FAA PPL Test Prep: Ch. 7 (1 of 2): Weather Services
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
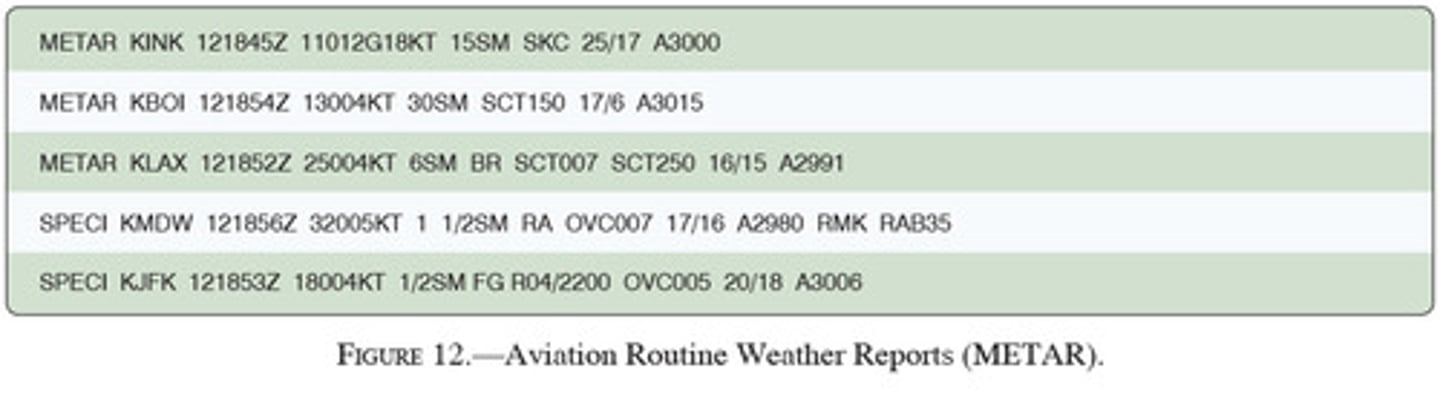
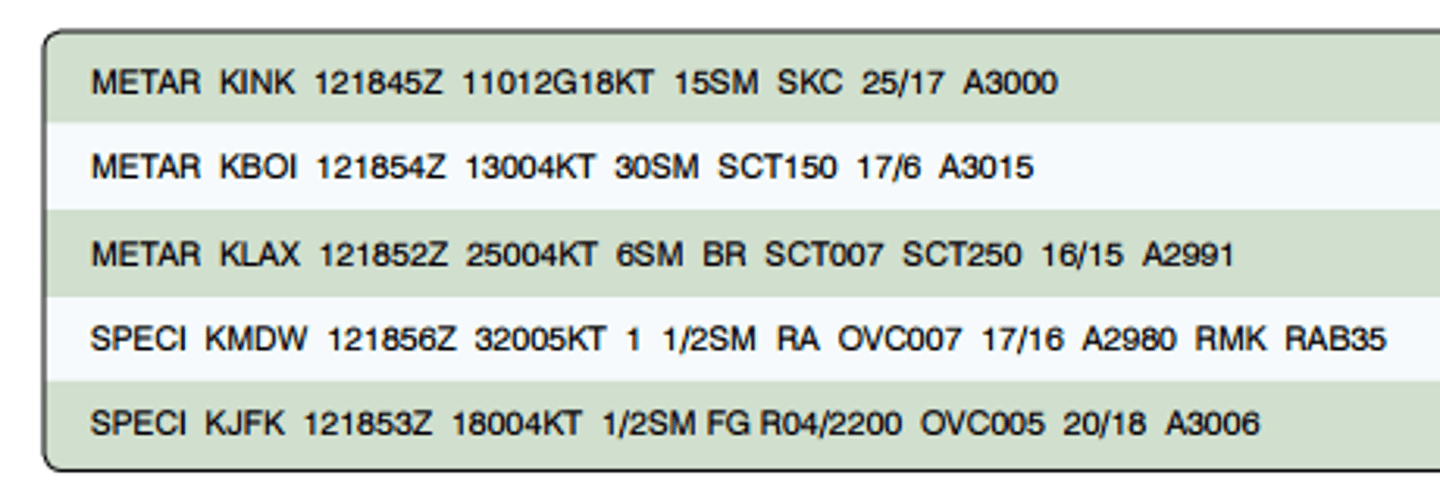
(Figure 12) Which of the reporting stations have VFR weather?
