EASC 2919 Part 3: Earth Systems and Climate
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
How are the Lithosphere - Atmosphere - Ocean - Biosphere connected?
How are the first 3 connected?
Fluxes of matter
Fluxes of heat
What timescale does direct atmospheric sampling give us climate info on?
1850s to present
What do we use for climate info prior to 1850s?
Proxies
What are proxies?
indirect measurements that serve as substitutes for direct measurements
What is the most important proxy?
Stable isotope analysis
What is fractionation?
Process of separation and differential concentration of different isotopes.
How do climate processes relate to fractionation?
Climate processes often cause fractionation, allowing us to use isotope concentrations as climate proxies
How far back do ice cores go?
800kya
What information do layers in ice cores provide?
Past annual snowfall
What information do bubbles in ice cores provide?
Samples of past atmosphere composition and greenhouse gas levels
What information do particles in the ice of ice cores provide (O isotopes, cosmogenic isotopes, ash)?
O isotopes provide past temperature
Cosmogenic isotopes provide past solar activity
Ash provides record of fires and volcanoes
What information does sediment type in sediment cores provide?
Climate processes affecting weathering/transport
What information does pollen in sediment cores provide?
Local climate based on type of plants
What information do microfossils in sediment cores provide?
Species type and isotope ratios in shells indicate ocean conditions
What information do tree rings provide?
Width provides growth conditions (temp, precipitation)
Scars provide fire information
Isotopes
What information do coral rings provide?
Width provides growth conditions (temp, nutrients, pH)
O-18 and Mg/Ca ratio
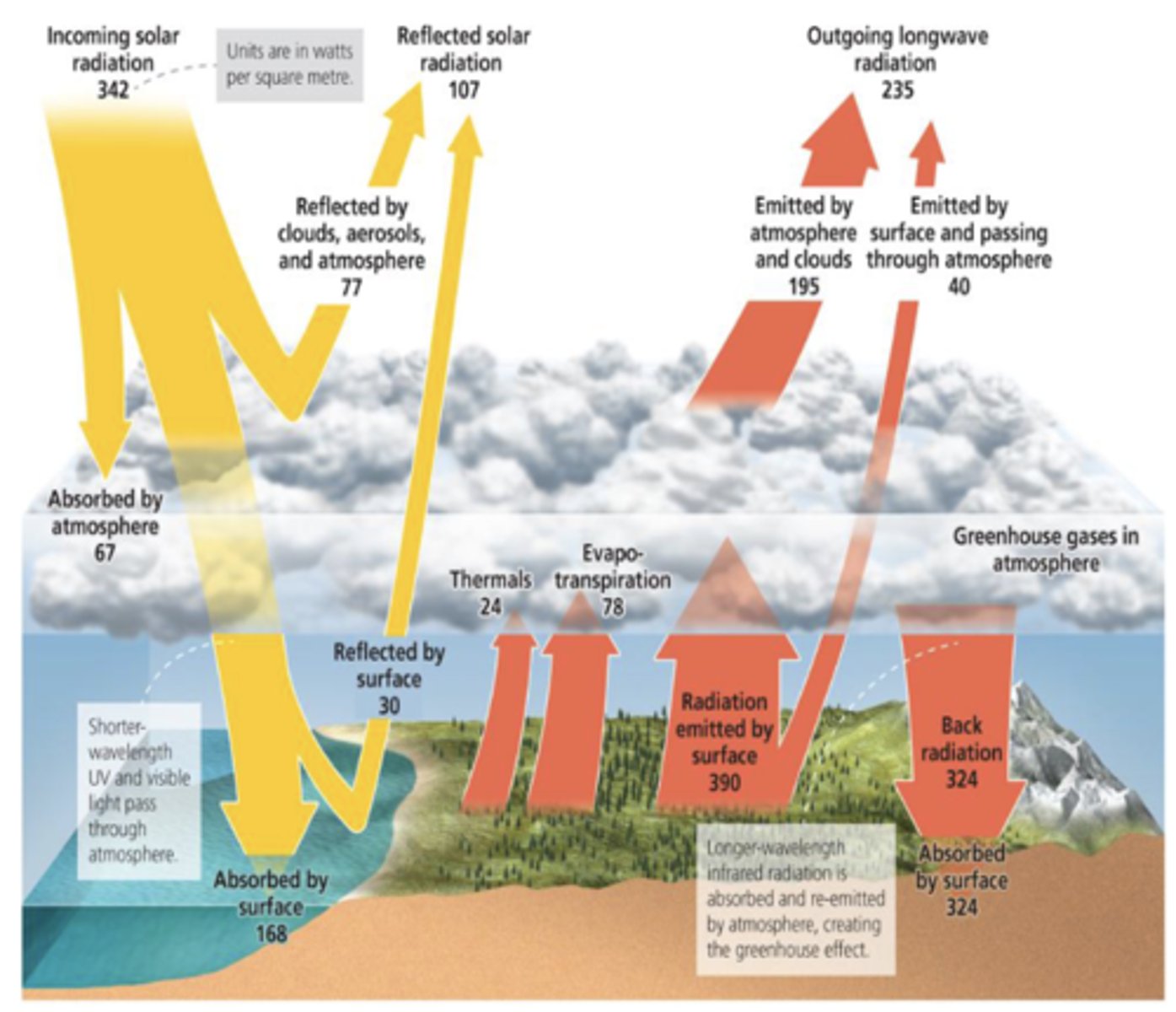
What is energy in?
