Pedes Exam 3
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
A child comes into the clinic with a fever of 99.0*F. Her parent tells the provider that she’d noticed fluid filled, bumps all over her daughter’s body, including her scalp. Some of the spots have begun crusting over. The mother also tells you that her daughter has been very fatigued and felt “yucky.” What disease does this child have?
a. Varicella
b. Measles
c. Rubella
d. Roseola
a. Varicella - s/s = low fever, polka dots sports on face, scalp and head which eventually turn into fluid filled blisters with crust; fatigue and malaise.
When is chicken pox most infectious?
a. 12 - 14 hours before fever begins
b. 14-19 hours after the rash appears
c. 12-14 hours before the rash starts
d. 48 hours after the blisters burst
c. 12-14 hours before the rash starts → because obviously it’s going to the most infectious before you can actually tell they have it
When does chicken pox become less contagious?
a. when the blisters finally burst
b. 12-14 hours before the rash
c. when the fever is still running low
d. when the blisters crust over
d. when the blisters crust over
SATA all the PPE necessary for caring for a patient with chicken pox.
a. gloves
b. gown
c. negative pressure room
d. goggles
e. non fit tested mask
f. fit tested n 95 mask
a. gloves
b. gown
c. negative pressure room → yes, best case scenario is negative pressure room!
f. fit tested n 95 mask
What kind of precautions should you use on a patient with chicken pox?
a. Droplet
b. Contact
c. Airborne
d. Standard
c. Airborne → this includes gown, gloves, N-95 fit tested mask, and negative air pressure room
A pregnant patient comes into the OB clinic asking for a chicken pox vaccine in order to prevent varicella in her fetus, even though she’d had no recent exposure. What would be the best response by the nurse?
a. “Yes absolutely! Antibodies through the vaccine can be spread through maternal blood.”
b. “We do not offer a vaccine during pregnancy because it can do more harm than good for you and your baby.”
c. “We do not offer a vaccine during pregnancy, but we do offer an immunoglobulin infusion to prevent the virus.”
d. “Yes - but first we have to do an IgG and IgM test to see if you have had the disease recently.”
a. “Yes absolutely! Antibodies through the vaccine can be spread through maternal blood.”
b. “We do not offer a vaccine during pregnancy because it can do more harm than good for you and your baby.”
c. “We do not offer a vaccine during pregnancy, but we do offer an immunoglobulin infusion to prevent the virus.” → the immunoglobulin infusion is only used to treat chicken pox when mom or baby is exposed
d. “Yes - but first we have to do an IgG and IgM test to see if you have had the disease recently.” → You only do IgG or IgM on german measles
A pregnant mother has been exposed to chicken pox. What is the latest you can administer the immunoglobulin to combat it?
a. 48 hours
b. 72 hours
c. 96 hours
d. You should never administer it
c. 96 hours → you administer immunoglobulin 48 hours after exposure if the patient is an infant
What is coryza?
a. Inflamed skin, especially around the mouth
