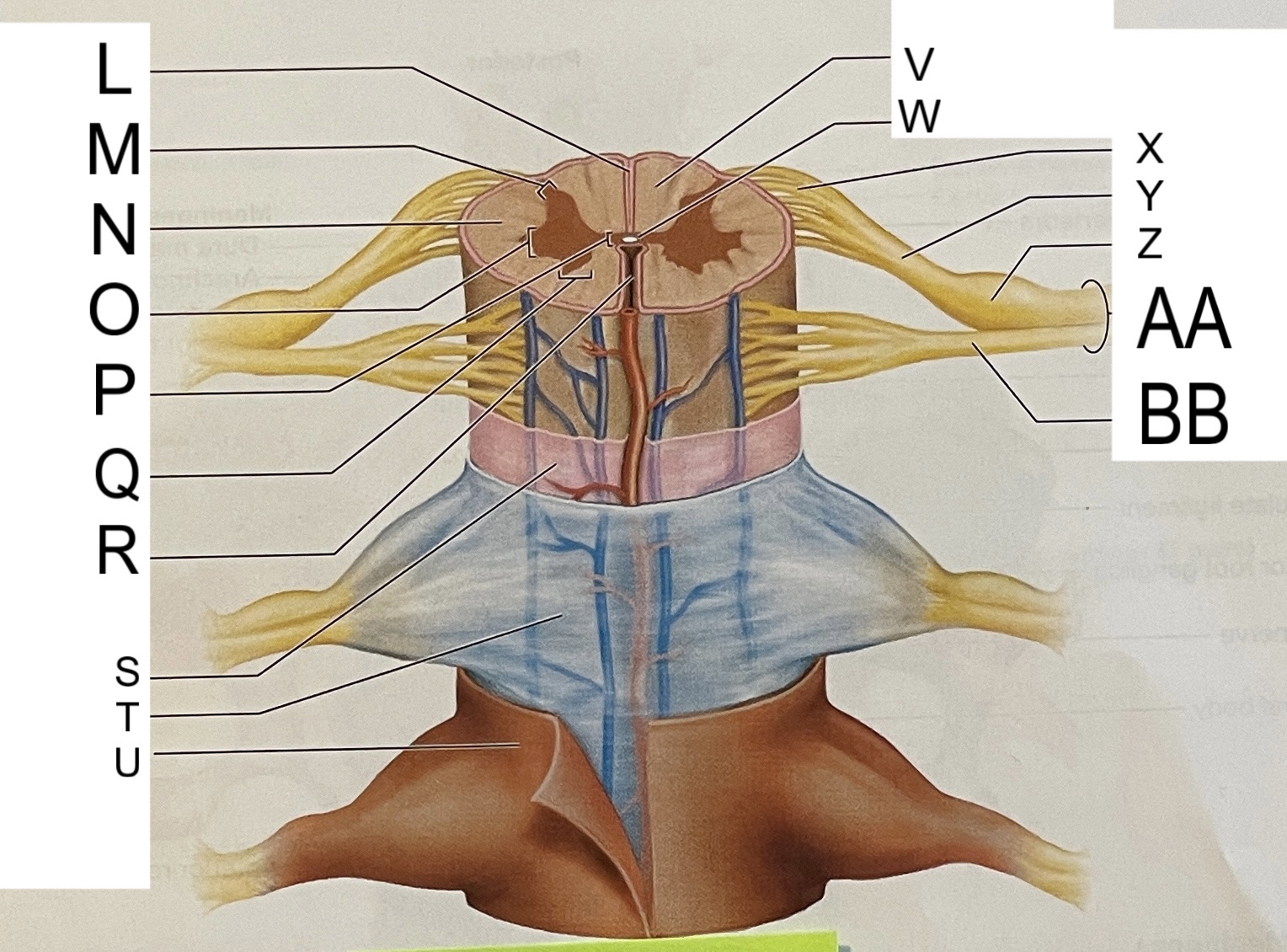
U
dura mater
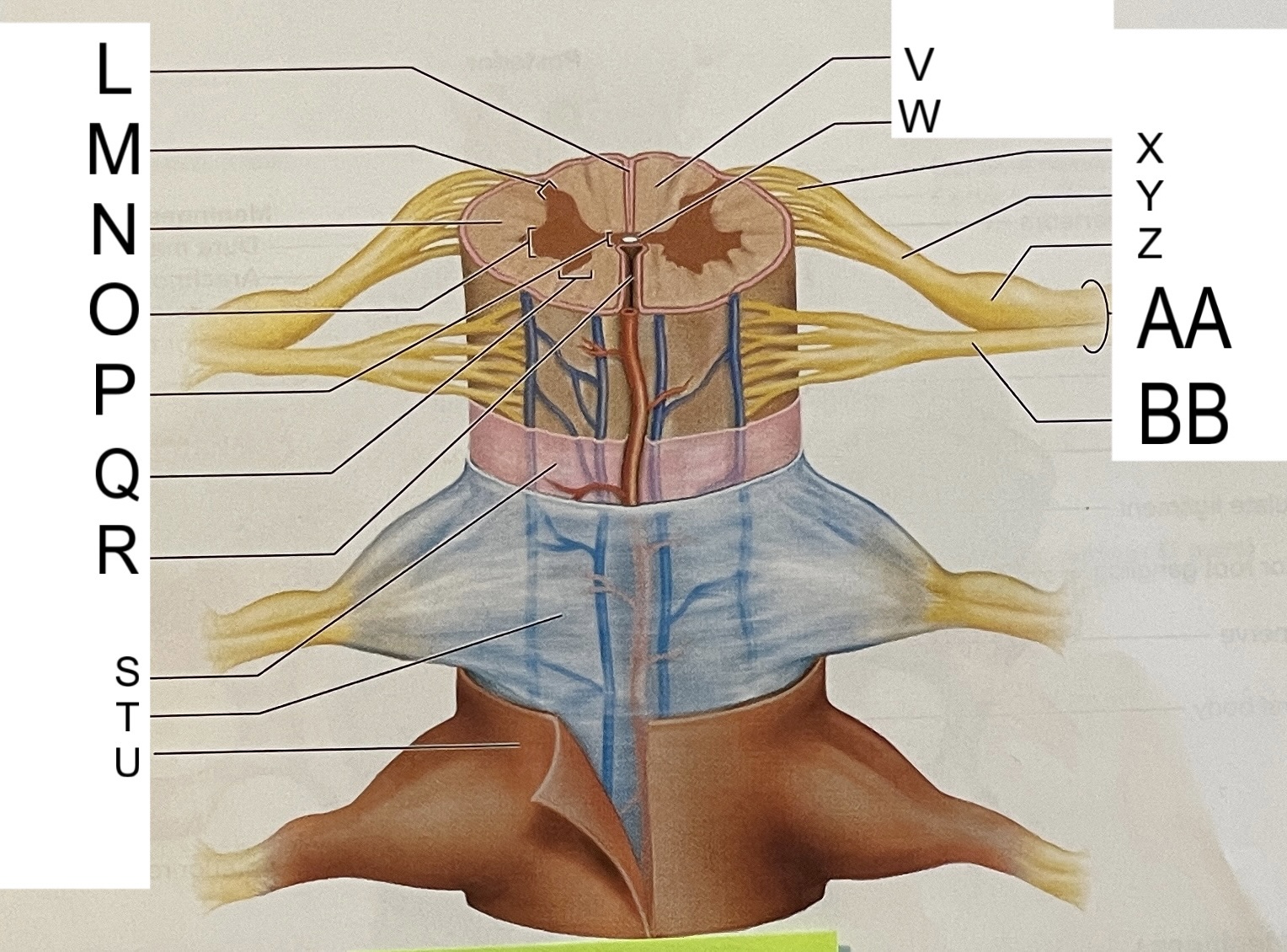
V
white matter
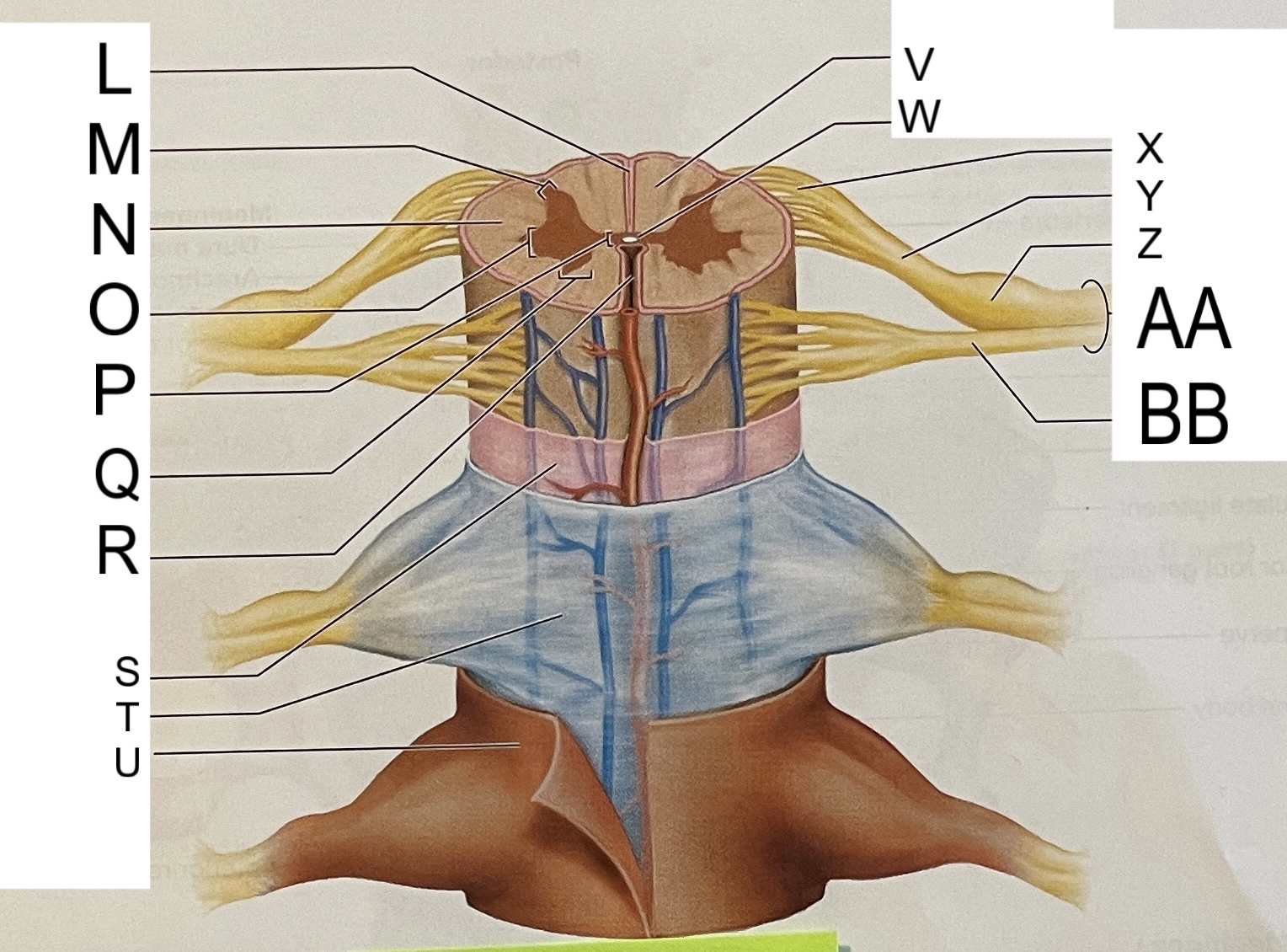
W
central canal
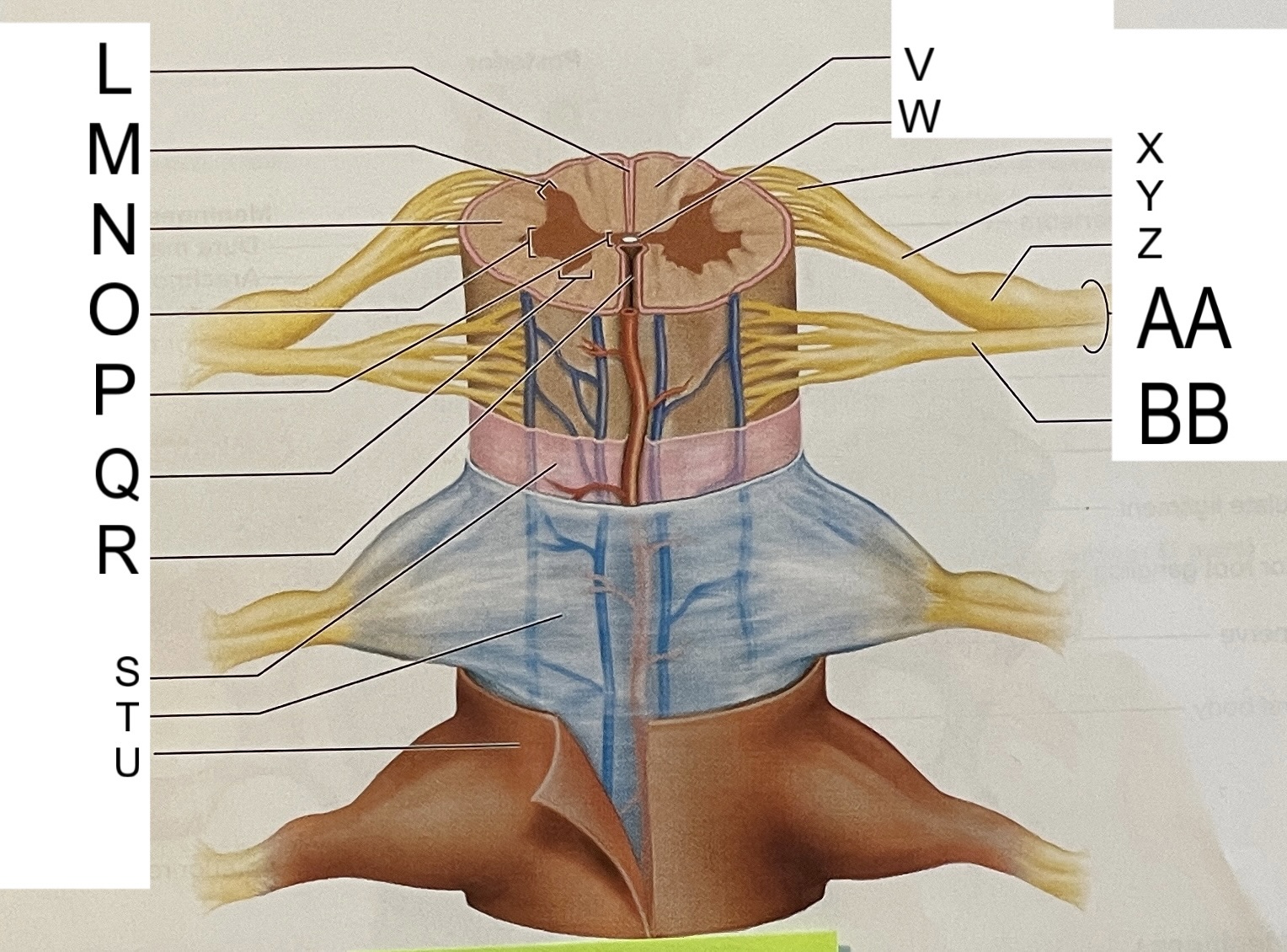
X
rootlets
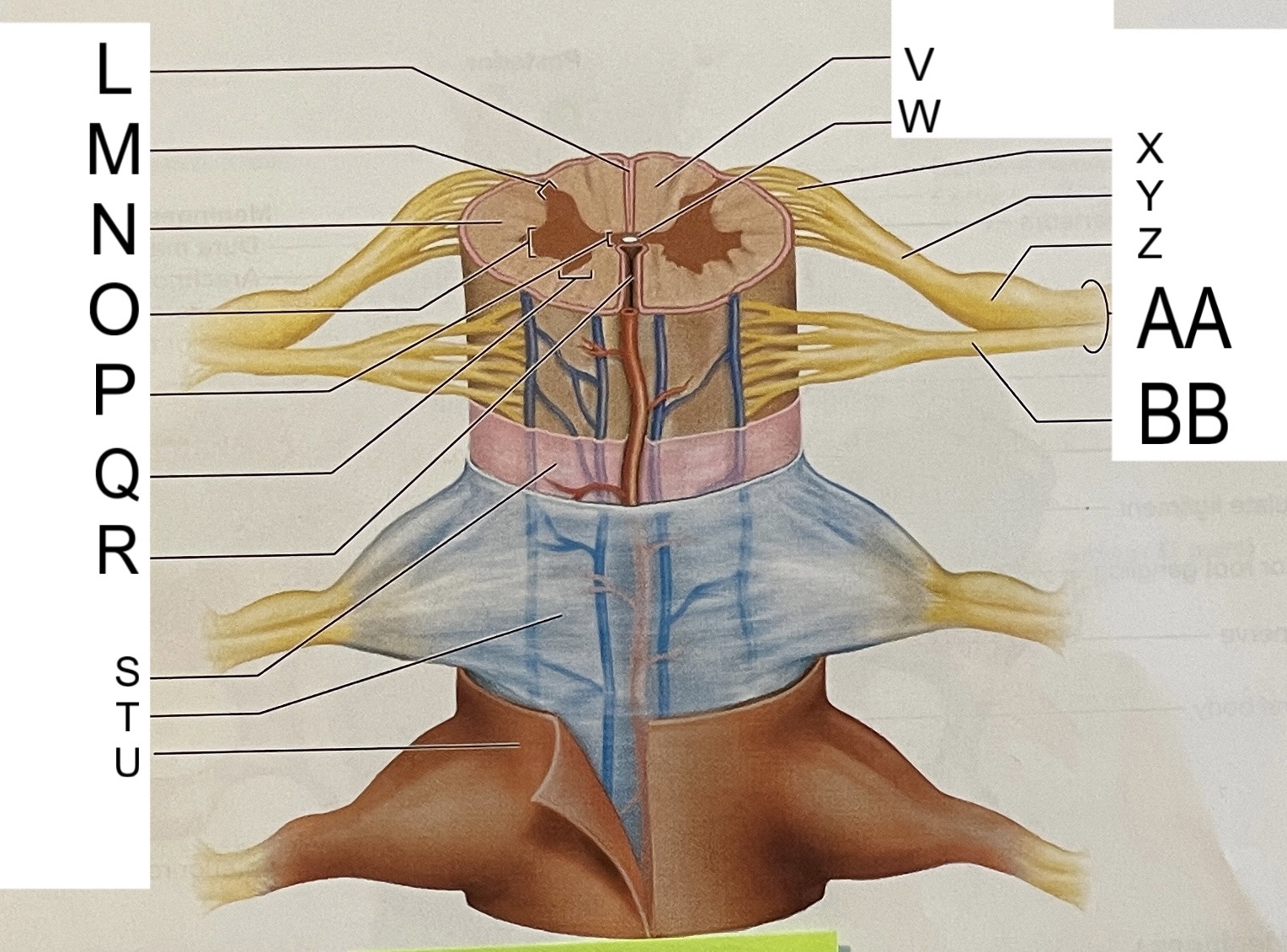
Y
posterior root of spinal nerve
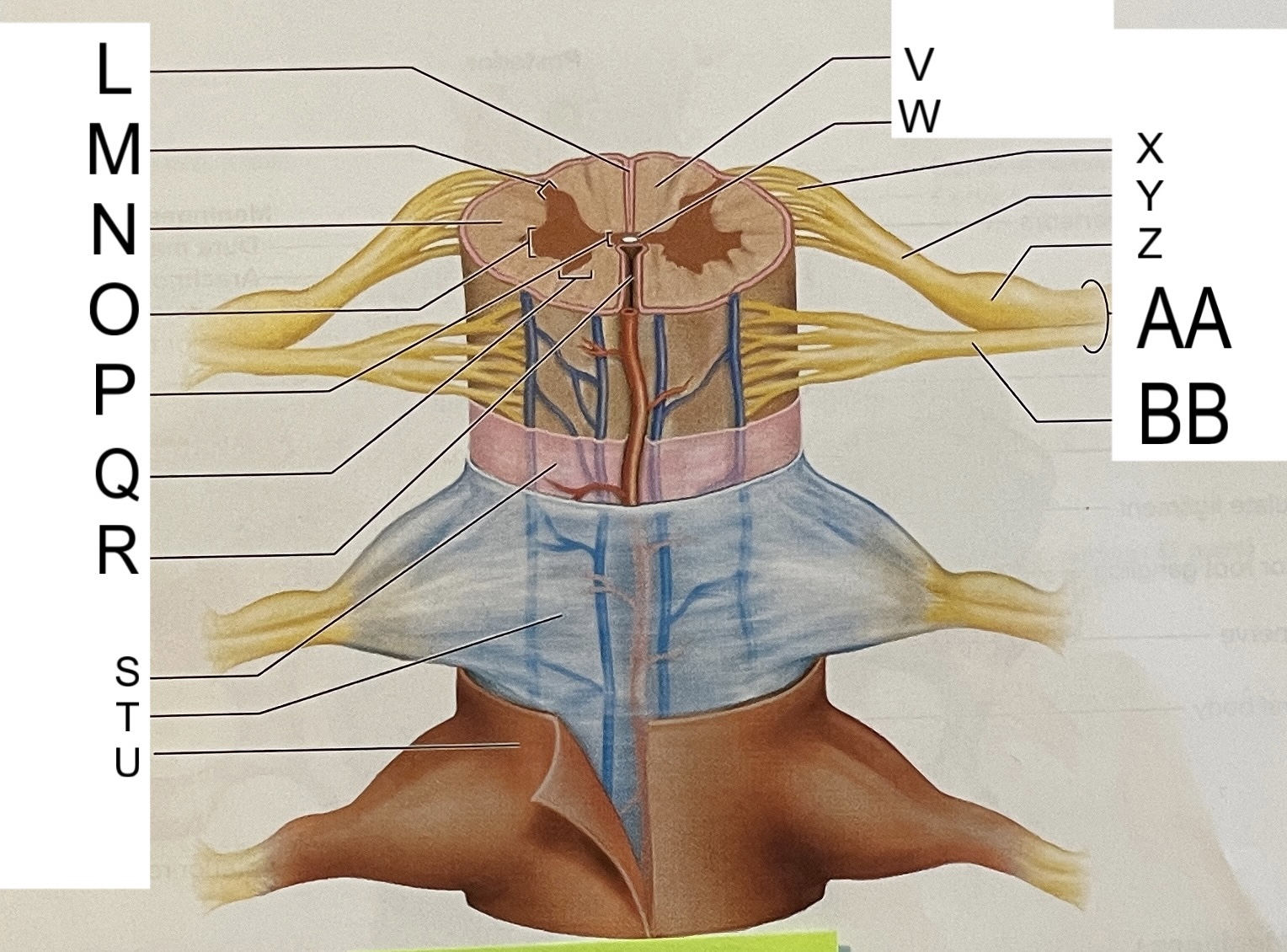
Z
dorsal root ganglion
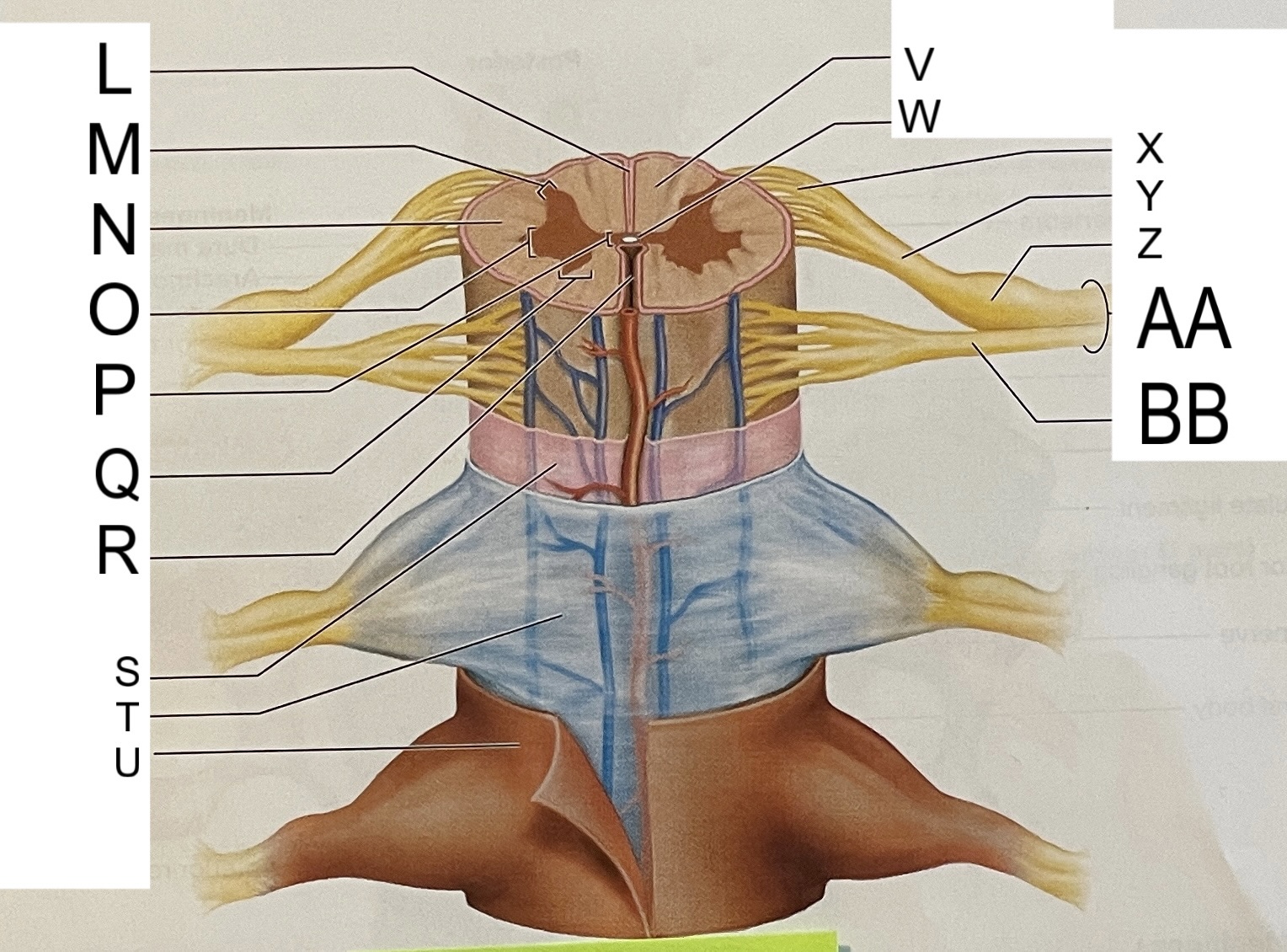
AA
Spinal nerve
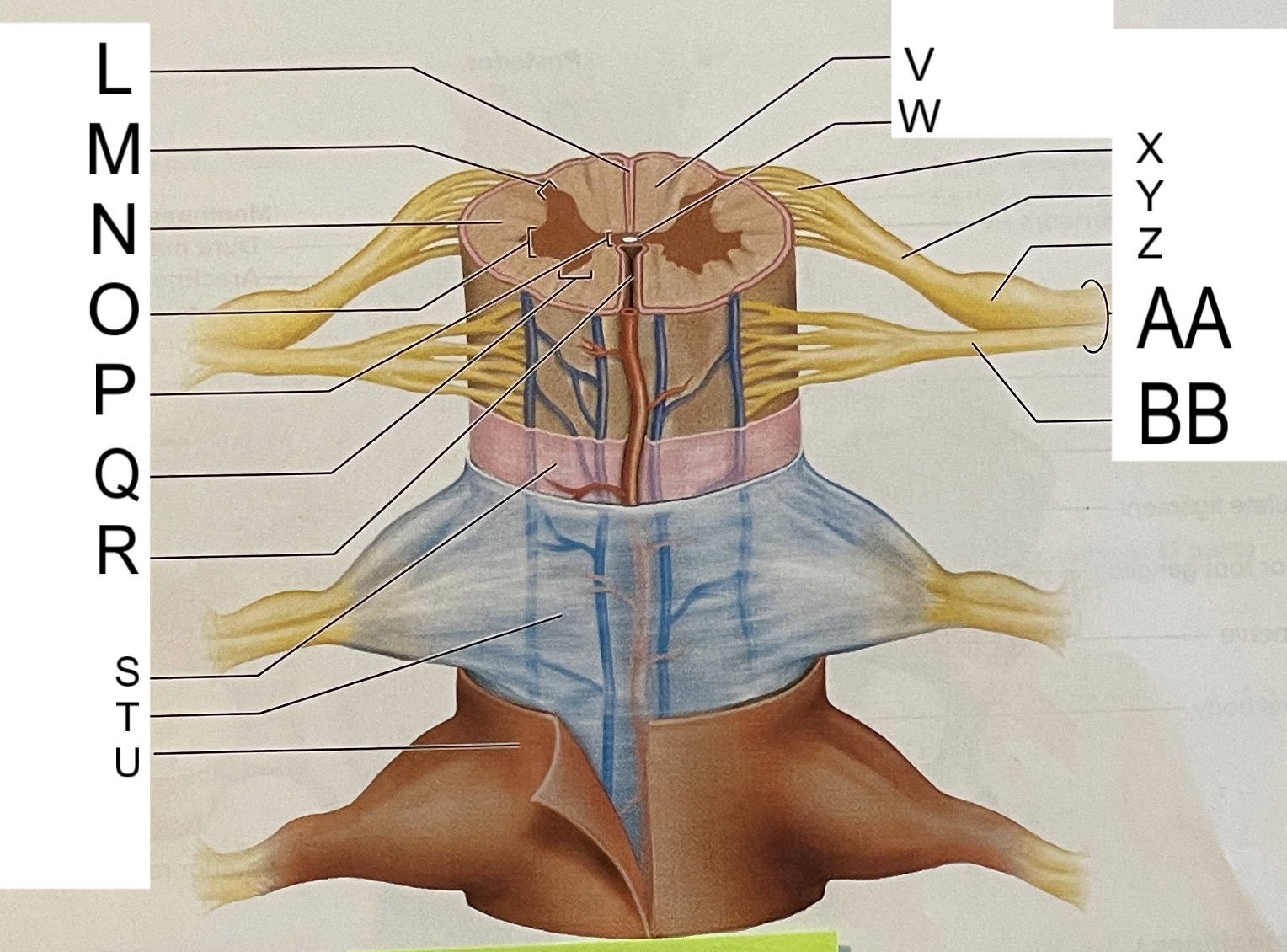
BB