Shortwave (UV and visible) from sun
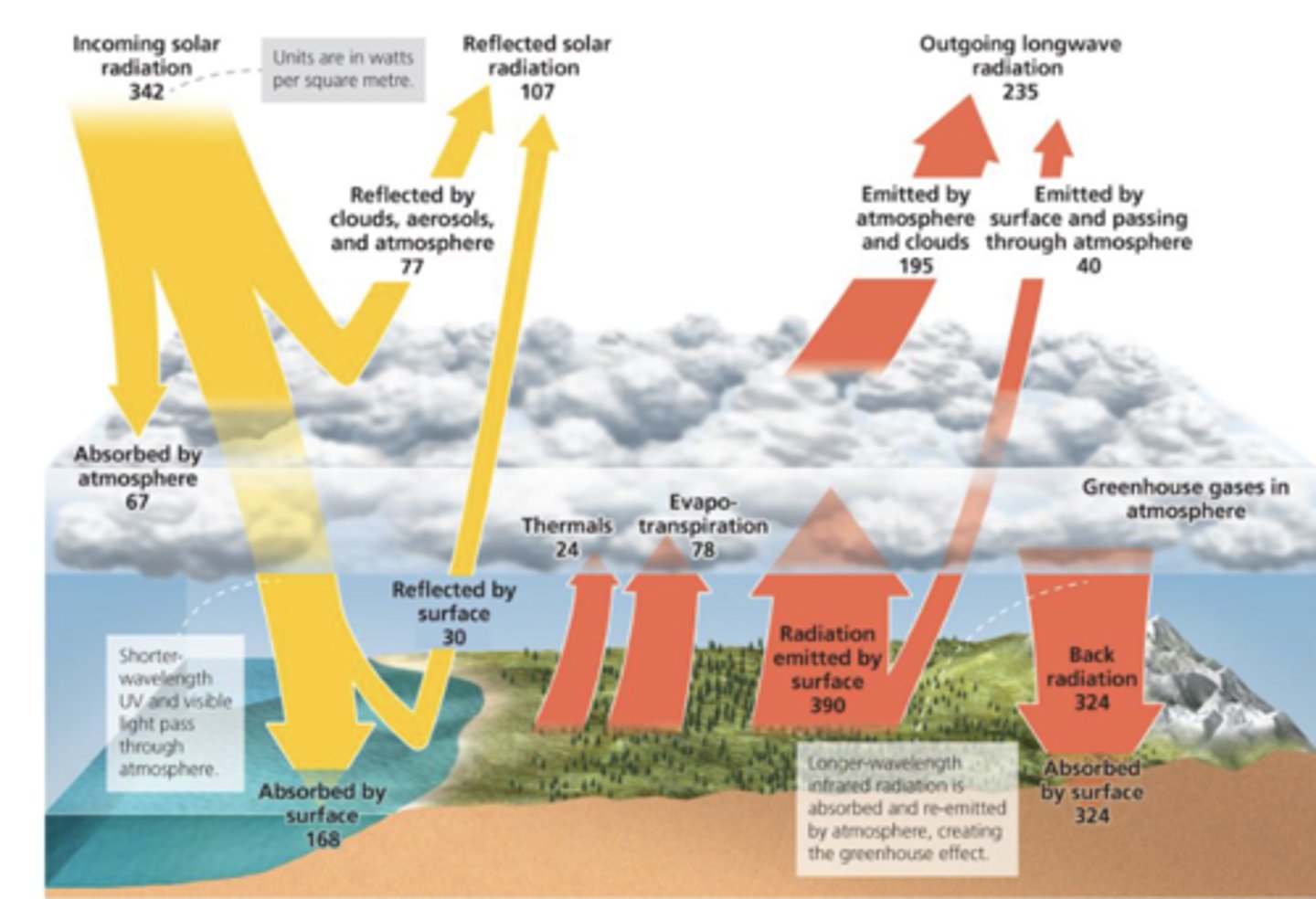
What is energy out?
Longwave (infrared) from earth
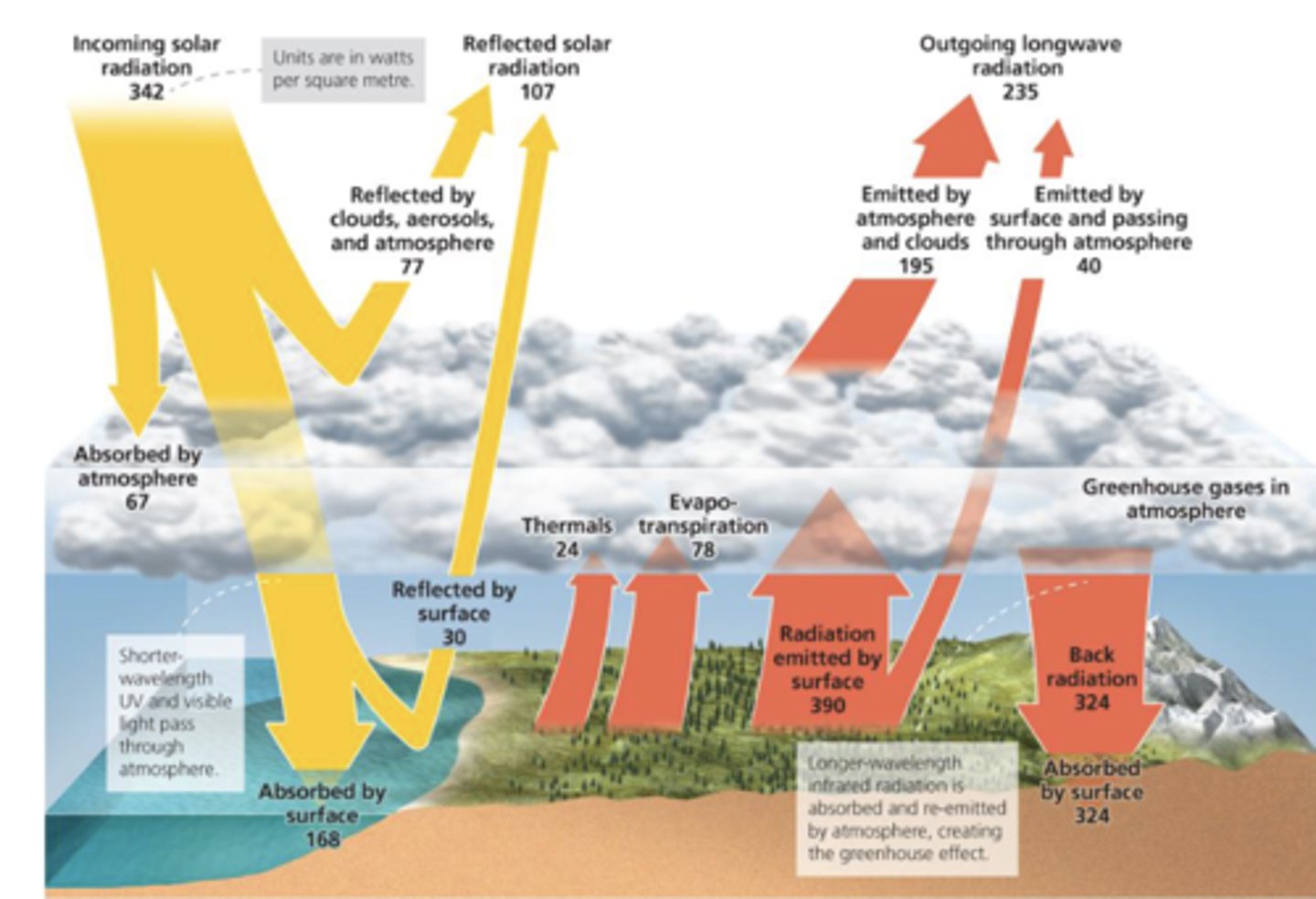
What happens to the 342 W/m^2 that comes in?
