Unit 7. Neuro
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
Name the four types of glial cells
Astrocytes
Ependymal
Oligodendrocytes
Microglia
What are astrocytes?
Most abundant glial cell
Regulation of metabolic environment
Repair neuron after injury
What are ependymals?
Found in roof of 3rd & 4th ventricles & spinal cord
From choroid plexus, produces CSF
What are oligodendrocytes?
Form myelin sheath in CNS
What are microglia?
Act as macrophages
Function of the frontal lobe?
Motor cortex
Function of the parietal lobe?
Somatic sensory cortex
Function of the occipital lobe?
Vision cortex
Function of the temporal lobe?
Auditory cortex & speech centers
What are two sub-areas of the temporal lobe?
Wernicke's - understanding speech
Broca's - motor control of speech
Name the 12 cranial nerves
1. Olfactory
2. Optic
3. Occulomotor
4. Trochlear
5. Trigeminal
6. Abducens
7. Facial
8. Vestibulocochlear
9. Glossopharyngeal
10. Vagus
11. Accessory
12. Hypoglossal
CN. 1
Olfactory
Sensory
Smell
CN. 2
Optic
Sensory
Vision
CN. 3
Occulomotor
Motor
Eye movement, pupil constriction
CN. 4
Trochlear
Both
Eye movement
CN. 5
Trigeminal
Both
V1 (opthalamic) - somatic sensation to face
V2 (maxillary) - somatic sensation to ant. 2/3 of tongue
V3 (mandibular) - mastication
CN. 6
Abducens
Motor
Eye movement
CN. 7
Facial
Both
Face movement (except mastication), eyelid closing, taste to ant. 2/3 of tongue
Name the branches of CN. 7
"Two Zebras Bit My Carrot"
Temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, cervical
CN. 8
Vestbulocochlear
Sensory
Hearing & balance
CN. 9
Glossopharyngeal
Both
Somatic sensation & taste to post. 1/3 of tongue
CN. 10
Vagus
Both
Swallowing
CN. 11
Accessory
Motor
Shoulder shrug
CN. 12
Hypoglossal
Motor
Tongue movement
Which cranial nerves control eye movements?
CN. 3, 4, 6
Which eye movements does CN. 4 control?
Superior oblique
Intorsion, depression
Which eye movements does CN. 6 control?
Lateral rectus
Abduction
Which cranial nerve controls all other eye movements?
CN. 3
Which CN resides in the central nervous system?
CN. 2 - all others reside in the peripheral nervous system
What is a complication of CN. 2 being in the CNS?
If you inject LA into the optic nerve when doing regional this would be a big problem
What is tic douloureux?
Trigeminal neuralgia, CN. 5, neuropathic pain in the face
What is Bell's palsy?
Injury to facial n. (CN. 7), ipsilateral facial paralysis
What is the function of CSF?
Cushions the brain, buoyancy, & delivers optimal conditions for neurological function
Where is CSF located?
Ventricles (left lateral, right lateral, 3rd, & 4th)
Cisterns
Subarachnoid space in brain & spinal cord
What regions of the brain are NOT protected by the BBB?
CRTZ, post. pituitary, pineal gland, choroid plexus, & parts of hypothalamus
What is the normal volume & specific gravity of CSF?
~150mL
1.002 - 1.009
Where & how much CSF is produced?
Produced by ependymal cells in choroid plexus at rate of 30mL/hr
What is the circulation of CSF?
"Love My 3 Silly 4 Lorn Magpies"
L&R lateral ventricles
Foramen of Monro
3rd vent
Aqueduct of Sylvius
4th vent
Foramen of Luschka
Foramen of Magendie
Where is CSF reabsorbed?
Venous circulation via the arachnoid villi in the superior sagittal sinus
What is the formula for CBF?
CBF = CPP / cerebral vascular resistance
What are the normal values for global, cortical, and subcortical flow? (mL/100g tissue/min)
Global = 45-55 (or 15% of CO)
Cortical = 75-80
Subcortical = 20
What are the 5 determinants of CBF?
