CH. 2 | Motion
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is Motion?
1) Change of position
2) The passage at time
2 Fundamental components of Motion
Change in position
Change in time
3 Important combinations of length and time
Speed
Velocity
Acceleration
Speed
Change in position with respect to time
tells you how FAST something is moving
Average speed
Most common measurement
Instantaneous speed
Time interval approaches zero
speed at any specific instant
Constant speed
Moving over equal distances in equal periods of time

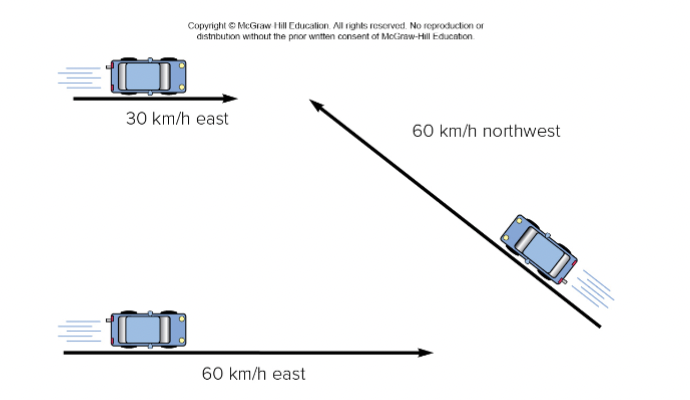
Velocity
Describes speed (How fast it is going?) and direction (Where it is going?)
Graphical representation of vectors: length = magnitude; arrowheads = direction
tells you how fast and in what DIRECTION
Acceleration
Rate at which motion changes over time
Speed and Direction can change
Can be negative

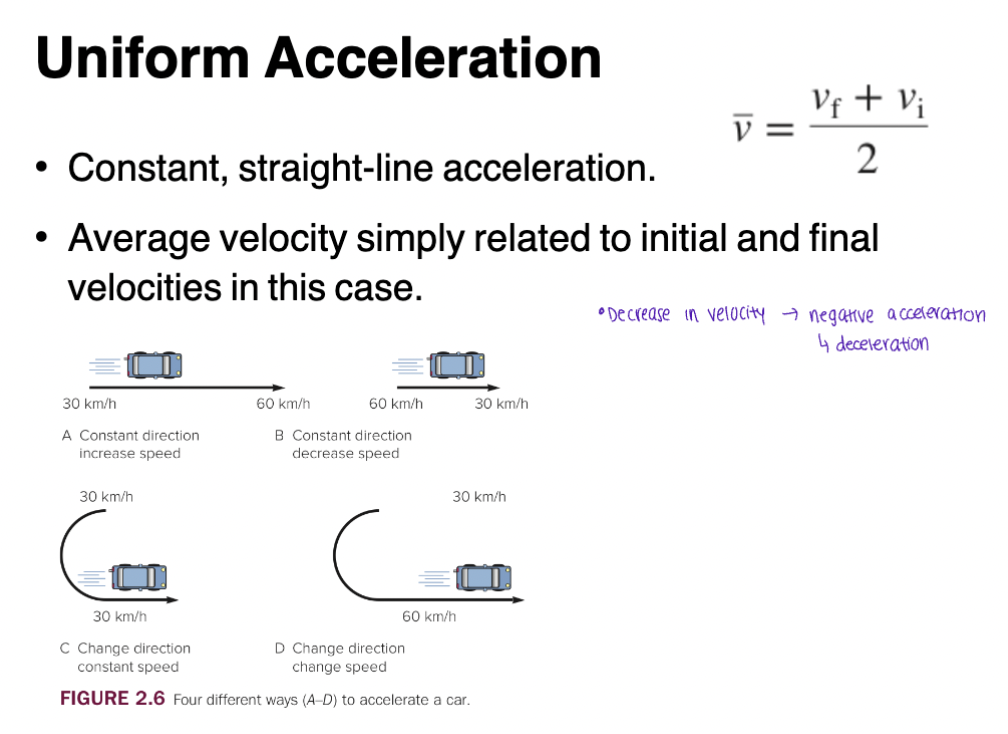
Uniform Acceleration
Constant, straight-line acceleration
Average velocity simply related to initial and final velocities in this case
- decrease in velocity → negative acceleration → deceleration
Force
A push or pull capable of changing an object’s state of motion.
Overall effect is determined by the (vector) sum of all forces - the “net force” on the object
net force : the sum of all forces acting on an object
Fundamental Forces
Gravitational
Electromagnetic
Weak force
Strong force

Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
Motion continues unchanged without unbalanced forces
Retarding force decreases speed
Boost increases speed
Sideways force changes direction
Free Falling Objects
Free fall
Falling under influence of gravity without air resistance
Distance proportional to time squared
Speed increases linearly with time
Trajectories exhibit up/down symmetries
Acceleration same for all objects
Compound Motion (3 Types)
Vertical motion
Horizontal motion
Projectile motion
Projectile Motion
An object thrown into air
i.e., football
Vertical projectile
Horizontal projectile

3 Laws of Motion
Isaac Newton
Developed calculus and a law of gravitation
Essential idea - forces
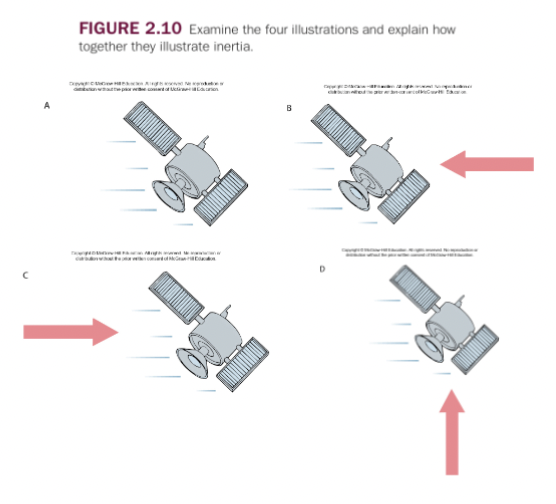
Newton’s First Law of Motion
“The Law of Inertia”
Every object remains at rest or in its state of uniform straight-line motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force
→ net force > (greater than) 0
An object in motion stays in motion
An object in rest stays at rest
Inertia resists any changes in motion
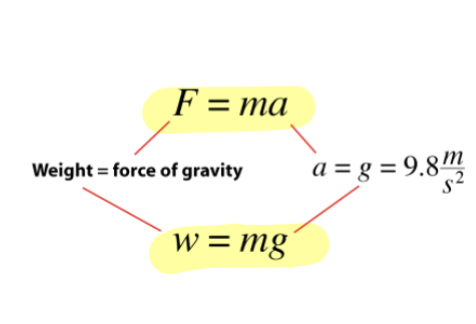
Newton’s Second Law of Motion
F = ma
1 newton = 1 N = 1 kg*m ∕ s2
Forces cause accelerations
Unit = Newton (N)
Proportionality constant = mass
More force, more acceleration
More mass, less acceleration
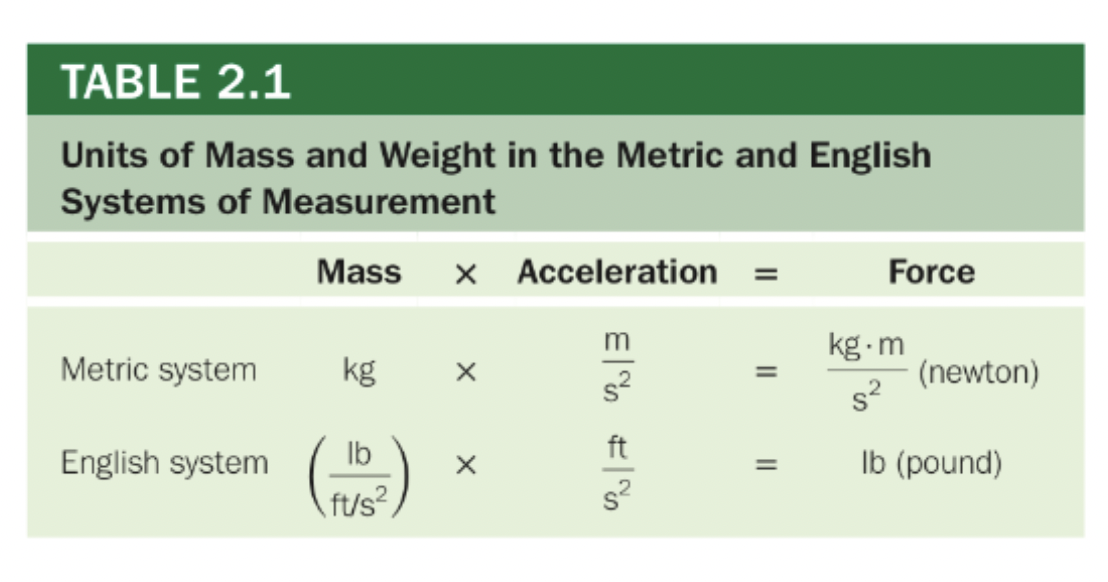
Weight and Mass
Weight
Force of gravity acting on the mass
Mass
Quantitative measure of inertia; the amount of matter
Kilogram
Measure of mass
Picture
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
F A due to B = F B due to A
i.e., 30N = 30N
Relates forces between objects
Source of force - other objects
Whenever 2 objects interact, the force exerted on one object is equal in size and opposite in direction to the force exerted on the other object
A single force does not exist by itself
Momentum
monmentum = mass * velocity
p = mv
Important property closely related to Newton’s Second Law
Includes effects of both motion (velocity) and inertia (mass)
Conservation of Momentum
The total momentum of a group of interacting objects remains the same in the absence of external forces
Applications: Collisions, analyzing action/reaction interactions

