Anatomy and Physiology of Joints: Types, Movements, and Disorders
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
Joint
A joint is a point of contact between two or more bones, cartilage and bone, or teeth and bone.
Articulation
A joint is also called articulation or arthrosis.
Classification of Joints
Joints can be classified in two ways: structurally and functionally.
Structural Classification
This classification considers whether there is a joint cavity and the type of connective tissue involved.
Functional Classification
This classification considers the degree of movement permitted and the type of movement allowed.
Fibrous Joints
A type of joint where dense connective tissue connects bones.
Cartilaginous Joints
A type of joint where cartilage connects bones.
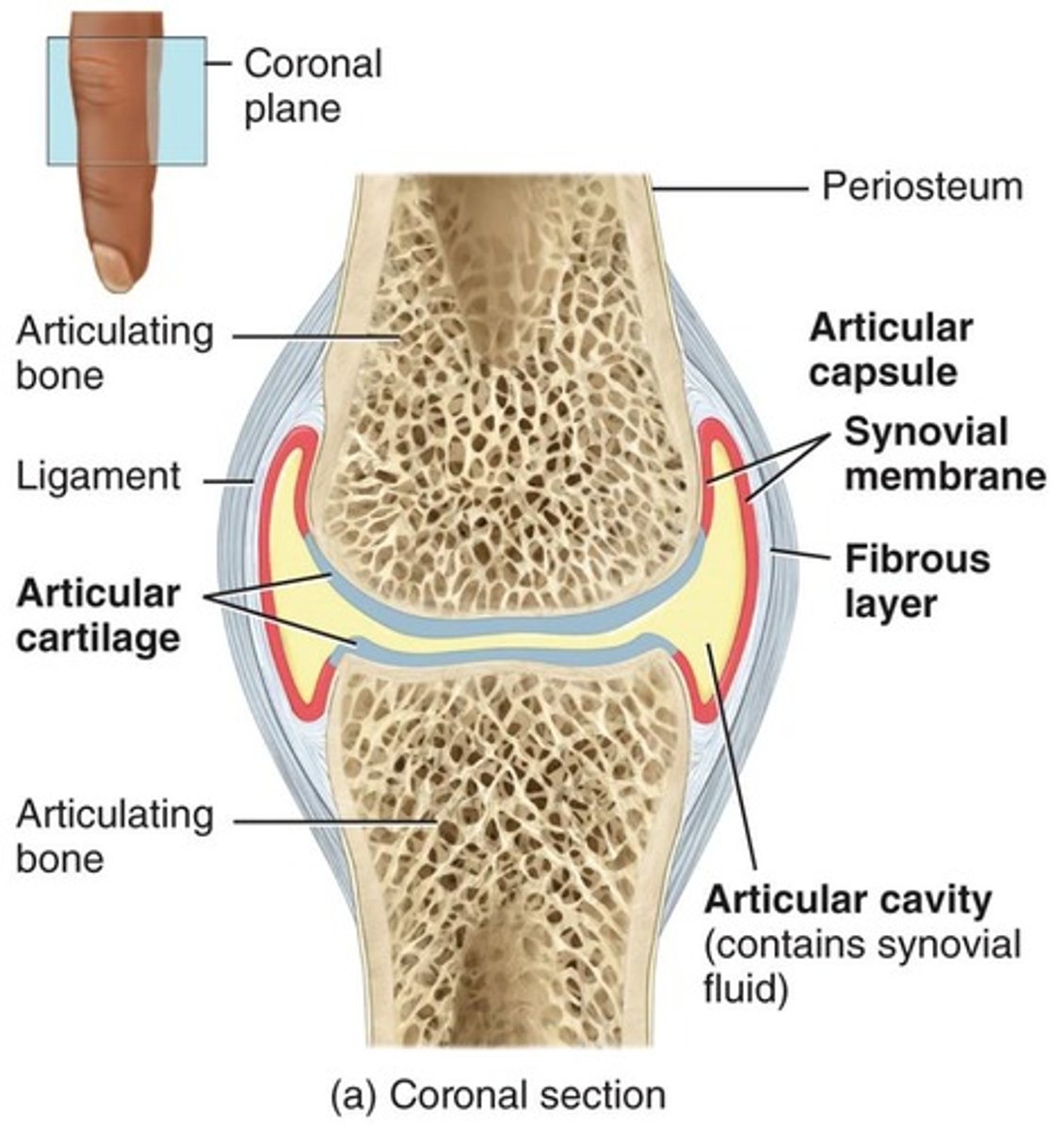
Synovial Joints
A type of joint characterized by a joint cavity filled with synovial fluid.