1. CMRO2
2. CPP
3. Venous pressure
4. PaCO2
5. PaO2
What is the normal value for CMRO2?
3.0 - 3.9 mL/O2/100g brain tissue/min
What factors cause CMRO2 to decrease?
Hypothermia (7% per 1 degree)
Halogenated gas
Propofol
Etomidate
Barbiturates
What factors cause CMRO2 to increase?
Hyperthermia
Szrs
Ketamine
N2O
What is the formula for CPP?
CPP = MAP - ICP (or CVP, whichever is higher)
What is the normal CPP?
50-150 mmHg
What happens if CPP is too low?
CBF becomes pressure dependent
Risk of cerebral hypoperfusion
What happens if CPP is too high?
CBF becomes pressure dependent
Risk of cerebral edema and hemorrhage
4 conditions that reduce CPP d/t increased venous pressure?
Jugular compression (improper head positioning)
Increased intrathoracic pressure (coughing, PEEP)
Vena cava thrombosis
Vena cava syndrome
What is the relationship between PaCO2 and CBF?
Linear relationship & pH of CSF around arterioles controls cerebral vascular resistance
PaCO2 40 = CBF 50 mL/100g brain tissue/min
At what PaCO2 does max cerebral vasodilation occur? What about constriction?
Max dilation = 80-100
Max constriction = 25
For every 1 mmHg increase (or ↓) in PaCO2, CBF will increase (or ↓) by 1-2 mL/100g brain tissue/min
What is the relationship between CMRO2 & CBF?
General rule:
Things that increase CMRO2 cause vasodilation (↑ CBF) & opposite is true for decreased CMRO2
Halogenated gas is the exception (they reduce CMRO2 but cause vasodilation)
How do acidosis & alkalosis affect CBF?
Resp. Acidosis = ↑
Resp. Alkalosis = ↓
Met. alk/acid does. not affect CBF b/c H+ cannot pass BBB
How does PaO2 affect CBF?
PaO2 < 50-60 = vasodilation & increases CBF
> 60 = no affect
What is the normal ICP?
5-15 mmHg
> 20 = cerebral HTN
When is ICP measurement indicated?
GCS
What is the gold standard for ICP measurement?
Intraventricular catheter
S/S of intracranial HTN
HA
N/V
Papilledema (swelling of optic nerve)
Focal neuro deficits
Deceased LOC
Szrs
Coma
What is the Monroe-Kellie hypothesis?
Brain lives in a rigid box (the skull) with 3 components: brain, blood, CSF. Equilibrium must remain, if one goes up in size or volume, one or both of the others must decrease
What is Cushing's triad?
HTN
Bradycardia
Irregular respirations
What does Cushing's triad indicate?
Intracranial HTN
Name 4 areas where brain herniation can occur?
Cingulate gyrus under the flax
Contents over tentorium cerebelli
Cerebellar tonsils through foramen magnum
Through surgery site or trauma
How does hyperventilation affect CBF?
CO2 dilates cerebral vessels = ↓ cerebral vascular resistance → ↑ CBF & ↑ ICP
Hyperventilation (PaCO2 30-35) constricts the vessels → ↓ CBF & ↓ ICP
How do NTG & Nitroprusside affect ICP?
Cerebral vasodilators → ↑ CBF & ↑ ICP
How does head position affect ICP?
Head elevation > 30 degrees facilitates venous drainage
Neck flexion or extension can compress the jugular veins, reduce venous outflow & ↑ ICP
Head down ↑ ICP
How does Mannitol decrease ICP?
Increases serum osmolarity & pulls water across the BBB towards the blood stream
What problems can arise when mannitol is given?