107 reflected by atmosphere, cloud, and land
67 absorbed by atm
168 absorbed by earth
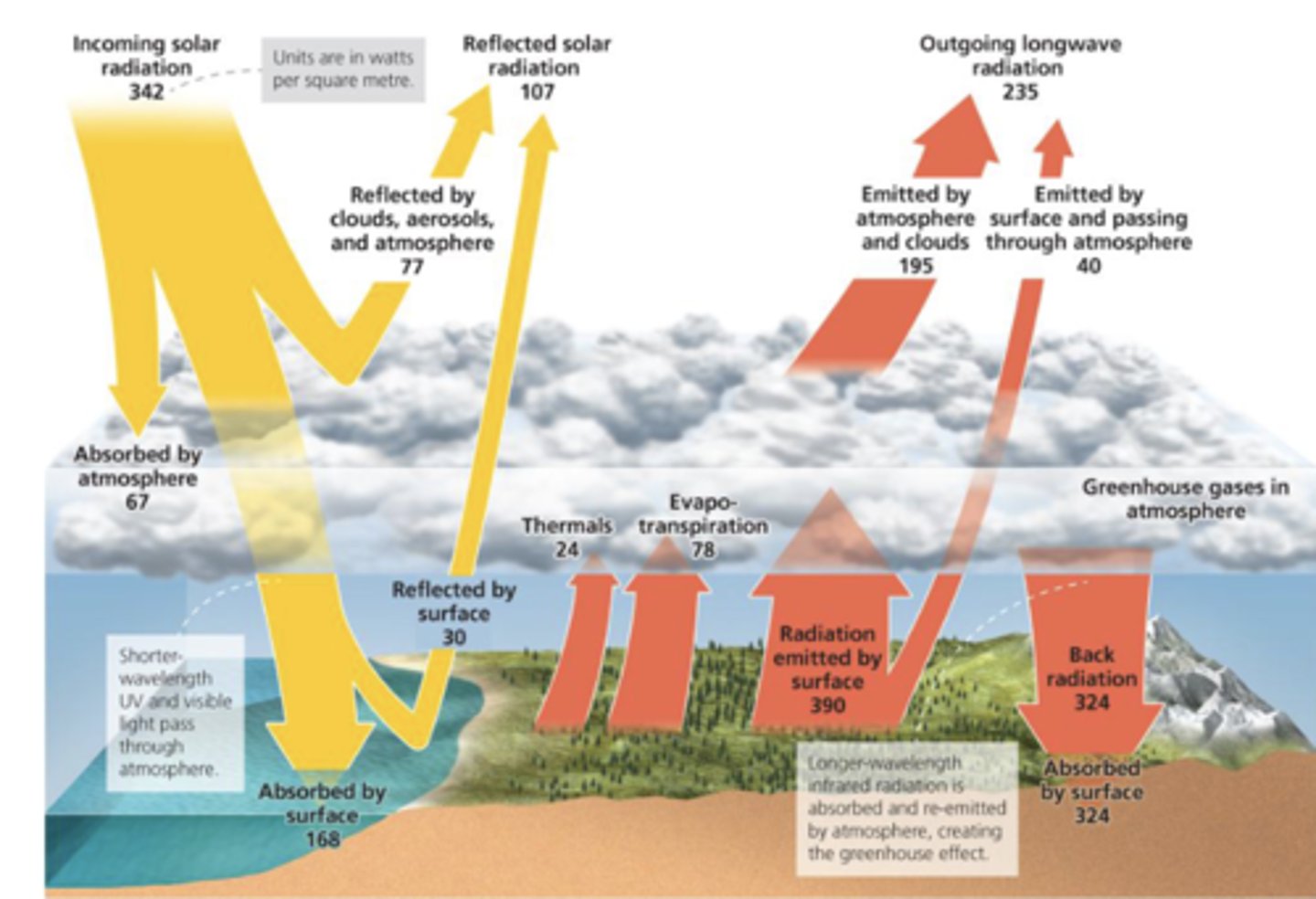
What is the energy flux into the earth?