A. All
B. KINK, KBOI, and KJFK
C. KINK, KBOI, and KLAX
C. KINK, KBOI, and KLAX
For aviation purposes, ceiling is defined as the height above the Earth's surface of the:
A. Lowest reported obscuration and the highest layer of clouds reported as overcast
B. Lowest broken or overcast layer or vertical visibility into an obscuration
C. Lowest layer of clouds reported as scattered, broken, or thin
B. Lowest broken or overcast layer or vertical visibility into an obscuration
(Figure 12) The wind direction and velocity at KJFK is from:
A. 180 true at 4 knots
B. 180 magnetic at 4 knots
C. 040 true at 18 knots
A. 180 true at 4 knots
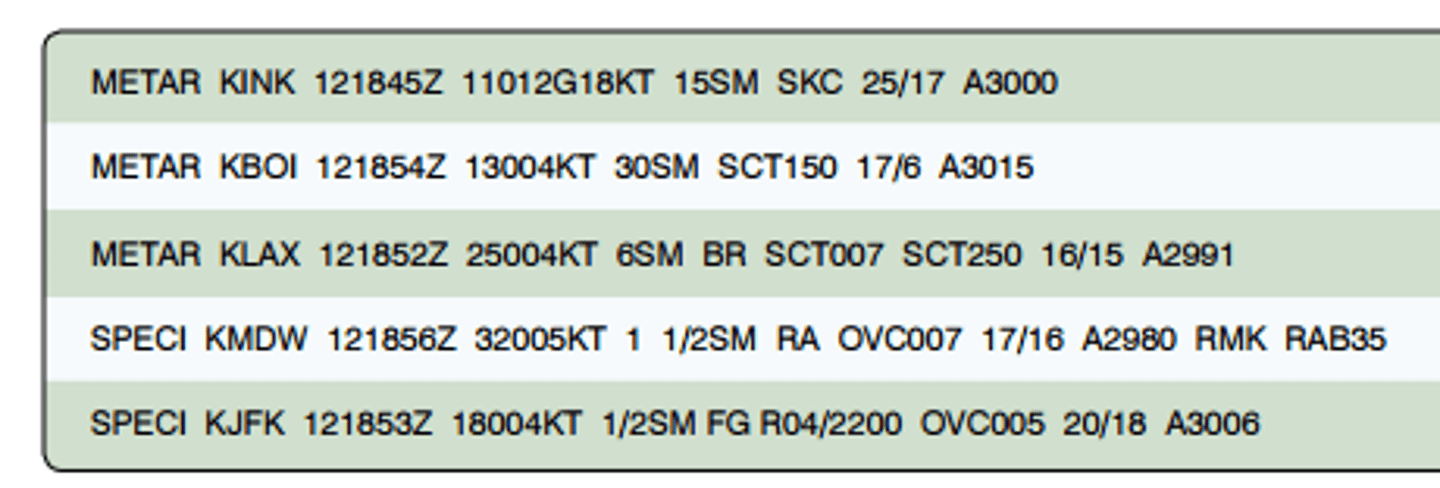
(Figure 12) What are the wind conditions at Wink, Texas (KINK)?
