Bot-Lec (Sem-1) - Chapter 16: Genetic Basis of Metabolism and Development
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
reproduction in living organisms
requires precise transmission of hereditary factors known as the chromosomes
chromosomes
thread-like structure located in the nucleus of the cell and control all its activities; made of protein and bears the DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid), the blueprint of what an individual may become
color; body
chroma; soma (meaning)
2-1400
range of number of chromosomes per cell
120
number of chromosomes per cell within Bambusa bambos
720
number of chromosomes per cell within Ophioglossum vulgatum
karyotype
visual representation of a chromosomes found in an organism; sex chromosomes and autosomes
Triticum aestivum
common wheat
histones
a protein that provides structural support for a chromosome
petite
what does the p in p (short) arm denotate?
metacentric; sub-metacentric; acrocentric; telocentric
types of chromosome structures
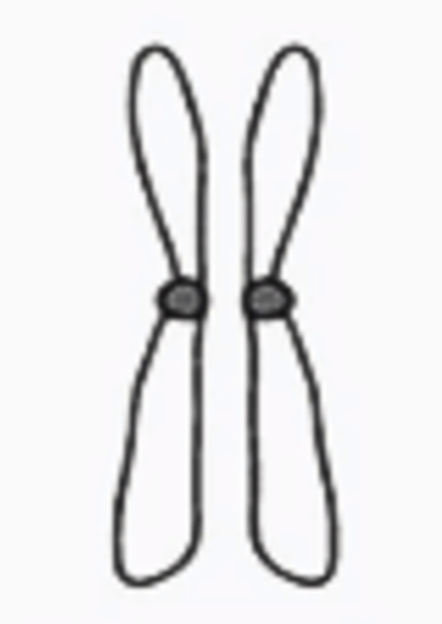
metacentric chromosome
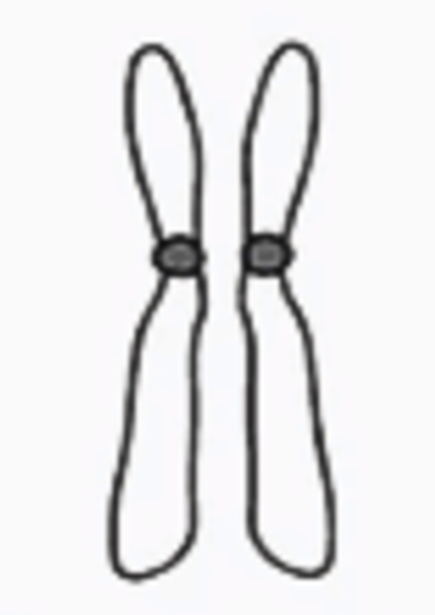
sub-metacentric chromosome
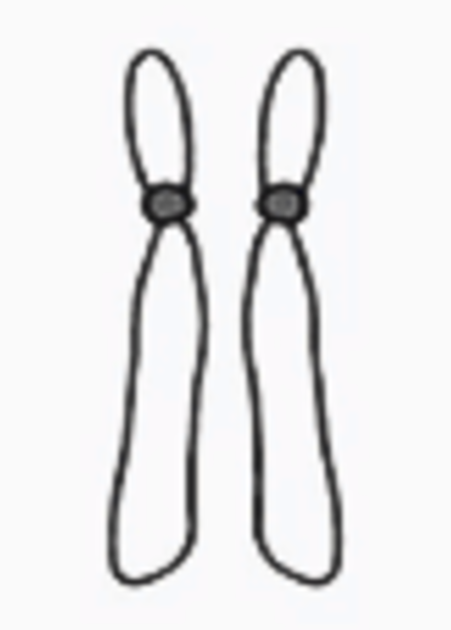
acrocentric chromosome
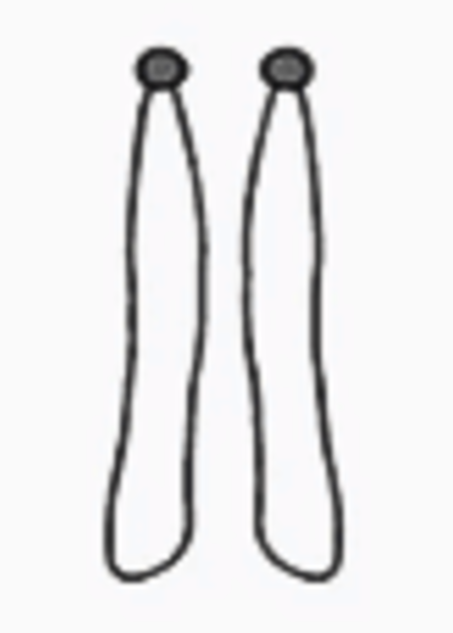
telocentric chromosome
genes
sequences of nucleotides making up the DNA that are copied and translated into proteins; may be transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA) which is brought to the cytoplasm where it is translated into protein; arranged linearly on chromosomes
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