anterior root of spinal nerve
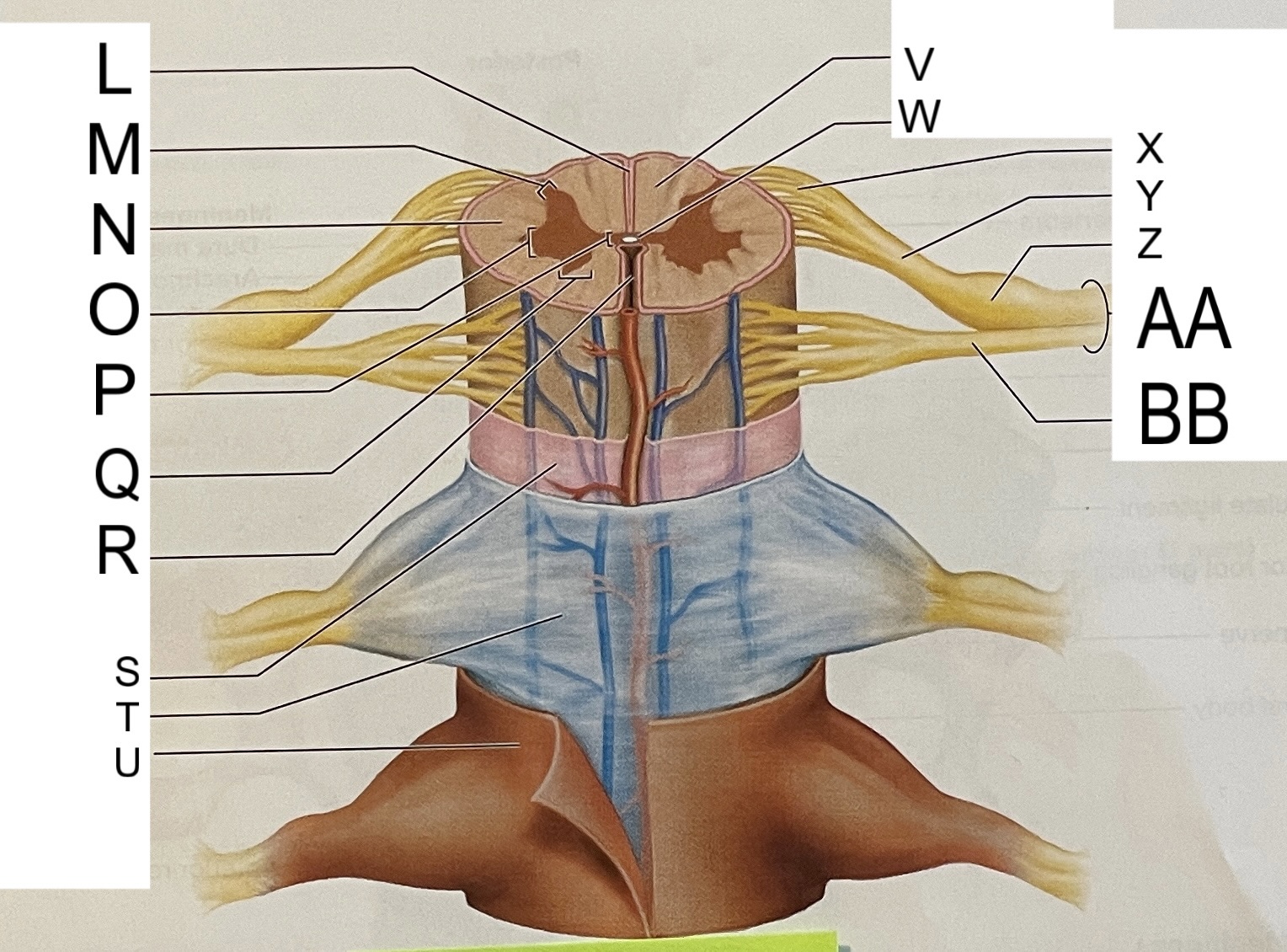
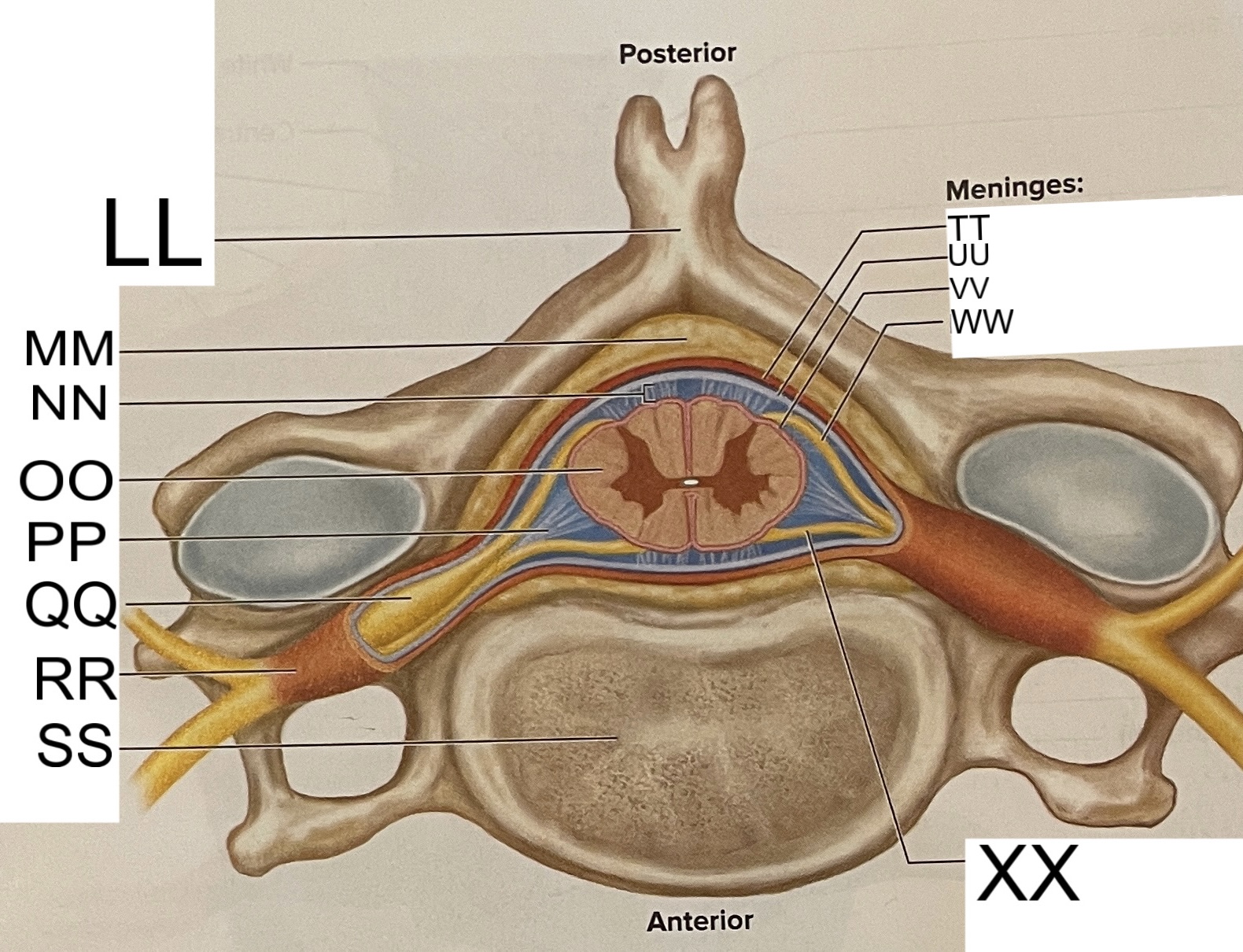
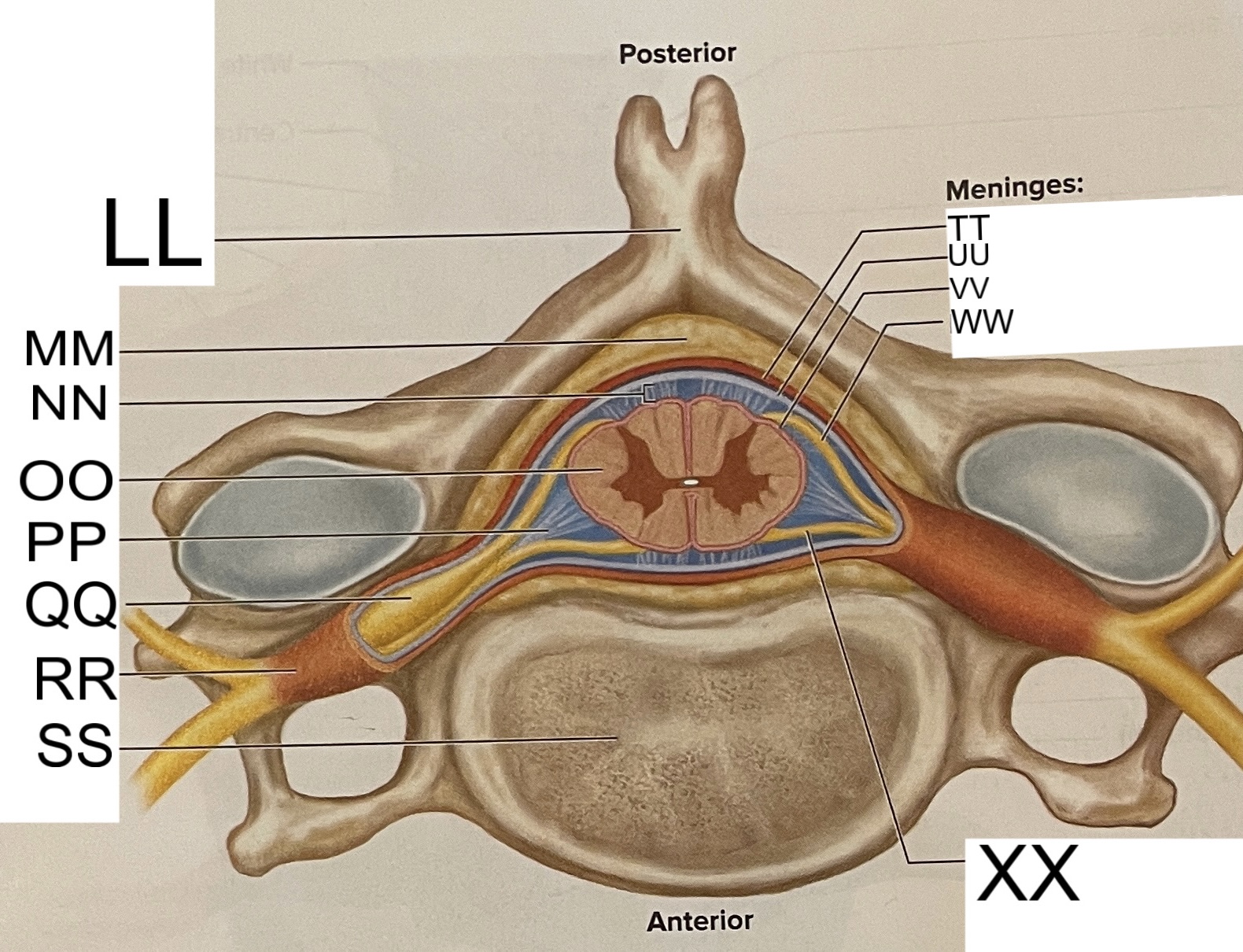
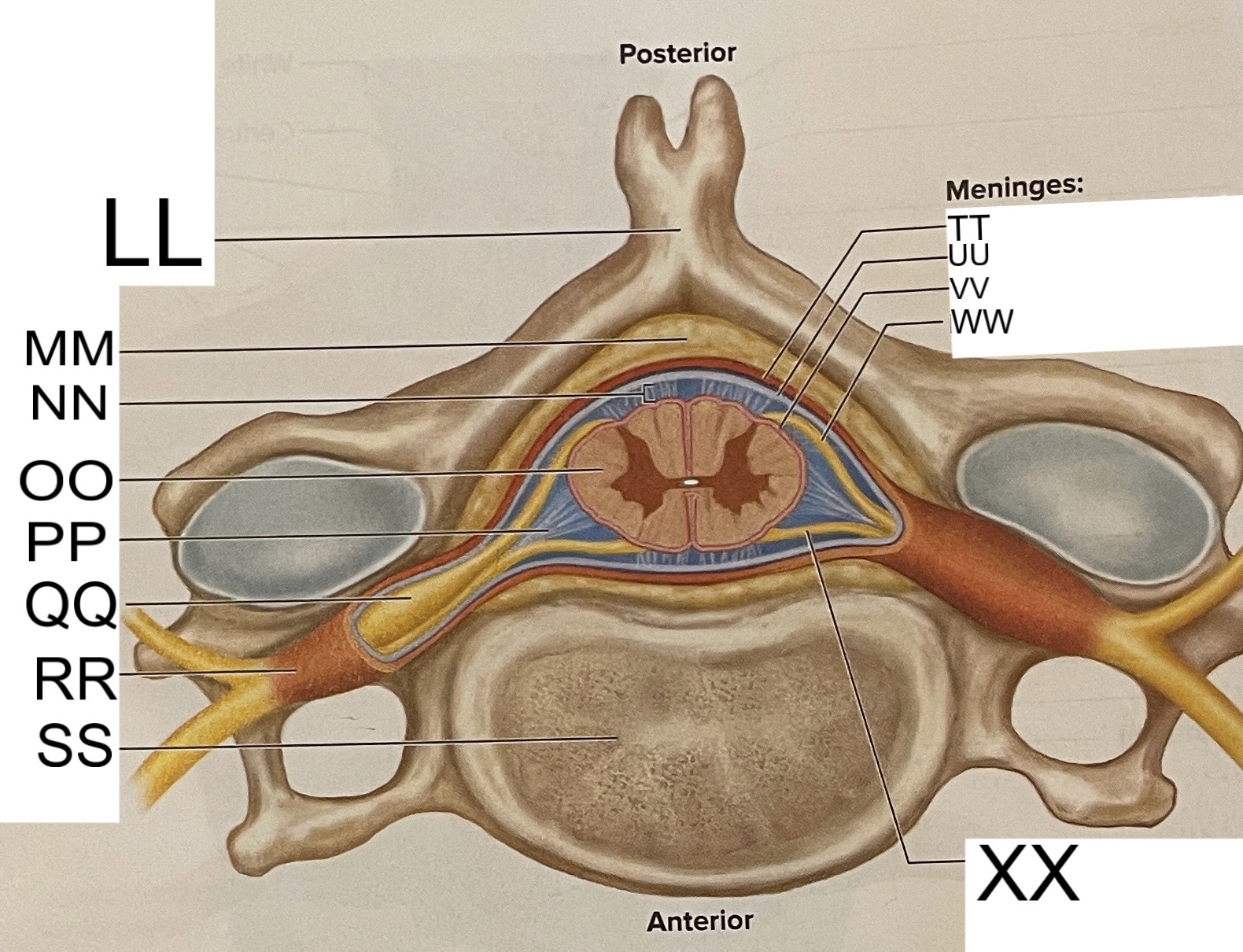
What are letters S, T, and U?
meninges
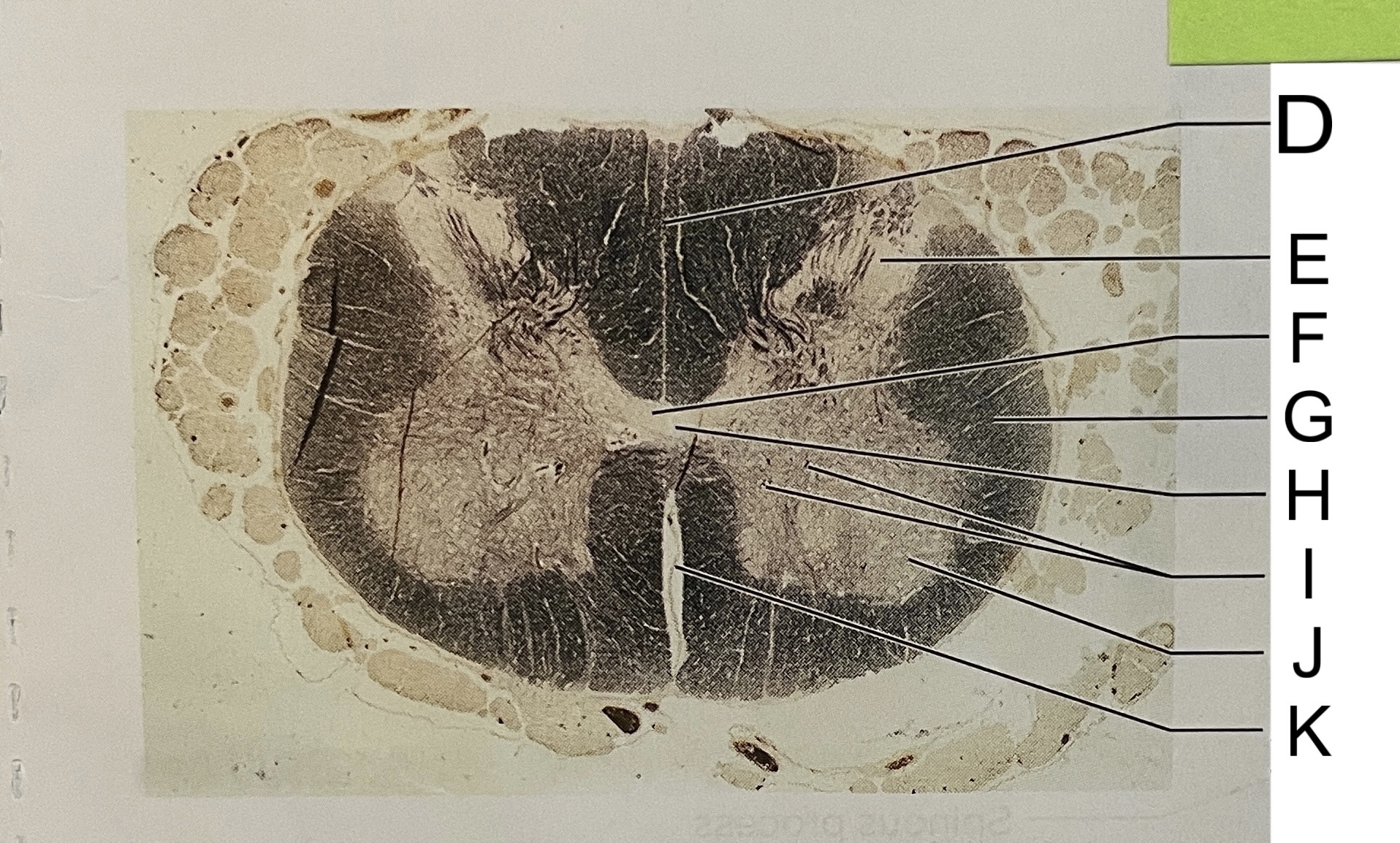
D
posterior median sulcus
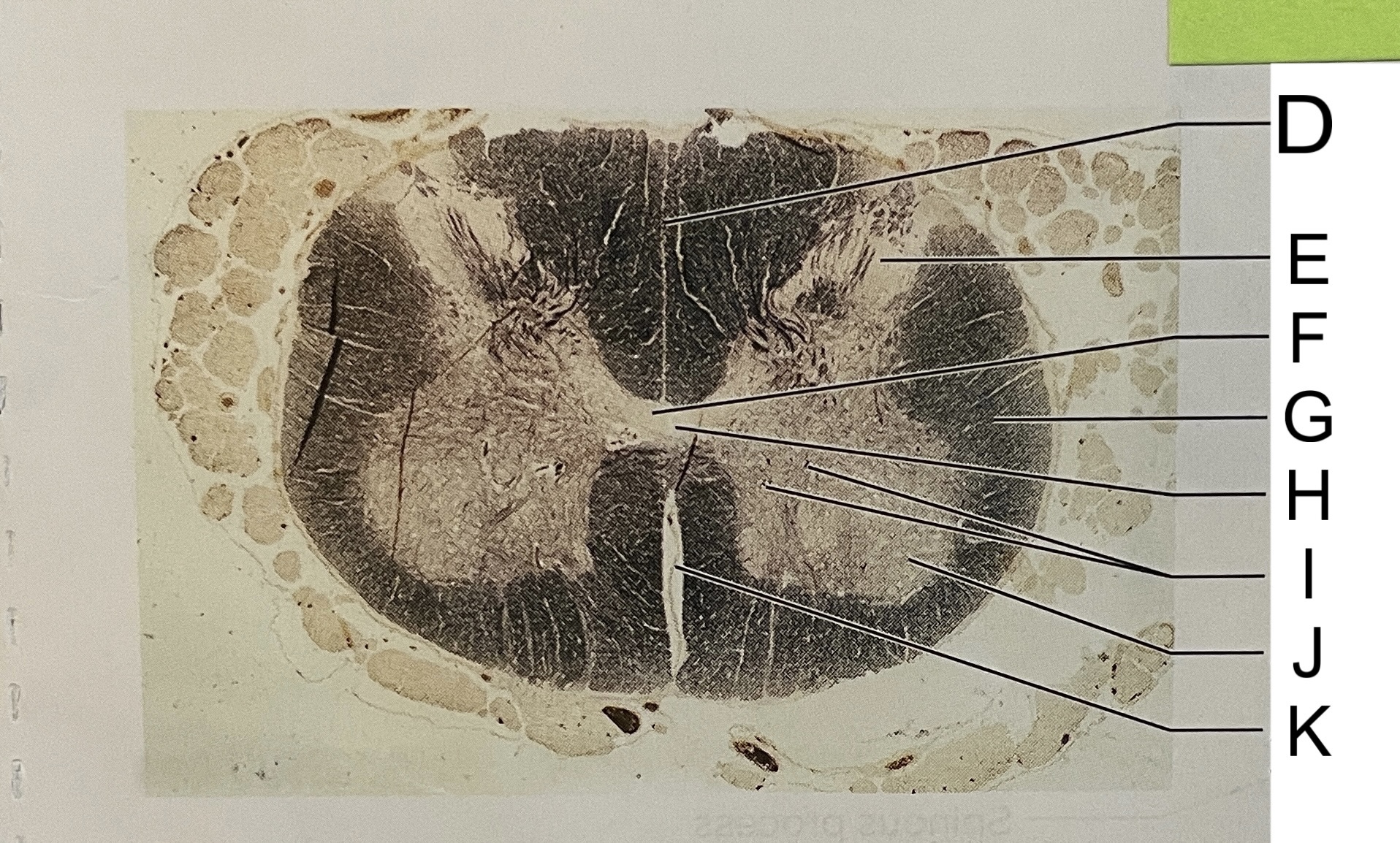
E
dorsal horn
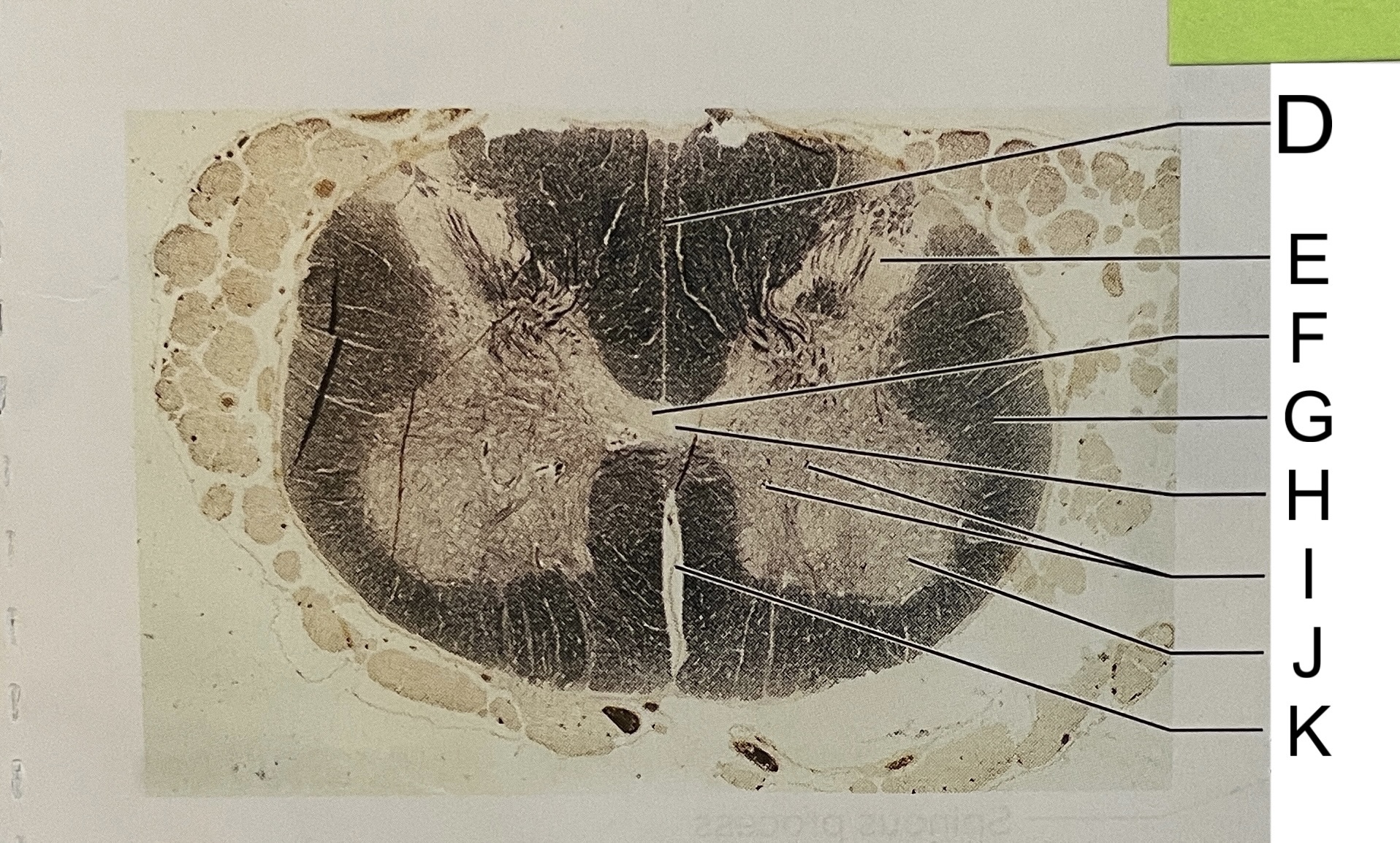
F
gray commissure
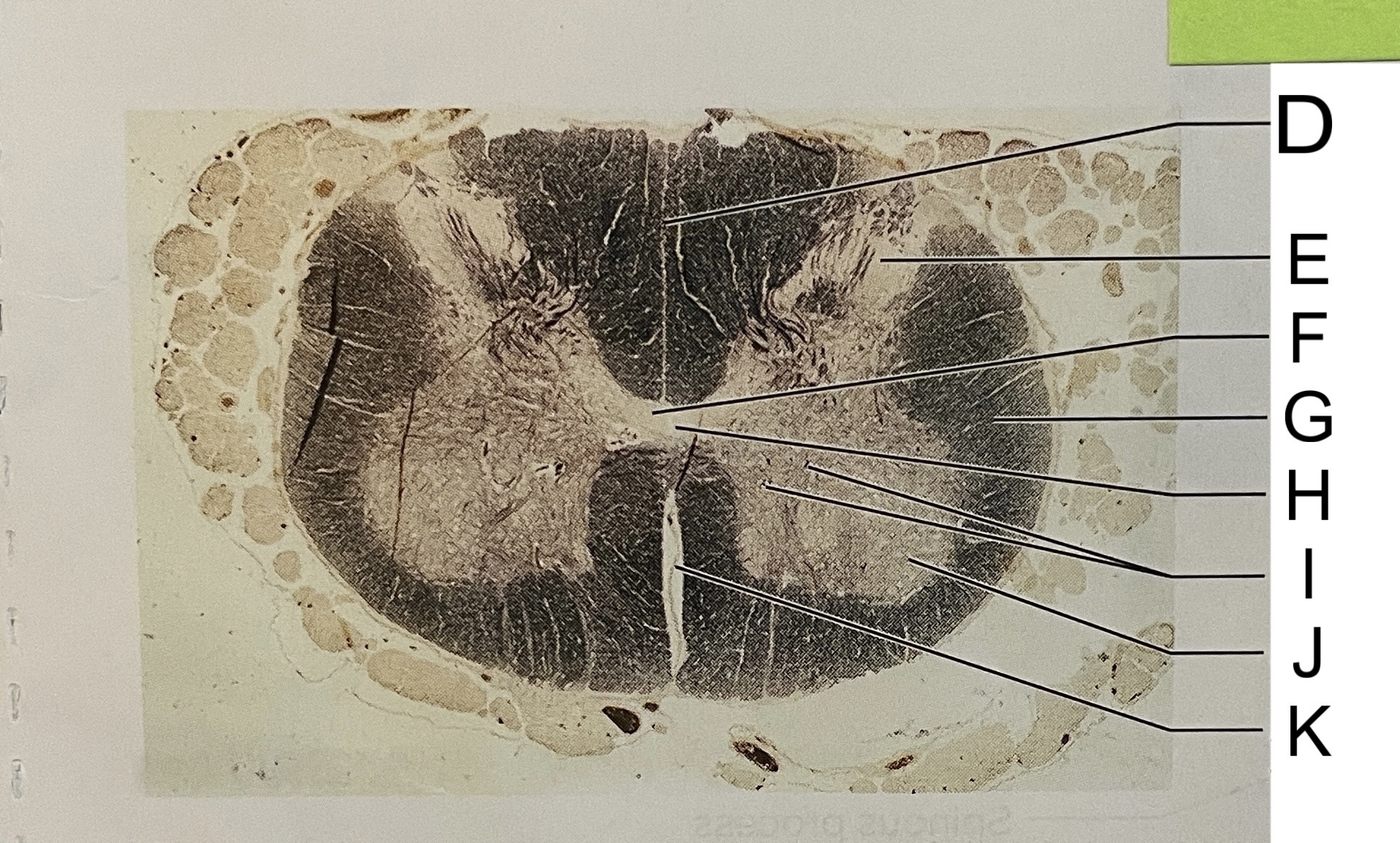
G
white matter
