Linear Algebra Prelim 1 Study Guide
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
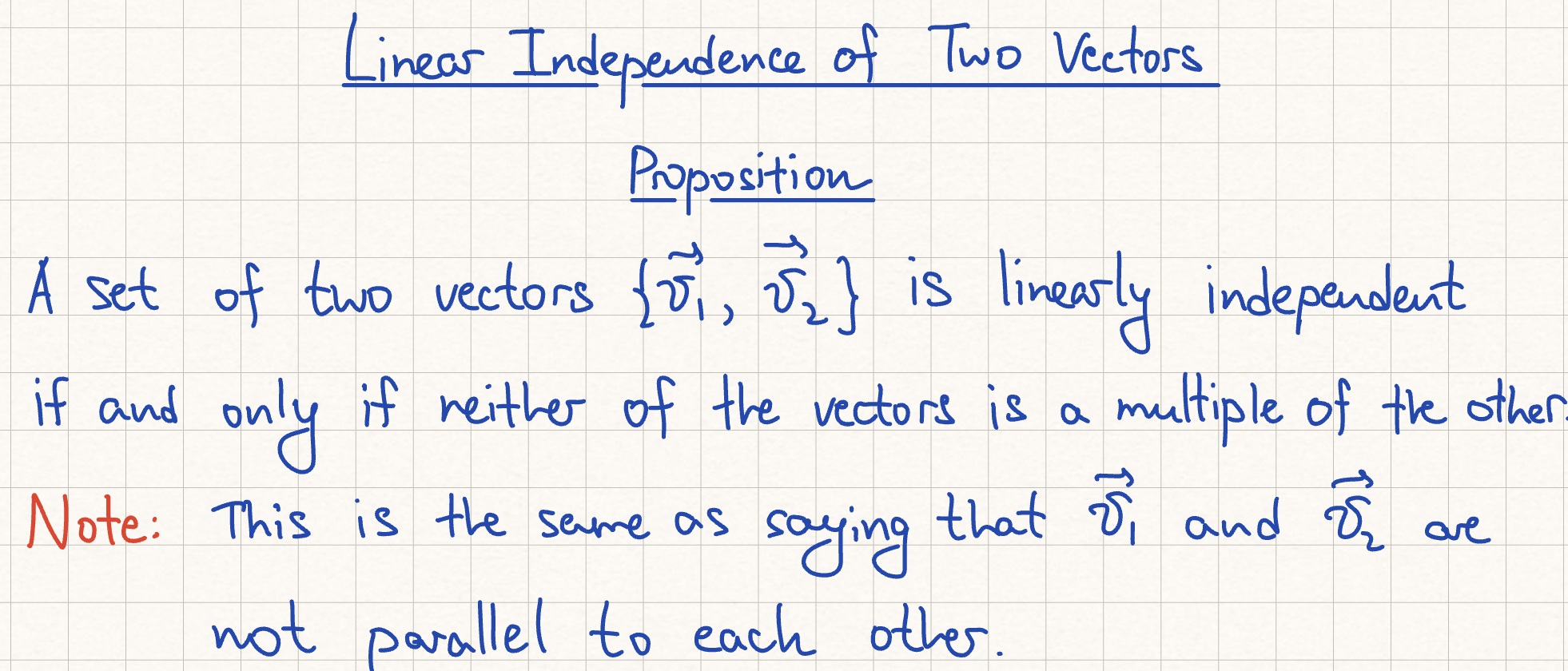
Linearly Independent Condition
i) the columns of matrix A are linearly independent
ii) see image
iii) there is a pivot in every column of A
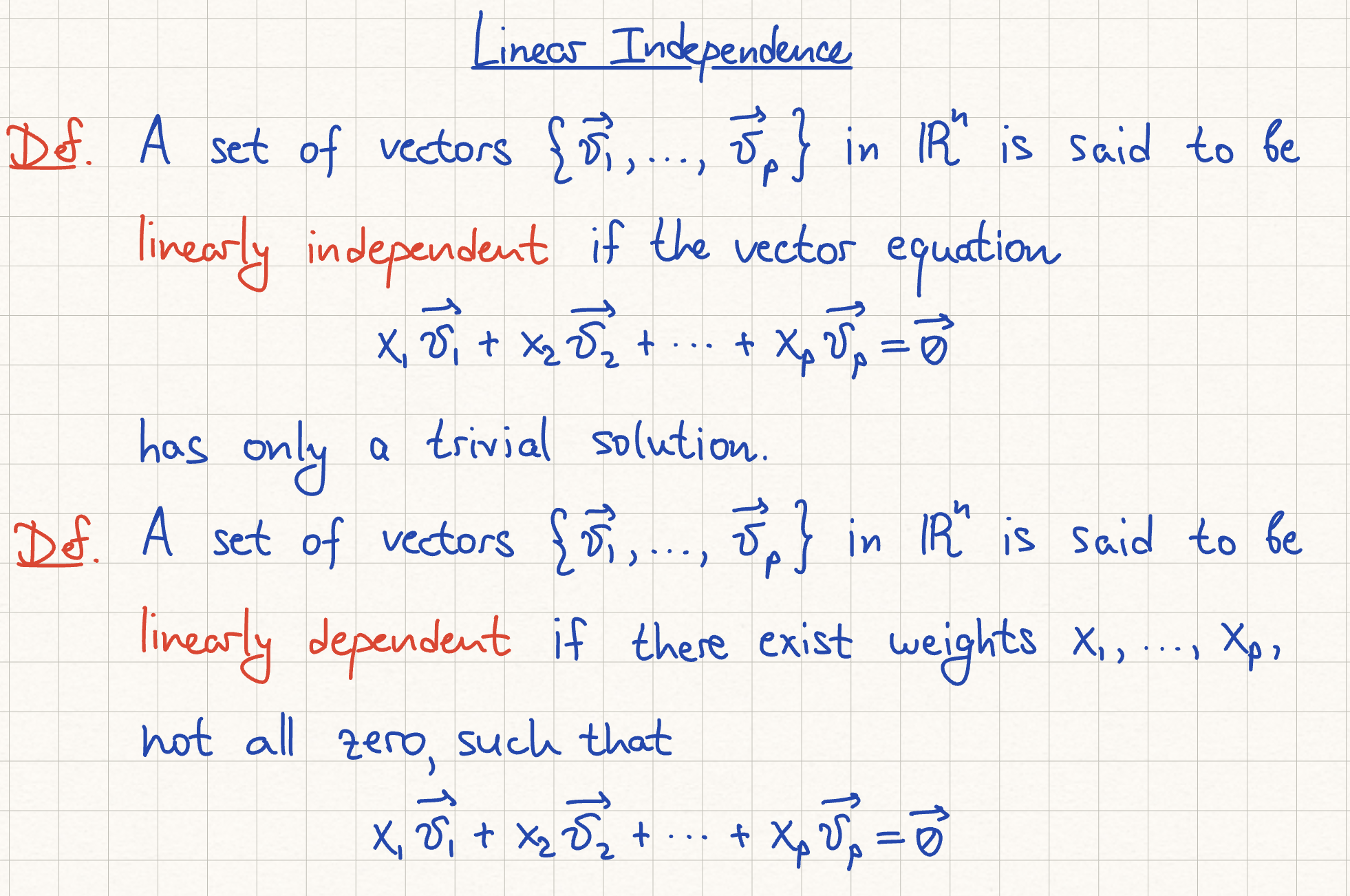
Linear Independence of Two Vectors
*does not generalize to 3 vectors, if subsets of 2 are linearly independent the set of 3 vectors can still be dependent
Connection Between Linear Independence and Linear Combination Theorem