b. inflamed nose
c. small blistery spots around skin
d. itchiness associated with rashes
b. inflamed nose
What are the three cardinal signs of measles? SATA
a. Coryza
b. Congestion
c. Cough
d. Constipation
e. Conjunctivitis
f. Cold intolerance
a. Coryza
c. Cough
e. Conjunctivitis
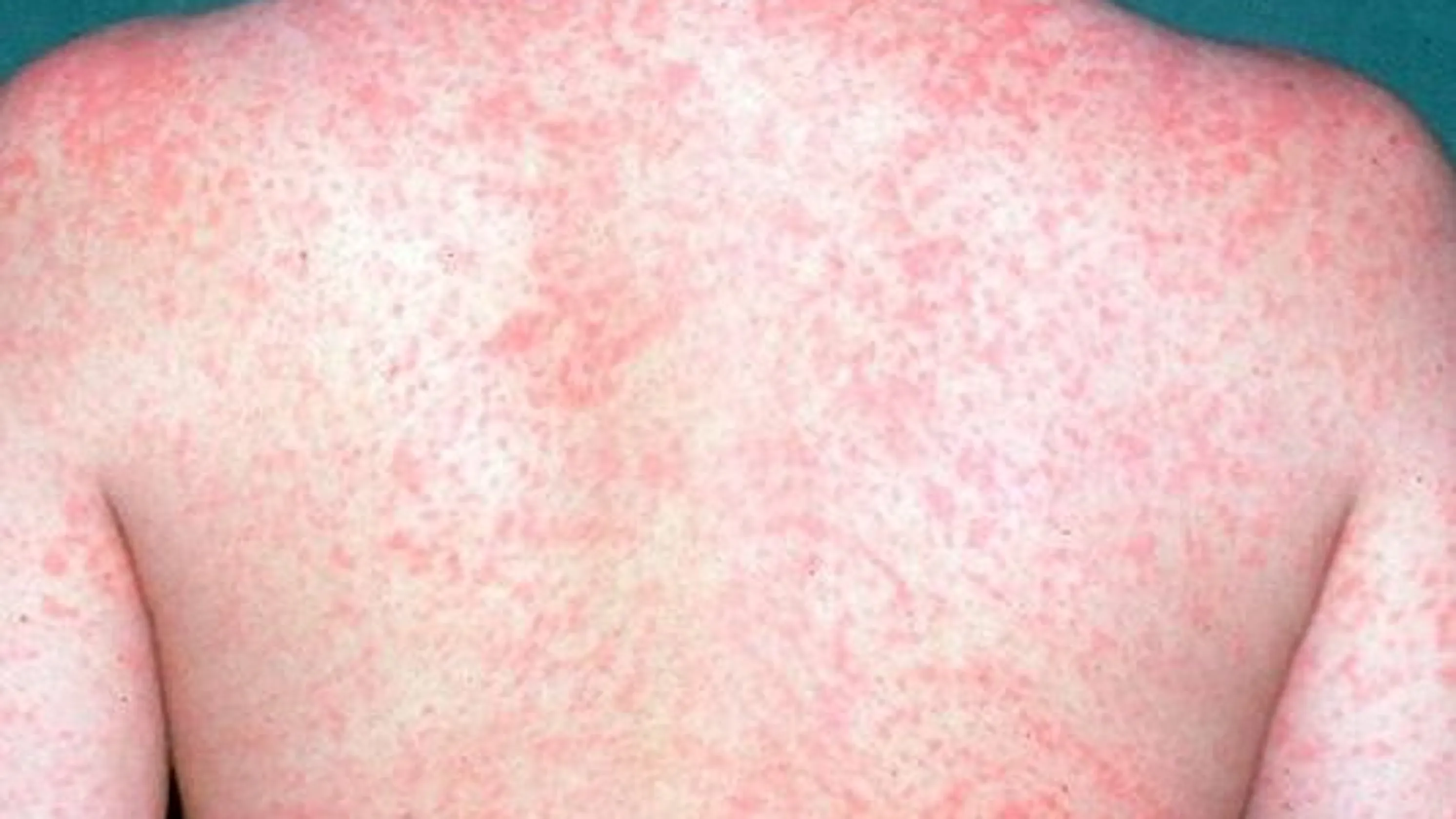
A patient comes in with a strong cough and reddish, swollen eyes. The young patient has little white spots in her mouth and a fever of 101.3*F. The patient also is starting to have a rash all around her body that looks like the picture. What disease do you think the patient has?
a. Varicella Zoster
b. Scarlet Fever
c. Measles
d. Mononucleosis
c. Measles
What is Measles (non-German kind) also known as?
a. Rubella
b. Rubeola
c. Roseola
d. Slapped Cheek Disease
a. Rubella → German measles
b. Rubeola
c. Roseola
d. Slapped Cheek Disease → fifth disease (scarlet fever also has a red cheeked look)
What is important patient education you should tell a parent taking care of a child with measles? SATA
a. “Make sure you clean all surfaces, as after coughing and sneezing, germs can stick on tables.”
b. “Make sure if you’re pregnant to get the measles vaccine because it can help you and your fetus!”
c. “Isolate your child from everyone else up until 4 days after the rash has appeared.”
d. “We need to run labs because it is known that measles can cause anemia in infants.”
a. “Make sure you clean all surfaces, as after coughing and sneezing, germs can stick on tables.”
b. “Make sure if you’re pregnant to get the measles vaccine because it can help you and your fetus!” → NO - if a pregnant mother is exposed, she should get immunoglobulin within 6 days of exposure
c. “Isolate your child from everyone else up until 4 days after the rash has appeared.”
d. “We need to run labs because it is known that measles can cause anemia in infants.” → Fifth Disease
What kind of room should you place a patient in if they have measles?
a. Cohort room with patients of other similar infections
b. Normal room - no special requirements needed
c. Negative air pressure room
d. Positive air pressure room
c. Negative air pressure room → people with measles are on airborne precautions and need to be in a negative air pressure room
What is an important nursing action to do if a young patient comes in with measles?
a. Report the new case to the health department
b. Convince the parents to give their sick child the MMR vaccine
c. Monitor for signs of hydrops fetalis
d. Monitor for signs of koplik spots
a. Report the new case to the health department
hydrops fetalis is a complication of 5th disease
A complication of measles is secondary infections, and high risk for early delivery or abortion if a pregnant mother has it
A young patient comes in with pin point spots that are concentrated around the face, neck and chest. The patient’s rash is just now starting to move down to the lower trunk from the top of their body. The patient has a fever of 99.0*F and swollen lymph nodes. They are also very tired and, as they say, feel very “icky.” You run an IgG and IgM on them. You find they are negative for IgG and positive for IgM. What do you think they have?