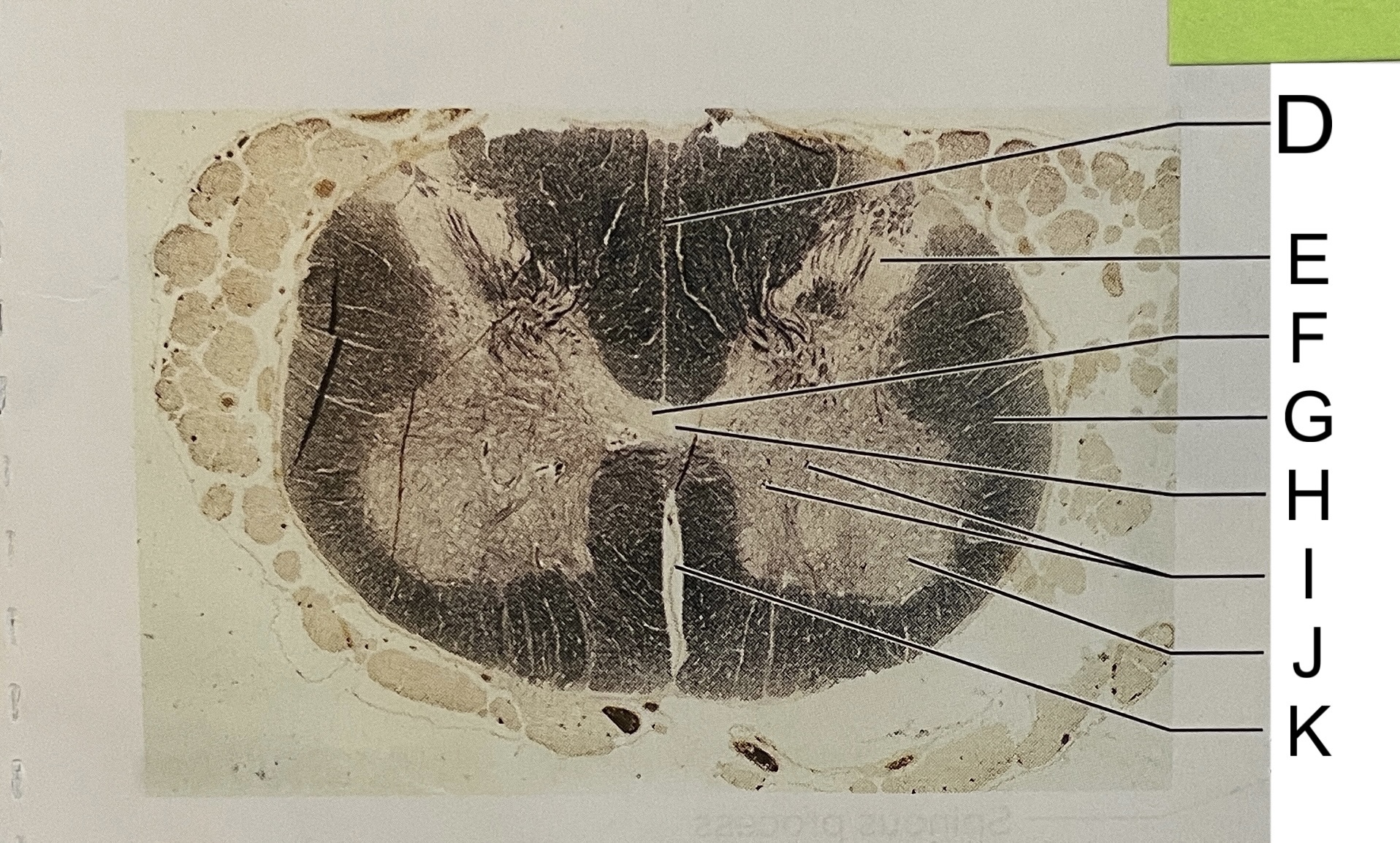
H
central canal
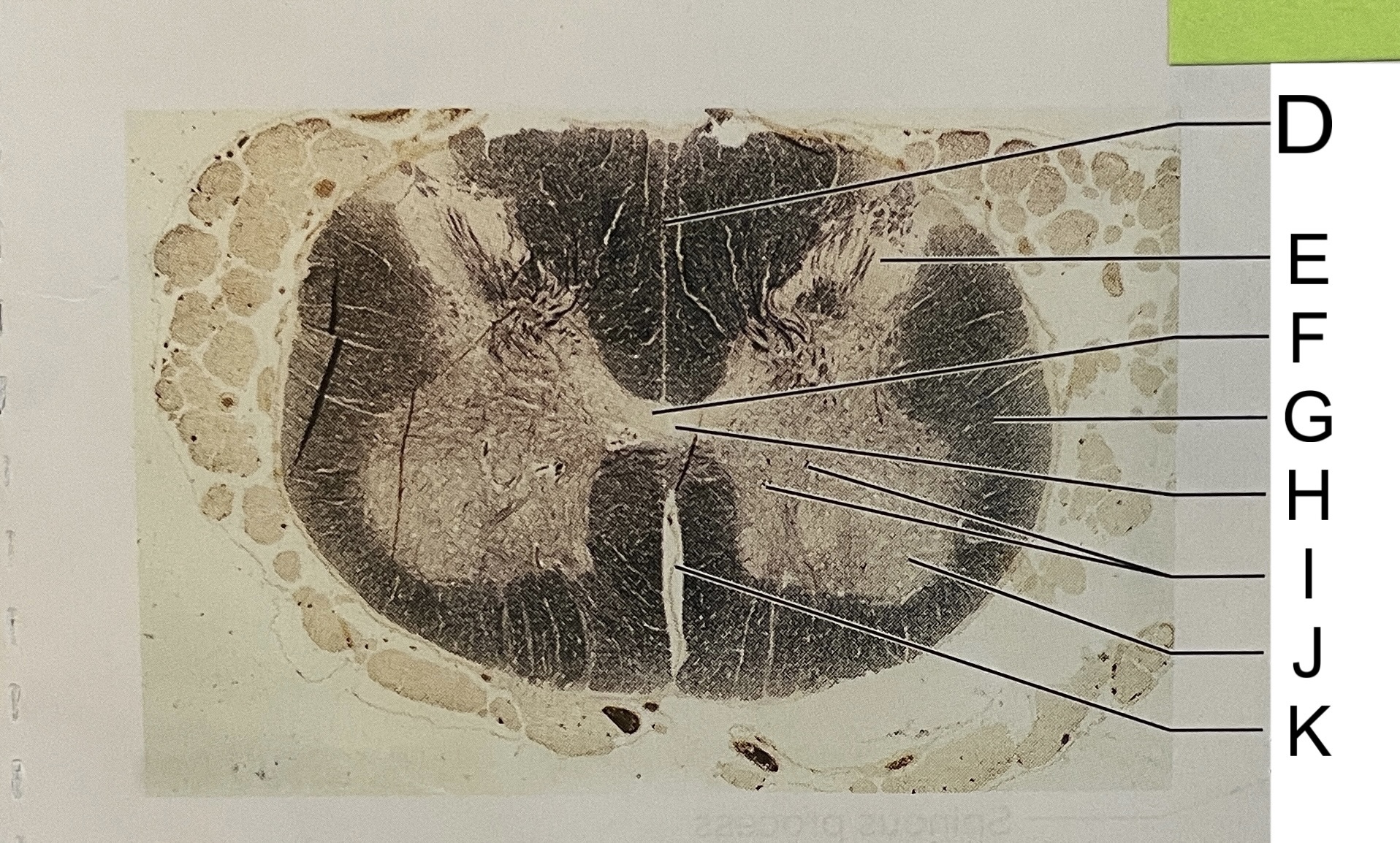
I
cell bodies
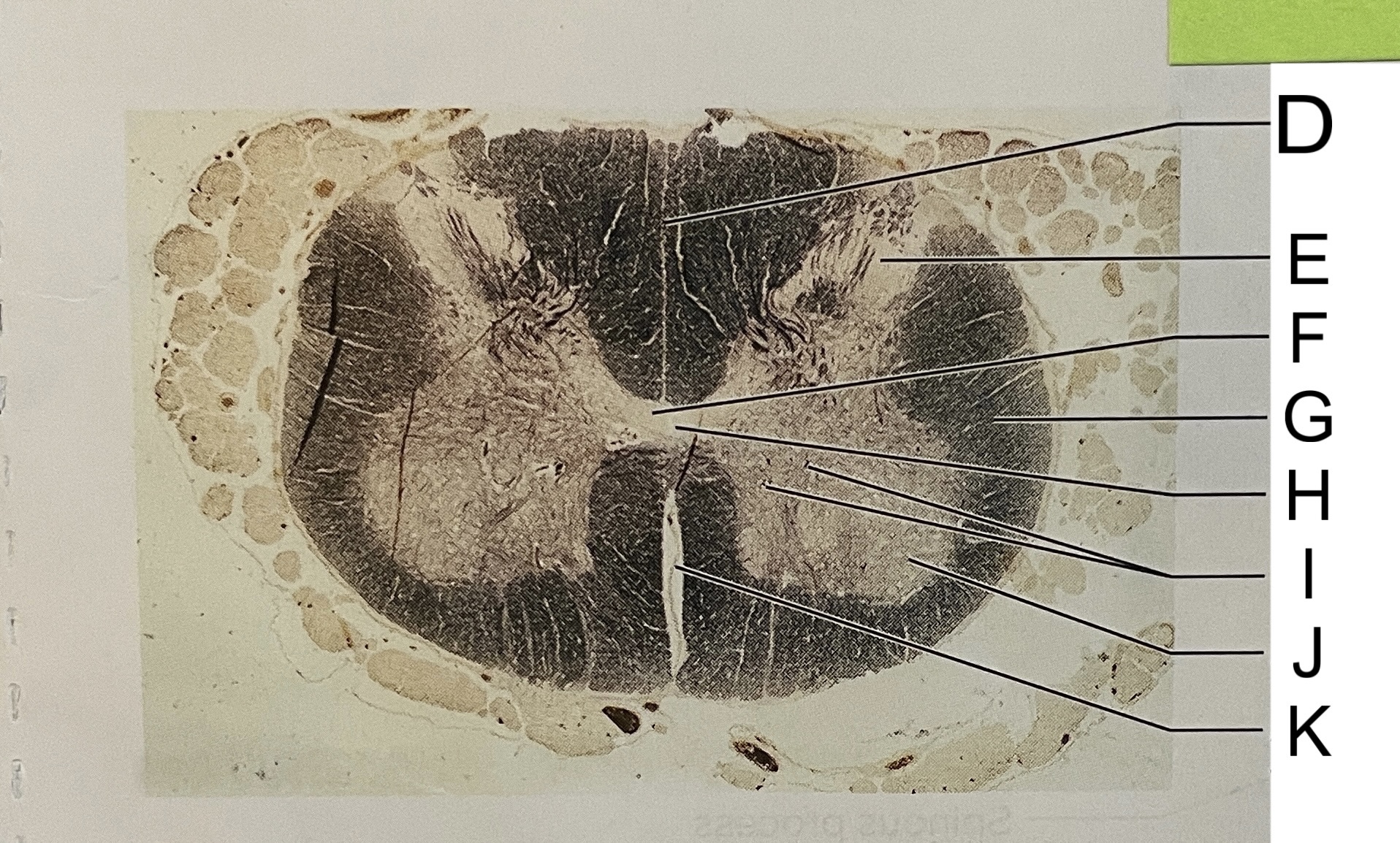
J
anterior horn
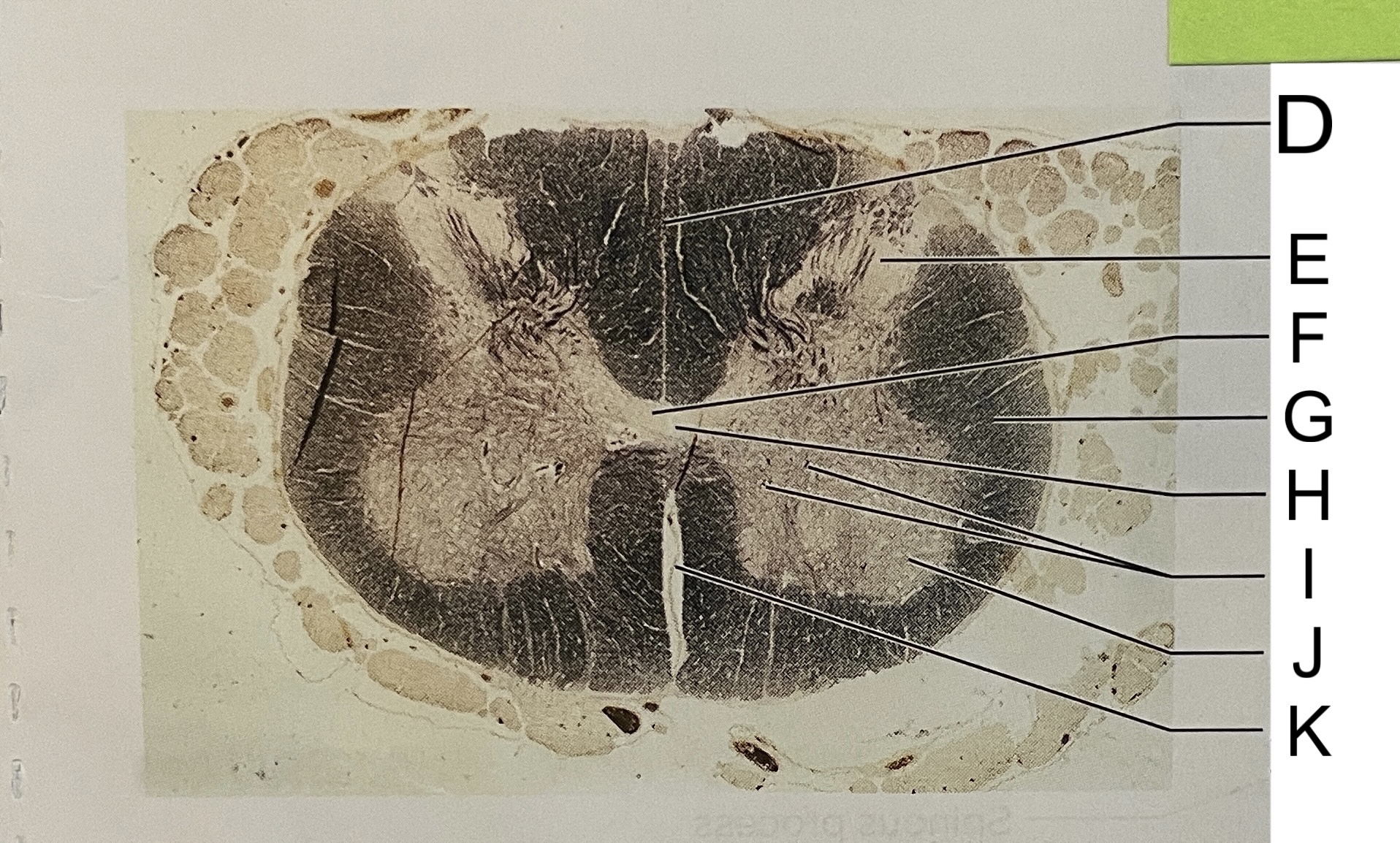
K
anterior median fissure
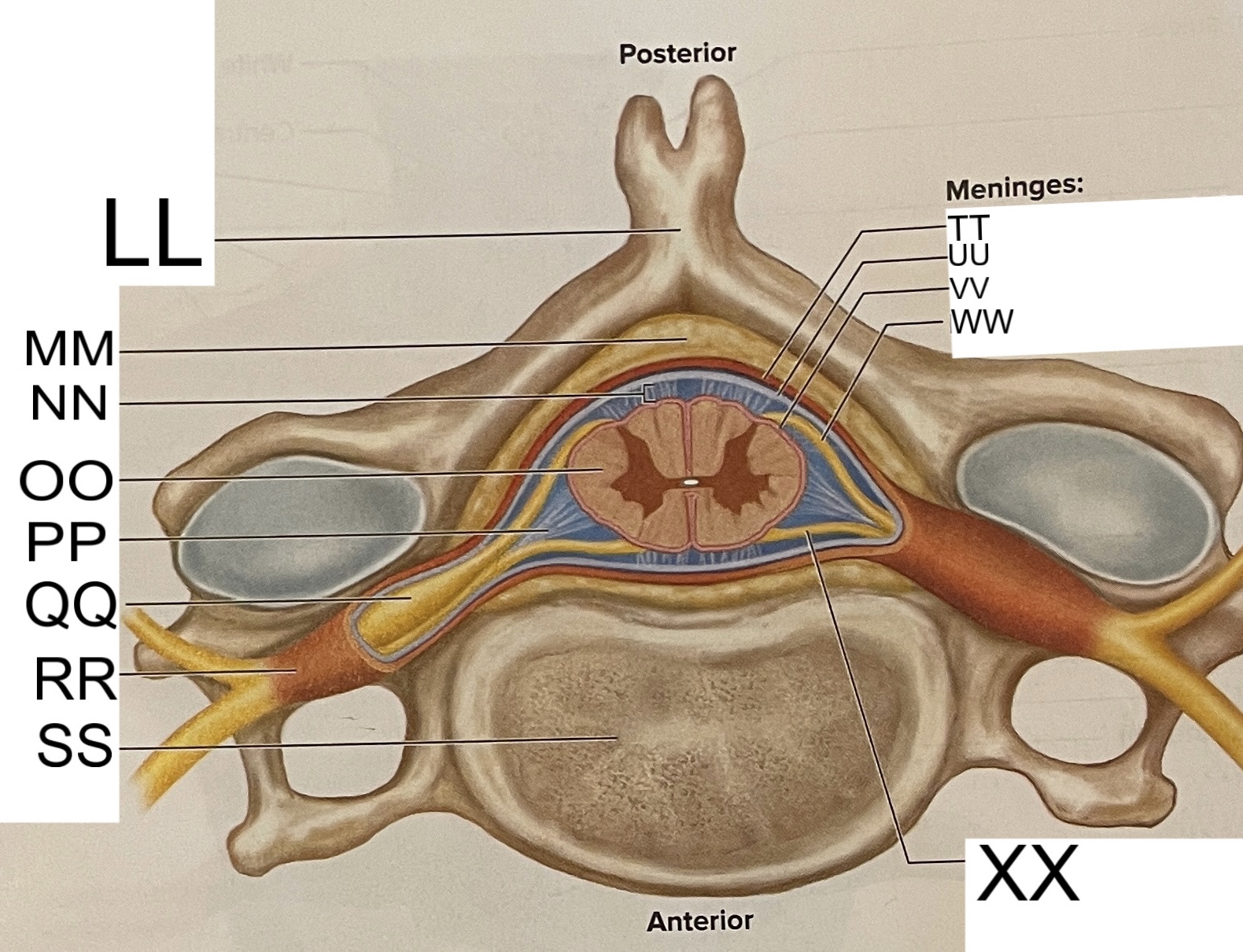
LL
spinous process of vertebra
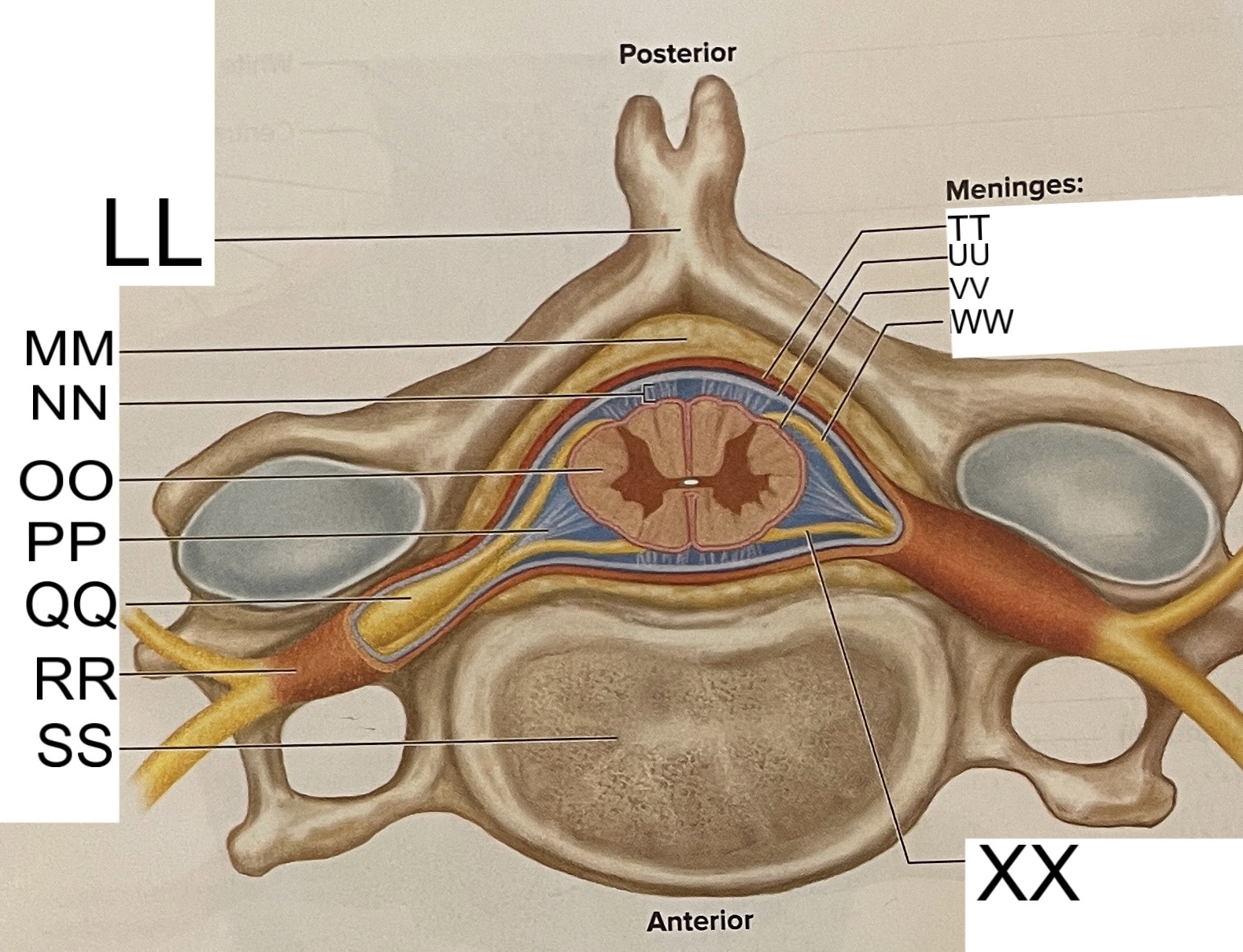
MM
fat in epidural space
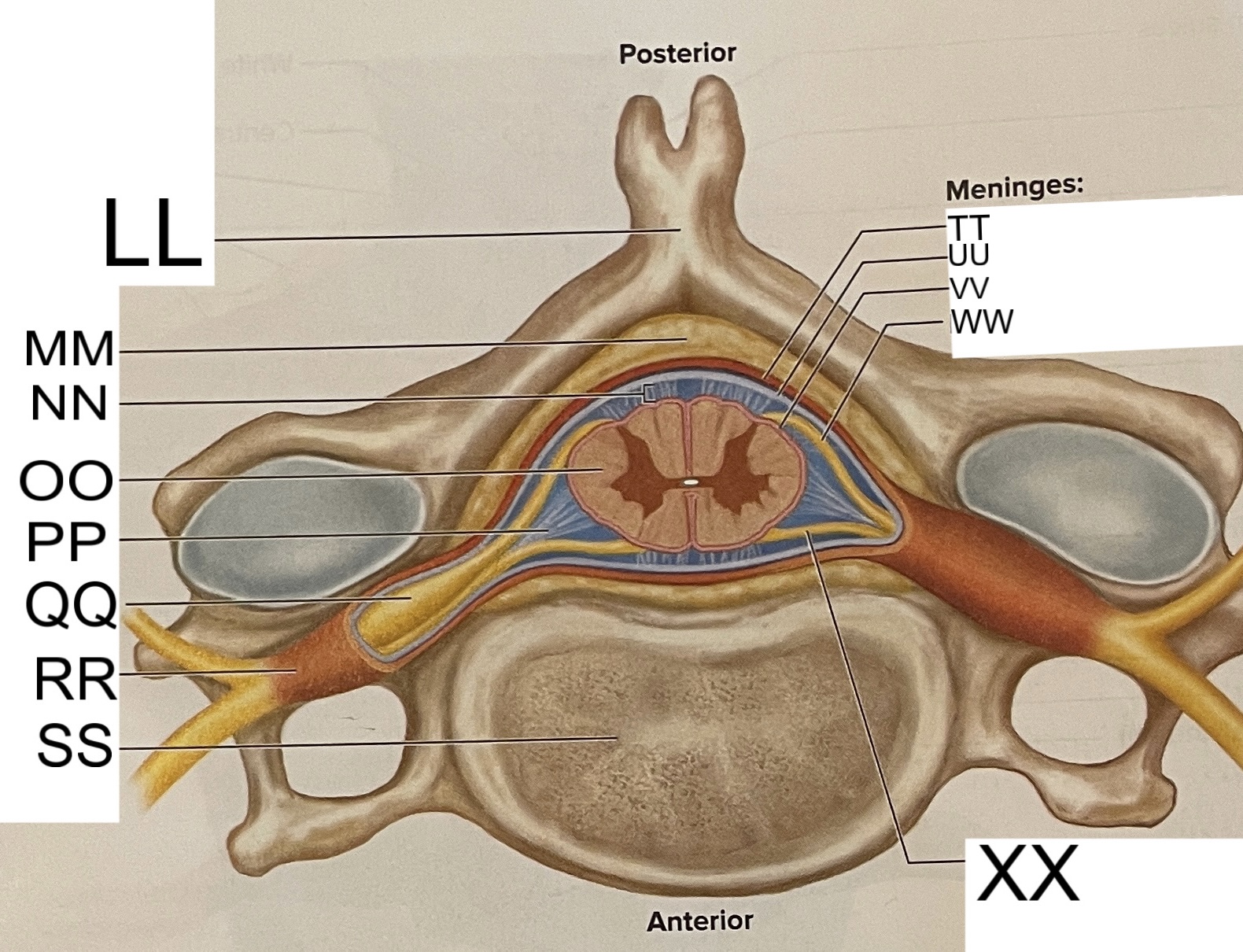
NN
subarachnoid space
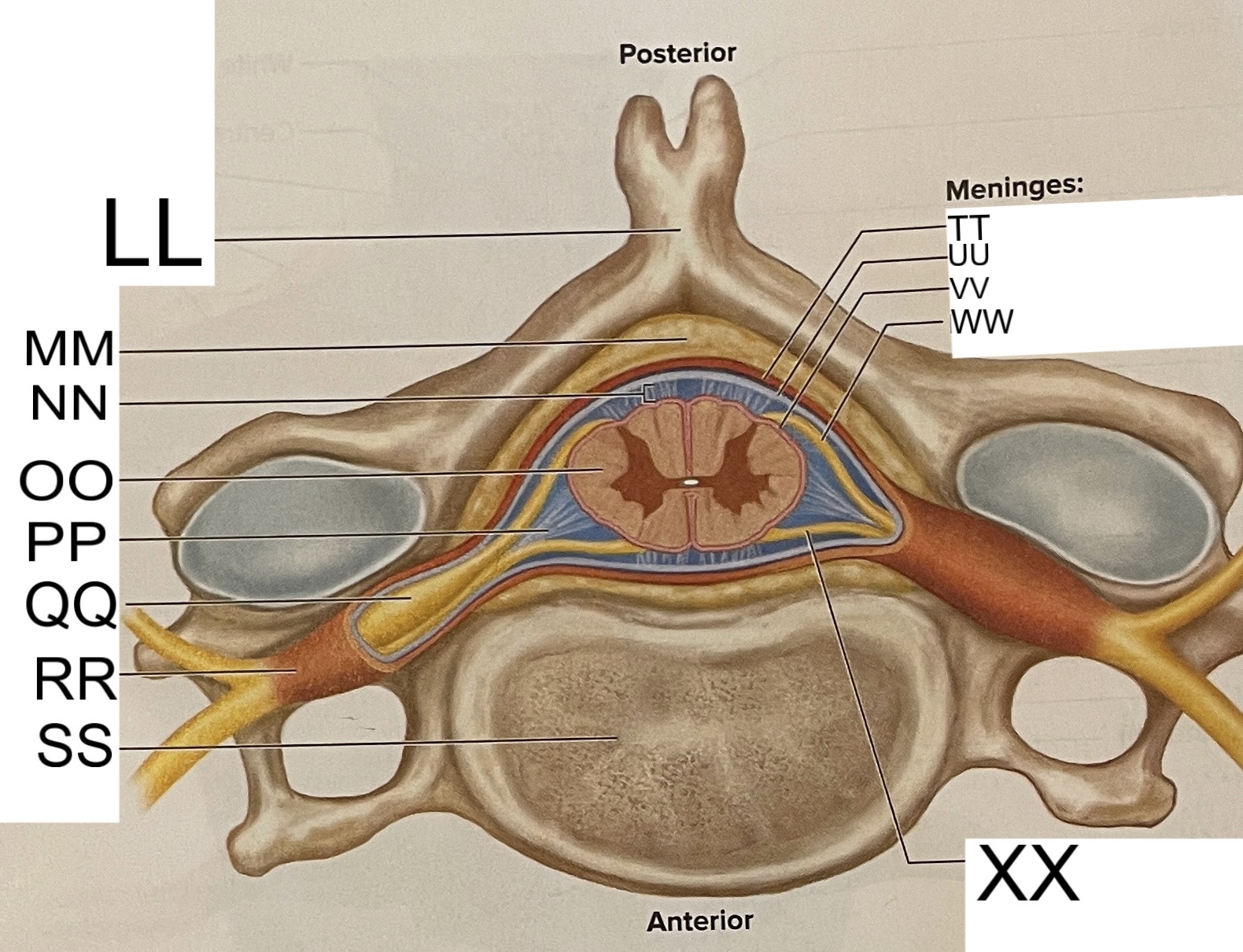
OO