Temporomandibular Joint
A joint that connects the jawbone to the skull, allowing for movements such as opening and closing the mouth.

Shoulder Joint
A joint that connects the arm to the body, allowing for a wide range of motion.

Elbow Joint
A joint that connects the upper arm to the forearm, allowing for bending and straightening of the arm.
Hip Joint
A joint that connects the leg to the pelvis, allowing for movements such as walking and running.

Knee Joint
A joint that connects the thigh bone to the shin bone, allowing for bending and straightening of the leg.
Types of Movement at Synovial Joints
Includes gliding, angular movements, and special movements.
Aging and Joints
Aging can affect the structure and function of joints.
Arthroplasty
A surgical procedure to restore the function of a joint.
Hip Replacements
A type of arthroplasty procedure where the hip joint is replaced.
Knee Replacements
A type of arthroplasty procedure where the knee joint is replaced.
Rheumatism
A term used to describe various painful medical conditions affecting joints and connective tissues.
Arthritis
An inflammation of one or more joints, causing pain and stiffness.
Lyme Disease
An infectious disease caused by bacteria transmitted through tick bites, which can affect joints.
Sprain
An injury to a ligament caused by overstretching or tearing.
Strain
An injury to a muscle or tendon caused by overstretching or tearing.
Tenosynovitis
An inflammation of the sheath that surrounds a tendon.
Dislocated Mandible
A condition where the jawbone becomes displaced from its normal position.
Sutures
Dense irregular connective tissue.
Synchondroses
Hyaline cartilage.
Synostosis
Eg., frontal suture.
Epiphyseal cartilage
Hyaline cartilage.
Syndesmoses
More dense irregular connective tissue than a suture.
Symphysis
Fibrous cartilage.
Gomphosis
Eg., pubic symphysis and intervertebral joints.
Synarthroses
Immovable.
Amphiarthroses
Slightly movable.
Diarthroses
Freely movable.
Sutures (example)
Eg., suture.
Gomphosis (example)
Eg., gomphosis.
Pubic symphysis (example)
Eg., pubic symphysis.
Intervertebral discs (example)
Eg., intervertebral discs.
Syndesmosis
Articulating bones united by a varying amount of dense irregular connective tissue, usually a ligament or membrane.
Symphyses
Connecting material is fibrocartilage.
Cartilaginous Joint
No Articular Cavity; Articulating Bones United by Hyaline Cartilage or Fibrous Cartilage.
Synchondrosis
Connecting material: hyaline cartilage. Immovable to slightly movable.
Example of Synchondrosis
Between first rib and manubrium of sternum; Epiphyseal cartilage between diaphysis and epiphysis of long bone.
Example of Symphysis
Pubic symphysis and intervertebral joints.