a. Scarlet Fever
b. Rubella (German Measles)
c. Roseola
d. Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
b. Rubella (German Measles) → negative for IgG means that they do not have resistance against rubella. Positive IgM means they have an active or are recovering from a rubella infection
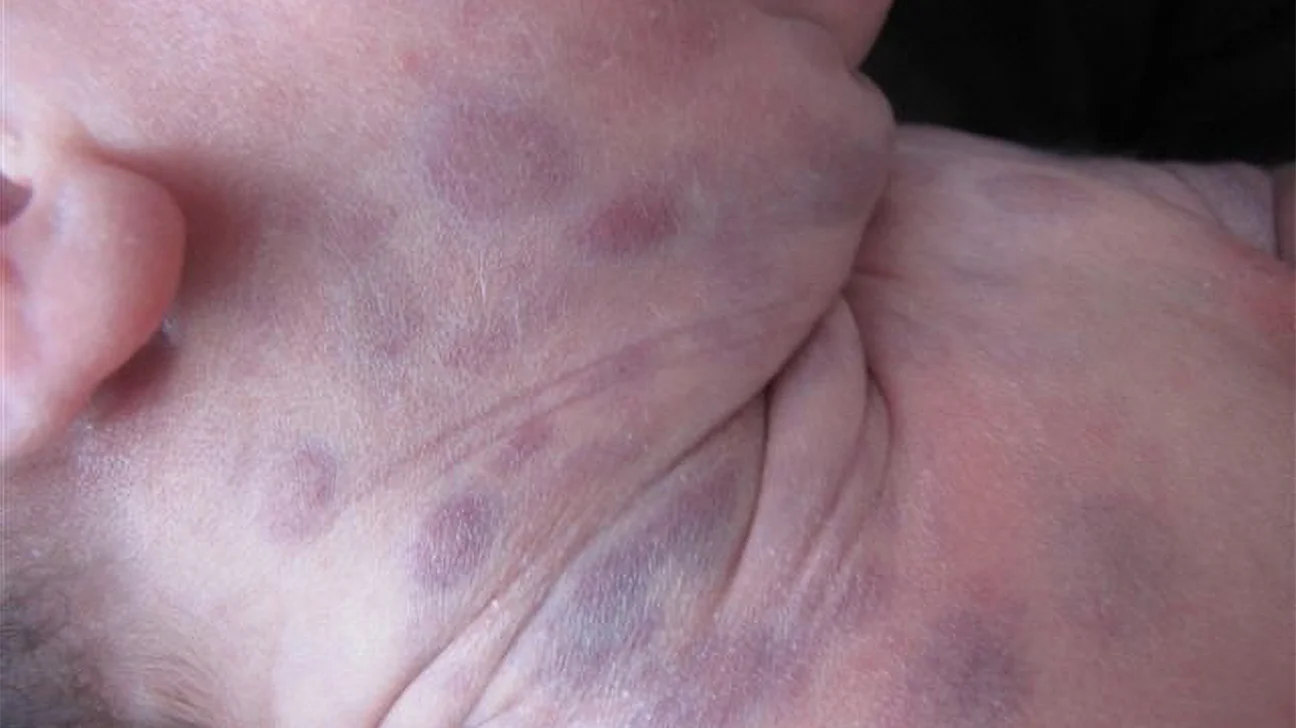
Which disease can cause blueberry muffin spots if their mother had it during pregnancy?
a. Varicella Zoster
b. Mumps
c. Rubella
d. Roseola
c. Rubella → occurs if the baby is born with Congenital Rubella Syndrome which can cause severe birth defects or even fetal death
What precautions would be placed on a patient with rubella?
a. Contact
b. Airborne
c. Droplet
d. Standard
a. Contact → this includes gown, gloves, hand washing and dedicated disposable equipment (a personal COW, stethoscope, BP cuff, etc)
Gabe says -> It's german you don’t want to touch a nazi
When can you give the MMR Vaccine? SATA
a. At 20 weeks of pregnancy
b. 96 hours after exposure
c. After birth, before discharge
d. 1 month before becoming pregnant
c. After birth, before discharge
d. 1 month before becoming pregnant
A 4 year old patient is brought in to the clinic because she says her daughter had a temperature of 101.5*F for the past three days. When you take her temperature it’s 98.9*F. You notice that the child has a pink, splotchy rash on her chest, cheeks and neck. You press on the rash and sees it blanches easily with light ring around the area of pressure. What disease does this patient have?
a. Fifth Disease
b. Roseola
c. Scarlet Fever
d. Whooping Cough
b. Roseola
In what ages is roseola most common?
a. 1-2 years
b. 7-9 years
c. 9-12 years
d. 3-5 years
d. 3-5 years
What are some nursing interventions to start for a patient suffering with roseola? SATA
a. Initiate seizure precautions
b. Help monitor the presence of open and leaky blisters.
c. Place a cold compress on the area of swelling.
d. Push fluids to prevent dehydration.
e. Place a gown and gloves on before entering the room and wash hands when leaving. ‘
f. Place the client in a negative pressure room.
a. Initiate seizure precautions → febrile seizures can occur!
d. Push fluids to prevent dehydration → the very high fever can cause seizures and severe dehydration!!
e. Place a gown and gloves on before entering the room and wash hands when leaving. → Contact precautions!
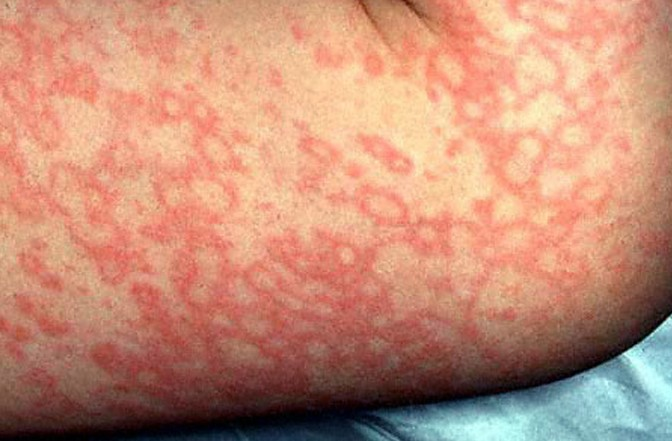
A child is brought into the clinic with red cheeks and lacy spots around the body. The child also tells the nurse she’s been having pain in her throat, head and stomach. She says she’s also very itching. You take her temperature and it’s 99.2*F. What disease do you suspect?
a. Fifth Disease
b. Scarlet Fever
c. Roseola
d. Mononucleosis
a. Fifth Disease
How longs does fifth disease last in kids between the ages of 4-12?
a. 7 days
b. 10 days
c. 12 days
d. 14 days
d. 14 days
What is hydrops fetalis?
a. Increased expelling of secretions, especially sweat.
b. Fluid buildup in the baby.
c. Increased blood volume from fever.
d. Fetal water loss in a baby causes hypovolemia.
b. Fluid buildup in the baby. → hydrops fetalis is a complication of fifth disease
it sounds lacy and feminine like the lacy rash (???? idk kirsten said it not me)
What are some complications of fifth disease? SATA
a. CRS
b. rheumatic fever
c. hydrops fetalis
d. Carditis
e. Anemia
c. hydrops fetalis
e. Anemia
What are some risks of fifth disease during pregnancy? SATA
a. Hydrops fetalis
b. Anemia
c. Heart Failure
d. Carditis
e. Stillbirth/miscarriage
a. Hydrops fetalis
b. Anemia
c. Heart Failure
e. Stillbirth/miscarriage
What virus causes Fifth disease?