A. Calm
B. 110 at 12 knots, peak gusts 18 knots
C. 111 at 2 knots, peak gust 18 knots
B. 110 at 12 knots, peak gusts 18 knots
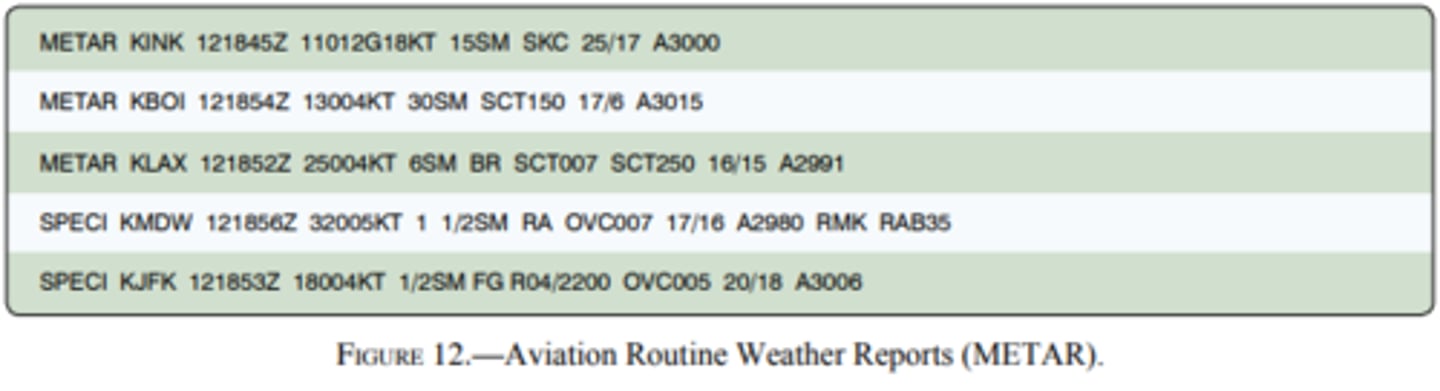
(Figure 12) The remarks section for KMDW has RAB35 listed. This entry means:
A. Blowing mist has reduced the visibility to 1-1/2 SM
B. Rain began at 1835Z
C. The barometer has risen 0.35 inches Hg
B. Rain began at 1835Z
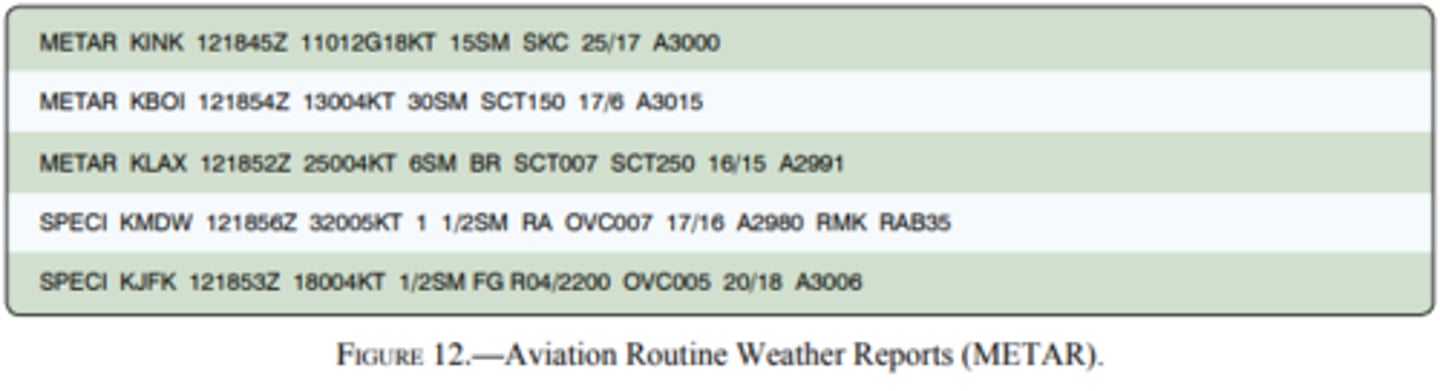
(Figure 12) What are the current conditions depicted for Chicago Midway Airport (KMDW)?
A. Sky 700 feet overcast, visibility 1-1/2SM
B. Sky 7000 feet overcast, visibility 1-1/2SM, Heavy rain
C. Sky 700 feet overcast, visibility 11, occasionally 2 SM, with rain
A. Sky 700 feet overcast, visibility 1-1/2SM
(Figure 14) The base and tops of the overcast layer reported by a pilot are:
A. 1,800 feet MSL and 5,500 feet MSL
B. 5,500 feet AGL and 7,200 feet MSL
C. 7,200 feet MSL and 8,900 feet MSL
C. 7,200 feet MSL and 8,900 feet MSL

(Figure 14) The wind and temperature at 12,000 feet MSL as reported by a pilot are:
A. 080 at 21 knots and -7 degrees C
B. 090 at 21 MPH and -9 degrees F
C. 090 at 21 knots and -9 degrees C
A. 080 at 21 knots and -7 degrees C

(Figure 14) If the terrain elevation is 1,295 feet MSL, what is the height above ground level of the base of the ceiling?