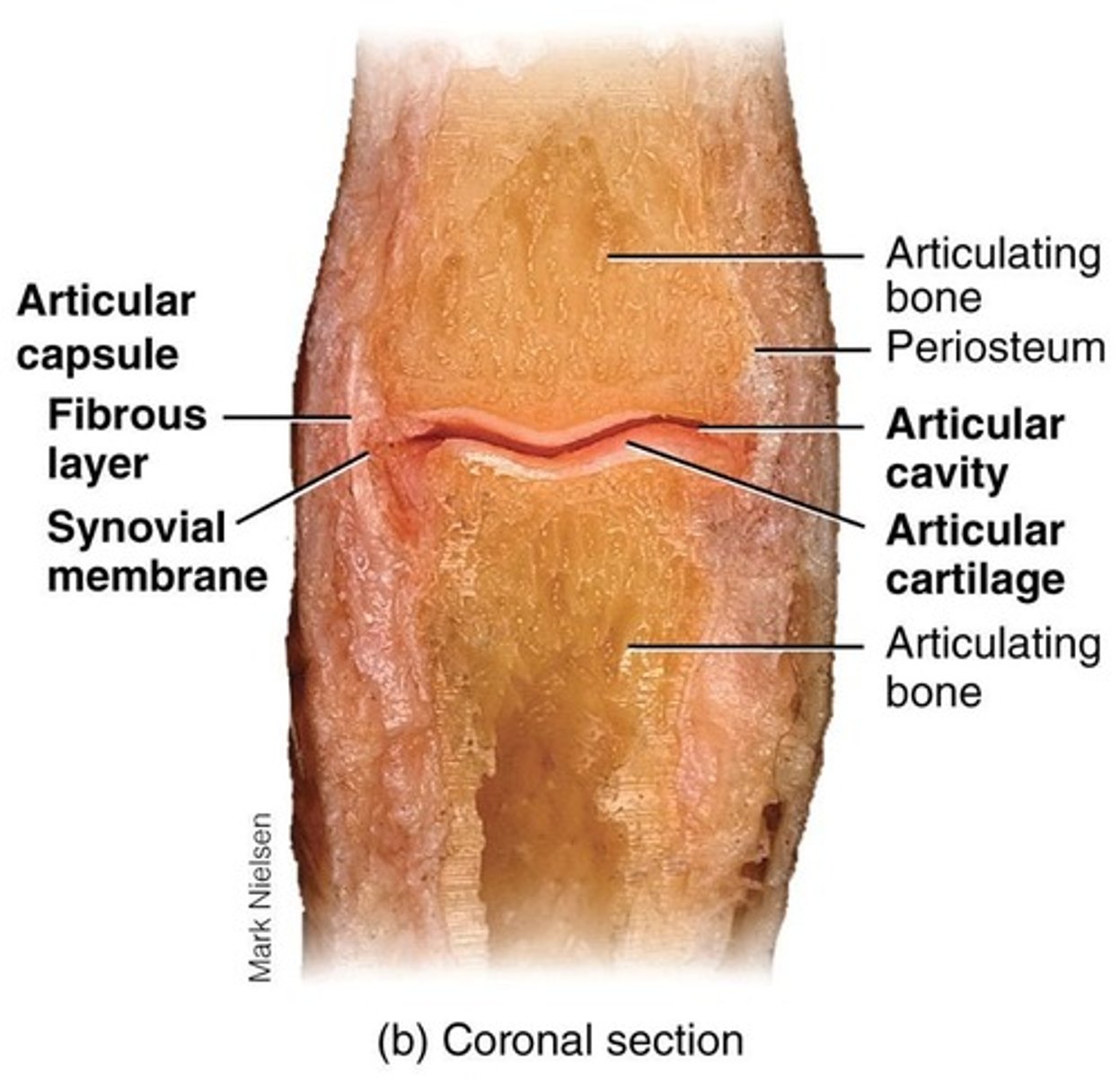
Synovial Joint
Synovial joints have a synovial cavity, articulating bones are covered with articular cartilage, held together by ligaments, contain synovial fluid, have a nerve and blood supply, and are surrounded by an articular capsule.
Bursae
Sac-like structures filled with synovial fluid that cushion movement of one body part over another.
Tendon Sheaths
A tube-like bursae that wraps around tendons subject to a great deal of friction.
Gliding Movement
Movement of relatively flat bone surfaces back-and-forth and side-to-side over another; little change in angle between bones.
