MGW 4-3 [Tuplets-Polyrhythm]
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Three (3) ways to syncopate in compound meters
1) tie into strong beats (replace tied sixteenth notes with eighth notes);
2) accent weak beats;
3) put rests on strong parts of the beat
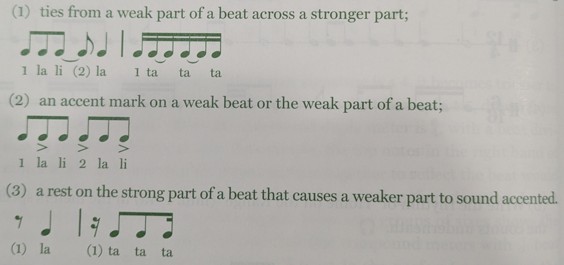
Triplet
a note that is borrowed from compound meter. Here, we divide the notes into three parts instead of 2. Most normally used in simple meter.
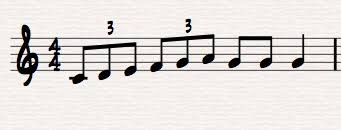
How do we count triplets?
1 la li, borrowed from compound meter
What does it mean to develop music?
It means to take an idea and to expand it out. (i.e., I could say I went to the park. But, if I develop this idea, I can restate it and say, I went to the park and saw a dog. It was a sunny day. Same happens in music!)
What is foreshadowing?
When concepts from the beginning of the piece allude to major musical moments that happen later.
Rule of Triplets
Triplets use 3 notes that are 1 beat unit smaller than the one you will replace. (i.e. 3 eighth notes are need for 1 quarter; 3 quarter notes are needed for 1 half, etc.)
Duplets
A borrowed rhythm from simple meter. The beat is separated into two notes instead of three.
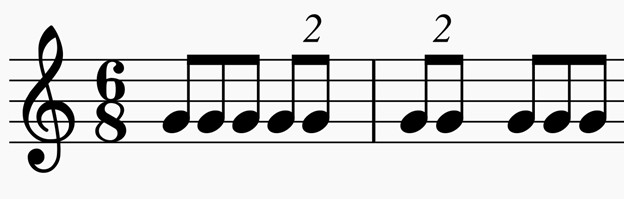
Quadruplets
A borrowed rhythm from simple meter. The beat is separated into four notes instead of three or six.

Tuplets
The name for borrowing different rhythms from different meters. This has triplets, duplets, and quadruplets all in it!
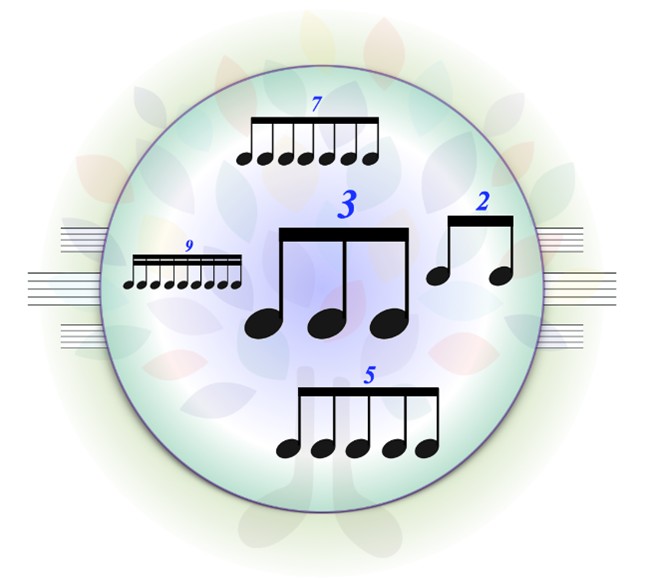

Tuplet Ratios
Read as X against X. In this case: “14 against 8”. The first number tells us how many notes are in the tuplet. The second number tells us how many numbers of notes are being replaced. In this case, if sixteenth notes were being replaced, there would be 14 thirty-second notes in the span of 8 sixteenth notes. Also used to show polyrhythm
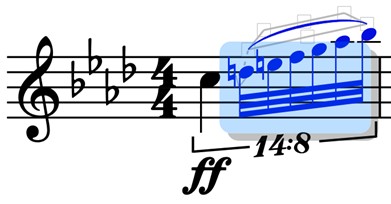
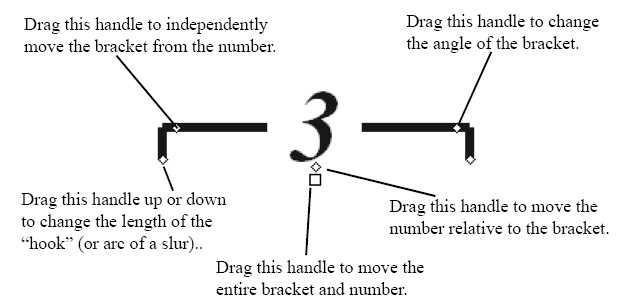
Bracket
Used to clarify how long the tuplet lasts, especially if there are multiple different lengths of notes in the tuplet
Secondary and Tertiary Beams
The beams underneath the main beam to tell us if it is a sixteenth or thirty-second note.
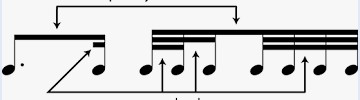
Tuplet Secondary and Tertiary Beams
Sometimes are broken or split up to clarify where the tuplet begins and ends

Polyrhythm
when two different beat divisions fight against each other. Makes it hard to know what meter is being played for the listener.

Most common polyrhythm
2:3 (two against three)
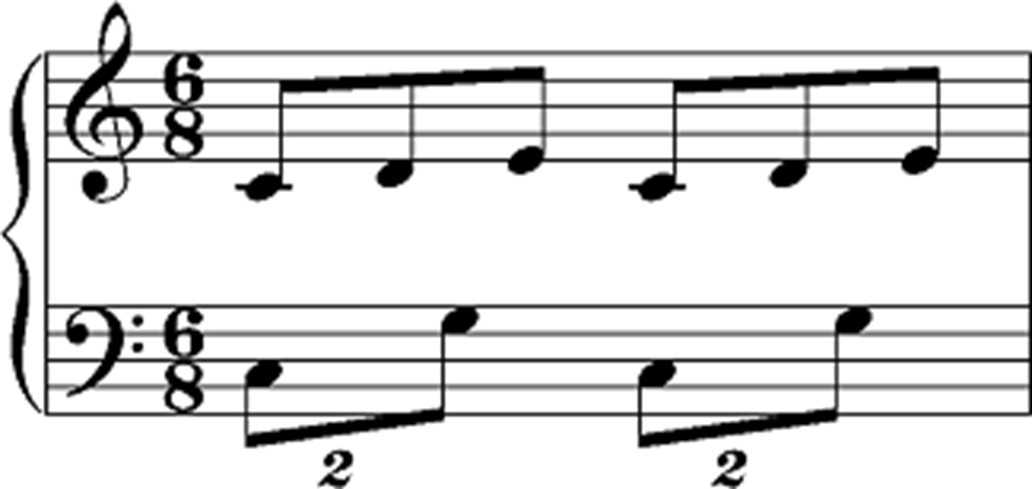

Phrase to remember how to play 2:3
Nice piece of cake