A. 505 feet AGL
B. 1,295 feet AGL
C. 6,586 feet AGL
A. 505 feet AGL

(Figure 14) The intensity of the turbulence reported at a specific altitude is:
A. Moderate from 5,500 feet to 7,200 feet
B. Moderate at 5,500 feet and at 7,200 feet
C. Light from 5,500 feet to 7,200 feet
C. Light from 5,500 feet to 7,200 feet

(Figure 14) The intensity and type of icing reported by a pilot is:
A. Light to moderate rime
B. Light to moderate
C. Light to moderate clear
A. Light to moderate rime

From which primary source should information be obtained regarding expected weather at the estimated time of arrival if your destination has no Terminal Forecast?
A. Low-Level Prognostic Chart
B. Weather Depiction Chart
C. Area Forecast
C. Area Forecast
(Figure 15) What is the valid period for the TAF for KMEM?
A. 1200Z to 1200Z
B. 1200Z to 1800Z
C. 1800Z to 1800Z
C. 1800Z to 1800Z

(Figure 15) In the TAF for KMEM, what does "SHRA" stand for?
A. Rain showers
B. A shift in wind direction is expected
C. A significant change in precipitation is possible
A. Rain showers

(Figure 15) Between 1000Z and 1200Z the visibility at KMEM is forecast to be?
A. 1/2 Statute mile
B. 3 Statute miles
C. 6 Statute miles
B. 3 Statute miles

(Figure 15) What is the forecast wind for KMEM from 1600Z until the end of the forecast?
A. Variable in direction at 6 knots
B. No significant wind
C. Variable in direction at 4 knots
A. Variable in direction at 6 knots

(Figure 15) In the TAF from KOKC, the "FM (FROM) Group" is forecast for the hours from 1600Z to 2200Z with the wind from:
A. 180 at 10 knots, becoming 200 at 13 knots
B. 160 at 10 knots
C. 180 at 10 knots
C. 180 at 10 knots

(Figure 15) In the TAF from KOKC, the clear sky becomes:
A. Overcast at 2,000 feet during the forecast period between 2200Z and 2400Z
B. Overcast at 200 feet with a 40% probability of becoming overcast at 600 feet during the forecast period between 2200Z and 2400Z
C. Overcast at 200 feet with the probability of becoming overcast at 400 feet during the forecast period between 2200Z and 2400Z
A. Overcast at 2,000 feet during the forecast period between 2200Z and 2400Z

(Figure 15) During the time period from 0600Z to 0800Z, what visibility is forecast for KOKC?
A. Greater than 6 statue miles
B. Not forecasted
C. Possibly 6 statute miles
A. Greater than 6 statue miles

(Figure 15) The only cloud type forecast in TAF reports is:
A. Nimbostratus
B. Cumulonimbus
C. Scattered Cumulus
B. Cumulonimbus

What is indicated when a current CONVECTIVE SIGMET forecasts thunderstorms?
A. Moderate thunderstorms covering 30 percent of the area
B. Moderate or severe turbulence
C. Thunderstorms obscured by massive cloud layers
C. Thunderstorms obscured by massive cloud layers
What information is contained in a CONVECTIVE SIGMET?
A. Tornadoes, embedded thunderstorms, and hail 3/4 inch or greater in diameter
B. Severe icing, severe turbulence, or widespread dust storms lowering visibility to less than 3 miles
C. Surface winds greater than 40 knots or thunderstorms equal to or greater than video integrator processor (VIP) Level 4
A. Tornadoes, embedded thunderstorms, and hail 3/4 inch or greater in diameter
SIGMET's are issued as a warning of weather conditions hazardous to which aircraft?
A. Small aircraft only
B. Large aircraft only
C. All aircraft
C. All aircraft
Which in-flight advisory would contain information on severe icing not associated with thunderstorms?
