Pharmacodynamics / pharmacokinetics
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
PK meaning
Action of animal on drug - absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion
PD meaning
Action of drug on animal
Clinical efficacy takes data from
In vitro sensitivity, PK, PD
Amoxicillin as semi synthetic anti microbial features
Penicillin with large spectrum of activity, not acid labile = oral
Synthetic antimicrobial example
Fluoroquinolone
Main MOA of antimicrobials
Prevent growth + survival of invading organisms while causing minimal damage to the host (selective toxicity to prokaryotes)
How antibiotics work - main MOA
Disrupt cell wall production + function
Disrupt cell membrane function
Distrust dna function
Disrupt protein synthesis
How antibiotics work - examples with MOA Disrupt cell wall production + function
Beta lactams, penicillins, cephalosporins
How antibiotics work - examples with MOA Distrust cell membrane
Ionophores
How antibiotics work - examples with MOA With dna disruption
Sulphonamides, fluoroquinolones, aminocoumarins
How antibiotics work - examples with MOA Distrust protein synthesis
Aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, macrolides, florphenicol

Antibiotic classifications - bacteriostatic vs bacteriocidal + eg
S- prevent replication, don’t kill susceptible (tetracyclines, macrolides)
C- kill susceptible (fluoroquinolones, beta lactams, trimethroprim)

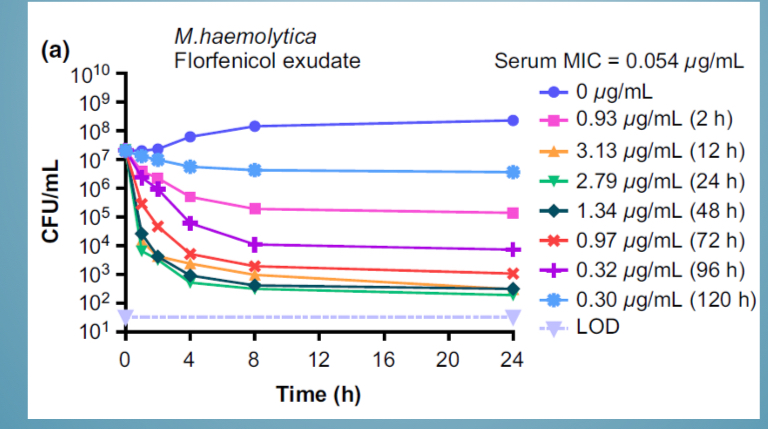
CFU meaning