spinal cord
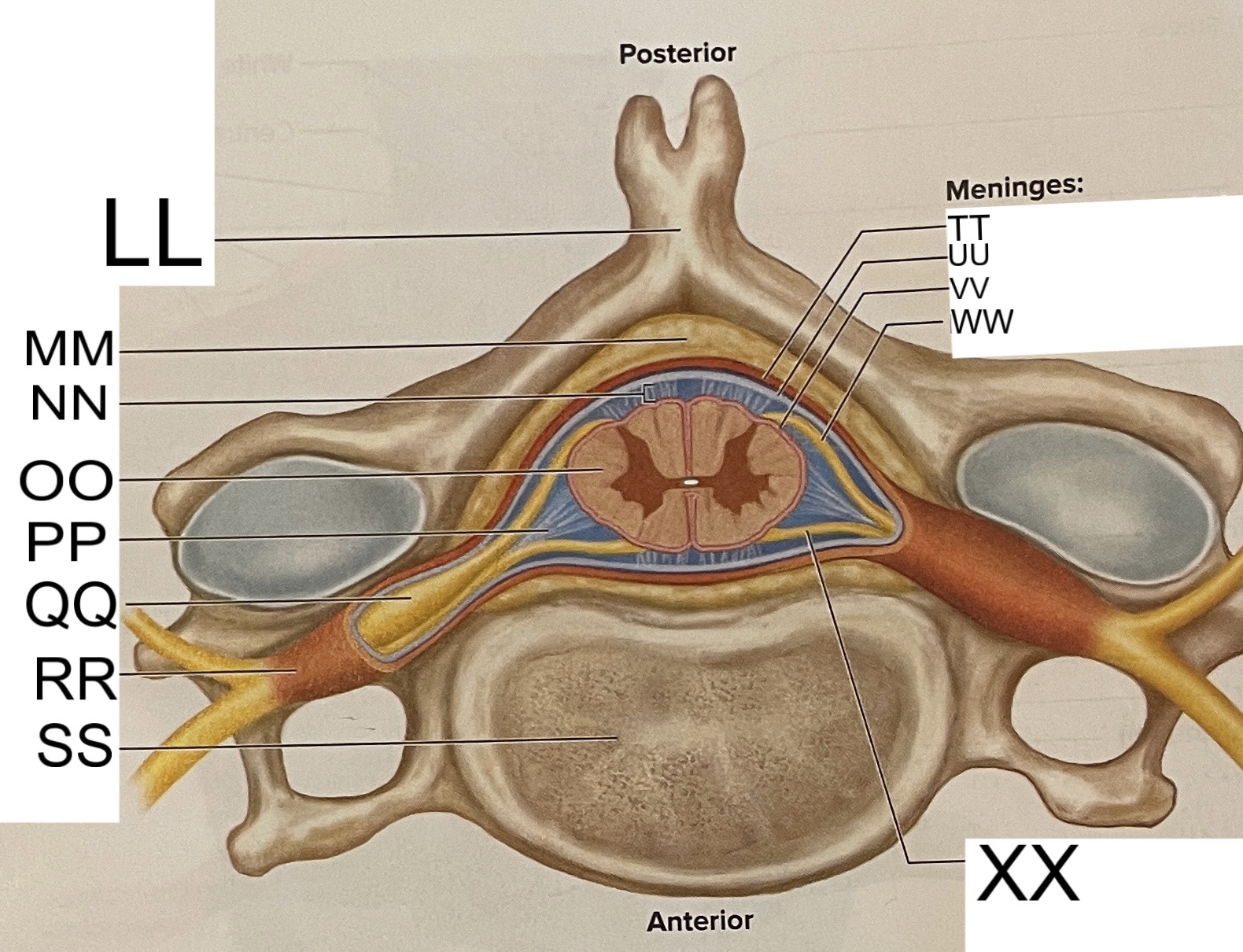
PP
denticulate ligament
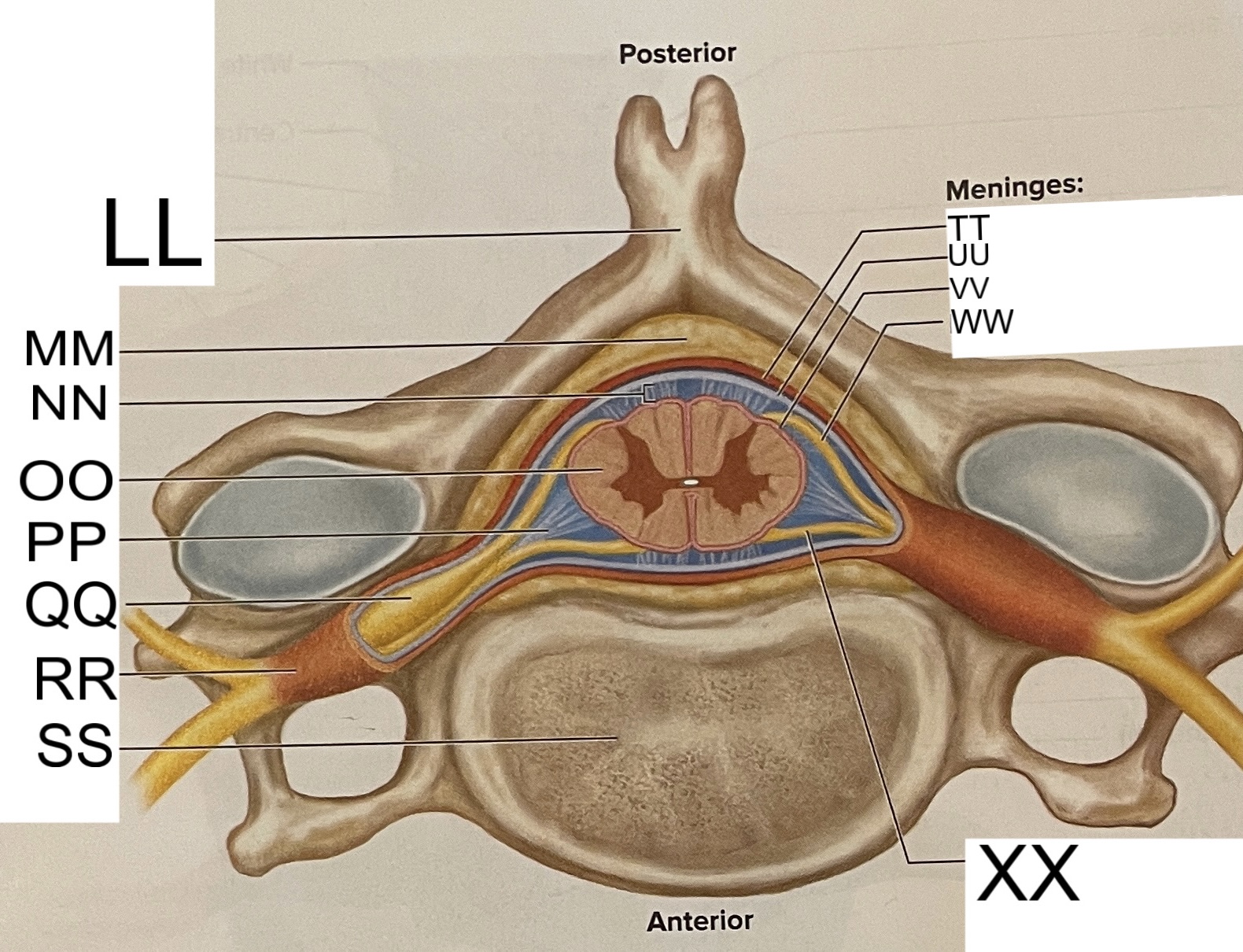
posterior root ganglion
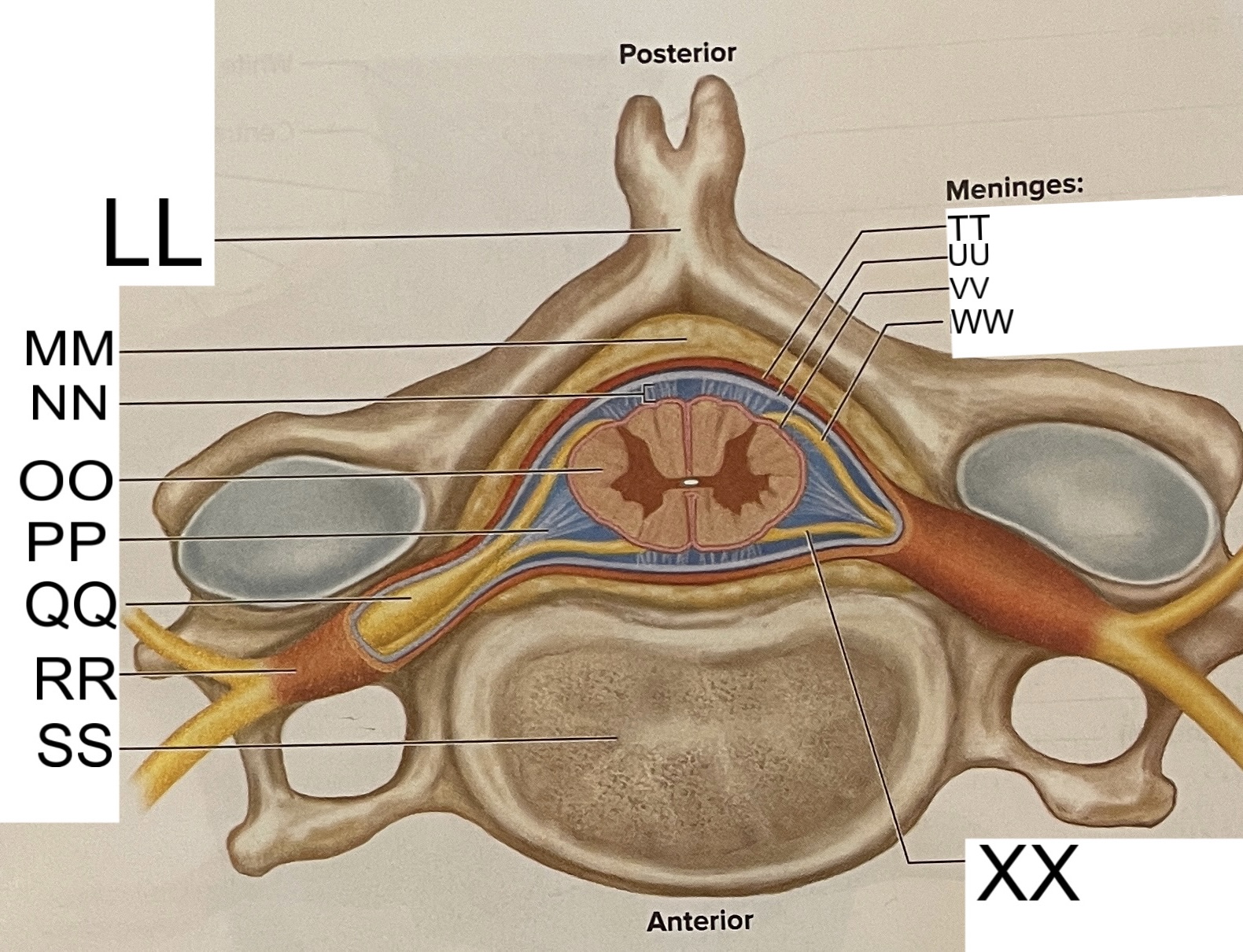
RR
spinal nerve
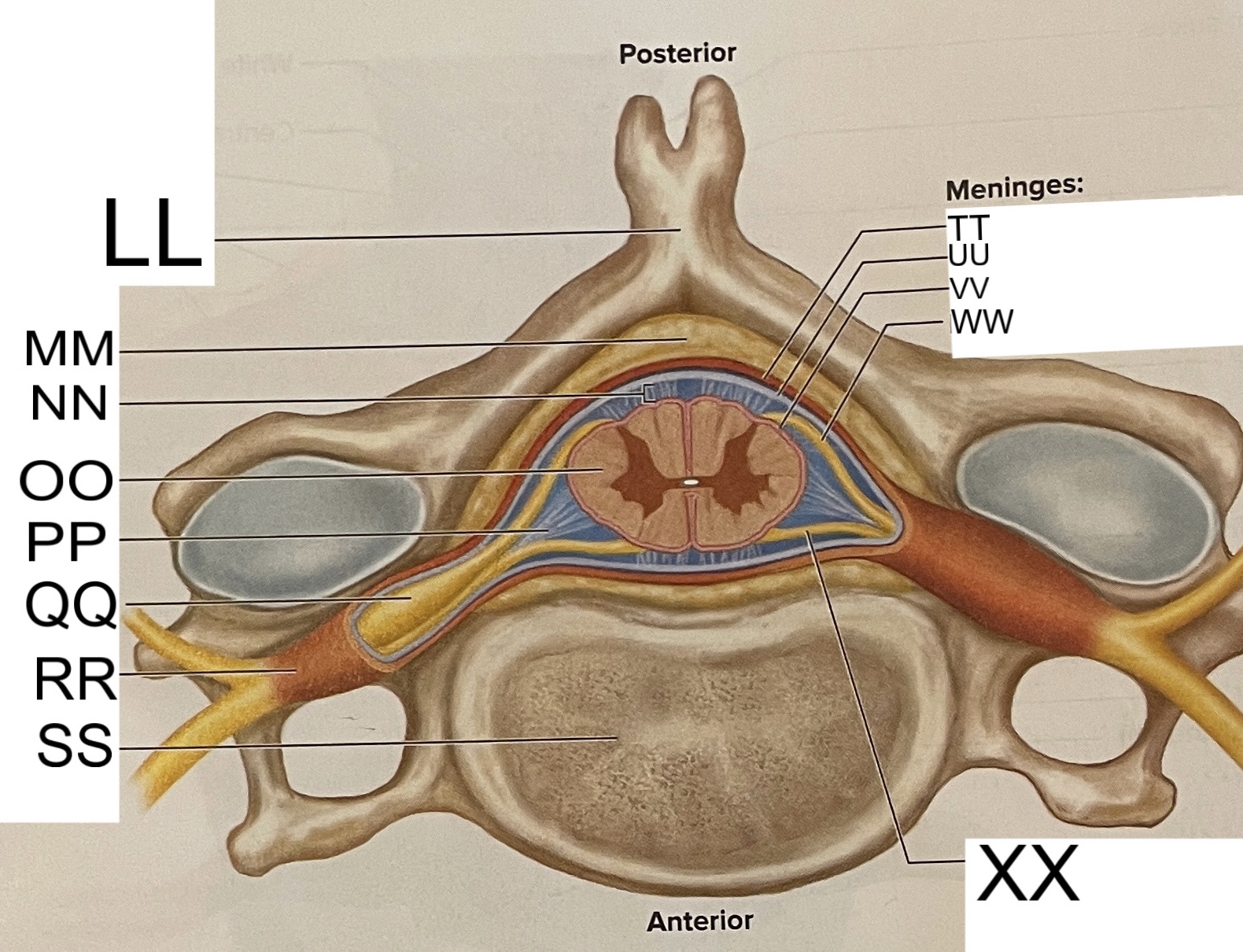
SS
vertebral body
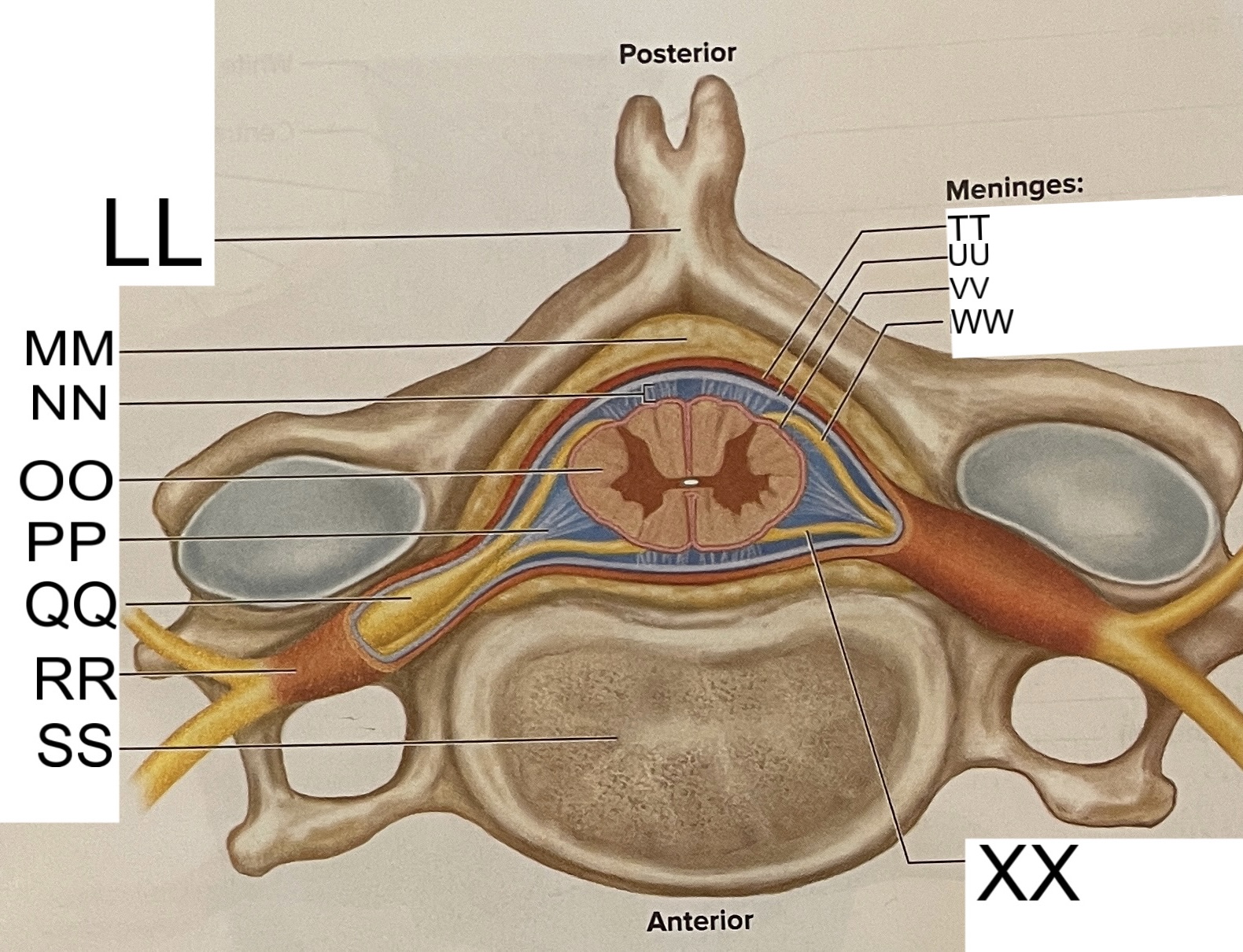
TT
dura mater
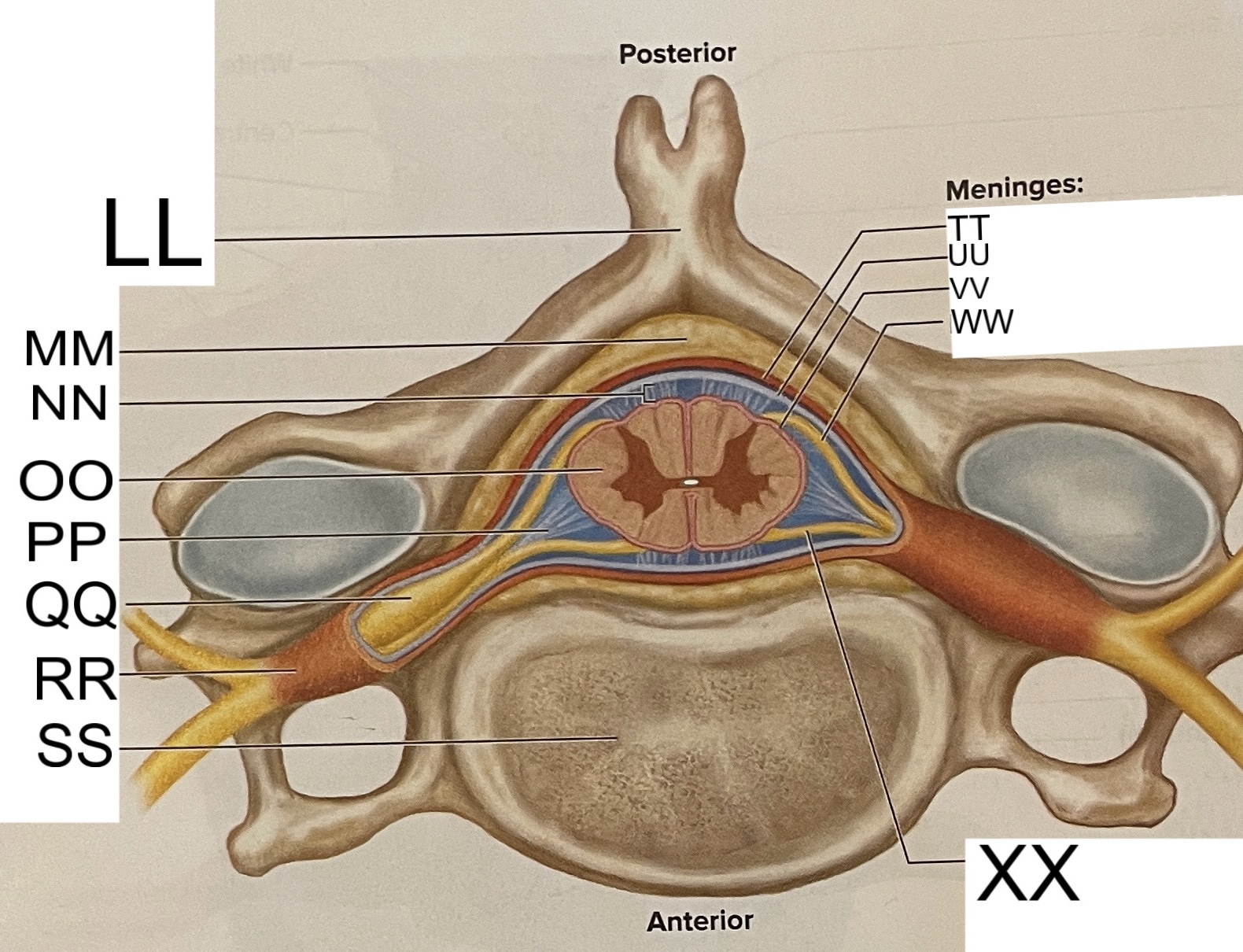
UU
arachnoid mater
VV
pia mater
WW
posterior root
XX
anterior root
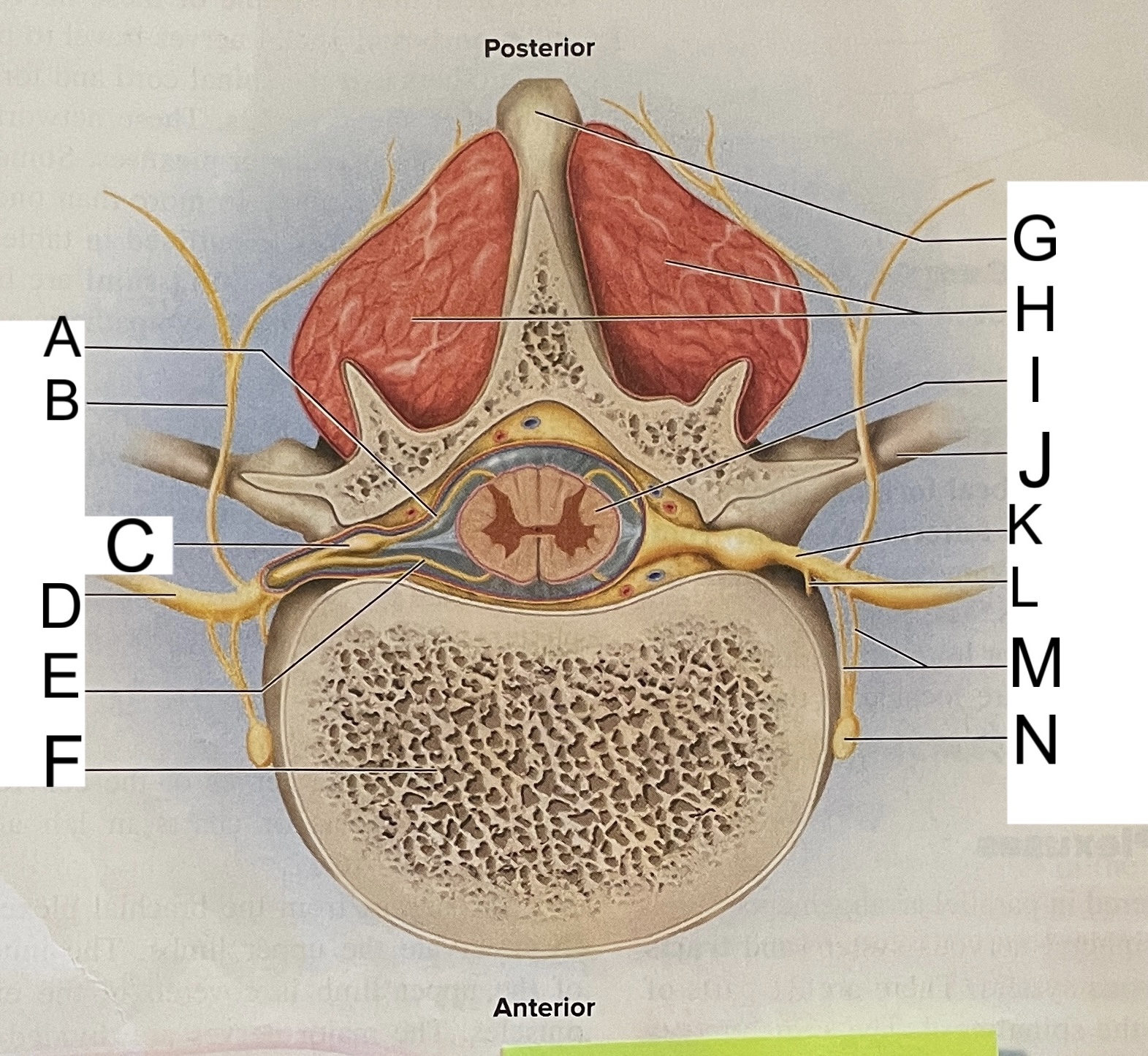
