(6) Electrocardiogram
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
See paper notes ECG
What are the uses for ECG?
(just know of tbh)
-Monitor cardiac electrical activity
Gain insight into:
- anatomical orientation of heart
- chamber sizes (heart chamber hypertrophy)
(takes time for electrical activity to go through)
- disturbance in rhythm and conduction
- extent, location, progress of ischemic dmg to myocardium (scar tissue, no electrical activity)
1) Electrode pairing is known as a __
2) We can a view of the electrical activity of the heart along the __
1) Lead
2) Reference line
1) Lead 1,2,3 combined are known as the __
2) Which lead most closely aligns w/ dispersal of electrical activity through the heart?
1) Einthoven’s triangle
2) Lead 2
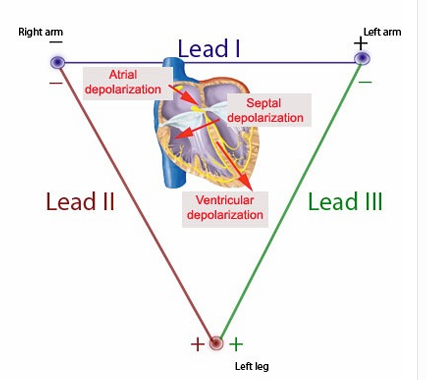
Describe the components of an ECG.
1) Isoelectric line = NO cardiac vector detected by lead (remains 0)
2) Upward deflection
- electropositive pole oriented TOWARDS positive electrode
3) Downward deflection
- electropositive pole orientated AWAY from positive electrode
General info about Lead 2
(quite intuitive but think about it as additional info)
1) cardiac vector is PARALLEL w/ lead 2
→ maximal upward deflection (i.e., electropositive pole is pointing toward positive electrode)
2) if NOT PARALLEL, lead 2 will only pick up the vector components parallel to lead 2
3) if PERPENDICULAR (cross), NO deflection
4) if PARALLEL but electropositive pole is pointing towards neg electrode = MAXIMAL DOWNWARD DEFLECTION
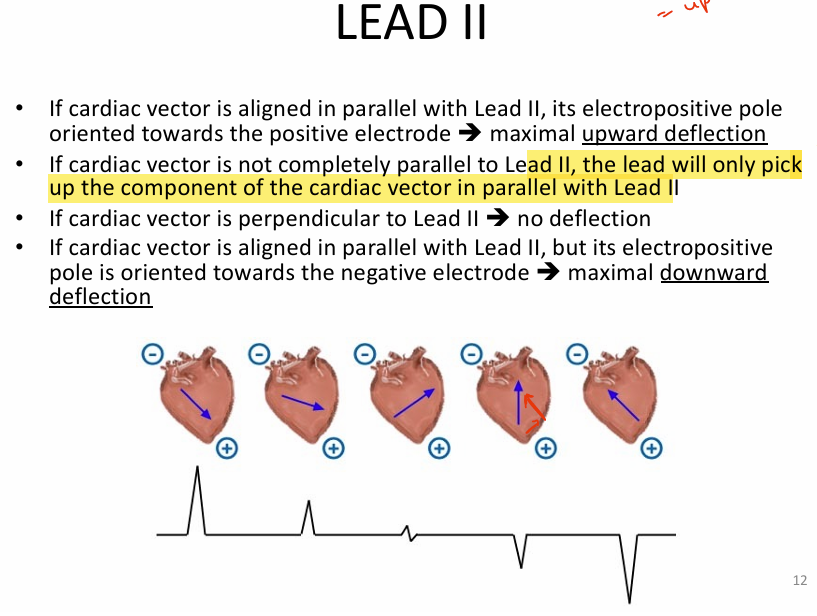

(don’t really memorize)
Point #3: Rz towards positive electrode = downward deflection (regular cell)
Point #4: Rz AWAY from positive electrode = upward deflection (seen in ventricular cells)
- b/c the epicardium Rz first before the endocardium (Rz goes opposite of the reference line/lead 2)
I didn’t really draw this
(don’t really memorize)