a. Varicella Zoster
b. Herpes
c. Parovirus
d. Scarlatina
c. Parovirus → specifically, Parovirus B19
What precautions would you place a patient on if they have Fifth Disease?
a. Contact
b. Airborne
c. Droplet
d. Standard
a. Contact
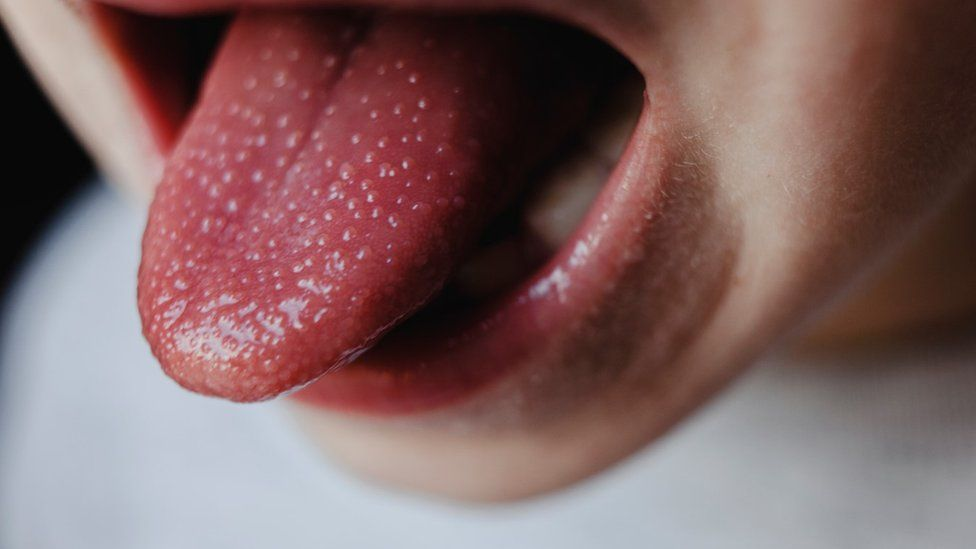
A 6 year old boy is brought in by his mother to the clinic with red cheeks. The boy has a rash that especially concentrates in the folds of the skin, like the groin and armpits. The rash looks like a sunburn and feels like sandpaper. also, the childs tongue looks like the image. The child has a fever of 99.3*F and a sore throat.
a. Roseola
b. Rubella
c. Scarlet Fever
d. Varicella Zoster
c. Scarlet Fever → s/s = strawberry tongue, sunburn and sandpaper rash (especially in pits and rash), sore throat, and low fever
What nursing intervention would you expect to do for a patient with scarlet fever?
a. Administer antivirals
b. Push fluids
c. Administer antibiotics
d. Place the child in a negative pressure room
c. Administer antibiotics → the disease is caused by group A streptococcus
A patient comes in with scarlet fever. What complications would the nurse expect to monitor? SATA
a. S/s of a secondary infection
b. Rheumatic fever
c. Febrile Seizures
d. Carditis
a. S/s of a secondary infection
b. Rheumatic fever
d. Carditis
What PPE would you wear for a patient with scarlet fever?
a. Gloves
b. Gown
c. Fit tested N95 mask
d. Non-fit tested mask
e. Goggles
f. Private room
a. Gloves
b. Gown
d. Non-fit tested mask
e. Goggles
f. Private room → if this does not happen, place them with a patient with similar disease. They do not need to be in a negative air pressure room.
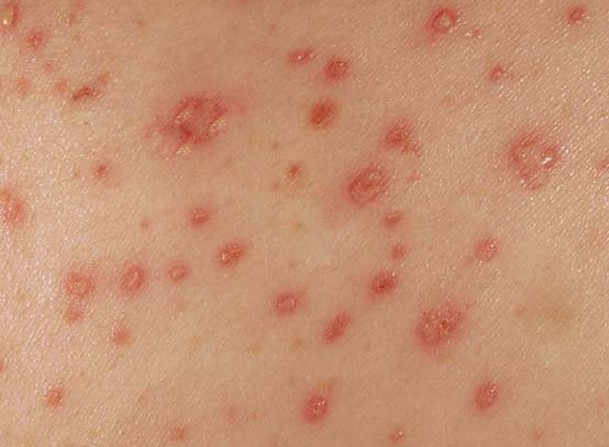
This rash is called a macropapular rash. What disease is this indicative of?
a. Scarlet Fever
b. Rubella
c. Mononucleosis
d. Mumps
c. Mononucleosis → macropapular rash
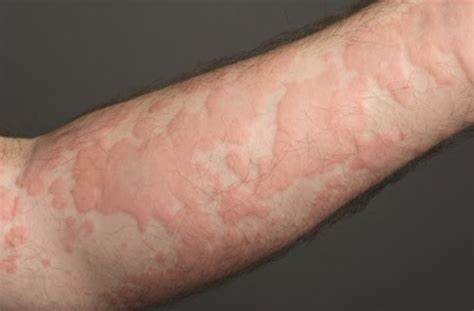
This rash is called urticaria or hives. What disease is this associated with?
a. Mononucleosis
b. Chicken Pox
c. Rubella
d. Measles
a. Mononucleosis
A 14-year-old patient is brought into the clinic by their mom. They’ve been very tired lately and they’re neck is a little swollen. They’re sclera are a pale yellow. They also have a macropapular and hives like rash. They’re temperature is 99.5*F. What disease do you think they have?