Colony forming units
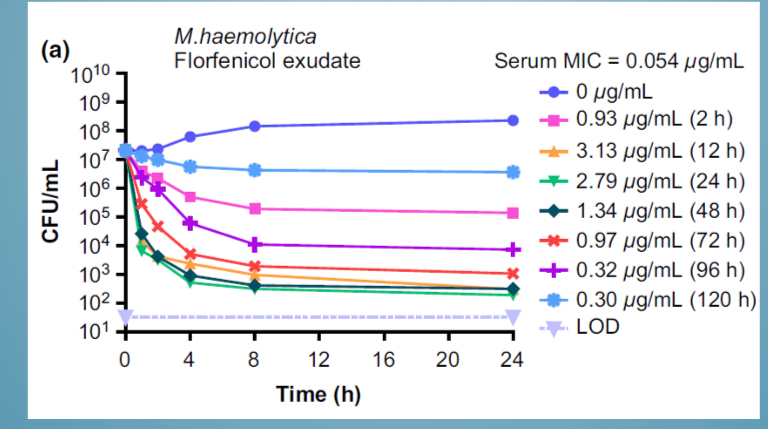
Antibiotic classifications - Conc + examples
Gentamicin cidal at high conc
Tetracyclines used at static dose
Antibiotic classifications - Bacteriostatic needs what from host as slow onset of action
Good immune response
Antibiotic classifications - Bacteriocidal need what cells
Active growing
Antibiotic classifications - Spectrum of activity + examples
Broad - don’t need to diagnose (penicillins, aminoglycosides, macrolides)
Narrow (sulphonamides, cephalosporins, tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones)
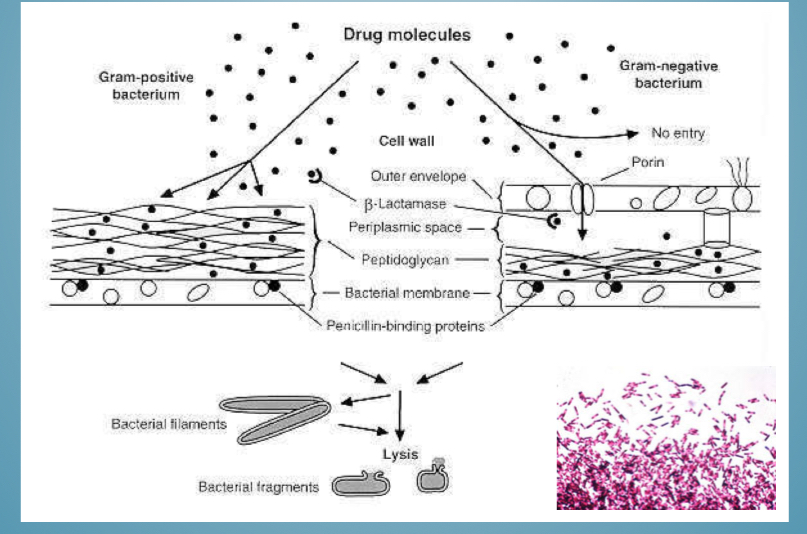
Is penicillin good against gram - or + (+why)
Gram +
Doesn’t cross outer membrane
Empiric therapy
Infecting organism not identified - broad spectrum use
Definitive therapy
Organism identified - narrow spectrum use
Prophylactic therapy
Prevent initial infection of recurrence (before CS)
Curative treatment
Treating sick animal/group following diagnosis + clinical disease
Regulation of prophylactic use
Ensure welfare, no routine use, ensure hygiene, not to increase production
metaphylaxis treatment
Treating group after diagnosis of infection + disease in part of group → prevent spread to those in close contact
Categories of antibiotic use
A - avoid
B- restrict
C- caution
D- prudence
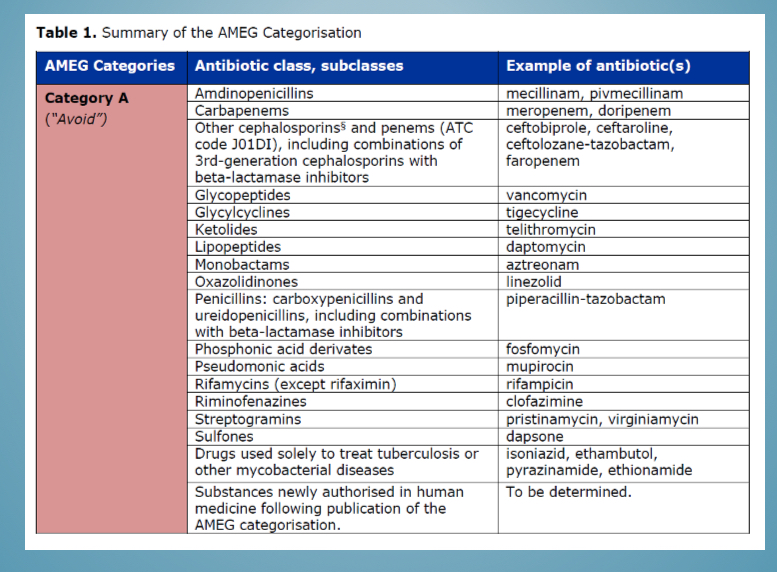
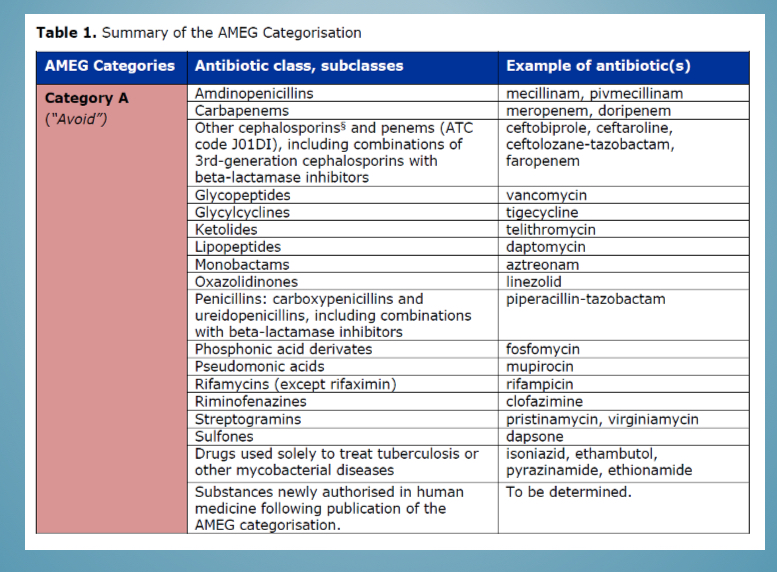
Categories of antibiotic use - classes in category a
Sulfones, amdinopenicillins