168 (absorbed from sun)
324 (GHG)
= 492 total
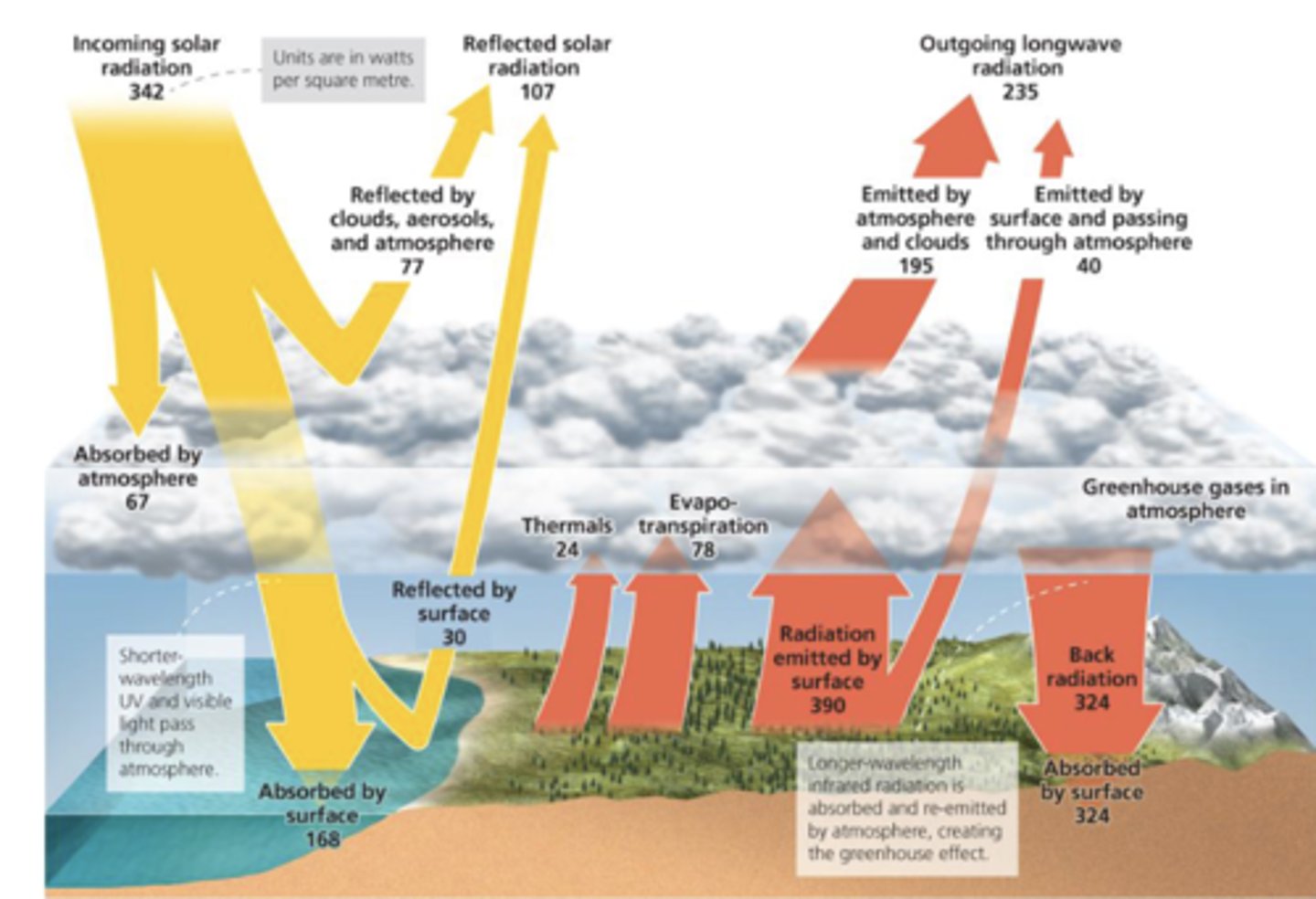
Why is energy from atmosphere down (324) so much bigger than the one going up (195)?
Greenhouse gases
The sun emits 7.4*10^7 W/m^2, how come the earth only receives 1361 W/m^2?
Because the suns energy spreads out in all directions
If "solar constant" is 1361 W/m2, why in our heat budget is the incoming solar radiation only 342 W/m^2
Because 342 is an average over 24hrs. Energy rarely comes in perpendicular, and half the Earth does not receive energy during the night
How does solar output vary on short time scales?
The number of sun spots changes the amount of energy released per m^2
How does solar output vary on the geological time scale?
The temperature of the sun didnt change but it grew in size which increases luminosity
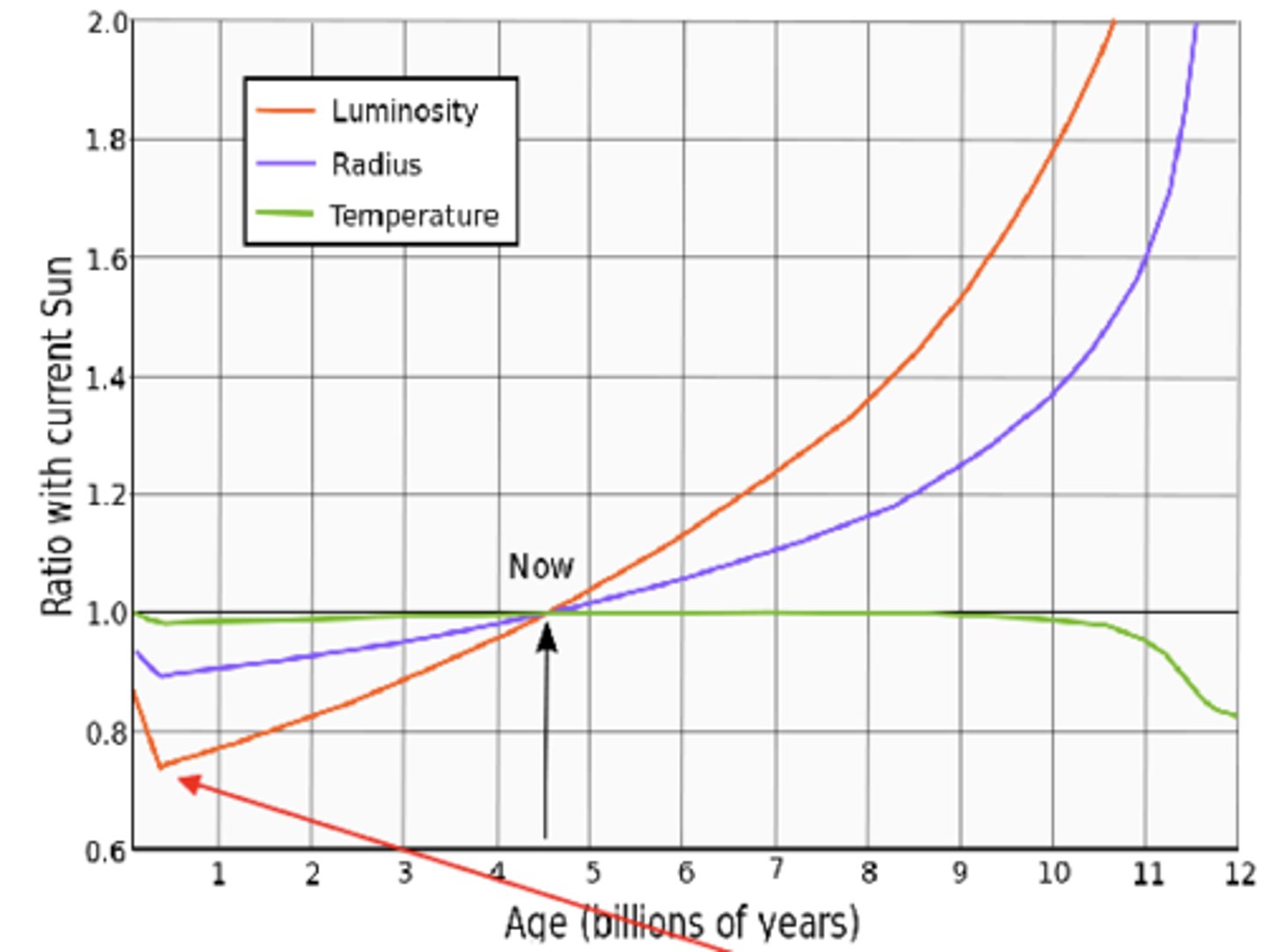
According to the faint sun paradox, the early sun was 70% as strong as now. How come earth's temperature did not change?