a. Measles
b. Mononucleosis
c. Hand, Foot, Mouth Disease
d. Fifth Disease
b. Mononucleosis - s/s= fatigue and lethargy, swollen lymph nodes, liver and spleen; jaundice; sore throat; mono rash = macroppapular and urticaria; low fever
What disease is infectious up to a year after illness?
a. Hand, Foot and Mouth
b. Fifth Disease
c. Scarlet Fever
d. Mononucleosis
d. Mononucleosis
What statement made by a patient with mono would indicate they need further teaching?
a. “I should avoid sharing food and drinks with people up to a year from now.”
b. “Mononucleosis is commonly spread through nose and throat secretions.”
c. “I am able to participate in sports again a week from now.”
d. “A common complication with mononucleosis is spleen rupture.”
c. “I am able to participate in sports again a week from now.” → Rest should be a priority with recovery. Sports should be started till at least 2 weeks after infection, and even then they need to get regular spleen ultrasounds.
A patient come in with blisters on their palms and on the soles of their feet. They have ulcers on the inside of their mouth and a sore throat. They say the sore throat began about 2 days ago. They’re temperature is 99.4*F. What disease do you think they have?
a. Hand, Foot and Mouth (HFM)
b. Chicken Pox
c. Mononucleosis
d. Scarlet Fever
a. Hand, Foot and Mouth - s/s = low fever, fatigue, malaise and sore throat which eventually leads to flat, spotty rashes within 1 to 2o days. The rash can also look like bumps and blisters. Appears mainly on palms, inside of the mouth and soles of feet
When are patients most like going to get Hand, Foot and Mouth? SATA
a. Summer
b. Spring
c. Fall
d. Winter
a. Summer
c. Fall → specifically in fall
*fun fact: this is a disease commonly caught in thrift stores (oh no sandra!)
How long does HFM last?
a. 3-4 days
b. 5-8 days
c. 7-10 days
d. 9-12 days
c. 7-10 days
What precautions should we place a patient on when they have HFM?
a. Contact
b. Airborne
c. Droplet
e. Standard
a. Contact
Which gland is affected in mumps?
a. Submandibular
b. Sublingual
c. Parotid
d. Sebaceous
c. Parotid
What are some other clinical manifestations of mumps? SATA
a. High fever
b. Low fever
c. Joint pain
d. Headache
e. Macropapular rash
f. Ulcers in mouth
a. High fever
c. Joint pain
d. Headache
What education should we correct a patient on if they say it about mumps?
a. “I should try use OTC medications in order to relieve my pain.”
b. “Cold and warm compresses are both appropriate to help manage the s/s of mumps.”
c. “Mumps can cause testicular and ovarian inflammation.”
d. “Mumps takes about a month to leave.”
e. “Deafness and infertility can occur with mumps.”
d. “Mumps takes about a month to leave.”
What isolation precaution do we place on a patient with mumps?
a. Contact
b. Airborne
c. Droplet
d. Standard
c. Droplet
What can occur to a pregnant woman or fetus if the mother has mumps?
a. Spontaneous abortion in first trimester
b. The baby is born with blueberry muffin spots
c. Increased risk of early delivery
d. Can cause the baby to be born with anemia and HF
a. Spontaneous abortion in first trimester
What are some s/s of whooping cough? SATA
a. Gets worse in the night.
b. High fever
c. Wheezing
d. Vomiting
e. Low fever
f. Crackles in the lungs
a. Gets worse in the night.
b. High fever
c. Wheezing
d. Vomiting → N/V can occur from coughing so hard
e. Low fever
f. Crackles in the lungs
How do we treat whooping cough?
a. Antivirals
b. Antibiotics
c. Antifungals
d. There’s no cure
b. Antibiotics

Which diseases should we place under droplet precautions? SATA
a. Measles
b. Whooping Cough
c. Scarlet Fever
d. Fifth Disease
e. Varicella
f. Mumps
b. Whooping Cough
c. Scarlet Fever
f. Mumps
Which diseases do we place on airborne precautions? SATA
a. Varicella
b. Measles
c. Mumps
d. Fifth Disease
e. Rubella
f. Roseola
a. Varicella
b. Measles
What is one non pharmaceutical way we can educate patients on how to help with whooping cough?
a. Go outside - fresh air improves s/s.
b. Take antivirals to their full extent to prevent the virus from returning
c. Splinting may help reduce the force of the coughing.
d. Breathe in and out with an “O” shaped mouth.
a. Go outside - fresh air improves s/s.
When is it safe to administer the pertussis vaccine to a pregnant woman?
a. Never - it can lead to fetal defects.
b. Around 16-32 weeks of pregnancy.
c. About a month before pregnancy occurs.
d. Immediately after delivery.
b. Around 16-32 weeks of pregnancy.
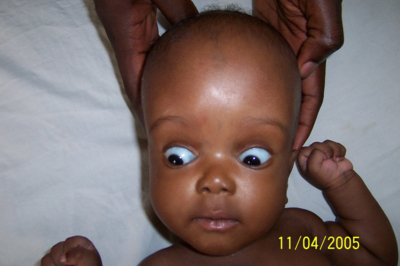
A baby comes into the emergency room, screaming with a high pitched cry. They are vomiting and have a bulging fontanelle. Their eyes look like the picture. The baby also keeps fading in and out of consciousness. What do you think is going on with the baby?
a. Early Increased ICP
b. Late Increased ICP
c. Partial Seizure
d. Brain Tumor
a. Early Increased ICP → sunset eyes, high pitched cry, vomiting, headache, bulging fontanelle, change in LOC
What are s/s of late increased ICP?
a. Sunset eyes
b. Bulging fontanelle
c. Lower LOC
d. Hyporeflexia
e. Hyperreflexia
f. Posturing.
c. Lower LOC
d. Hyporeflexia
f. Posturing. → The only s/s I’m forgetting is a change in VS!