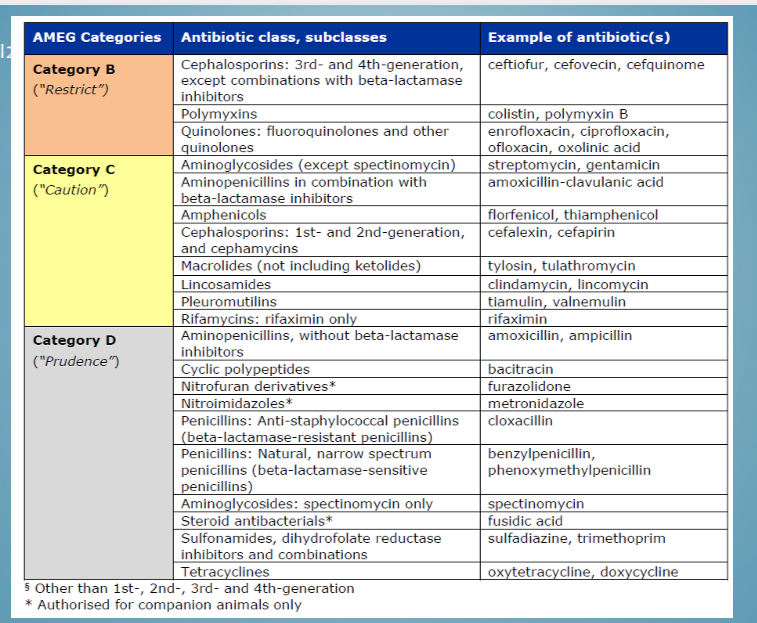
Categories of antibiotic use - classes in category b
3+4 cephalosporins, quinolones
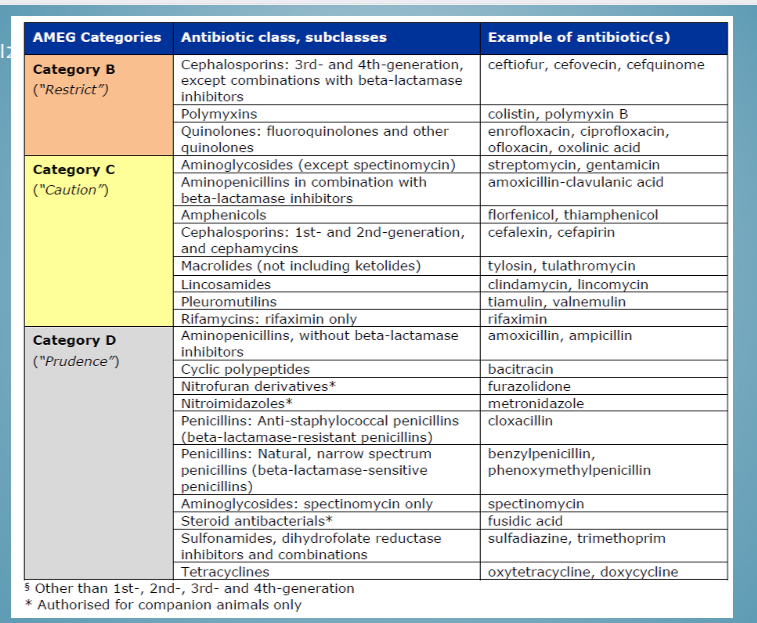
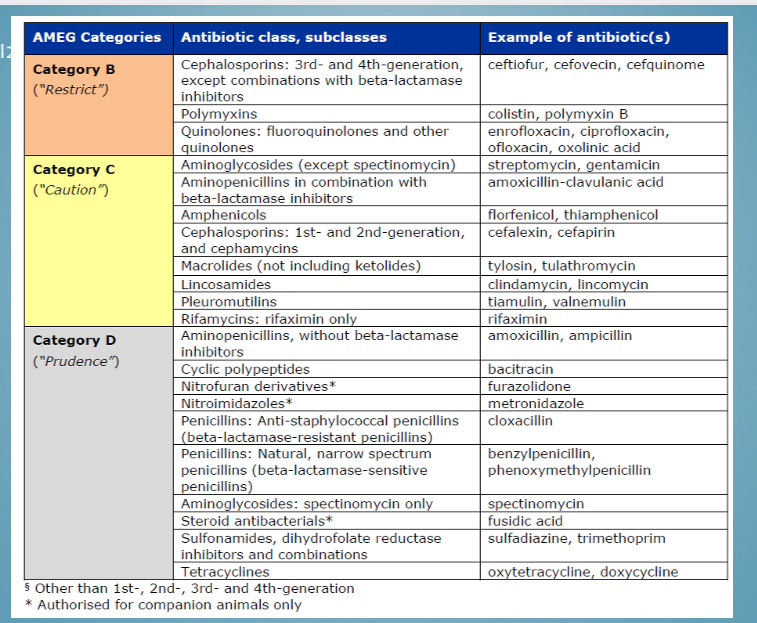
Categories of antibiotic use - classes in category c
Aminoglycosides, 1+2 cephalosporins
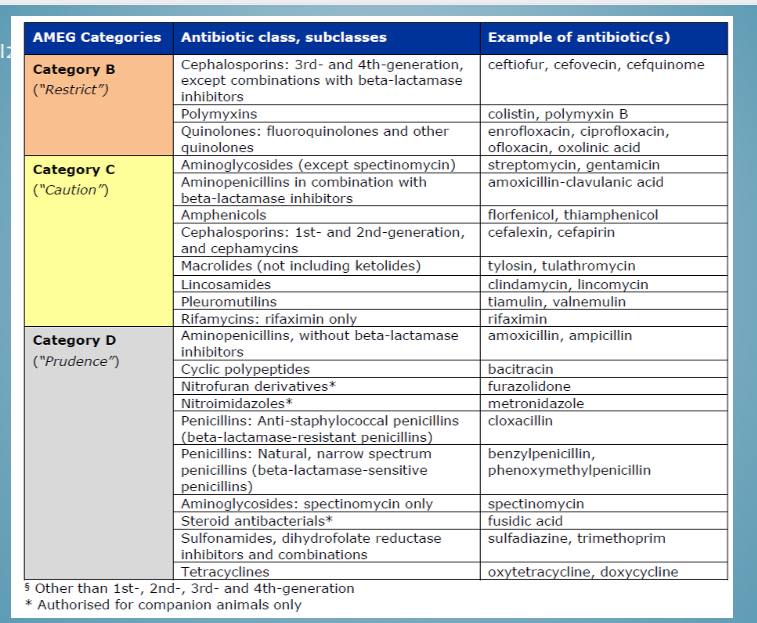
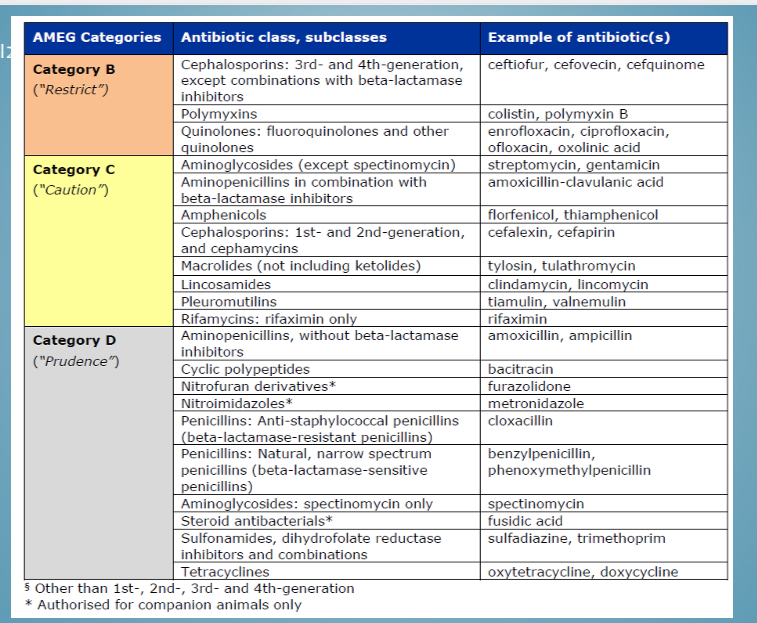
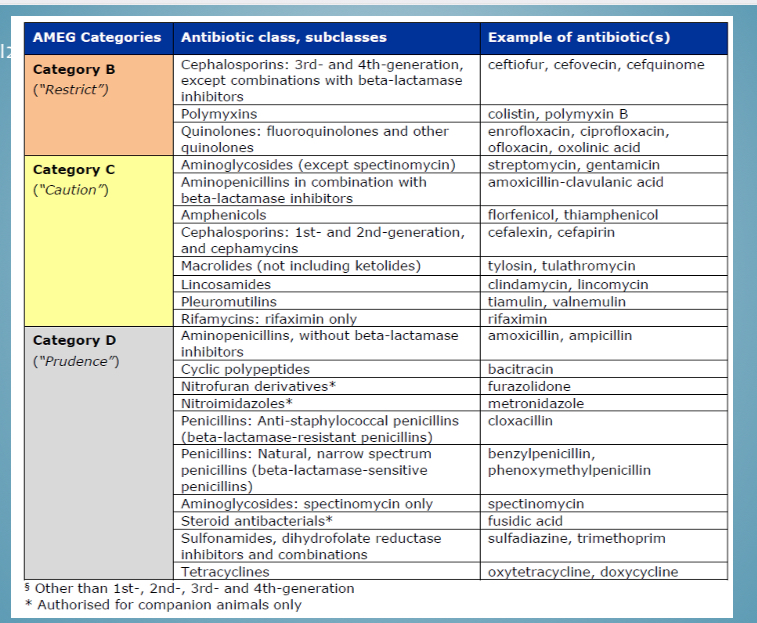
Categories of antibiotic use - classes in category D
Penicillins, steroids, sulfonamides
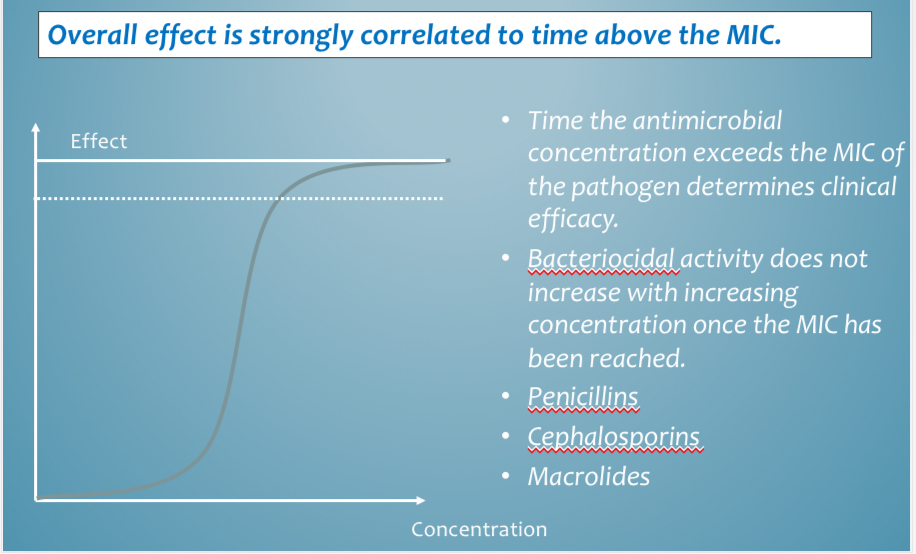
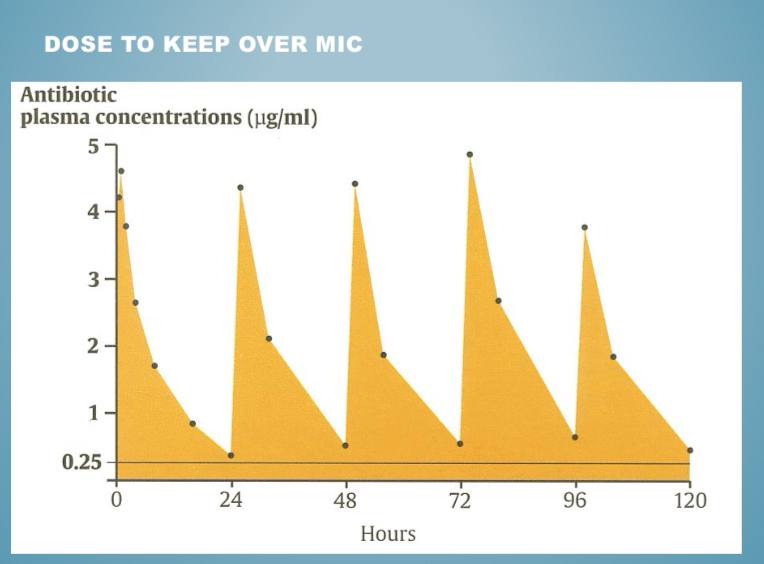
Length of treatment MOA - time over MIC dependent examples
Penicillins, cephalosporins, tetracyclines, macrolides
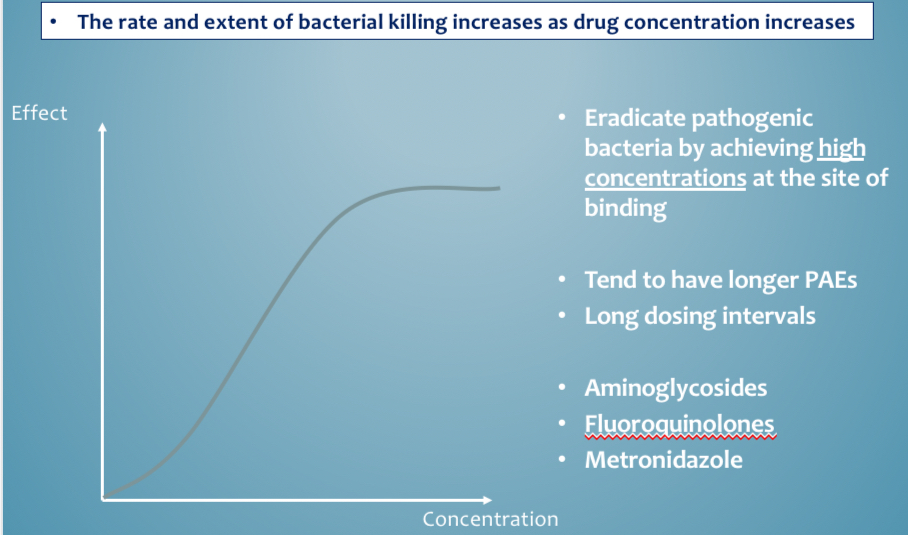
Length of treatment MOA - conc dependent examples
Aminoglycosides
Length of treatment MOA - area under curve dependent examples
Fluoroquinolones
Post antibiotic effect (PAE) meaning
Ability of drug to suppress/kill bacteria after drug conc has dropped below MIC
What affects systemic availability of drug
Dose, route of administration, dose rate, access to site of infection
Route of administration - injection features (pros+cons)
Severe infection
+for poor absorption, no GI absorption, quicker onset (IV)
-client training, compliance, pain, cost, aseptic technique, higher initial conc in other places, soluble prep
Route of administration - IV features (pros+cons)
Enters cells via passive diffusion
+total dose enters circulation