There were much more greenhouse gases back then
Explain orbital forcing
The amount of solar energy Earth receives changes based on its distance and angle from the sun. These changes are called milankovic cycles
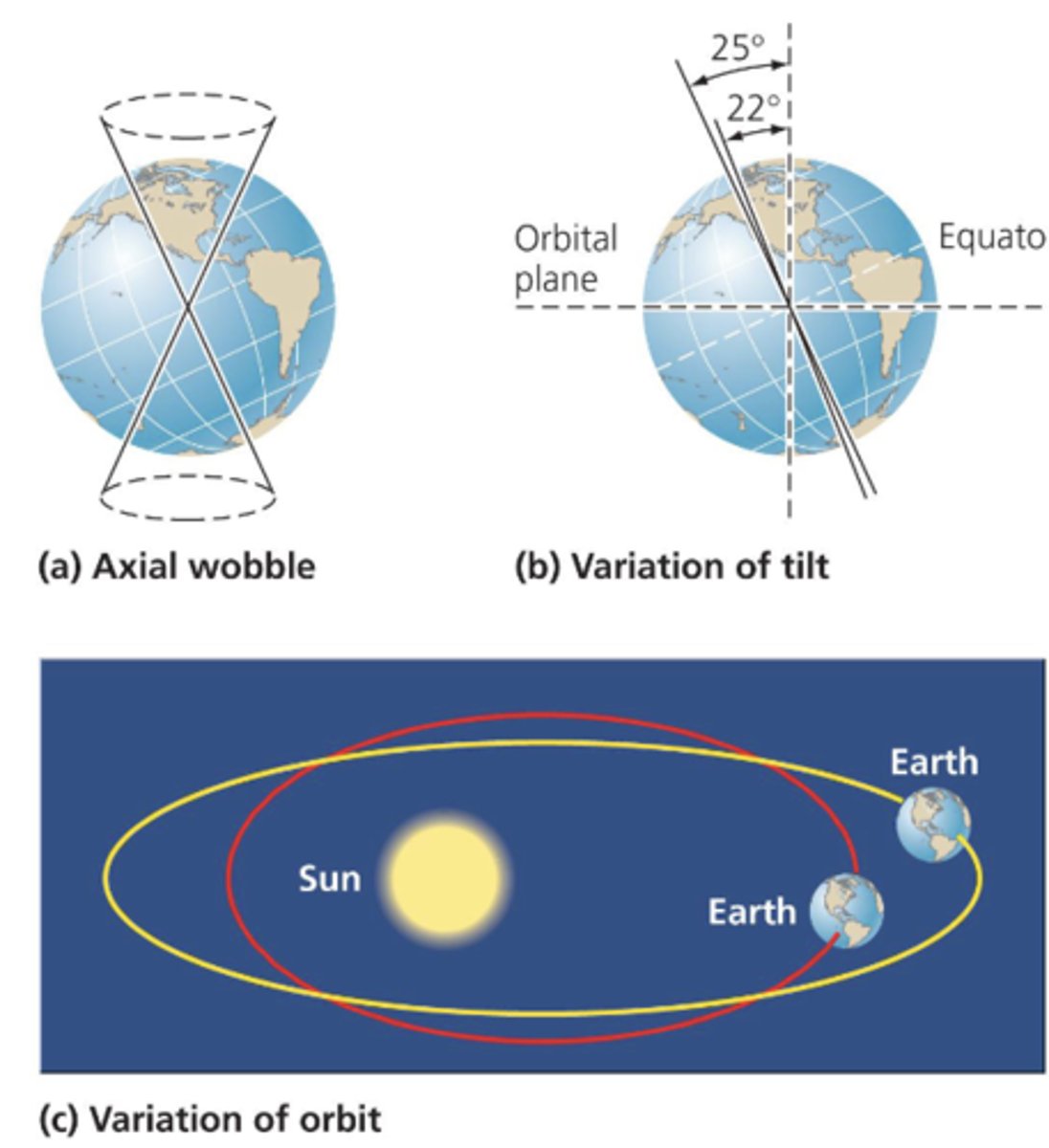
What 3 processes compose the Milankovic cycle?
Axial wobble, tilt variation, and orbit variation
Is there a correlation between climate and orbital forcing?