What is the diagnostic criteria for epilepsy?
a. Having 2 unprovoked seizures within 2-4 weeks time period
b. Having 1 unprovoked seizure every 3 months
c. Having 2 unprovoked seizures within 24 hours
d. Having 4 or more unprovoked seizures within 1 year
c. Having 2 unprovoked seizures within 24 hours
What is the purpose of a lumbar puncture?
a. To look for congenital abnormalities in the CSF
b. To monitor for signs of seizures, brain death or subdural hematomas
c. To monitor for hemorrhages, obstructions or infections in the CSF
d. To assess for inflammation caused by tumors or neural tube defects
c. To monitor for hemorrhages, obstructions or infections in the CSF
What are some nursing interventions for a patient needs a lumbar puncture (SATA)?
a. Hold the baby in a C shape
b. Ensure there is no metal in or around the baby
c. Sedate the patient to keep them calm
d. Keep flat for 1 hour after procedure
a. Hold the baby in a C shape
d. Keep flat for 1 hour after procedure
Which type of scan is a noninvasive xray that looks at tissues and its structures?
a. CT scan
b. EEG
c. MRI
d. EFG
a. CT scan
What is the purpose of a CT scan?
a. To assess for tumor inflammation and neural tube defects
b. To diagnose congenital abnormalities.
c. To measure the electrical activity of the brain.
d. To monitor for seizures, brain death and hemorrhages.
b. To diagnose congenital abnormalities.
What is most important for a patient to be when undergoing a CT or EEG scan?
Stay still!
What can an EEG diagnose? SATA
a. seizures
b. brain death
c. tumors
d. subdural hematomas
e. hemorrhages
all o dem!
What is a nursing intervention that may need to be implemented prior to an EEG?
a. Sedate them!!!!
b. Hold anticonvulsants
c. idk hold em down
d. metal is no no big no no no
b. Hold anticonvulsants
What does an MRI diagnose?
a. Tumor inflammation
b. Hemorrhaging
c. Obstructions and infections
d. Secret twins you absorbed in the womb
e. Neural tube defects
a. Tumor inflammation
e. Neural tube defects
d. Secret twins you absorbed in the womb → TBH wouldn’t be surprised
What are some important teaching points for patients who are suffering from seizures? SATA
a. Call 911 if the seizure lasts more than 5 minutes.
b. Do not stop the medications being administrated.
c. Avoid triggers, such as low sleep or strobe lights.
d. Make sure for febrile seizures to administer rectal Tylenol.
all o dem!
What is the best diagnostic tests do we use on a 4-month-old infant with hydrocephalus?
a. Cranial ultrasound
b. MRI
c. Lumbar puncture
d. CT scan
a. Cranial ultrasound
MRI is used for older kids
What are the tests we can use to diagnose hydrocephalus? SATA
a. MRI
b. Fundoscopic examination
c. Lumbar puncture
d. CT
e. Cranial examination
all o dem!
Fill in the blank: SATA
Seizure precautions include, maintain airway, lower bed, protect patient, _________________, and __________________.
a. Lay the patient on their back to prevent asphixiation.
b. Place the patient in semi-fowlers position to aid with breathing
c. Administer oxygen to facilitate perfusion
d. Pad rails.
e. Place patient on their side.
d. Pad rails.
e. Place patient on their side.
What are some important interventions for infants suffering from hydrocephalus? SATA
a. Administer oxygen.
b. Tightly swaddle the infant
c. Hold the infant at a 50* angle
d. Make sure to constantly hold the infant to comfort the infant.
e. Make sure the patient’s EVD is below the laser line.
f. Monitor strict I&Os.
a. Administer oxygen.
b. Tightly swaddle the infant
c. Hold the infant at a 50* angle → hold them at a 30* angle
d. Make sure to constantly hold the infant to comfort the infant. → NO minimal handling!
e. Make sure the patient’s EVD is below the laser line.
f. Monitor strict I&Os.
What color should CSF be?
a. slightly opaque and white
b. Slightly yellow or clear
c. Light green and opaque
d. Pink tinged and clear
b. Slightly yellow or clear
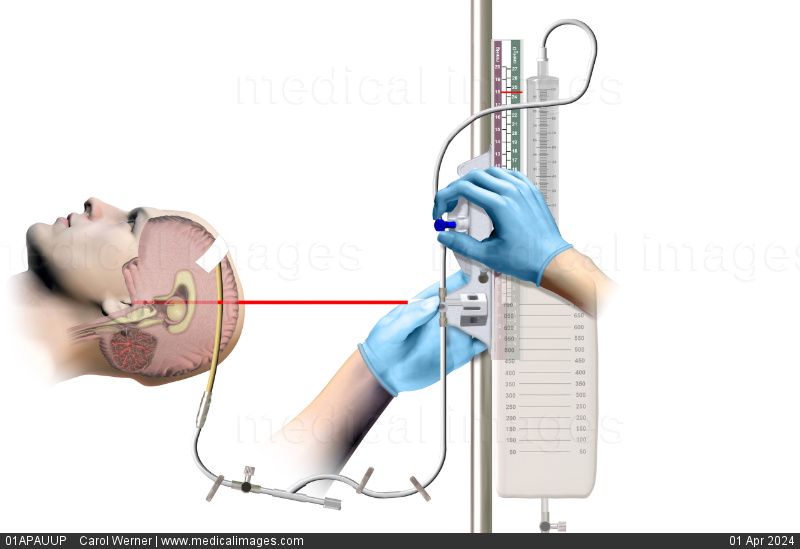
What is an important intervention to consider when taking care of a patient with an EVD?