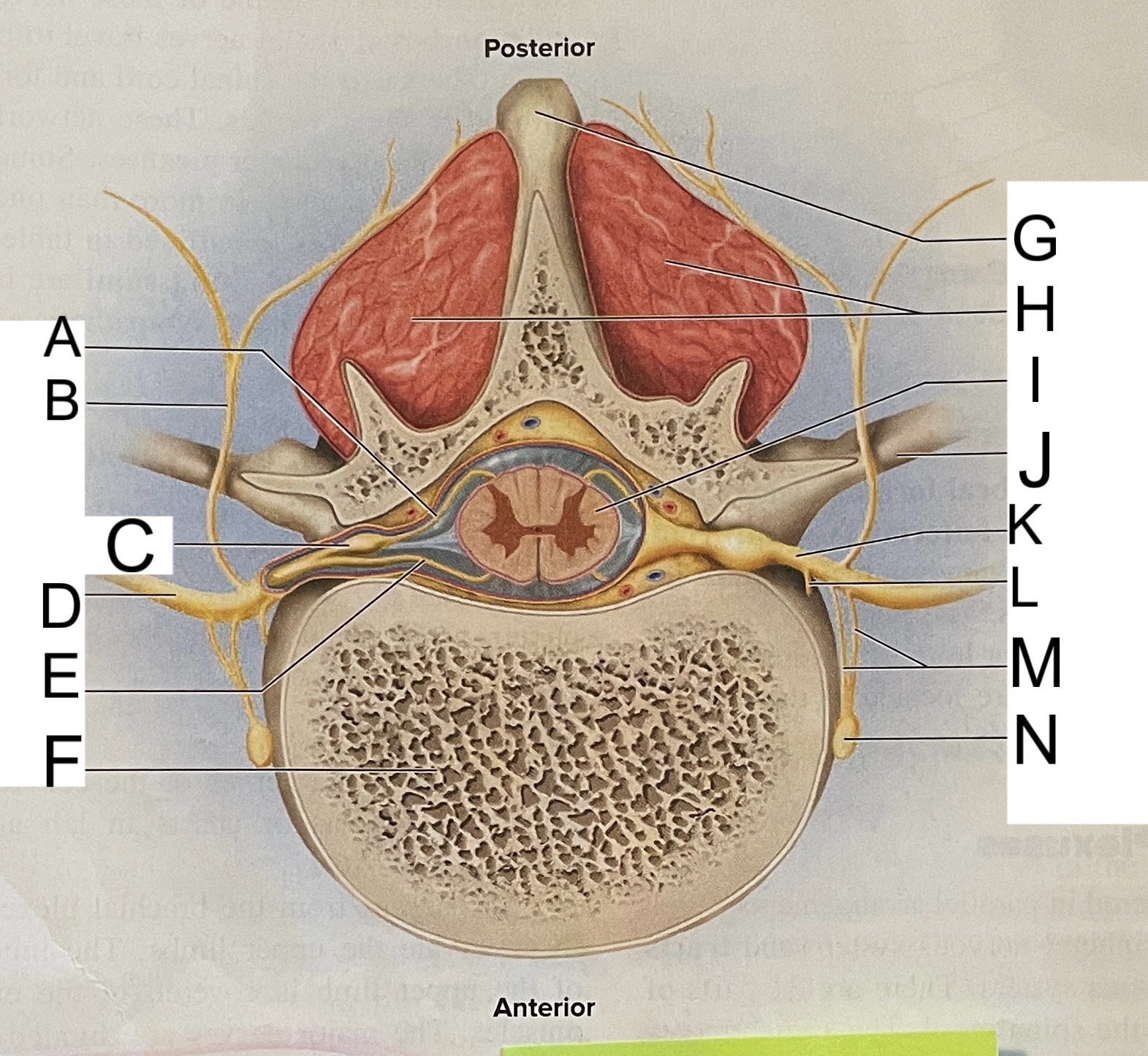
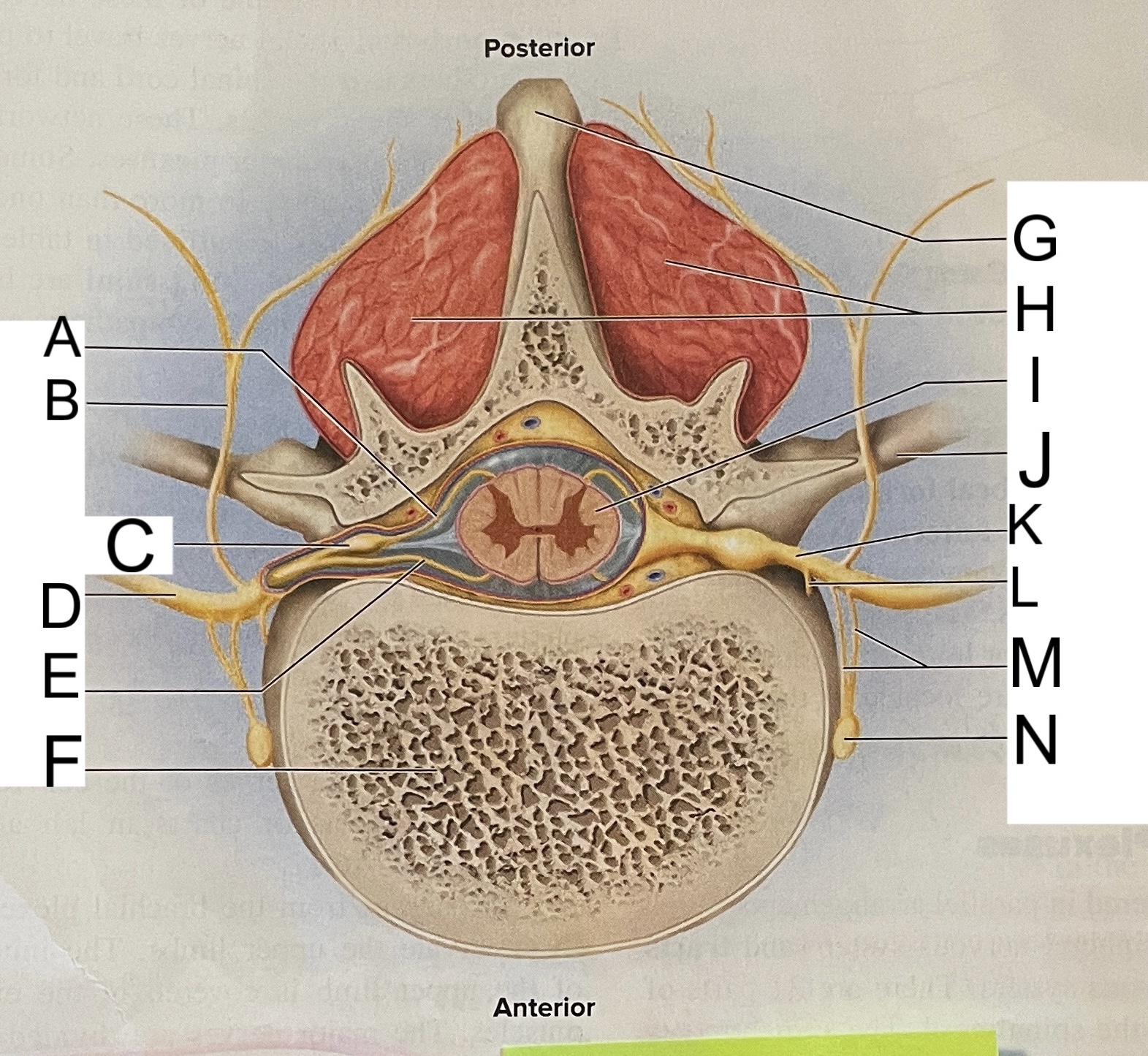
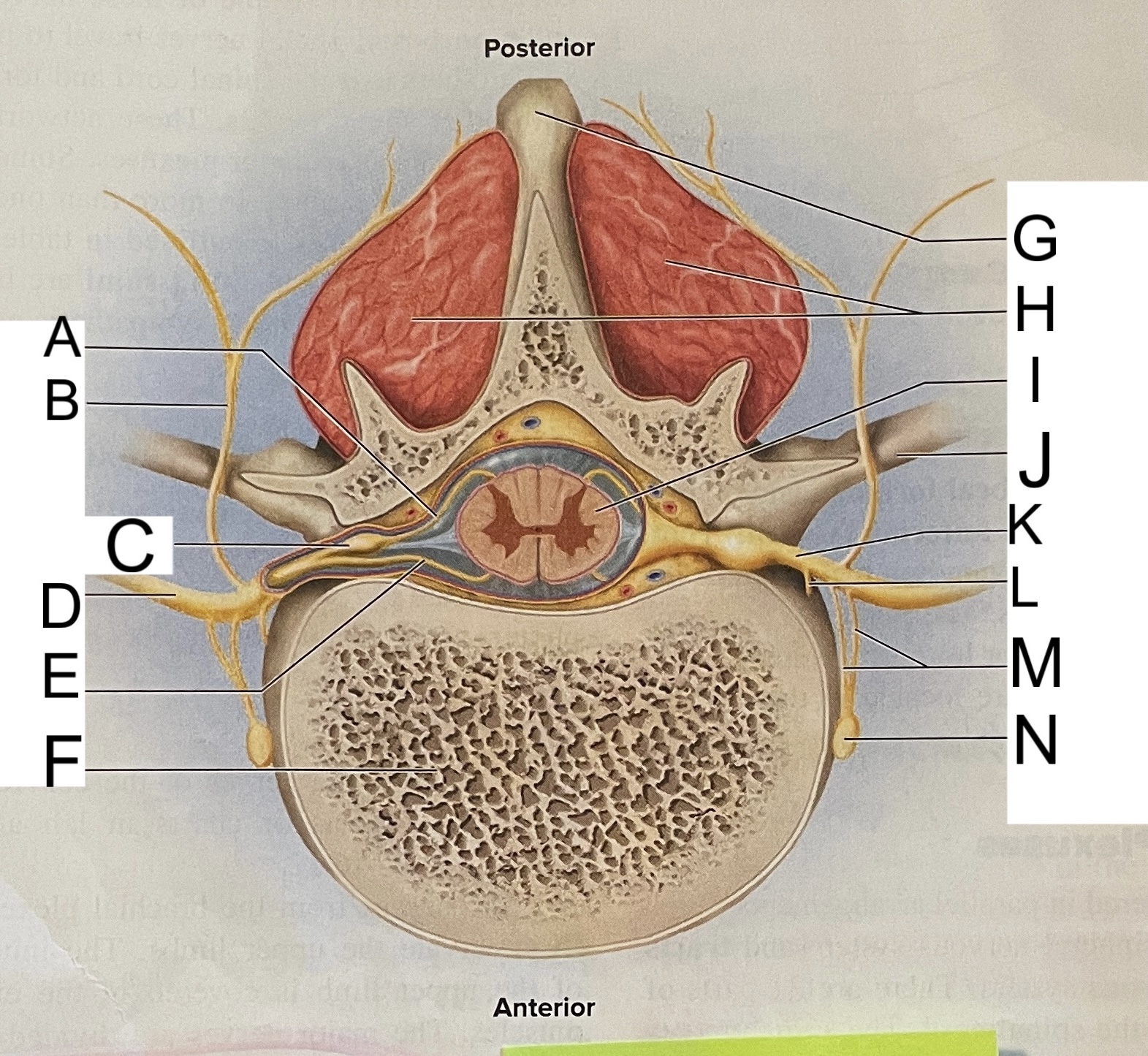
A
posterior root
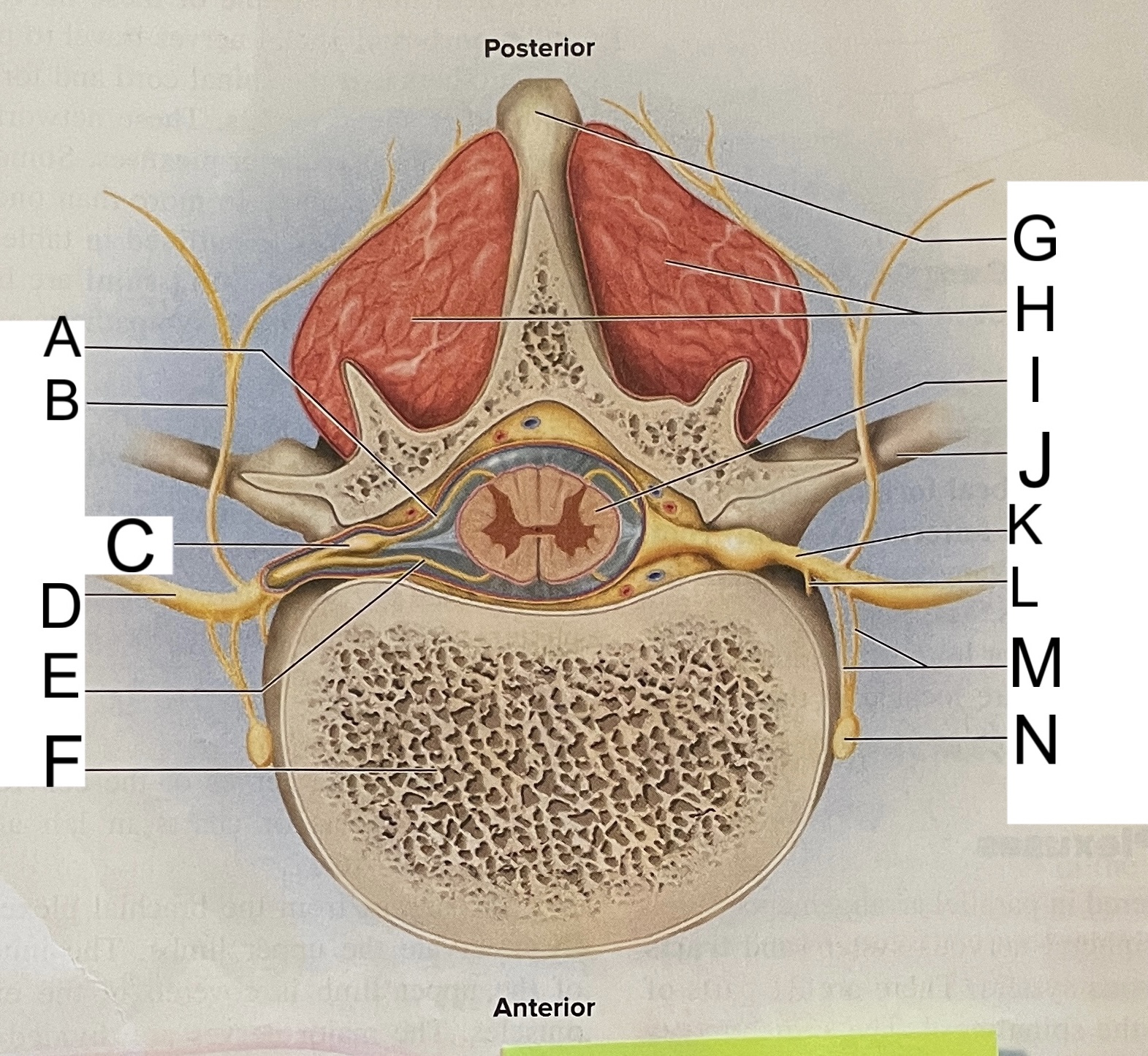
B
posterior ramus
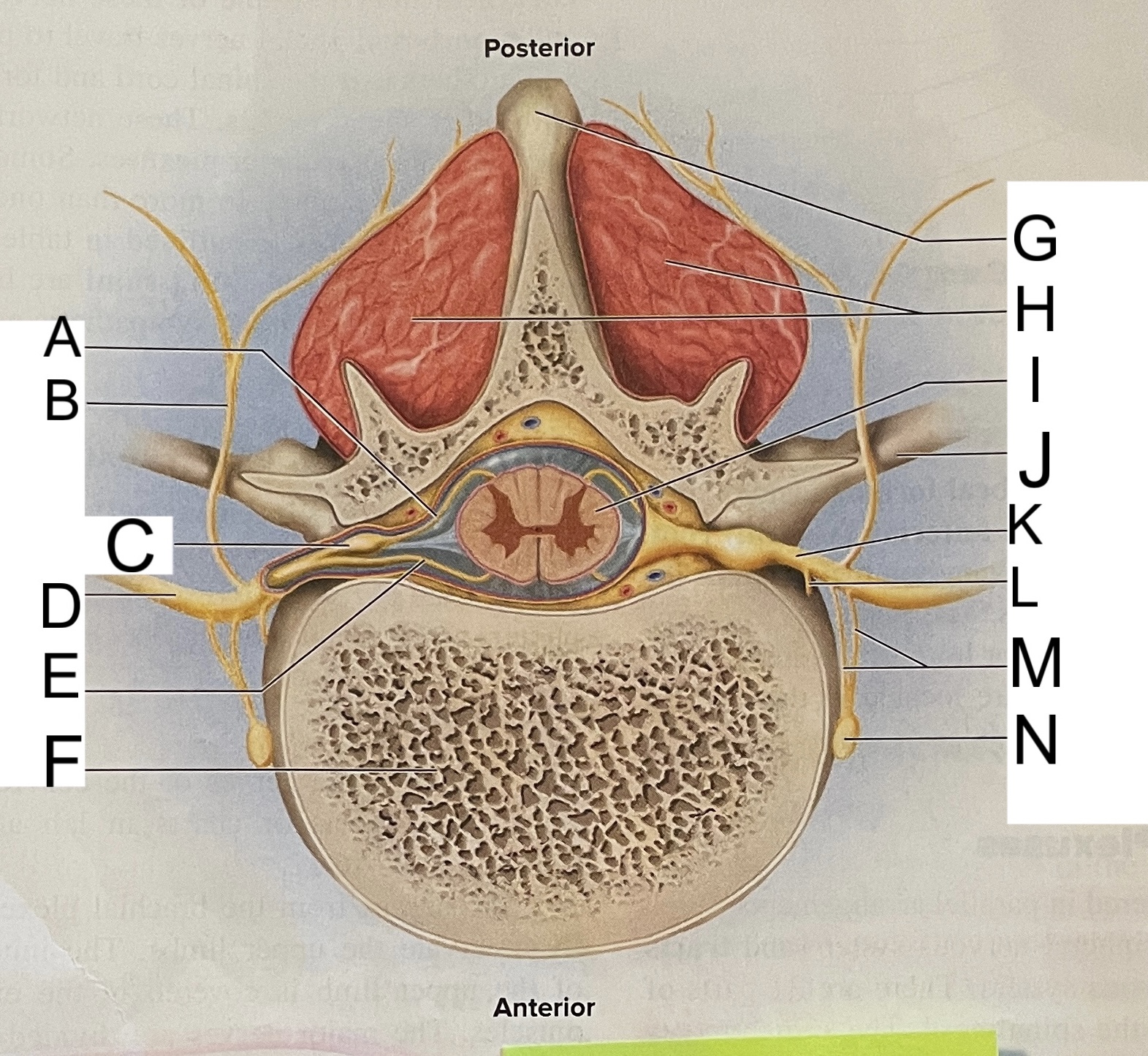
C
posterior root ganglion
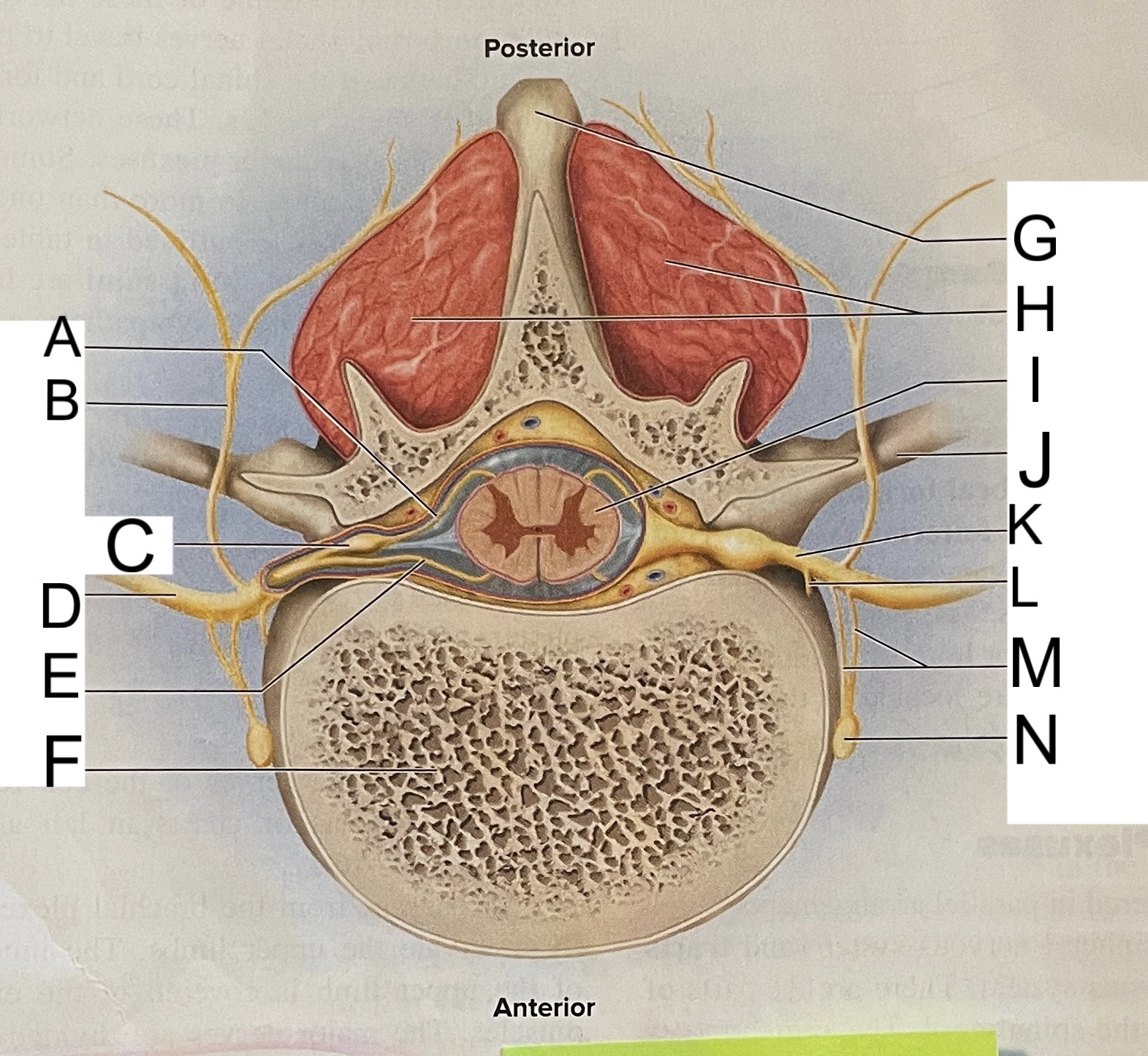
D
anterior ramus
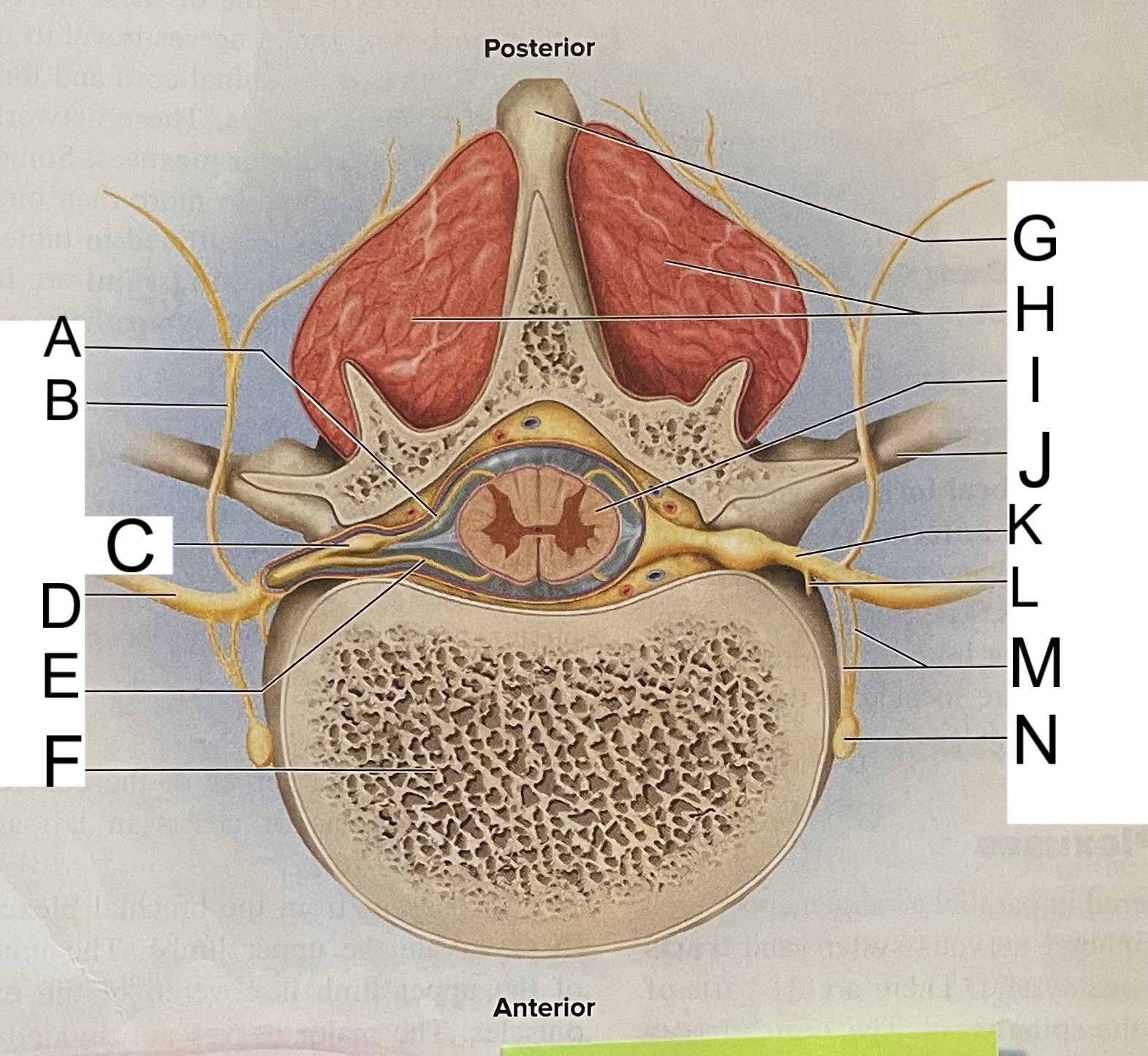
E
anterior root
F
vertebral body
G
spinous process of vertebra
H
muscles of back
I
spinal cord
J
transverse process of vertebra