-high conc quickly declines (give slowly)
Route of administration - IM,SC features (pros+cons)
+rapid absorption
-pain, scar, withdrawal period, no large vol
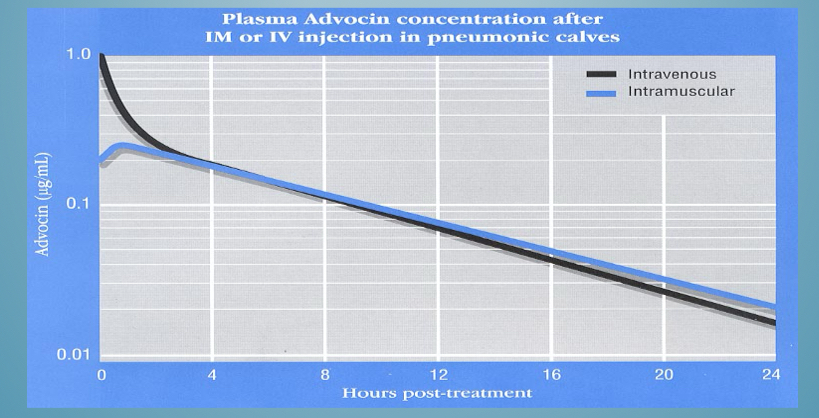
What needs to be good for route of admisnitatrion to have no effect
Absorption
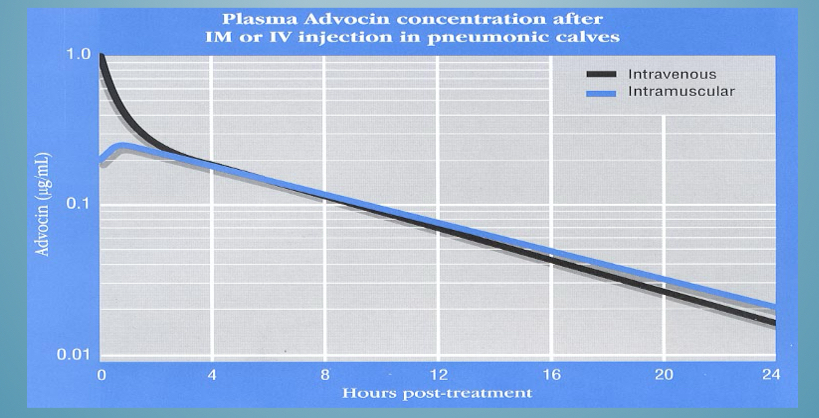
Route of administration - oral features (pros+cons)
-need to take GI tract into account (rumen dilutes), less bioavailability, hepatic portal vein (first pass metabolism), affected by food
What affects systemic drug distribution
Blood flow, cell barrier penetration, diffusion/perfusion, binding to plasma proteins (available to kill bacteria, urine excretion, long acting), selective location binding
Vol of distribution def
Reflection of amount left in blood after drug absorbed (large = doesn’t remain in blood)
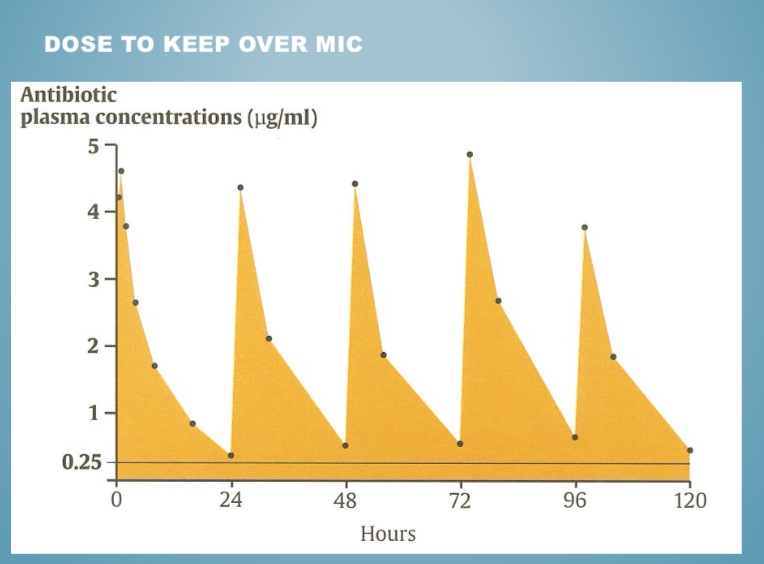
Half life def
Time required for plasma conc to half after reaching pseudo-equilibrium distribution
Synergism def + what affects it
potentiation of 1 drug action by another (preventing drug or bacterial metabolism)
Conc, bacterial life cycle phase, L-form inhibition
Half life vs clearance
C- ability to eliminate drug
HL- overall elimination during terminal phase (depends on clearance + distribution)
Methods of drug elimination
Kidney, liver, bile, sweat, milk, faeces
Methods of clearance
Liver metabolism, unchanged excretion in kidney
Fraction unchanged (fu) meaning