a. Make sure to keep the bag above the laser line.
b. The patient can have the EVD running while using the bathroom.
c. Make sure to clamp the tubing before the patient gets up.
d. Make sure the patient knows how to take care of the EVD at home.
a. Make sure to keep the bag above the laser line. → no keep it below
b. The patient can have the EVD running while using the bathroom. → no
c. Make sure to clamp the tubing before the patient gets up.
d. Make sure the patient knows how to take care of the EVD at home. → they typically don’t take it home
When does the lower esophageal sphincter develop?
a. 2 weeks
b. 1 month
b. 2 months
d. 3 months
b. 1 month
How much liquid can newborns hold in their stomachs?
a. 10-20 mL
b. 200 mL
c. 1500 mL
d. 2000-3000 mL
a. 10-20 mL
b. 200 mL → 2 months
c. 1500 mL → 16 years
d. 2000-3000 mL → adult
When do pancreatic enzymes reach maturity?
a. At birth
b. 1 month
c. 16 months
d. 2 years
d. 2 years
Who has more body fluids - an adult or infant?
infant
What is a huge risk for children during illness, but not for adults?
a. Dehydration
b. Seizures
c. Vomiting
d. diarrhea
a. Dehydration
How long is the average intestine of an infant?
a. 50 cm
b. 100 cm
c. 250 cm
d. 600 cm
c. 250 cm
adults it’s 600 cm
When do we want to do an ultrasound? SATA
a. Abnormal liver tests
b. Foreign Body
c. Rectal Prolapse
d. Duct stones
e. Large organs or masses
f. Pain
a. Abnormal liver tests
e. Large organs or masses
f. Pain
Which order would we question for a patient going to get an ultrasound?
a. The doctor has ordered the patient to take barium before the exam.
b. The patient is going to get an ultrasound for their inflamed intestines.
c. The patient had abnormal liver labs, prompting the ultrasound order.
d. The patient may be pregnant.
a. The doctor has ordered the patient to take barium before the exam. → barium decreases visualization
Which patient would most likely X ray done?
a. The patient is suffering from a possible small bowel obstruction.
b. The patient has intussusception.
c. The patient has to get their dysphagia diagnosed.
d. The patient has unexplained N/V/D.
a. The patient is suffering from a possible small bowel obstruction. => reasons for X ray are constipation, pain, foreign body, ascites, large mass and distension
When would a doctor order a barium enema?
a. when the patient is pregnant.
b. To look for dysphagia.
c. To monitor for infection.
d. When we want to look for intussusception.
d. When we want to look for intussusception. → we used barium enemas to visualize the colon and correct intussusception → we also use it to track constipation, rectal prolapse, and bleeding.
When do we want to do a barium swallow?
a. When we want to visualize the colon and correct intussusception.
b. When we can to see the hepatobiliary system by instilling contrast
c. When we want to visualize the upper GI tract.
d. To see the rate at which teh stomach empties food.
c. When we want to visualize the upper GI tract.
When do we use a HIDA scan?
a. When we want to visualize the bladder,
b. When we want to visualize the lungs.
c. When we want to visualize the pancreas.
d. When we want to visualize the gallbladder.
d. When we want to visualize the gallbladder.
What is hemoccult?
a. blood in sputum
b. blood in poo
c. when bacteria is in the blood
d. a pool of blood under the skin
b. blood in poo
A patient has an olive shaped mass in their RUQ of their abdomen. The mother says that she is always feeding her child. She says her baby is projectile vomiting almost 3 times a day, but then immediately after vomiting she wants to feed again. She is concerned about her child becoming dehydrated. What disease do you think the child has?
a. Intussusception
b. Malrotation
c. Pyloric Stenosis
d. Celiac Disease
c. Pyloric Stenosis
When can kids start feeding again after a pyloric stenosis surgery?
a. 1-2 days post op
b. 2-4 days post op
c. 3-5 days post op
d. 6-7 days post op
a. 1-2 days post op
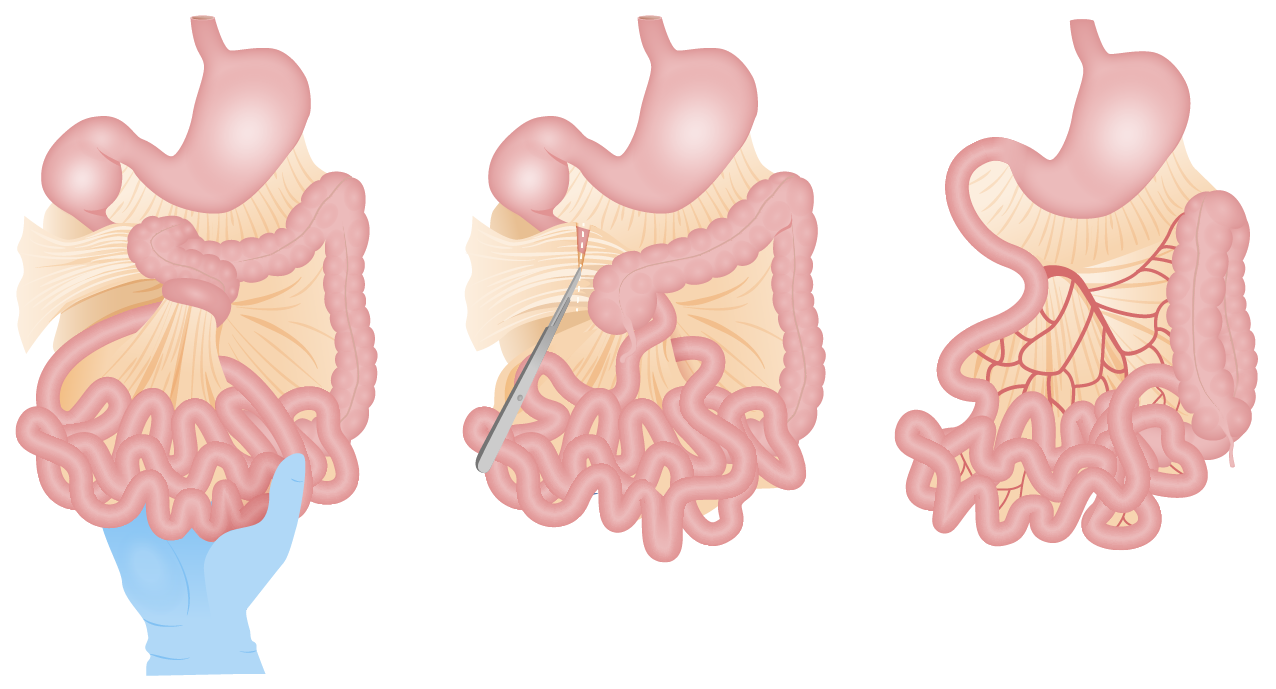
The leftmost image is depicts a volvulus. What disease causes a volvulus?