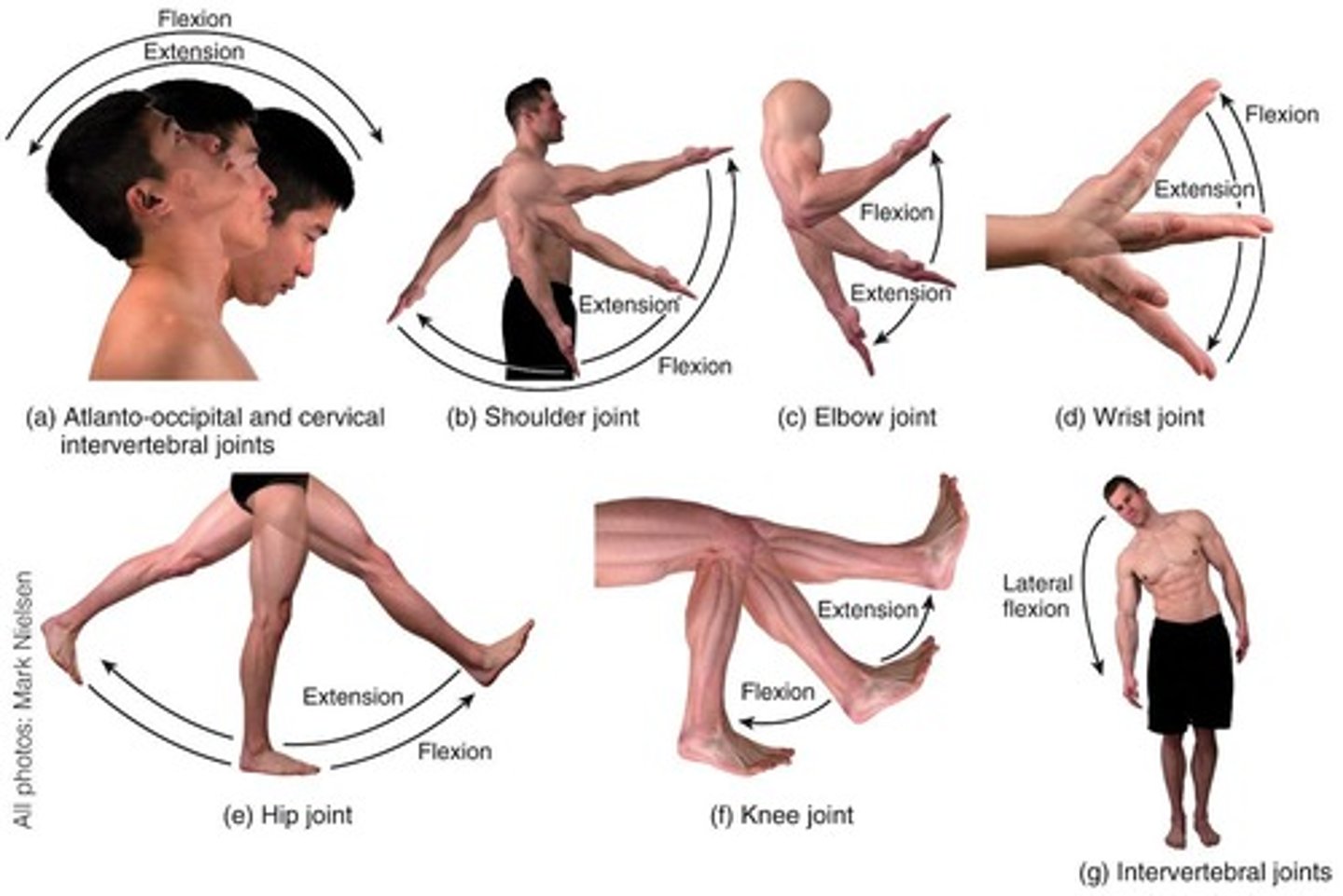
Angular Movement
Increase or decrease in angle between bones.
Flexion
Decrease in angle between articulating bones, usually in sagittal plane or an anterior movement at a ball-and-socket joint.
Lateral Flexion
Movement of trunk in frontal plane.
Extension
Increase in angle between articulating bones, usually in sagittal plane or a posterior movement at a ball-and-socket joint.
Abduction
Movement of bone away from midline, usually in coronal plane.
Adduction
Movement of bone toward midline, usually in coronal plane.
Circumduction
Flexion, abduction, extension, adduction, and rotation in succession (or in the opposite order); distal end of body part moves in circle.