genetic blueprint of all living organisms; made up of a base consisting of sugar, phosphate and one nitrogen base
adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C)
the four nitrogen bases
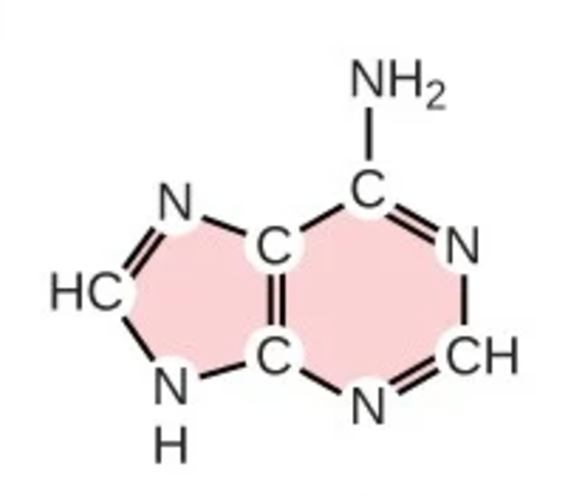
adenine
A; purine; nitrogenous base
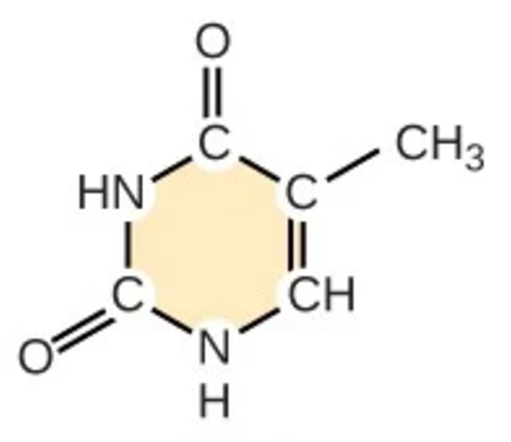
thymine
T; pyrimidine; nitrogenous base
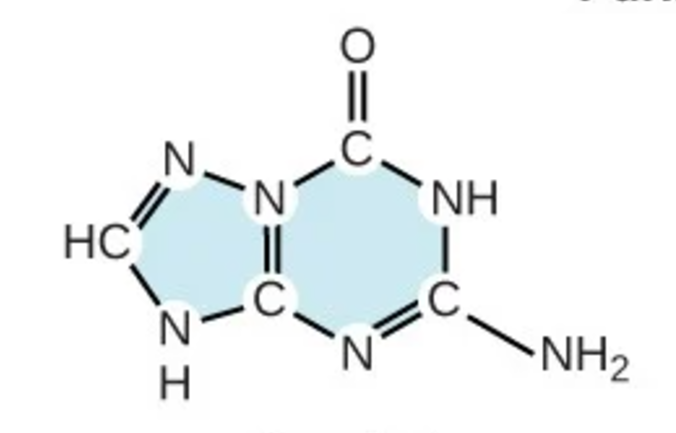
guanine
G; purine; nitrogenous base
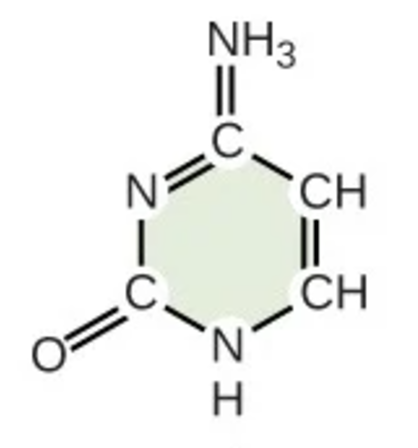
cytosine
C; pyrimidine; nitrogenous base
A & T and G & C
complementary base pairing
deoxyribose
sugar
major and minor grooves of the DNA
brought about by the double helix of DNA wherein one groove is larger than the other; can be used to tell the base sequence of a specific DNA molecule; proteins must be able to recognize specific DNA sequences on which to bind for proper functioning of cells
major groove
occurs when the backbones are far apart
minor groove
occurs when they are close together
messenger RNA (mRNA)
what DNA is converted into through transcription; guides the synthesis of proteins during translation
storage of genetic information; directing protein synthesis; genetic coding; metabolic activities, evolution, heredity, and differentiation
functions of DNA (according to Sir Inoc)
storage of genetic information
function of DNA; DNA acts as the cell's blueprint; encodes instructions for processes such as growth, photosynthesis, and reproduction; genetic information is organized into sequences called genes, which are often arranged in chromosomes within the nucleus
directing protein synthesis
function of DNA; DNA provides the template for the production of proteins, essential for plant cellular processes.