a. Malrotation
b. Intussusception
c. Appendicitis
d. Celiac
a. Malrotation
SATA s/s of malrotation.
a. Bilious vomiting.
b. Currant jelly stools.
c. Sausage shaped mass in RUQ.
d. Olive shaped mass in RUQ.
e. Bloody stool.
f. Abdominal pain and distension.
a. Bilious vomiting.
e. Bloody stool.
f. Abdominal pain and distension.
What is a possible complication of intestinal malrotation?
a. Perforation
b. Anemia
c. Amenorrhea
d. Bowel Necrosis
d. Bowel Necrosis
What tests do we use to diagnose a malrotation? SATA
a. Upper GI series
b. Barium enema
c. ALT/AST
d. KUB
a. Upper GI series
d. KUB → X ray or Ultrasound used to look at kidneys, ureter, bladder
What disease may need an ostomy?
a. Appendicitis
b. Malrotation
c. Intussusception
d. Celiac Disease
b. Malrotation
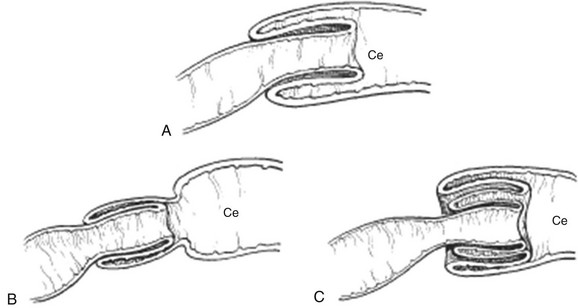
This picture shows the small intestine telescoping into itself. What disease process does this picture indicate?
a. Malrotation
b. Intussusception
c. Appendicitis
d. Celiac
b. Intussusception
What typically causes intussusception? SATA
a. Diverticulitis
b. Cysts
c. Polyps
d. Tumors
e. A weird appendix
all o dem
What would be some expected findings of a patient with intussusception? SATA
a. Abdominal pain
b. Olive shaped mass
c. Sausage shaped mass
d. Currant jelly stools
e. steatorrhea
f. Hunger after vomiting
g. Bilious vomiting
a. Abdominal pain
b. Olive shaped mass → Pyloric stenosis
c. Sausage shaped mass
d. Currant jelly stools
e. Steatorrhea → celiac disease
f. Hunger after vomiting → pyloric stenosis
g. Bilious vomiting → malrotation
What do we use to both treat and test for intussusception?
a. Air or barium enema
b. CT scan and radioscopic examination
c. Colonoscopy
d. EGD and small bowel series
a. Air or barium enema
A patient comes into the clinic with a sudden onset of cramping. The patient tells you that they have been having currant jelly stools and severe N/V/D. They have also been very tired. What disease do you think they have?
a. Malrotation
b. Pyloric Stenosis
c. Appendicitis
d. Intussusception
d. Intussusception
Where does pain for appendicitis typically manifest?
a. RUQ
b. RLQ
c. LLQ
d. LUQ
b. RLQ → am i the only one who’s thought it was RUQ this whole time?
A patient has come in for appendicitis. Before they had a fever of 99.0*F. It is now 102.3*F. They’re stomach is also distended and tender throughout the abdomen. What do we think is most likely occurring?
a. Sepsis
b. Appendix Rupture
c. Constipation
d. Pancreatitis
b. Appendix Rupture → a patient’s fever will spike with an appendix rupture
A patient comes into the clinic with vague pain in their right lower abdomen. They are nauseas and have vomited once this morning. They are having very small bowel movements, and they have a fever of 99.2*F. Upon palpation they have a positive McBurney’s sign. You also have to help place them on the table and lay them down because they pain is so bad. What disease do you think they have?
a. Pyloric Stenosis
b. Malrotation
c. Intussusception
d. Appendicitis
d. Appendicitis
A patient comes into the clinic with the following labs:
elevated WBC
Elevated C-reactive protein
They are also experiencing pain near their right side. What disease do you expect they have?
a. Celiac disease
b. Malrotation
c. Appendicitis
d. Pyloric Stenosis
c. Appendicitis
When would you want to start antibiotic therapy on a patient with appendicitis?
AFTER IT RUPTURES! → do not start AB’s before that!