A. Convective SIGMET
B. SIGMET
C. AIRMET
B. SIGMET
AIRMET's are advisories of significant weather phenomena but of lower intensities than SIGMET's and are intended for dissemination to:
A. Only IFR pilots
B. All pilots
C. Only VFR pilots
B. All pilots
(Figure 17) What wind is forecast for STL at 9,000 feet?
A. 230 true at 32 knots
B. 230 magnetic at 25 knots
C. 230 true at 25 knots
A. 230 true at 32 knots
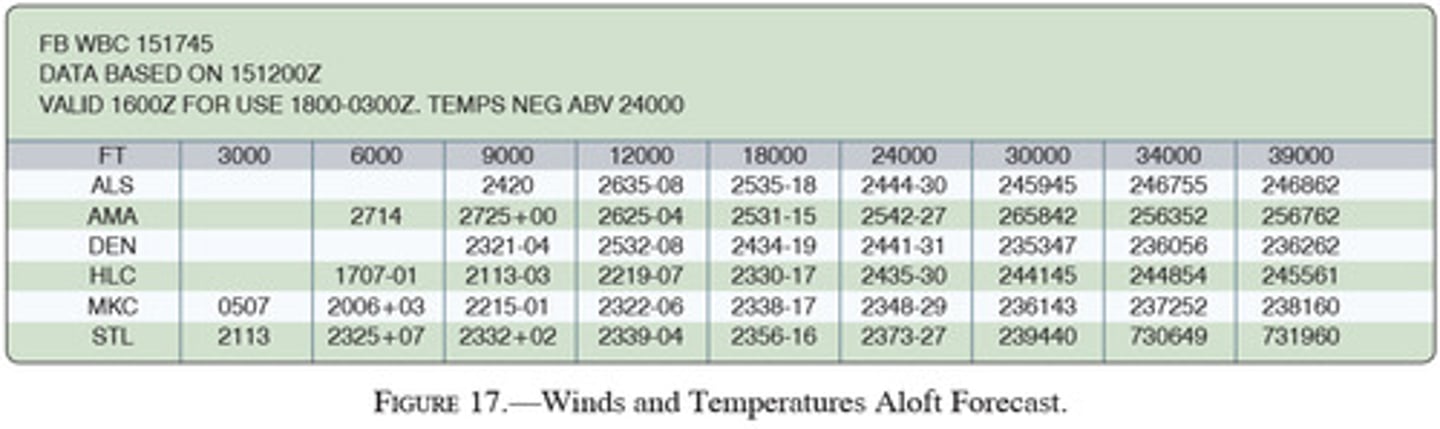
(Figure 17) What wind is forecast for STL at 12,000 feet?
A. 230 true at 56 knots
B. 230 true at 39 knots
C. 230 magnetic at 56 knots
B. 230 true at 39 knots
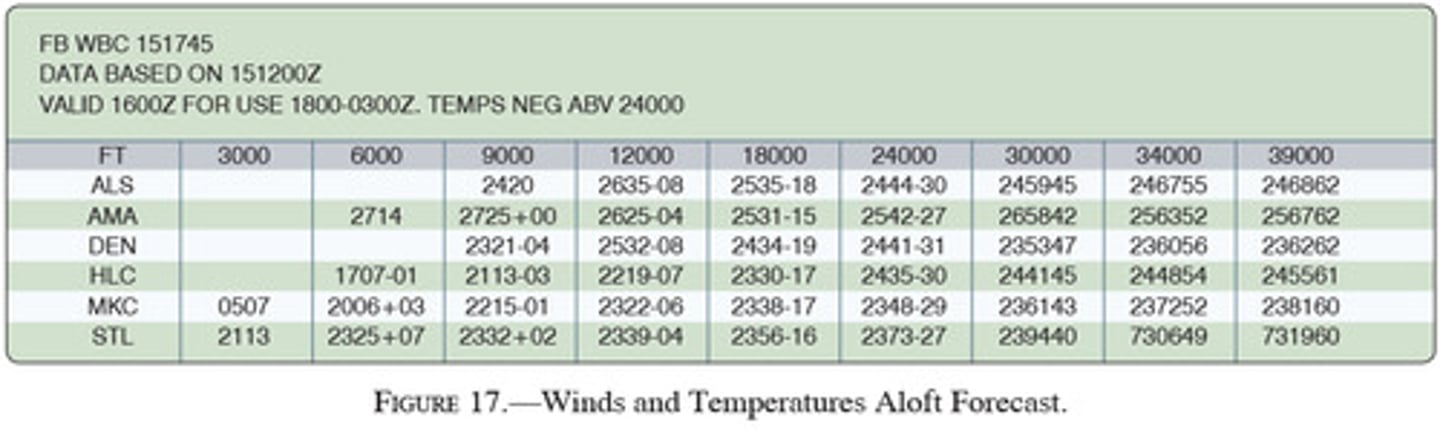
What values are used for Winds Aloft Forecasts?