Rotation
Movement of bone around longitudinal axis; in limbs, may be medial (toward midline) or lateral (away from midline).
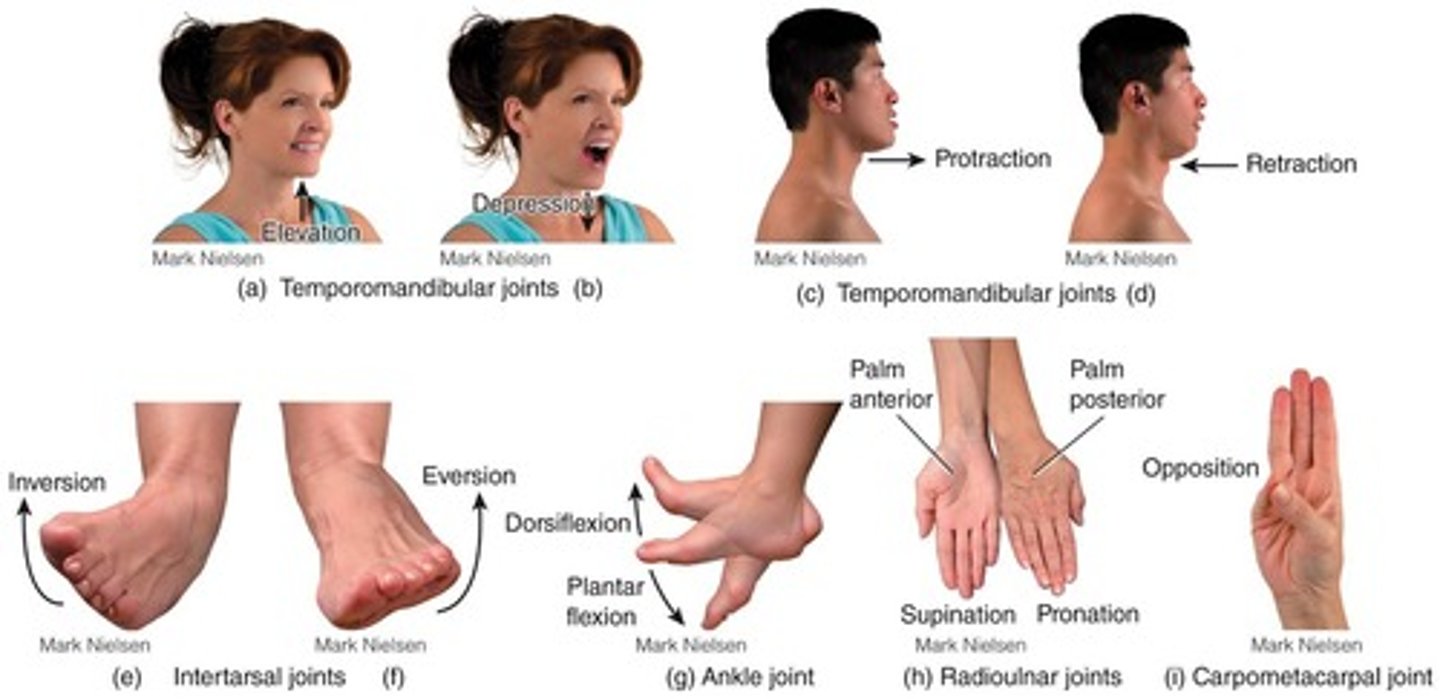
Elevation
Superior movement of body part.
Depression
Inferior movement of body part.
Protraction
Anterior movement of body part in transverse plane.
Retraction
Posterior movement of body part in transverse plane.
Inversion
Medial movement of sole.
Eversion
Lateral movement of sole.
Dorsiflexion
Bending foot in direction of dorsum (superior surface).
Plantar Flexion
Bending foot in direction of plantar surface (sole).
Supination
Movement of forearm that turns palm anteriorly.
Pronation
Movement of forearm that turns palm posteriorly.
Opposition
Movement of thumb across palm to touch fingertips on same hand.