Yes, higher orbital forcing tends to lead to warming
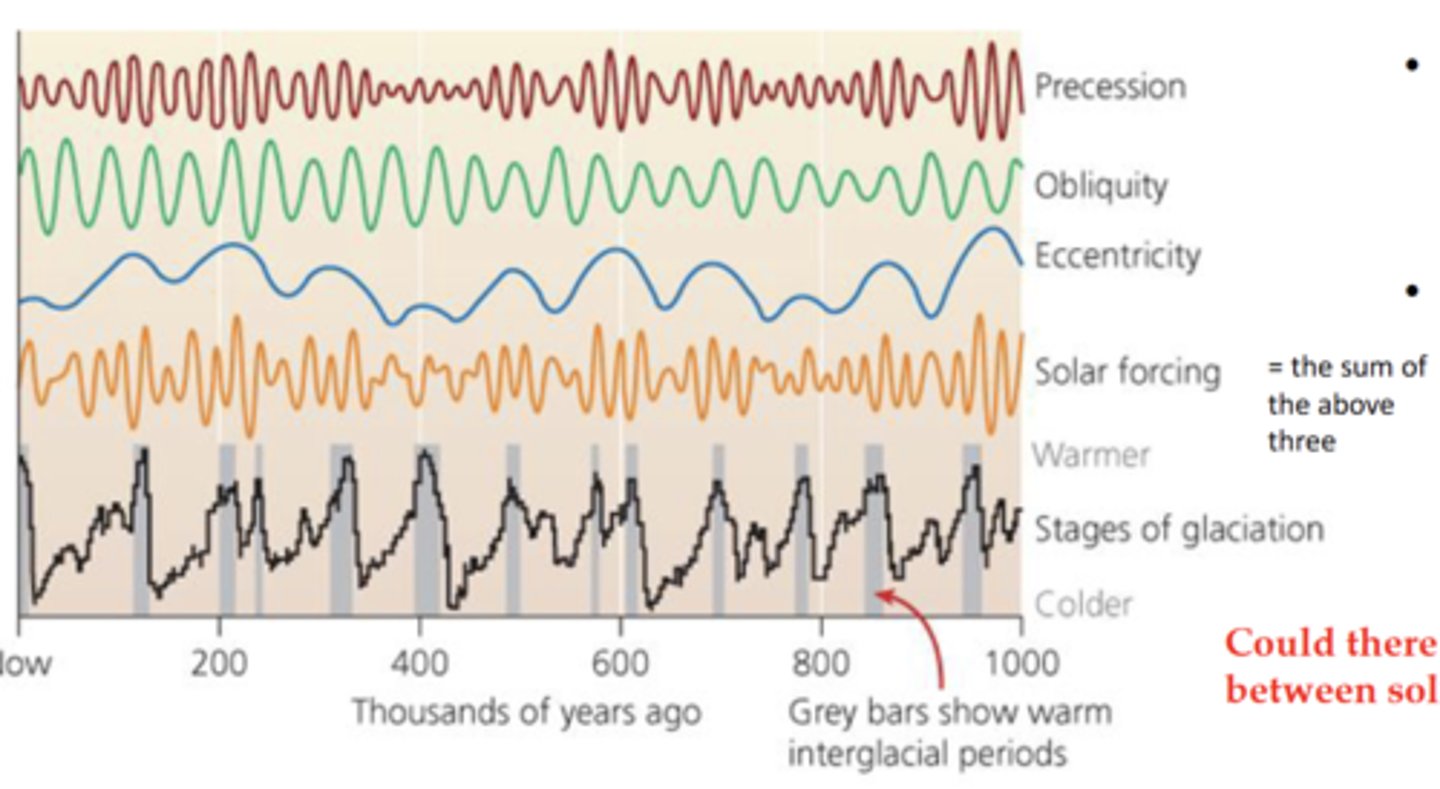
Why doesnt orbital forcing sufficiently account large changes in global heat?
Milankovic cycles act as triggers, which are then amplified by several positive feedback systems
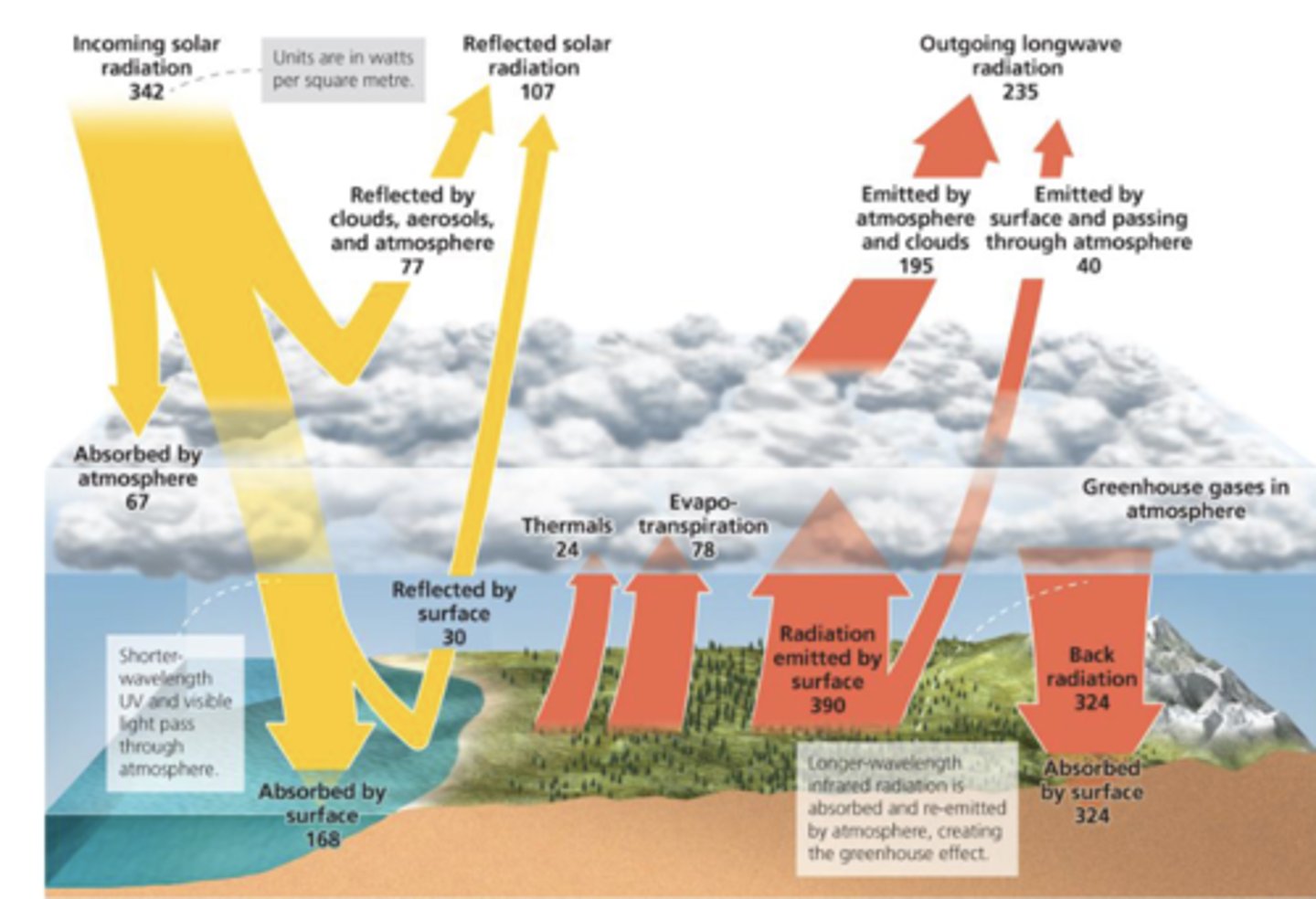
How much solar radiation is reflected by albedo? Be able to find this from the image.