If BBB is disrupted, mannitol enters the brain & promotes cerebral edema
Its transiently increases blood volume, which can ↑ ICP & stress the failing heart
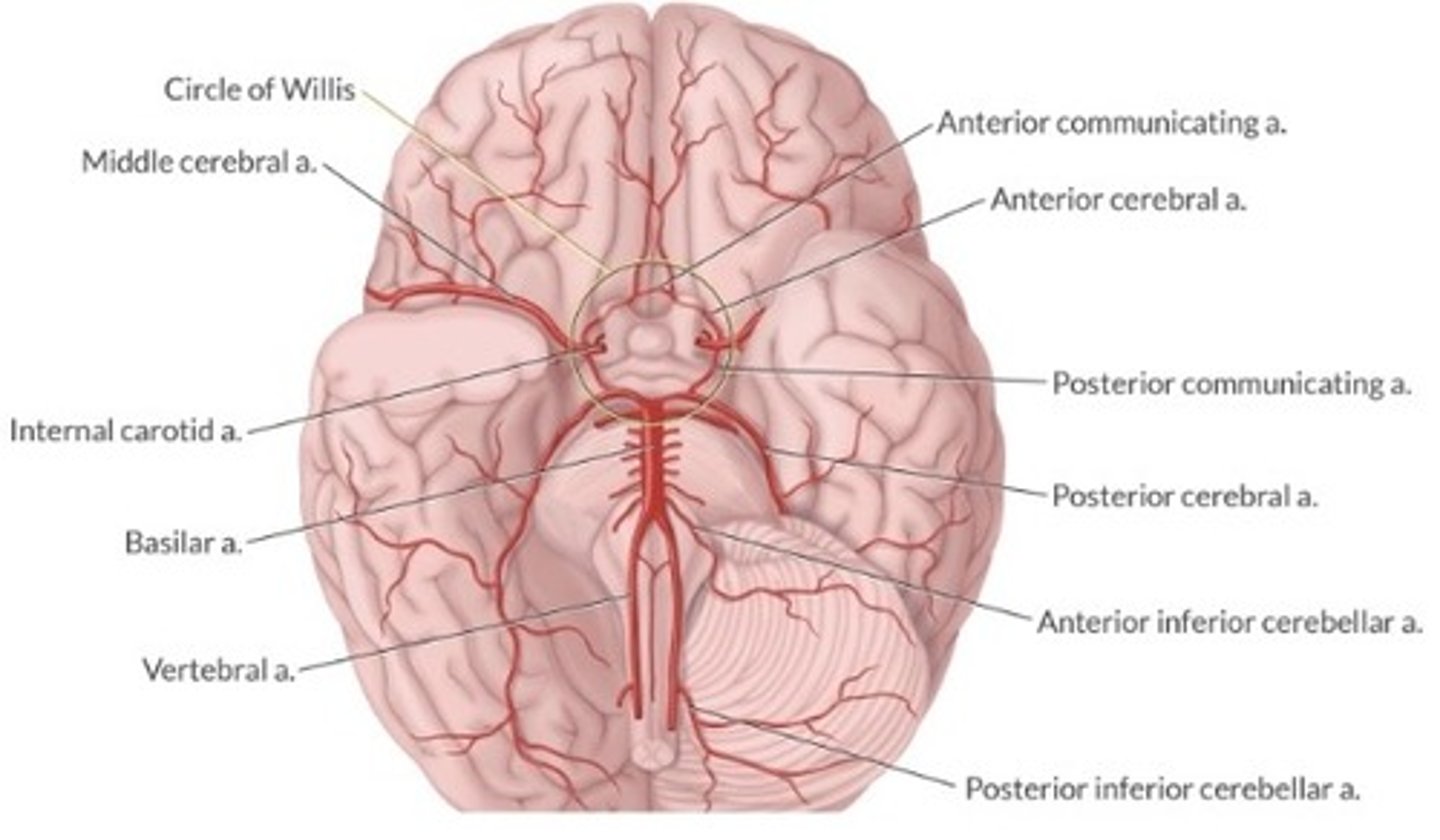
Discuss the anterior circulation of the brain
Internal carotid arteries supply ant. circulation
Enter the skull through foramen magnum
Aorta → carotid a. → internal carotid a. → circle of willis → cerebral hemispheres
Discuss the posterior circulation of the brain
Vertebral arteries supply post. circulation
Enter skull through foramen magnum
Aorta → subclavian a. → vertebral a. → basilar a. → post. fossa structures & cervical spinal cord
Discuss the anatomy of the Circle of Willis
What population of stroke pts should be given a thrombolytic agent?