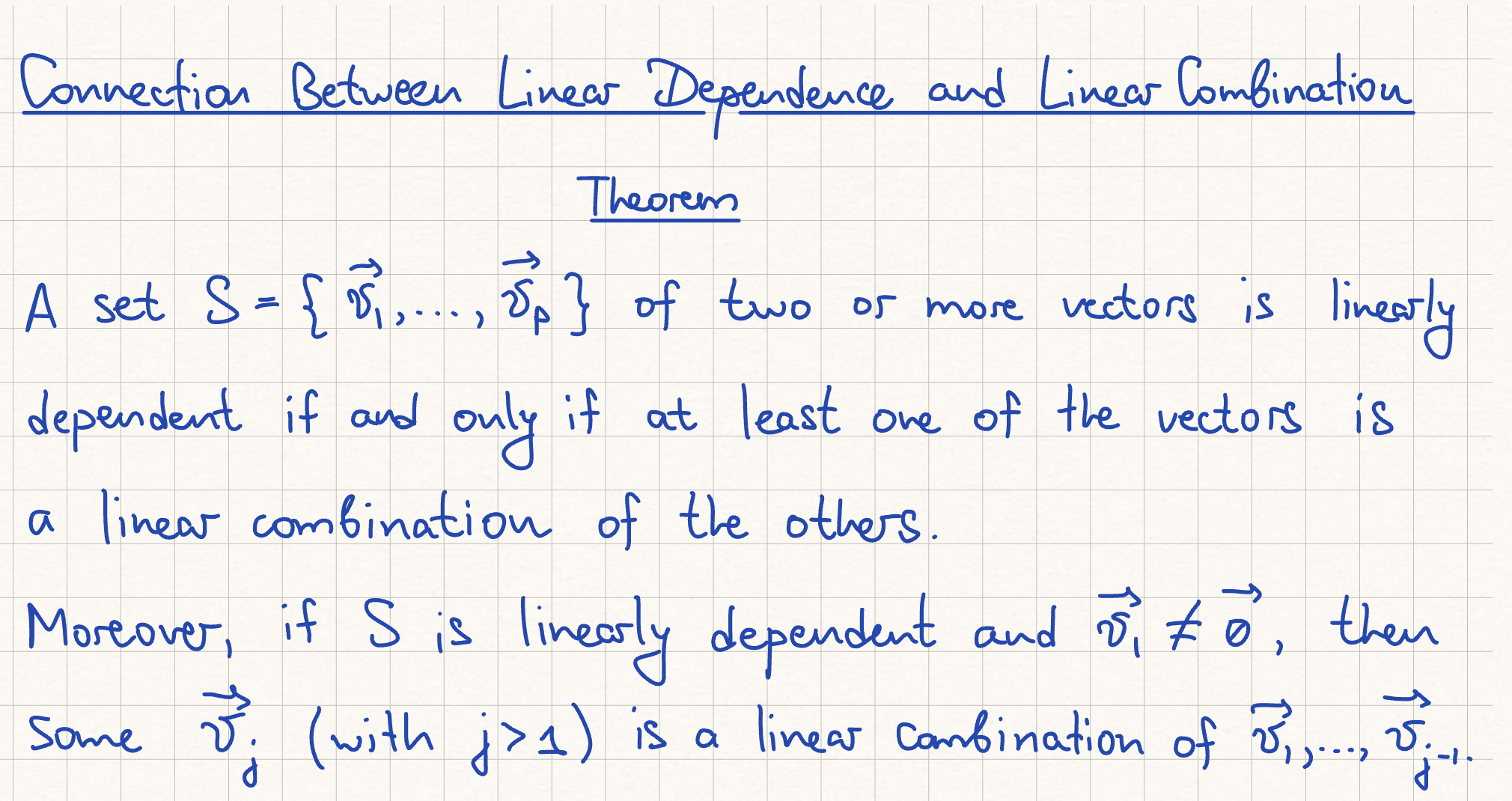
T/F If S is a linearly dependent set, then each vector is a linear combination of the other vectors in S
False, it guarantees some vector is, not each vector
T/F If a set contains fewer vectors than there are entries in the vectors, then the set is linearly independent.
False, it could be linearly dependent
(T/F) The columns of any 4 x 5 matrix are linearly dependent.
True, five vectors in R4 must be linearly dependent.
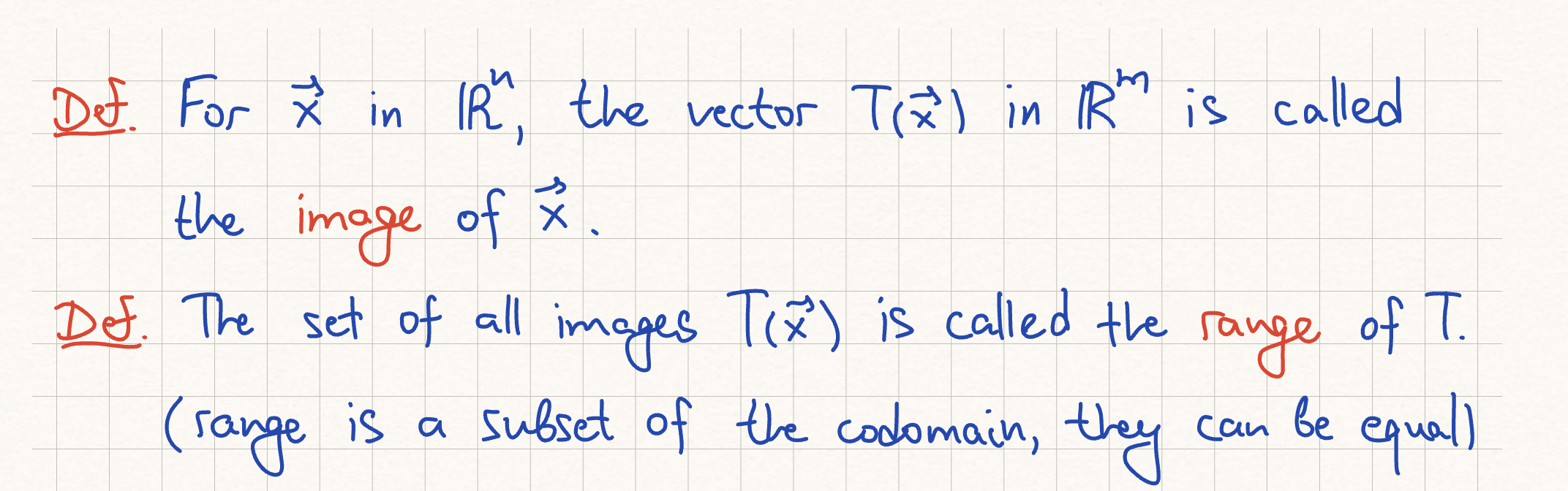