(77 + 30) / 342 = 30%
Explain the ice-albedo feedback
Higher temperatures (initiated by Milankovic) causes ice to melt which reduces albedo causing higher temperatures
Why is the climate most sensitive to the Arctic summer conditions, rather than winter or antarctica?
In summer, a few degree change causes more melting.
In winter, a few degrees doesnt matter
Antarctica is too cold
How do greenhouse gases work?
They let shortwave through, but absorb and re-radiate longwave
How much heat does the greenhouse effect account for? How much has been added due to humans?
30C
Humans have added 1.5
Explain greenhouse gas concentration in early atmosphere
Much more CH4 and CO2
How did oxygen change greenhouse gas concentration in the atmosphere?
CH4 became CO2, and CO2 became organic C
What 4 feedbacks drive climate change?
T and Ice albedo
T and CO2
T and CH4
T and H2O
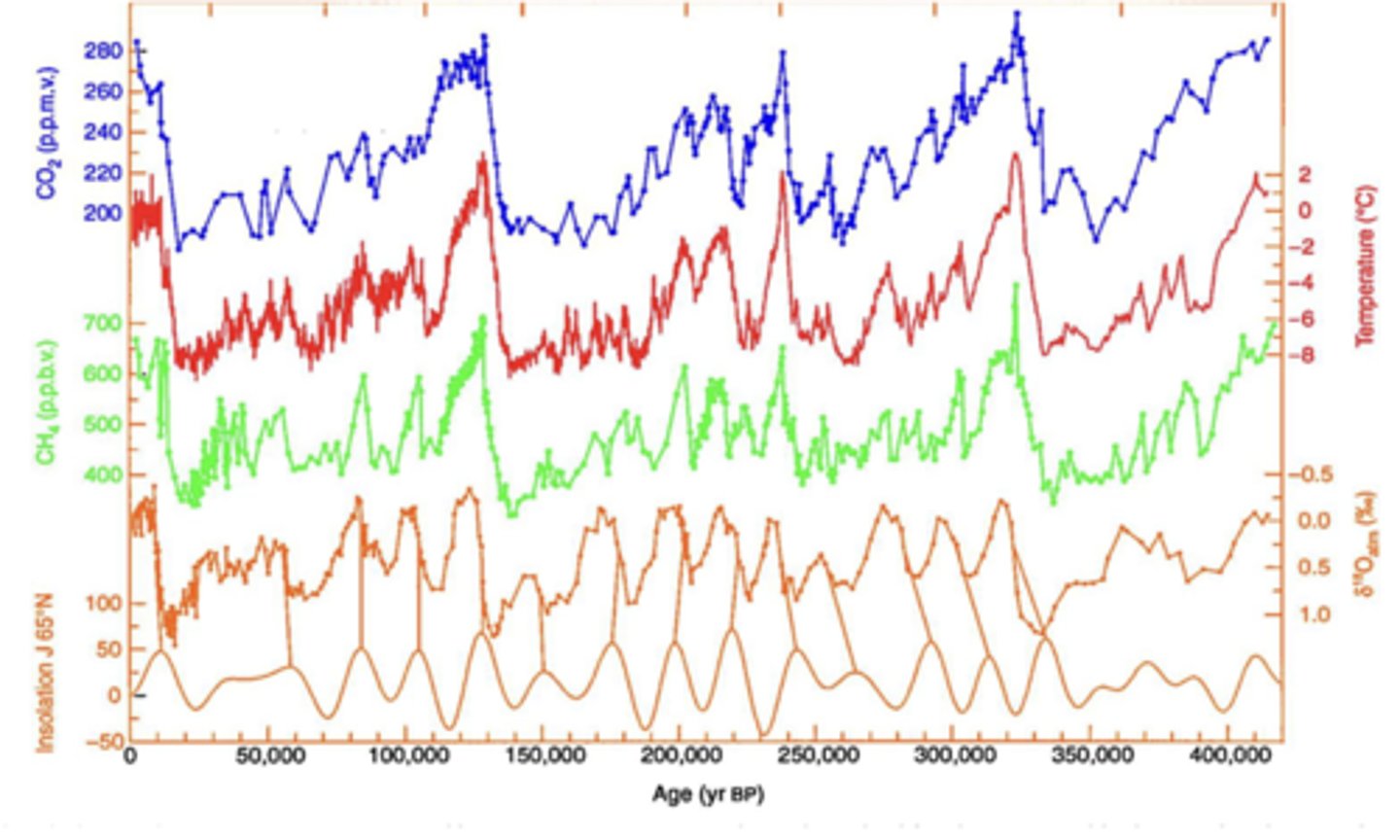
Explain the CO2 positive feedback
At higher T, CO2 outgasses from water
Explain the CH4 positive feedback
At higher T, permafrost melts and releases CH4
How much of the preindustrial greenhouse effect is water vapor responsible for?