A. Magnetic direction and knots
B. Magnetic direction and miles per hour
C. True direction and knots
C. True direction and knots
When the term "light and variable" is used in reference to a Winds Aloft Forecast, the coded group and windspeed is:
A. 0000 and less than 7 knots
B. 9900 and less than 5 knots
C. 9999 and less than 10 knots
B. 9900 and less than 5 knots
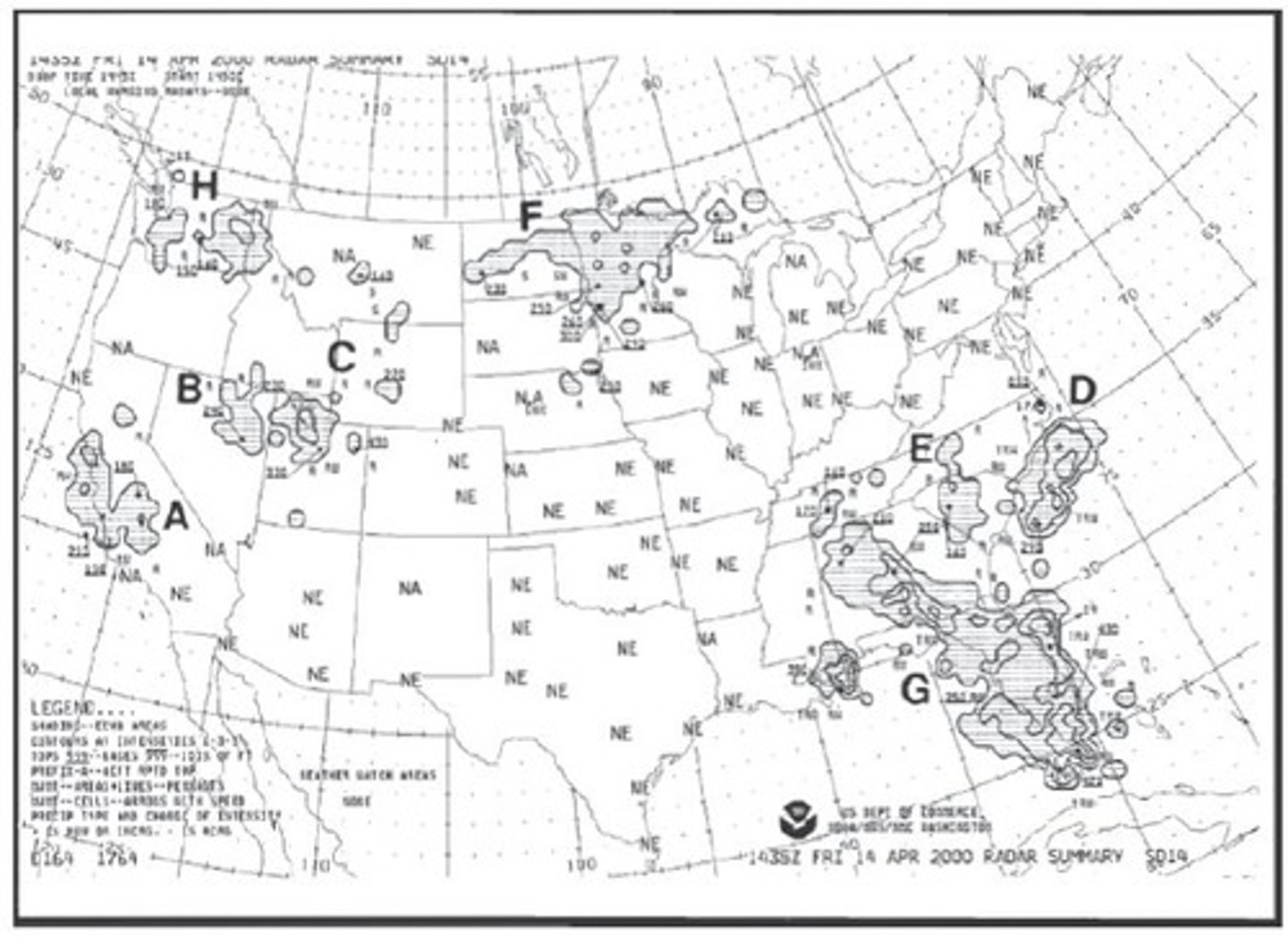
Radar weather reports are of special interest to pilots because they indicate:
A. Location of precipitation along with type, intensity, and cell movement of precipitation
B. Location of precipitation along with type, intensity, and trend
C. Large areas of low ceilings and fog
A. Location of precipitation along with type, intensity, and cell movement of precipitation
How are low-level significant weather (sigwx) prognostic charts best used by a pilot?