domain, codomain of transformation
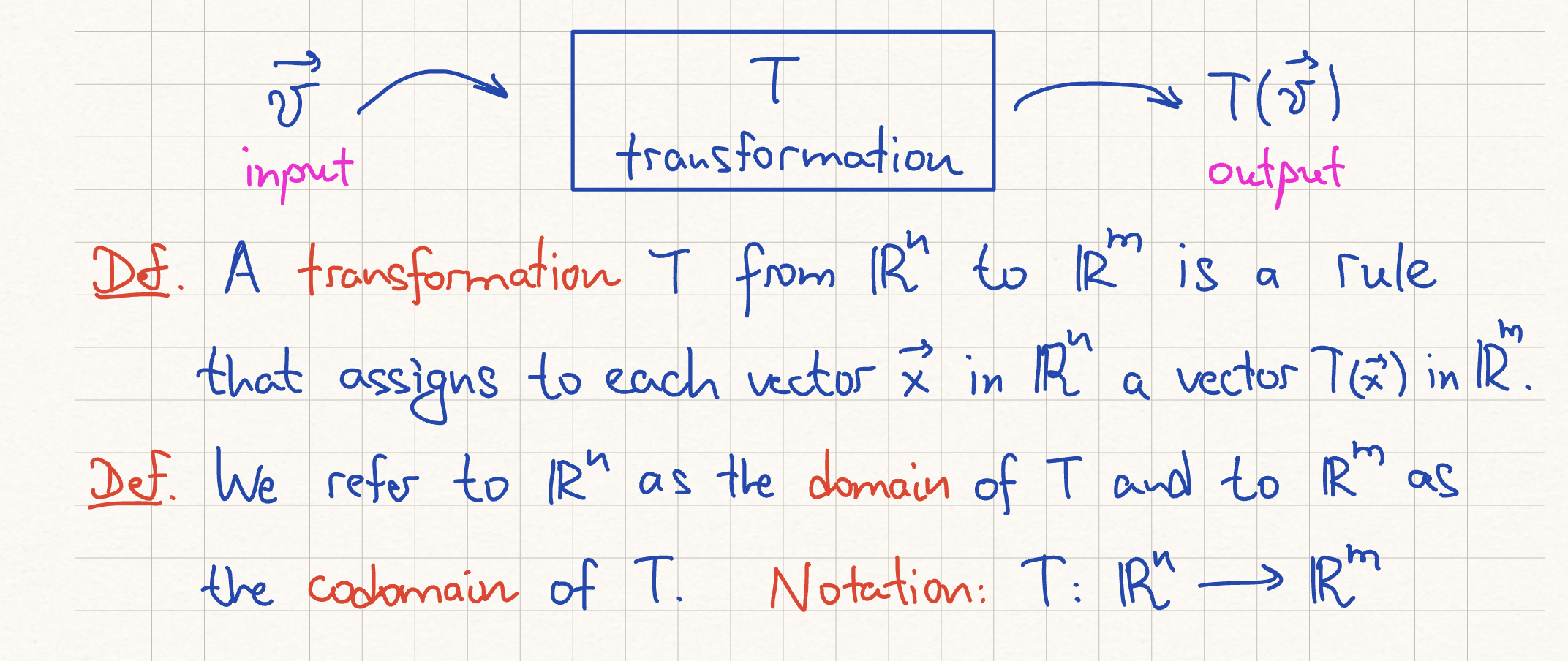
image, range of transformation
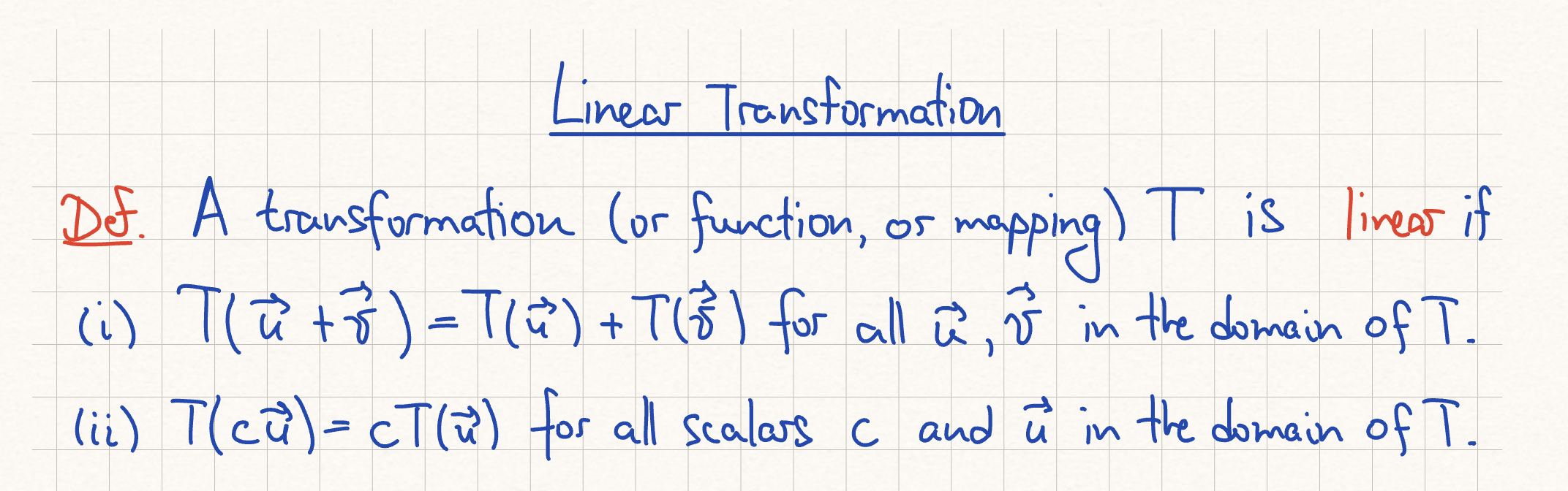
Linear Transformation Conditions
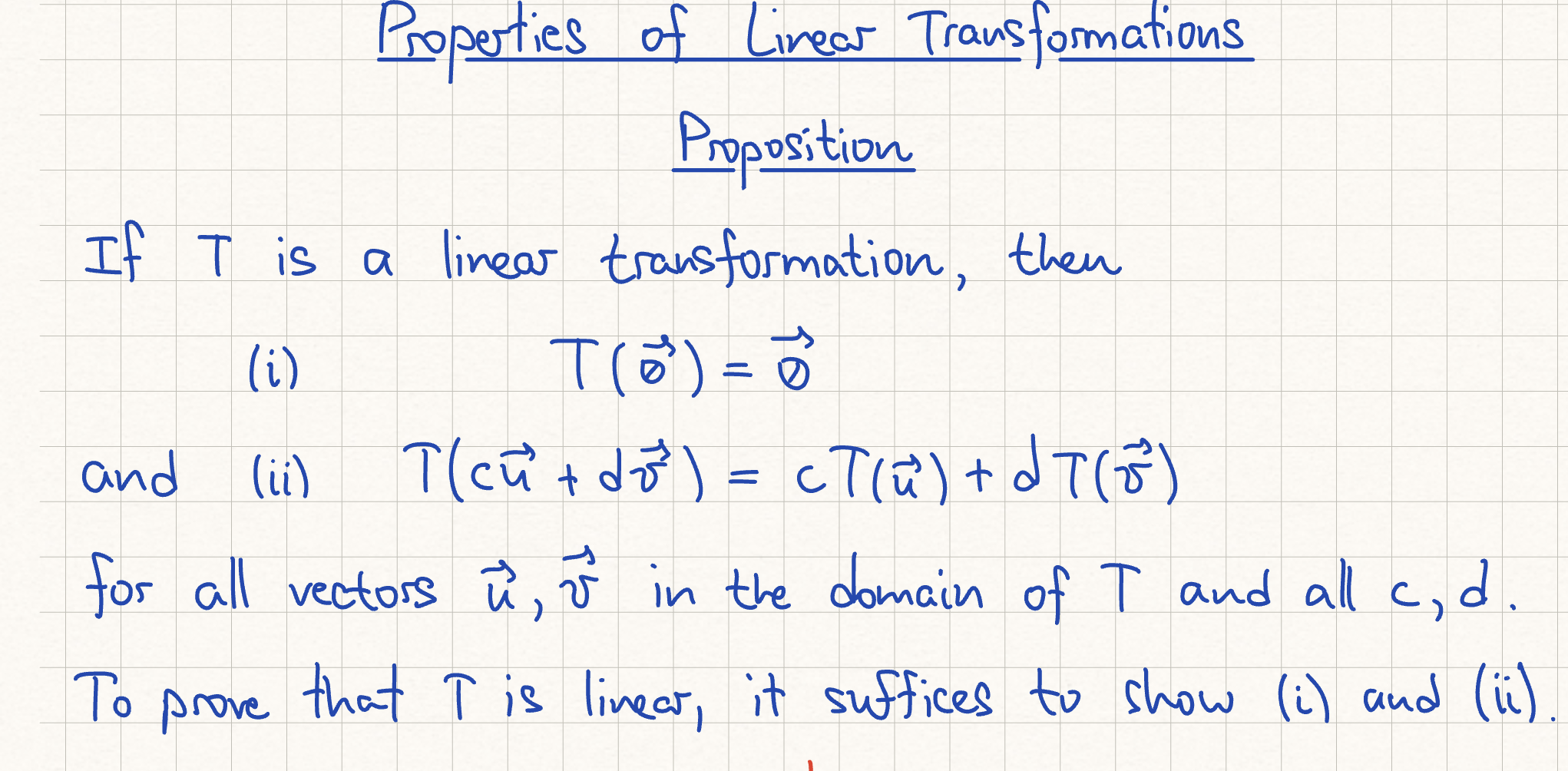
Linear Transformation Properties
matrix transformations and linear transformations
Every linear transformation is a matrix transformation and vice versa
superposition principle
The superposition principle in physics is a direct application of the properties of linear transformations. It states that