Photons
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
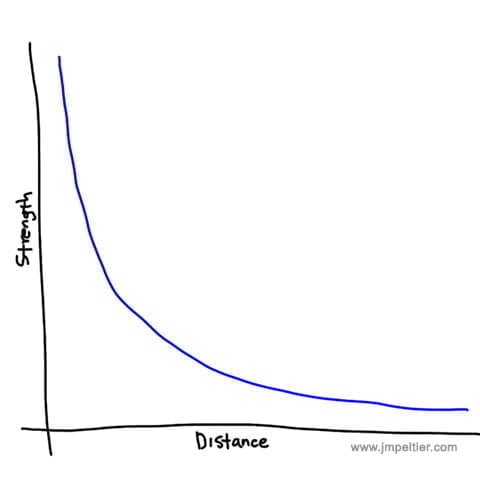
State the Inverse Square Law.
The intensity of the radiation is INVERSELY PROPORTIONAL to the squared distance away from the source.
Draw graph to represent the inverse square law relationship. (Y=intensity)
Define attenuation
Attenuation results from ENERGY TRANSFER from the beam to the medium it travels through.
What may the interactions that happen due to attenuation cause ?
The photons to be completely absorbed or to be scattered.
What is the relationship between the thickness of the medium and intensity of the beam? (Draw graph)
Inverse exponential relationship
What is HVL?
Half life layer - the thickness of a specified material that will reduce intensity of a photon to one half of its original value.
What is HVL used as ?
Measure f beam quality.
What does having a higher HVL mean ?
Fewer lower energy photons.
Describe elastic scatter ( images if possible ) .
Incident photon has less energy than electron binding energy.
No changes to atom.
Scattering mostly forward
Photon energy unchanged
Describe photo electric absorption
Dominant prices up to 500 KeV
Photons energy absorbed by inner shell electron
Electron ejected
Lower orbital shell is filled by another electron
Low energy characteristic x-ray is emitted.
Describe Compton scatter
Photon interacts with orbiting electron
Orbiting electron is ejected
Lower orbital shell energy photon is scattered
Describe pair production
Photon energies >1.02 MeV
Electron and positron created
Positron annihilated forming 2 × 0.51 MeV photons
Name the variation in energies of the net reaction process from lowest to highest.
Elastic scatter → photoelectric absorption → Compton scatter → pair production (linac)
What is dose?
Energy deposited in mass of material.
What is attenuation directly related to and what are it’s exceptions ?
Directly related to the CHANGE IN THE POWER of the BEAM but :
Loss in beam intensity after passing though medium is not absorbed dose.
Some energy in scattered photons (not deposited in medium)
Energy imparted to electrons from photon interactions contributes to absorbed dose.
What does dose require?
Requires transfer of kinetic energy to electrons.
Electrons then deposit energy.
Give 3 features of ejected electrons.
Lose energy continuously
Travel in a forward direction
Have a finite range of travel (depending on their initial K.E)
Define KERMA
K.E released to the charged particles (electrons) per unit of mass.
Is NOT the same as deposited dose.
What is charged particle equilibrium (CPE) ?
A condition in an irradiated medium:
Number + energy of charged particles = to those leaving it energy ring a small volume.
What does a CPE result in ?
Results in a steady state where absorbed dose = collision KERMA.
What happens to KERMA in the presence of attenuation ?
KERMA is not constant due o the attenuation of the beam .
Fall in dose after CPE.
Further from radiation dose = lower beam intensity = drop in K.E as we move through material .
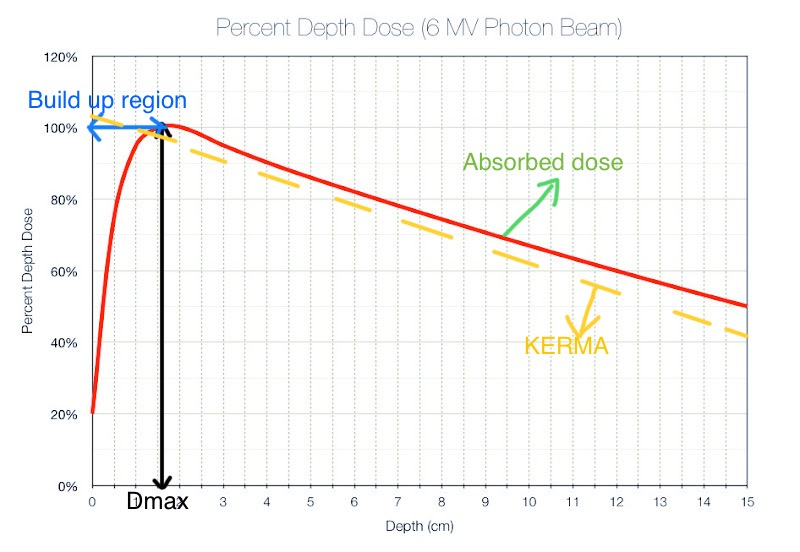
Draw graphs for Inverse square law, attenuation, build up and % depth dose.
DRAW MV depth dose curve including 4 regions.
After the Dmax is the fall of region.