Proportion of drug cleared by kidneys
Fraction unchanged (1-fu) meaning
Fraction of drug cleared by metabolism
What affects drug elimination by liver
Blood flow, enzyme activity (inactive + active metabolites), liver damage, other drugs (enzymes)
What affects drug elimination by milk (acidic)
Dose, lipid soluble, ionisation at blood pH (alkaline), disease (mastitis)
Best classes for udder + lung infection
Macrolides
Which groups are beta lactams
Penicillins, cephalosporins
Beta lactams - groups + examples
Simple penicillins = penicillin G, penethamate
Broad spectrum penicillins - ampicillin, amoxicillin, cloxacillin
Cephalosporins
Beta lactams MOA
Interferes with cross links in cell wall in growth → weaken cell wall → lyses
Classes of penicillins 5 + examples
Natural - penicillin G, penicillin V
Beta lactamase resistant - cloxacillin
Aminopenicillins - amoxicillin, ampicillin
Extended agents - ticarcillin, carbenicillin
Augmented agents - amoxicillin + clavulanate
form of penicillin for farm animals (reduces pain)
Procain penicillin
Penicillins + cephalosporins main properties
Kidney excretion, not enter CNS, weak acid, 50% plasma protein bound
Penicillins + cephalosporins side effects
Immune mediated reactions - haemolytic anaemia, thrombocytopenia (type 2 hypersensitivity), anaphylaxis (type 1 hypersensitivity)
Procaine reactions- CNS stimulation
Aminopenicillins - examples
Ampicillin, amoxicillin
Aminopenicillins - Treats
Gram - aerobes (salmonella, E. coli)