the net response at a given place and time caused by two or more stimuli is the sum of the responses that would have been caused by each stimulus individually. just the conditinos applied
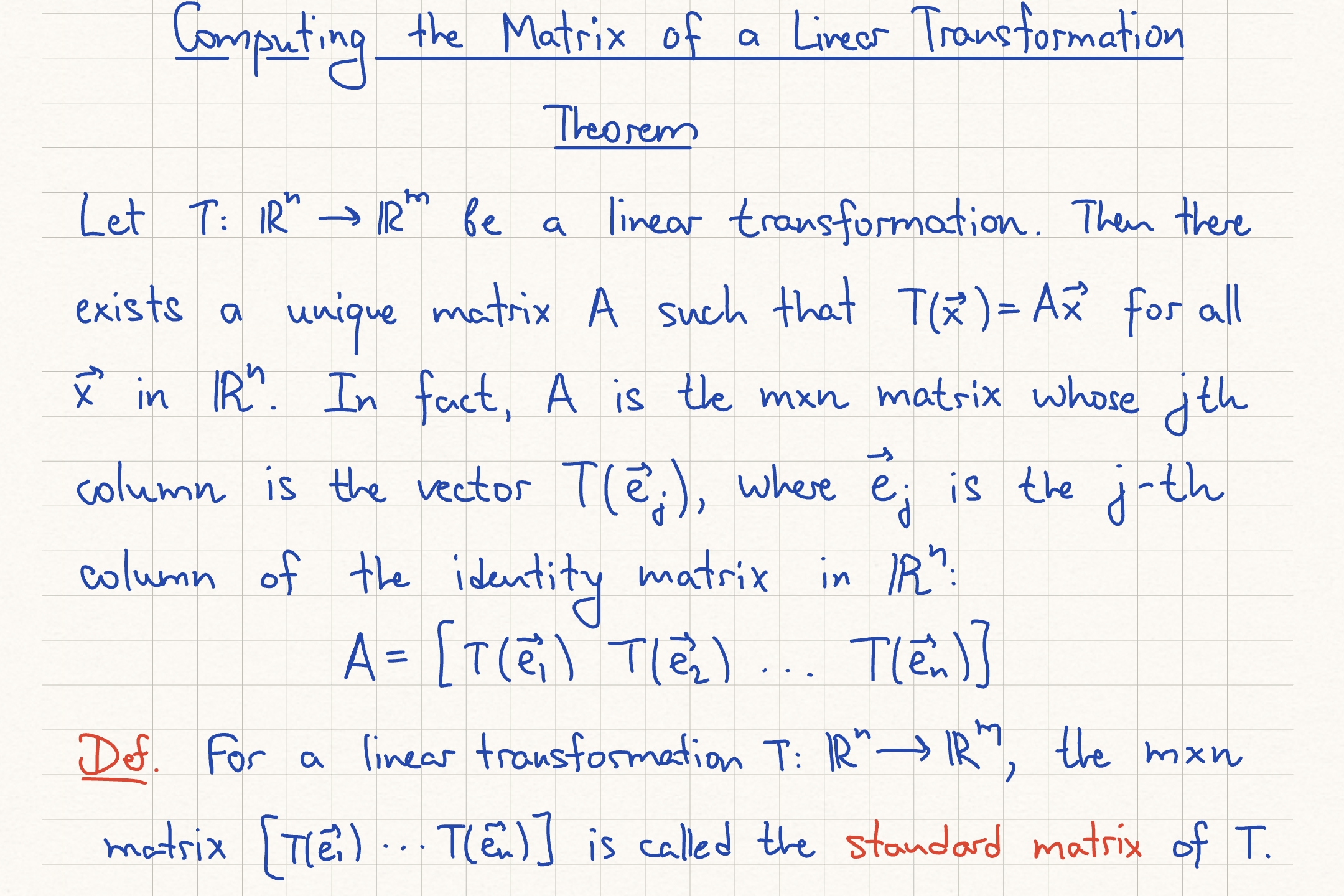
Computing Matrix of Linear Transformation Theorem
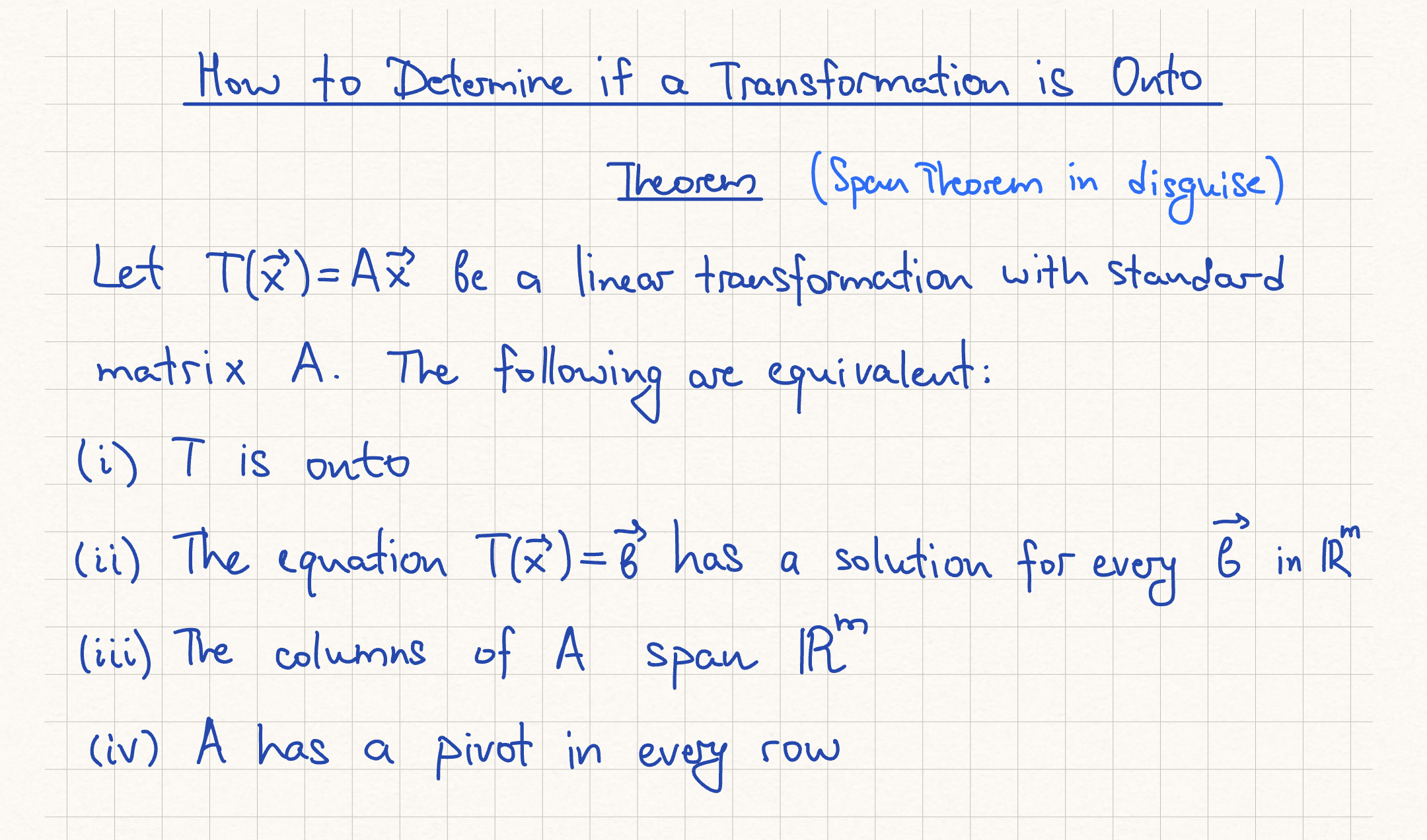
Onto Transformation Theorem
One-to-One Transformation Theorem

(T/F) The columns of the standard matrix for a linear transformation from Rn to Rm are the images of the columns of the nxn identity matrix.