Within 4.5 hours of onset of symptoms of ischemic stroke
Should diagnose with a non-contrast CT first
What is the relationship between hyperglycemia & cerebral hypoxia?
During cerebral hypoxia, glucose is converted to lactic acid. Cerebral acidosis destroys brain tissue & associated with worse outcomes. Treat with insulin
How is transmural pressure calculated (regarding cerebral aneurysm)?
MAP - ICP (MAP is pressure pushing outwards, ICP is pressure pushing inward)
What is the most common clinical finding in a pt with a subarachnoid hemorrhage?
"Worst headache of my life"
What are other S/S?
LOC (50%)
N/V
Photophobia
Fever
Obstructive hydrocephalus
What is the most common cause of morbidity & mortality in pts with SAH?
Cerebral vasospasm
What is the incidence of cerebral vasospasm & when is it most likely to occur?
25% of pts following SAH
Most likely to occur 4-9 days following SAH
What is the treatment for cerebral vasospasm?
Triple H therapy → Hypervolemia, hypertension, and hemodilution (Hct 27-32%)
Nimodipine is the only CCB shown to reduce morbidity and mortality associated with vasospasm. It does not relieve the spasm, but instead increases collateral blood flow
During endovascular coil placement for a cerebral aneurysm, it ruptures. What is the best tx at this time?
Give protamine (1mg/100U of heparin), MAP should be lowered into low/normal range
GCS
How do you treat the pt with an intracerebral bleed who is on Warfarin?
FFP, prothrombin complex, and/or recombinant factor VIIa
(Vit. K is not best for acute reversal)
How do you treat the pt with an intracerebral bleed who is on clopidogrel?
Platelet transfusion
What are 2 common ways of reducing ICP that should specifically be avoided in the pt with TBI?
Hyperventilation
Steroids
Is N2O safe in the pt with TBI?
No
Describe Grand Mal szr
Generalized tonic-clonic
Respiratory arrest
Grand Mal tx
Acute: propofol, diazepam, thiopental
Surgical: vagal nerve stim, resection of foci
Describe Focal Cortical szr
Localized to cortical region
Can be motor or sensory
Usually no LOC
Describe Absence (Petit Mal) szr
Temporary loss of awareness (but remains awake)
More common in kids
Describe Akinetic szr
Temporary LOS & postural tone
Can result in fall = head injury
More common in kids
Describe Status Epilepticus
Szr that lasts > 30min or 2 grand mal w/o regaining consciousness in between
Respiratory arrest
Acute tx for status epilepticus
Phenobarbital
Thiopental
Phenytoin
Benzos
Propofol
GA
What is the relationship between etomidate & szrs?
Etomidate can cause myoclonus. This is not associated with ↑ EEG activity in pts that do not have epilepsy
Can be used to determine where szr foci is during mapping
Describe the patho of Alzheimer's
Development of diffuse beta amyloid-rich plaques and neurfibrillary tangles in the brain
Dysfunctional synaptic transmission
Apoptosis
What class of drugs is used to tx Alzheimer's?
Cholinesterase inhibitors (tacrine, donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine)
How do cholinesterase inhibitors interact with Sux?
They increase the DOA of Sux
Describe the patho of Parkinson's
Dopaminergic neurons in the basal ganglia are destroyed
What drugs increase the risk of extrapyramidal s/s in the pt with parkinson's?
Drugs that antagonize dopamine
Metoclopramide
Butyrophenones (haloperidol & droperidol)
Phenothiazines (promethazine)
What is the most common eye complication in the periop period?
Corneal abrasion
What is the most common cause of vision loss in the periop period?
Ischemic optic neuropathy