Which species is oral admiration of penicillin not used
Rabbits, Guinea pigs, hamsters, gerbils, small herbivores
Augmented amoxicillin - treats (better than aminopenicillins)
Gram - and gram +
1st gen cephalosporins - treats + examples
Gram + Aerobes, gram - aerobes
Cephapirin, cephalexin, cephalonium
2nd gen cephalosporins - treats
Some gram + aerobes, gram - aerobes, gram - anaerobes
3rd gen cephalosporins - treats + examples (not for general practice)
Mainly gram - aerobes, some gram + aerobes, pseudomonas
Ceftriaxone, cefotaxime
4th gen cephalosporins - treats + examples (cattle, horse, pigs only)
Gram + aerobes, gram - aerobes, pseudomonas
Cefquinome
Protein synthesis inhibitors - bind to what
Bacteria ribosomes
Protein synthesis inhibitors - Example groups
Aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, macrolides, lincosamides
Protein synthesis inhibitors - Aminoglycosides examples
Gentamicin, amikacin
Protein synthesis inhibitors - Aminoglycosides features
Polar, water soluble → can’t cross lipid cell membranes → synergistic with beta lactams
Need active oxygen carrier to enter cell → not for anaerobes
Protein synthesis inhibitors - Aminoglycosides MOA
Irreversibly bind to 30S ribosomes → disrupt initiation of protein synthesis, misread mRNA → bacteriocidal
Protein synthesis inhibitors - Aminoglycosides treats
Gram + aerobes, gram - aerobes
Protein synthesis inhibitors - Aminoglycosides distribution
Extra cellular fluid (not CSF)