True (T). The columns of the standard matrix for a linear transformation from Rn to Rm are the images of the columns of the n×n identity matrix. As explained in problem 23, the standard matrix for a linear transformation T is constructed by applying the transformation to the standard basis vectors e1,…,en and using the resulting vectors as the columns of the matrix. The j-th column of the standard matrix is the vector T(ej).
names of theorems
know em
diagonal matrix
a_ij = 0 for all i =/= j
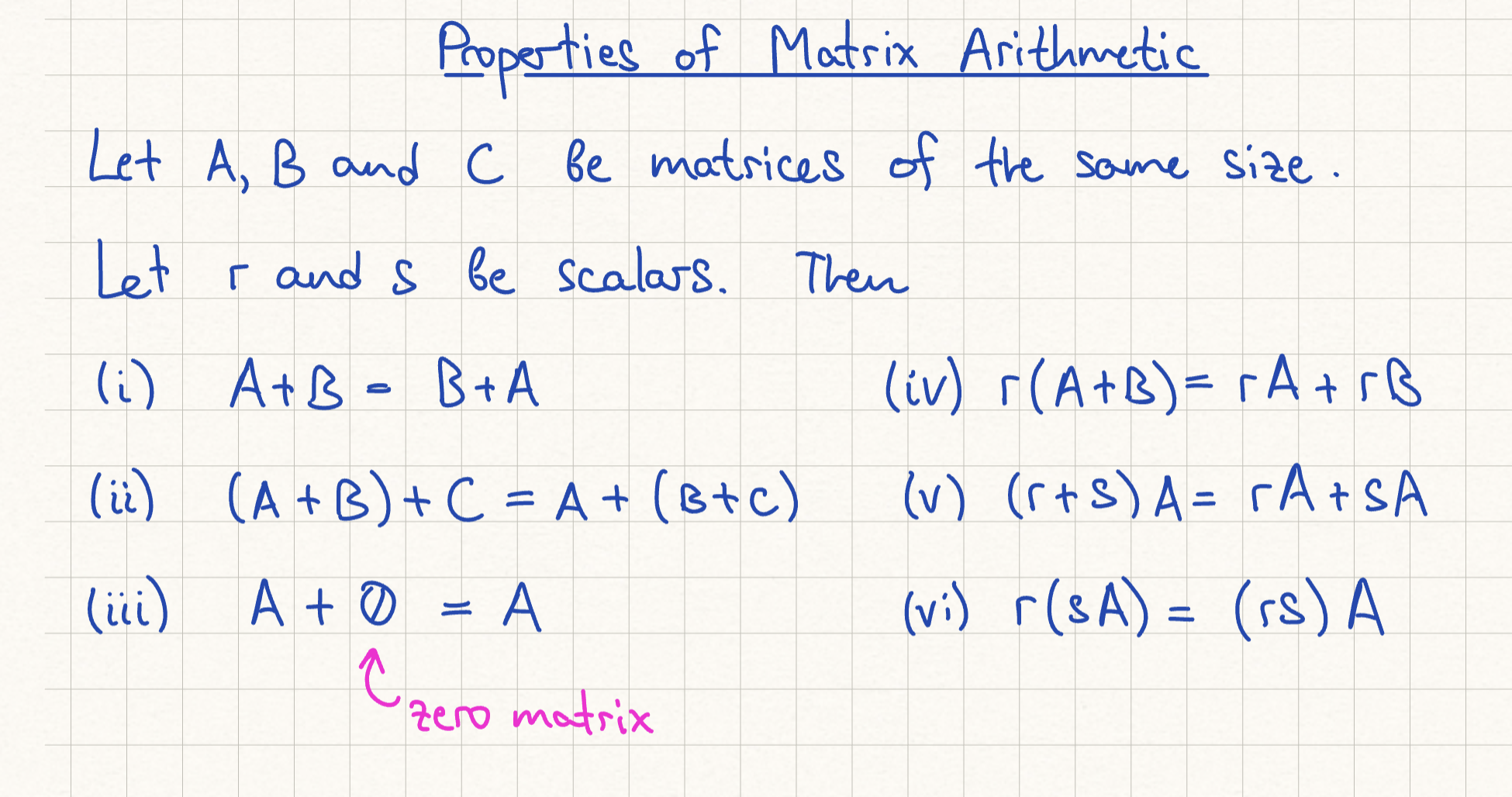
Properties of Matrix Arithmetic
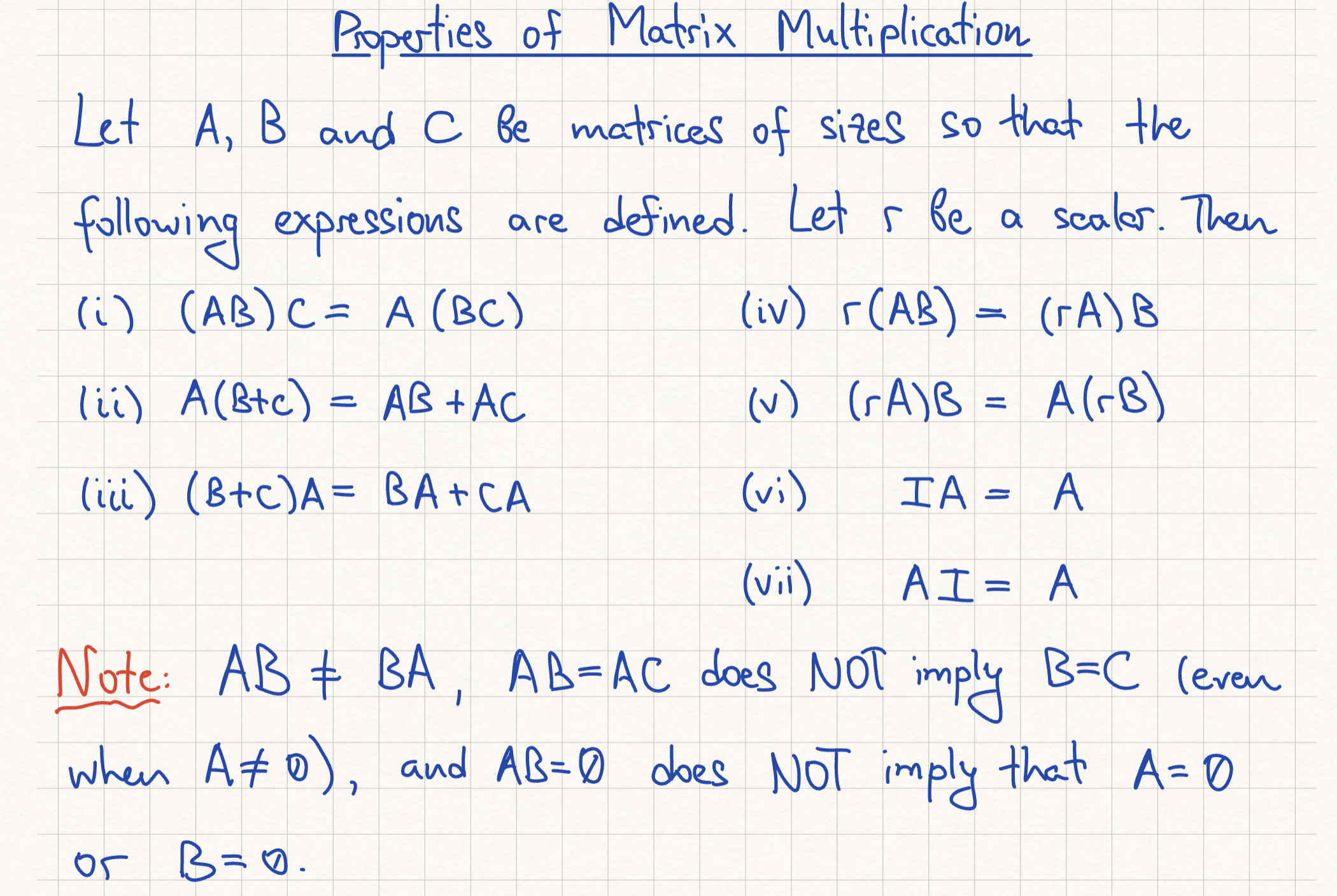
Properties of Matrix Multiplication
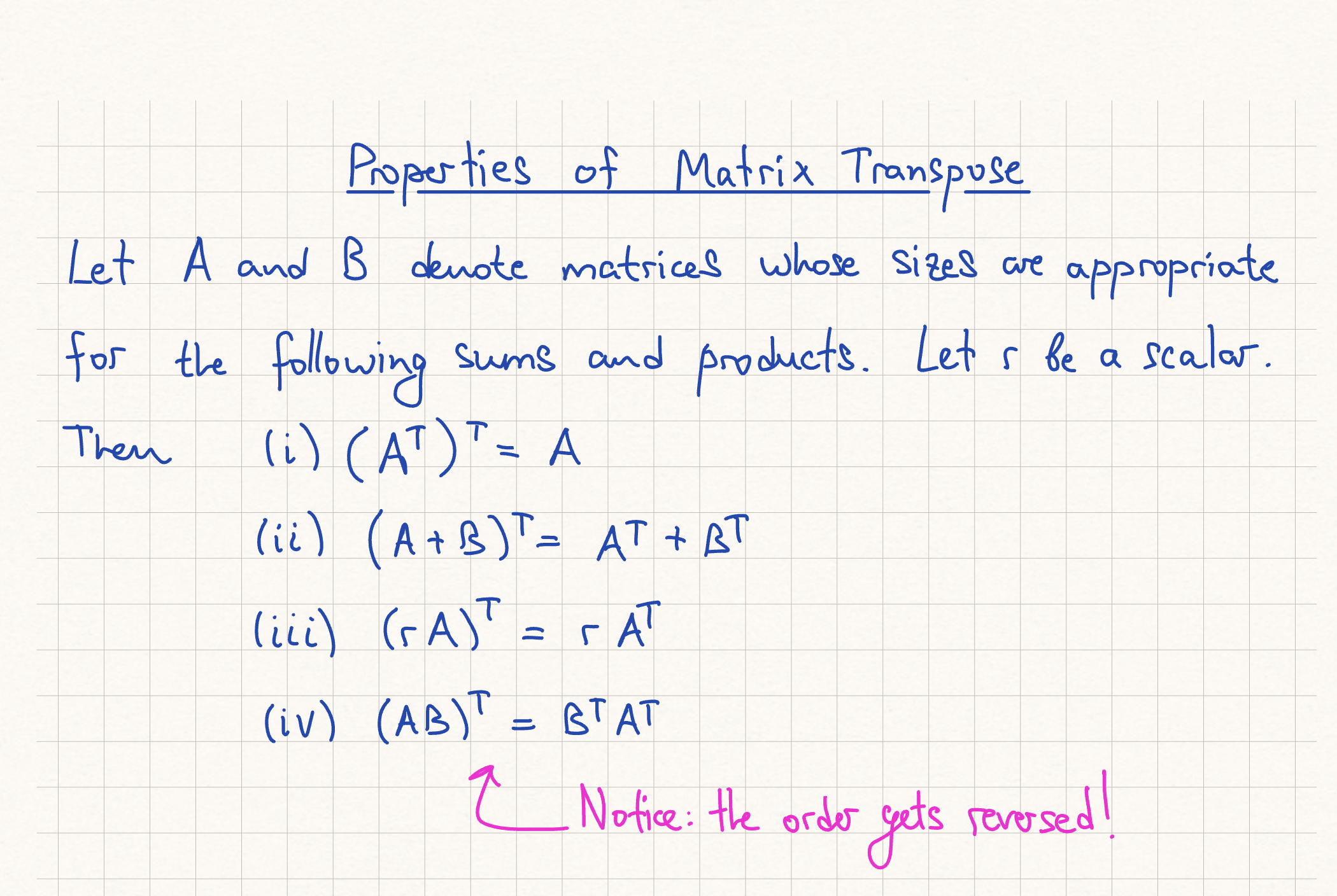
Properties of Matrix Transpose
(T/F) Each column of AB is a linear combination of the columns of B using weights from the corresponding column of A.
The correct rule of matrix multiplication is that each column of the product AB is a linear combination of the columns of A using weights from the corresponding column of B. The statement reverses the roles of matrices A and B.
Suppose the last column of AB is all zeros, but 𝐵 itself has no column of zeros. What can you say about the columns of 𝐴?
Let the last column of B be bk. We are given that Abk=0 and bk=0. This means that the equation Ax=0 has a non-trivial solution, namely x=bk. By the Invertible Matrix Theorem, if Ax=0 has a non-trivial solution, then the columns of A are linearly dependent.
is the inverse unique
Inverse is Unique Theorem: If an inverse of a matrix exists, it is unique.