genetic coding
function of DNA; genes, segments of DNA, encode specific proteins that drive vital functions in plants, such as producing chlorophyll for photosynthesis
regulating metabolic activities
function of DNA; DNA indirectly controls metabolic processes by coding for enzymes and proteins involved in plant-specific chemical reactions
driving evolution
function of DNA; variations in plant DNA sequences, through mutations and recombination, are the foundation of evolutionary change
heredity
function of DNA; DNA is the hereditary material passed from parent plants to their offspring through seeds or vegetative reproduction
cell differentiation
function of DNA; allows cells to develop into types with specialized functions, such as root cells for absorption, leaf cells for photosynthesis, or xylem cells for water transpor
encoding protein; inheritance; regulation of cellular activities; role in evolution
functions of DNA
regulation; transcription; translation
encoding protein of genes
regulation
encoding protein of genes; controls the timing, location, and amount of gene expression
transcription
encoding protein of genes; a gene’s DNA sequence is transcribed into mRNA by RNA polymerase
translation
encoding protein of genes; the mRNA is translated into amino acids, which are linked together to form a protein; occurs in the cytoplasm at the ribosome
inheritance
a function of genes; genes pass traits from parents to offspring
regulation of cellular activities
a function of genes; genes are responsible for controlling metabolism, growth, development, and repair processes
role in evolution
a function of genes; mutations or changes in genes can lead to variations that drive evolution by natural selection
recombinant DNA; chimera
the general name for taking a piece of one DNA and combining it with another strand of DNA
transformation; phage introduction; non-bacterial transformation
three methods of making a recombinant DNA
plasmids
circular DNA found in the cytoplasm of a bacterium and other microscopic organism
enzymes
used to cut specific DNA sequences
better crops; drought and heat-resistant; insecticide production
significance of recombinant DNA in plants
genetic engineering
process of manipulating genes and introducing them to another organism to produce new traits which may not be found in the original organism; the organism is now transformed and will now have the ability to express the trait encoded by the inserted gene; the organism now may be termed as transgenic organism
genetic engineering; agriculture; nucleic acid hybridization; restriction endonucleases; restriction fragment length polymorphism; DNA cloning
recombinant DNA techniques
genetic engineering
recombinant DNA technique; a process that uses laboratory-based technologies to alter the DNA makeup of an organism; usually used in research and industries such as agriculture and developing medicines; GMO
genetically modified organisms (GMO)
organisms that have had their gene structure changed
agriculture
recombinant DNA technique; developing of drought resistant crops which requires less irrigation
nucleic acid hybridization
recombinant DNA technique; denaturation of double stranded DNA and formation of single stranded DNA
DNA reannealing
renaturation of double-stranded DNA after cooling and certain conditions are met
restriction endonucleases
recombinant DNA technique; recognize and binds to specific DNA sequences and cleave it, it is also known as restriction enzymes
restriction fragment length polymorphism
recombinant DNA technique; analysis on the DNA fragments of two closely related species would have the same sequence
DNA cloning
recombinant DNA technique; incorporating DNA fragments to bacteria and cultured to produce the genetic material with the fragment; plasmids serves as good vectors to proliferate genetic material containing the gene of interest