Impulse
impulse = Ft
A force acting on an object for some time (t)
An impulse produces a change in momentum
Applications: airbags, padding for elbows and knees, and projectile plastic barrels on highways
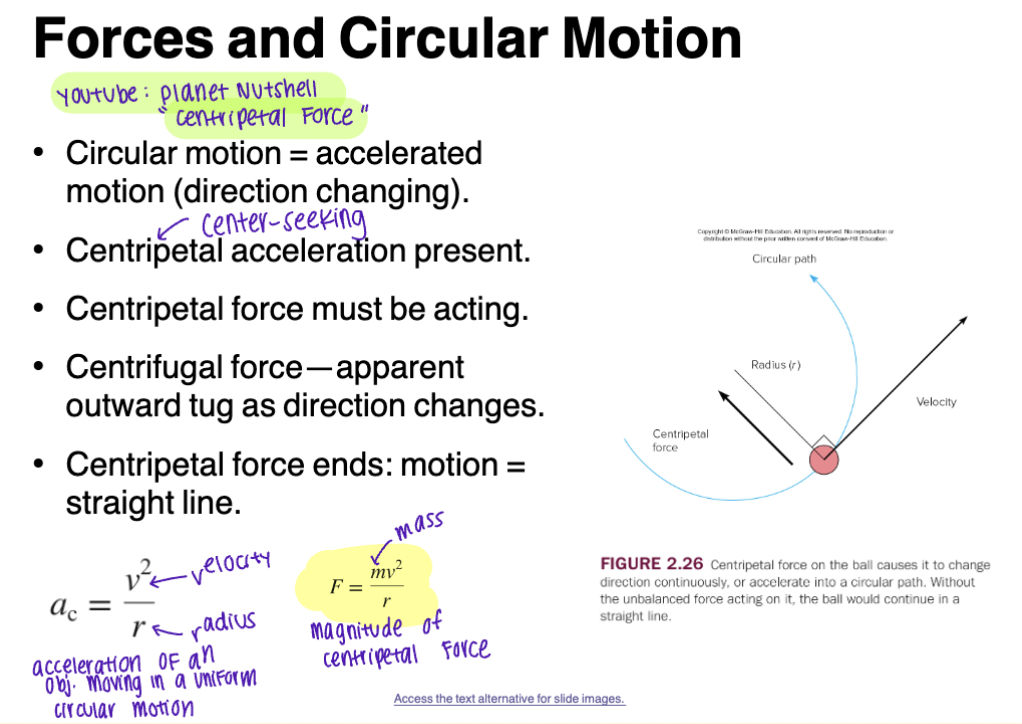
Forces and Circular Motion
Circular motion = accelerated motion (direction changing)
Centripetal (center seeking) acceleration is present
Centripetal force must be acting
Centrifugal force - apparent outward tug as direction changes
Centripetal force ends: motion = straight line
Newton’s Law of Gravitation
F = G m1m2 ∕ d2
Gravity is an attractive force between all masses
Proportional to product of the masses
Inversely proportional to separation distance squared
Provides centripetal force for orbital motion