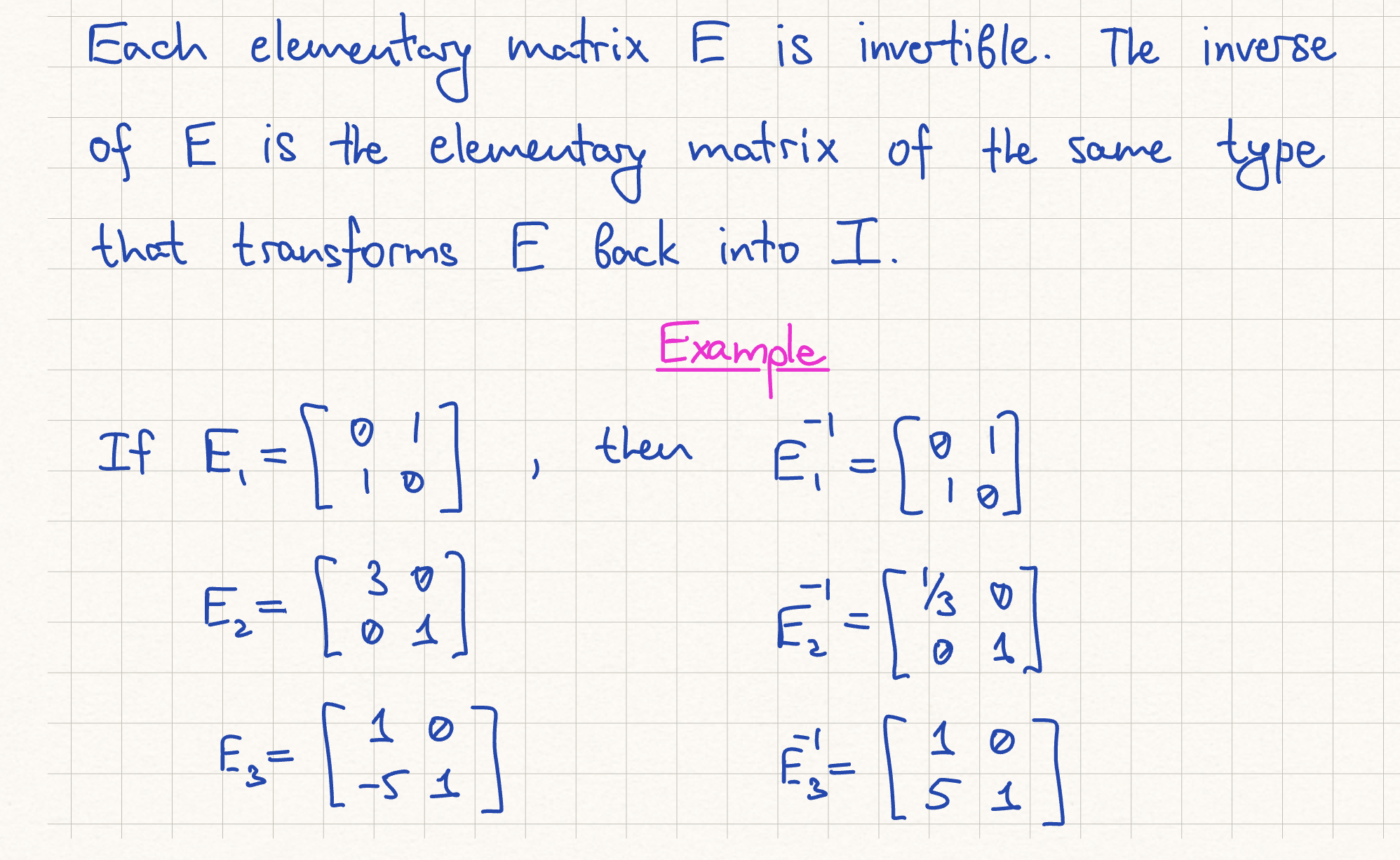
Elementary Matrix Relationship
It turns out that applying an elementary row operation to an mxn matrix A is equivalent to multiplying A by a corresponding mxm elementary matrix from the left. Get that matrix by applying the row operation to I
Invertible if and only if row equivalent to In theorem

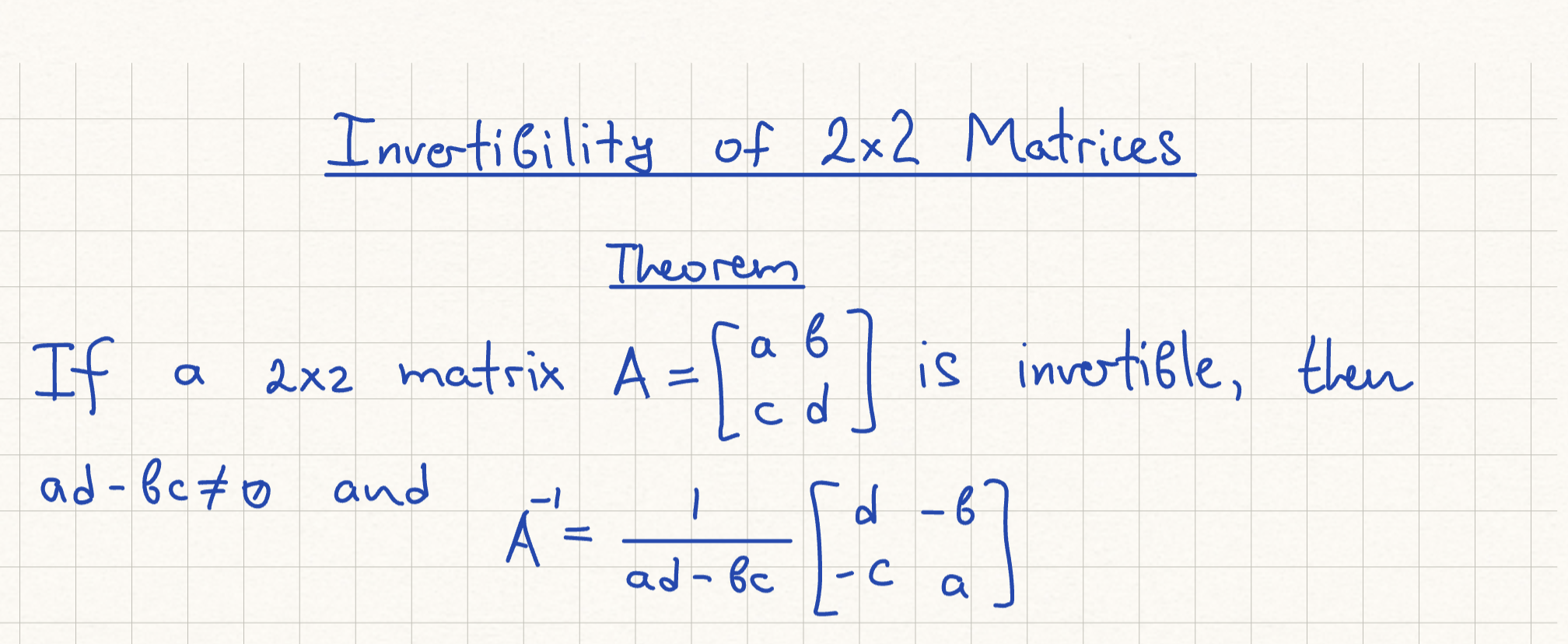
Invertibility of 2×2 Matrices Theorem
Invertible Unique Solution Theorem

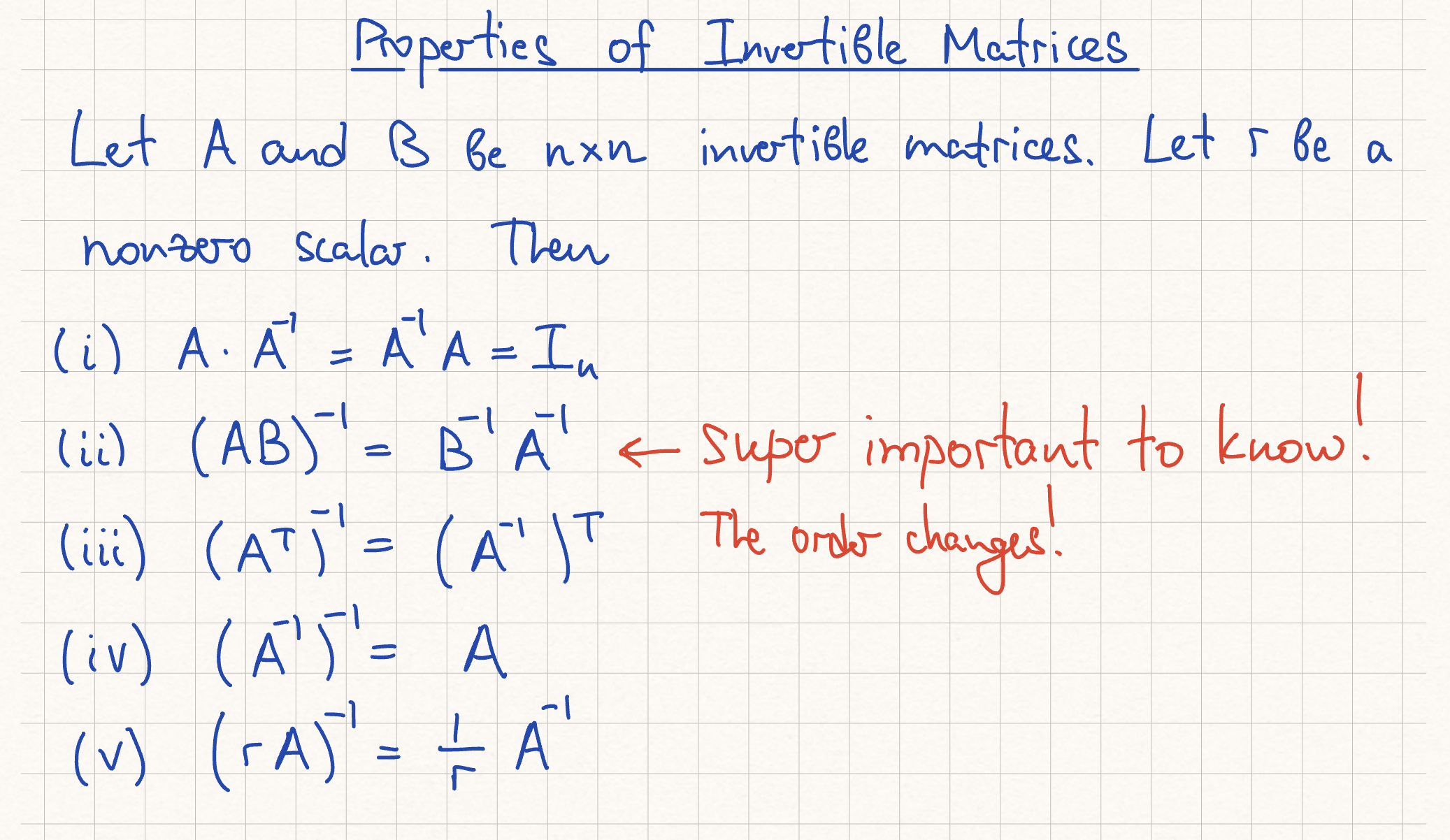
Properties of Invertible Matrices
Elementary Matrices Invertible?