K
spinal nerve
L
meningeal branch
M
communicating rami
N
sympathetic ganglion
How many cranial nerves are there?
12
How many spinal nerves are there?
31
Neuroglia of the CNS
astrocyte, microglia, oligodendrocyte, ependymal
Neuroglia of the PNS
Schwann cells, satellite cells
Most common type of neuroglia?
astrocyte
Function of astrocyte
Regulating blood brain barrier
Clearing excess neurotransmitters
Help synapse formation
Nourishes neurons
Function of microglia
Phagocytosis
Injury repair
Brain development
Function of oligodendrocyte
Generate and maintain myelin in CNS
Increase speed of axonal signal conduction
Function of ependymal cells
Control production and flow of cerebrospinal fluid
Brain metabolism
Waste clearance
Function of satellite cells
Support cells that surround soma of PNS
Function of Schwann cells
Produce myelin in PNS
Where are the ganglia of the ANS found?
Along the brainstem and spinal cord
What are the rami?
branches of spinal nerves: meningeal, communicating, dorsal, ventral
What are sulci?
shallow grooves of brain
What are fissures?
deep grooves of brain
Where does the CSF flow within the meninges?
the subarachnoid space
What types of tests could test cerebellar function?
Test of balance, finger to nose, heel to shin
What are gyri?
ridge on the cerebral cortex
What does rostral mean?
towards the nose (anterior part of head)
What does caudal mean?
towards the tail