A. For overall planning oat all altitudes
B. For determining areas to avoid (freezing levels and turbulence)
C. For analyzing current frontal activity and cloud coverage
B. For determining areas to avoid (freezing levels and turbulence).
Short range surface prognostic (prog) charts provide depictions of forecast
A. Surface pressure systems, fronts, and precipitation
B. Aviation weather hazards such as MFVR and IFR conditions, turbulence, icing, and IFR conditions.
C. Areas of probable precipitation, including ice, snow, and thunderstorms
Surface pressure systems, fronts, and precipitation
Low-level significant weather (SIGWX) charts provide depictions of forecast
B - Aviation weather hazards such as MFVR and IFR conditions, turbulence, and freezing levels.
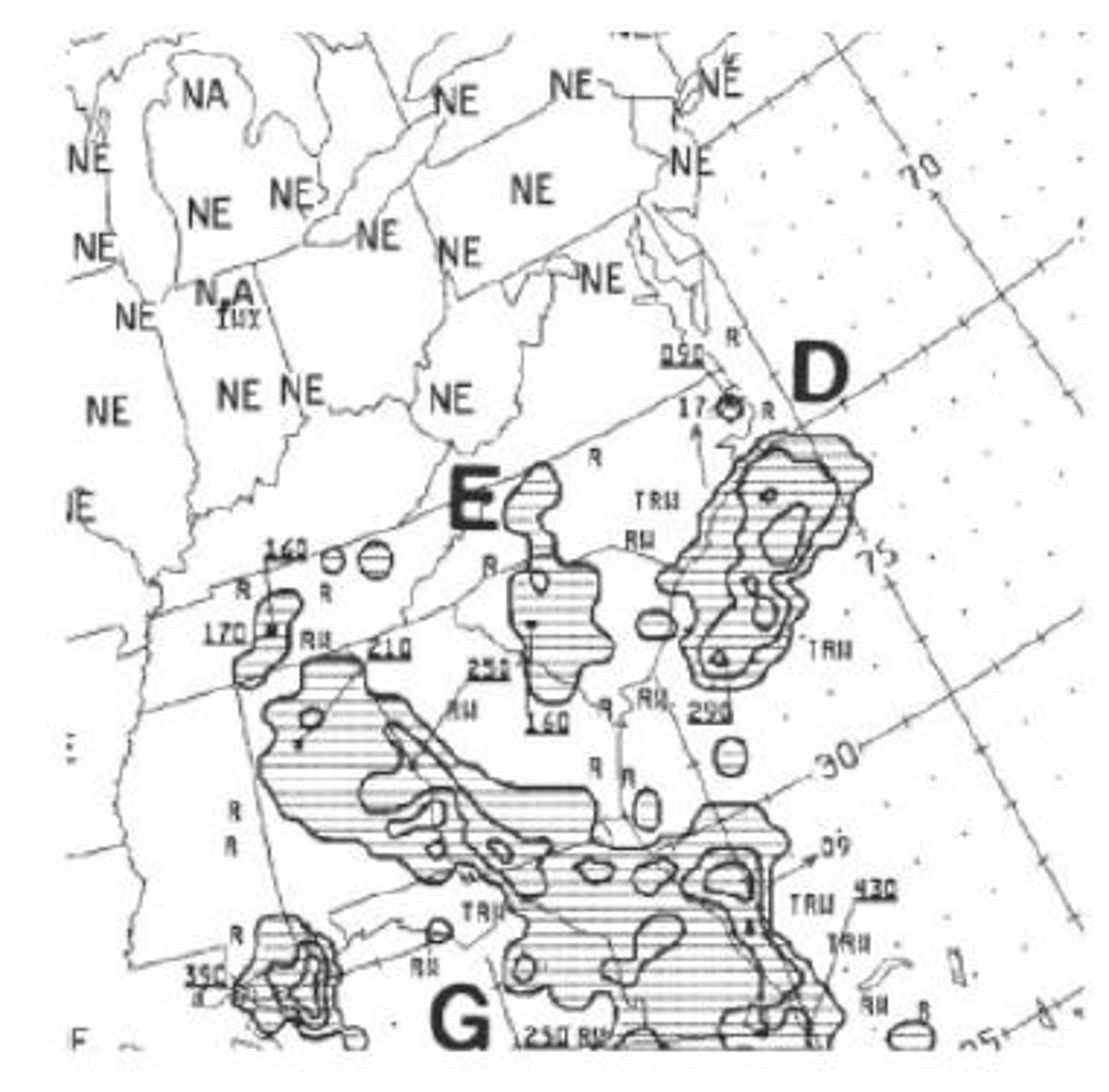
To get a complete weather briefing for the planned flight, the pilot should request:
A. A general briefing
B. An abbreviated briefing
C. A standard briefing
C. A standard briefing
Which type weather briefing should a pilot request, when departing within the hour, if no preliminary weather information has been received?
A. Outlook briefing
B. Abbreviated briefing
C. Standard briefing
C. Standard briefing
Which type of weather briefing should a pilot request to supplement mass disseminated data?
A. An outlook briefing
B. A supplemental briefing
C. An abbreviated briefing
C. An abbreviated briefing
To update a previous weather briefing, a pilot should request:
A. An abbreviated briefing
B. A standard briefing
C. An outlook briefing
A. An abbreviated briefing
A weather briefing that is provided when the information requested is 6 or more hours in advance of the proposed departure time is:
A. An outlook briefing
B. A forecast briefing
C. A prognostic briefing
A. An outlook briefing
When requesting weather information for the following morning, a pilot should request:
A. An outlook briefing
B. A standard briefing
C. An abbreviated briefing
A. An outlook briefing
When telephoning a weather briefing facility for preflight weather information, pilots should state:
A. The aircraft identification or the pilot's name
B. true airspeed
C. fuel on board
A. The aircraft identification or the pilot's name
You plan to phone a weather briefing facility for preflight weather information. You should
A - Provide the number of occupants on board
B - Identify yourself as a pilot
C - Begin with your route of flight
B - Identify yourself as a pilot
When speaking to a flight service weather briefer, you should state
A - The pilot in command's full name and address
B - A summary of your qualifications
C - whether the flight is VFR or IFR
C- Whether the flight is VFR or IFR
To obtain a Flight Service briefing over the internet, go to
A - FSS.gov and enter your pilot certificate number
B - 1800wxbrief.com and sign up using your pilot credentials
C - AviationWeather.gov and select Standard Briefing
B - 1800wxbrief.com and sign up using your pilot credentials
What considerations apply when using a cockpit display of radar data obtained from FIS-B
A - Echoes and terrain that are close to your aircraft can shield echoes that are farther away.
B - The radar echoes that are depicted on the cockpit display can sometimes be more than 20 minutes old.
C - The in-cockpit radar display lacks the accuracy and integrity of radar mosaics obtained from Flight Service.
B - The radar echoes that are depicted on the cockpit display can sometime be more than 20 minutes old
You planned a route and obtained preliminary weather information to determine the feasibility of your flight. On the morning of your flight, an FAA-approved briefing consists of
A- Obtaining a standard briefing at 1800wxbrief.com