Invertible Matrices Theorem
h) the columns of A span Rn
i) the linear transformation T(x) = A(x) is onto Rn
j) there is an nxn matrix C such that CA.= I
k) there is an nxn matrix D such that AD = I.
l) A^T is an invertible matrix.

Geometrically, the solution set of A(vec_x) = (vec_b) is the result of translation of the solution set A(vec_x) = vec_0 by a vector vec_p.
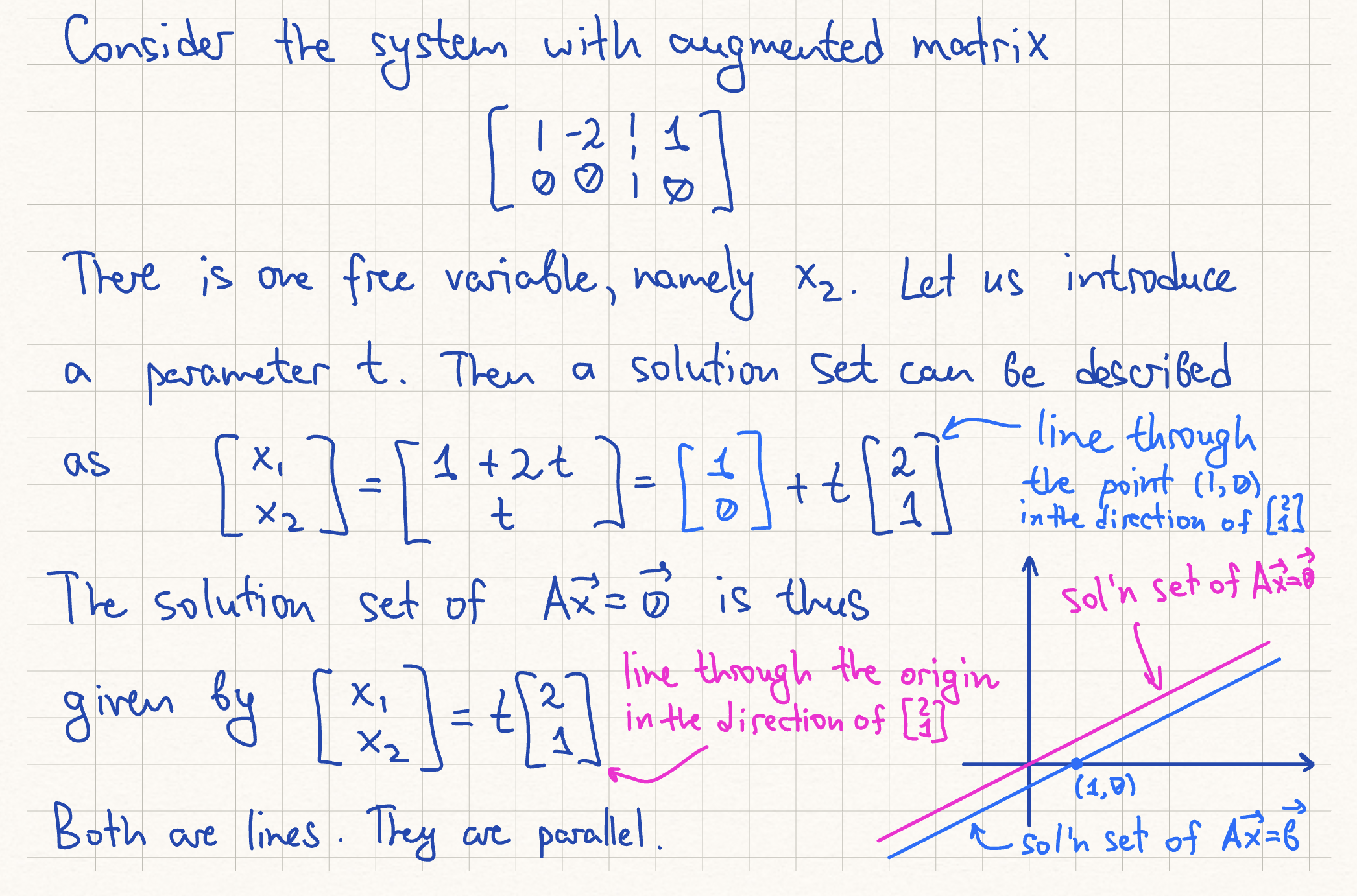
vec_p is a vector such that A(vec_p) = vec_b
vec_v1..., vec_vk are solutions to the associated homogeneous system A(vec_x) = 0.
t1...tk are parameters