Protein synthesis inhibitors - Aminoglycosides elimination
Kidney
Protein synthesis inhibitors - Aminoglycosides side effects
Nephrotoxicity (PCT damage) → azotaemia
Ototoxicity → CN8 damage
Protein synthesis inhibitors - tetracyclines MOA
Enter bacteria with active transport → Bind to 30S ribosomes → bacteriostatic
Protein synthesis inhibitors - tetracyclines treats
Gram +, gram -, mycoplasmas
Protein synthesis inhibitors - tetracyclines excretion
Kidney (doxycycline intestine), bile,
Protein synthesis inhibitors - tetracyclines examples
Doxycycline
Protein synthesis inhibitors - tetracyclines distrubition
In tissues (not CNS), pneumonic lung tissue
Protein synthesis inhibitors - tetracyclines side effects
Discolour bone, inhibit foetal bone growth, tubular necrosis, chelate calcium
Protein synthesis inhibitors - macrolides examples (synthetic = broader spectrum, better)
Erythromycin, clarithromycin, azithromycin
Protein synthesis inhibitors - macrolides MOA
Reversibly bind to 50S ribosome → inhibit RNA dependent protein synthesis → bacteriostatic, bacteriocidal at high conc
Reduced activity at low pH (pus)
Protein synthesis inhibitors - macrolides Treats
Gram + aerobes, gram - aerobes, anaerobes, atypical bacteria
Protein synthesis inhibitors - macrolides Absorption (erythromycin, azithromycin)
E- destroyed by GI acid
A- acid stable
Protein synthesis inhibitors - macrolides Distribution
Extensive, minimal CSF
Protein synthesis inhibitors - macrolides Elimination (erythromycin, azithromycin)