66-85%
Does water vapor trigger or amplify climate change?
Water vapor only amplifies it already-happening changes
Explain the T and water vapor positive feedback
Higher T means water evaporates more, and air can hold more water before forming clouds
How do clouds at different altitudes affect climate?
Low clouds cool the earth, high clouds heat the earth.
Influence of clouds depends on lots of factors
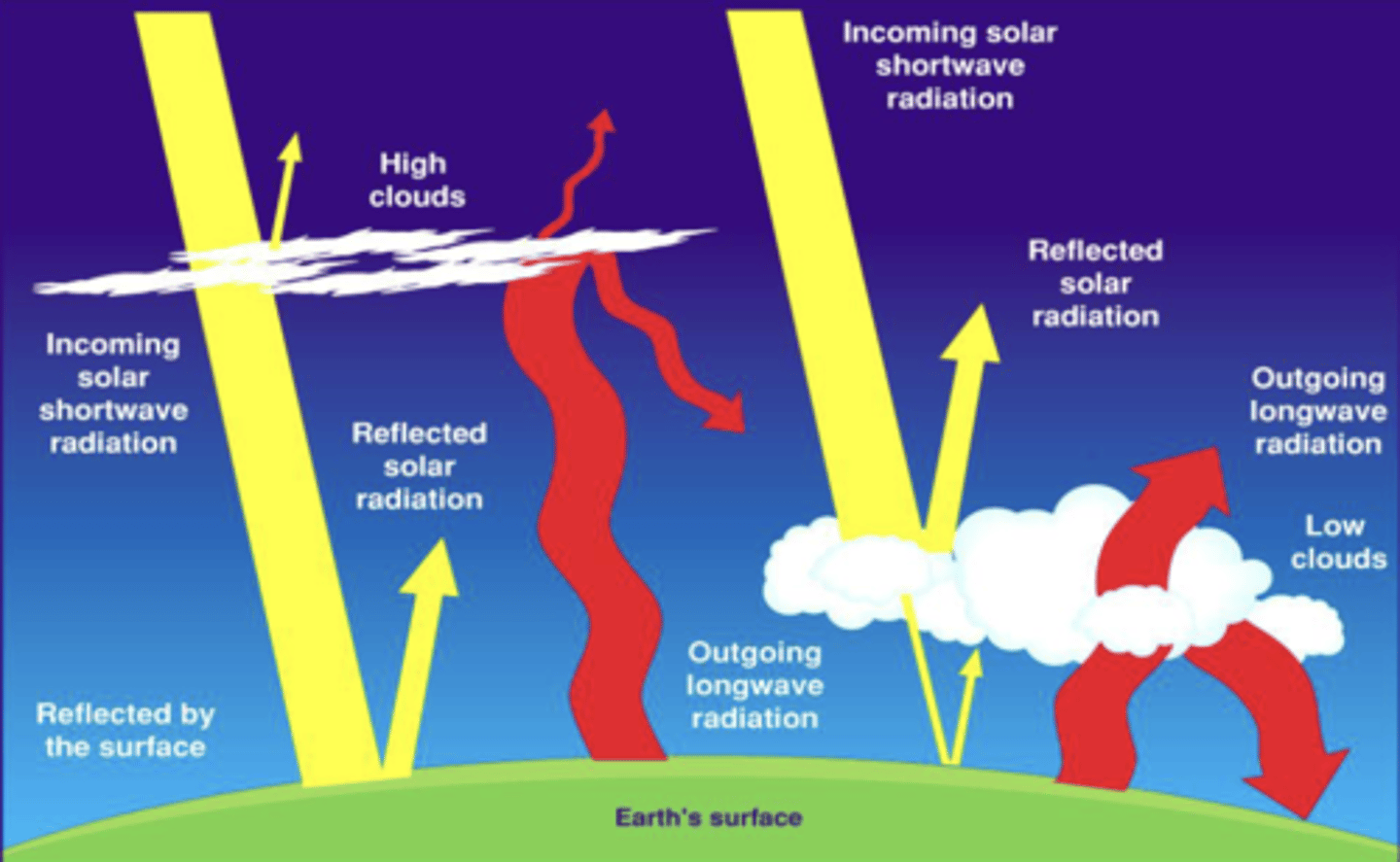
What 2 factors affect cloudiness?
Temperature
Particulates
How does temperature affect cloudiness? How does this affect earth's energy budget?
Higher temp causes more water vapor in air, while simultaneously forming less clouds.
More GHG and less cloud cooling => warming
How does presence of particles affect cloudiness?
Particles act as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN)
Will a cloud over land or ocean have a larger cooling affect?
Over ocean, because ocean has lower albedo than land
Why is DMS from plankton particularly important as a CCN?
Because clouds over ocean are limited by CCNs rather than amount of water vapor, and ocean has lower albedo
Where do CCNs come from?
Volcanoes, dust storms, biology, humans
What effect do human emissions have?
Emissions actually increase clouds, causing cooling
Explain the direct and indirect effects of aerosols on radiative balance
Direct: Reflected (sulphates) or absorbed (soot)
Indirect: serve as CCN
What are 2 major geological sources of aerosols?
Volcanoes
Wildfires
What 3 ways does ocean impact climate?
Absorb and redistribute heat from equator
Ice albedo
Absorb CO2
Source of water vapor and CCN
What happens if THC shuts down?
No more Carbon will be brought to the bottom
How does lithosphere directly impact climate?
Volcanoes (GHG heat, aerosols cool)
How does lithosphere indirectly impact climate?
Ocean circulation
Recycling Carbon through subduction
Weathering and transport brings Si and micronutrients, causing plankton blooms
How does biology impact climate?
Oxygen lowered CO2
Albedo and evaporation
Calcareous shells remove CO2