E- bile, enterohepatic recycling
A- bile
Protein synthesis inhibitors - macrolides Example used in farm animals (feed)
Tylosin
Protein synthesis inhibitors - macrolides Side effects
GI motilin agonists → stimulate motility, diarrhoea
Hyperthermia, hepatoxicity
Protein synthesis inhibitors - lincosamides examples
Lincomycin, clindamycin
Protein synthesis inhibitors - lincosamides Vs macrolides
L- not for gram - aerobic
M - gram - aerobic
Protein synthesis inhibitors - lincosamides MOA
Reversibly bind to 50S ribosome → inhibit RNA dependent protein synthesis → bacteriostatic, bacteriocidal at high conc
Protein synthesis inhibitors - lincosamides treats
Gram + aerobes, gram + anaerobes, gram - anaerobes, mycoplasma
Protein synthesis inhibitors - lincosamides side effects
Colitis (herbivores)
Bacteriostatic example of dna metabolism inhibitor
Sulfonamides
Bactericidal examples of dna metabolism inhibitor
Potentiated sulfonamides, fluoroquinolones, metronidazole
Bacteriostatic example of dna metabolism inhibitor - sulfonamides MOA
Block production of pyrimidines + purines (PABA) for dna synthesis
Doesn’t affect mammalian cells (folate)
Bacteriostatic example of dna metabolism inhibitor - sulfonamides example
Trimethoprim
Bacteriostatic example of dna metabolism inhibitor - sulfonamides absorption
GI tract (binds to feed)
Bacteriostatic example of dna metabolism inhibitor - sulfonamides distribution
Tissues, lung, CSF, protein bound