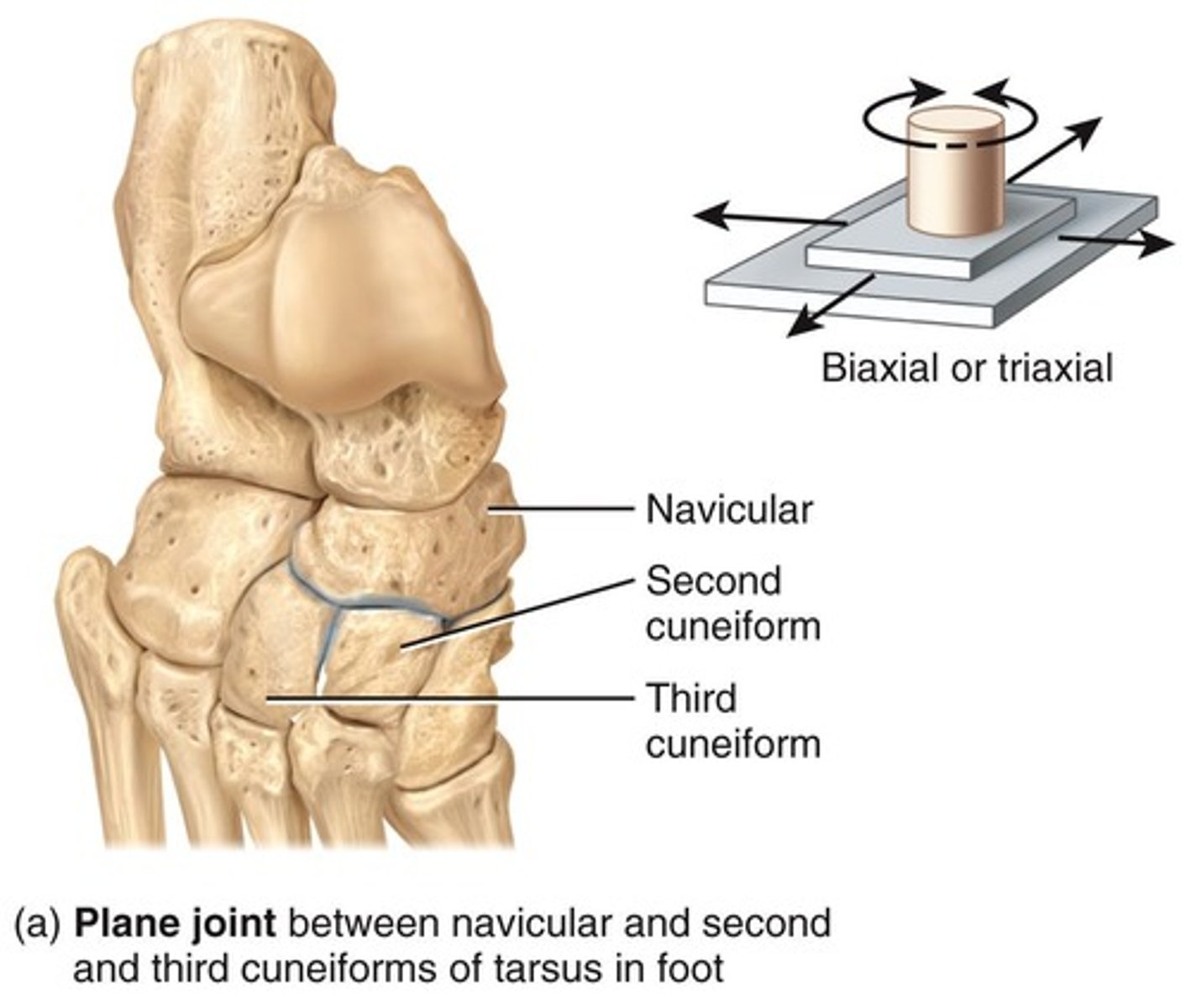
Plane Joint
Articulated surfaces flat or slightly curved. Example: Intercarpal, intertarsal, sternocostal, and vertebrocostal joints. Many are biaxial: back-and-forth and side-to-side movements. Some are triaxial: back-and-forth, side-to-side, rotation.
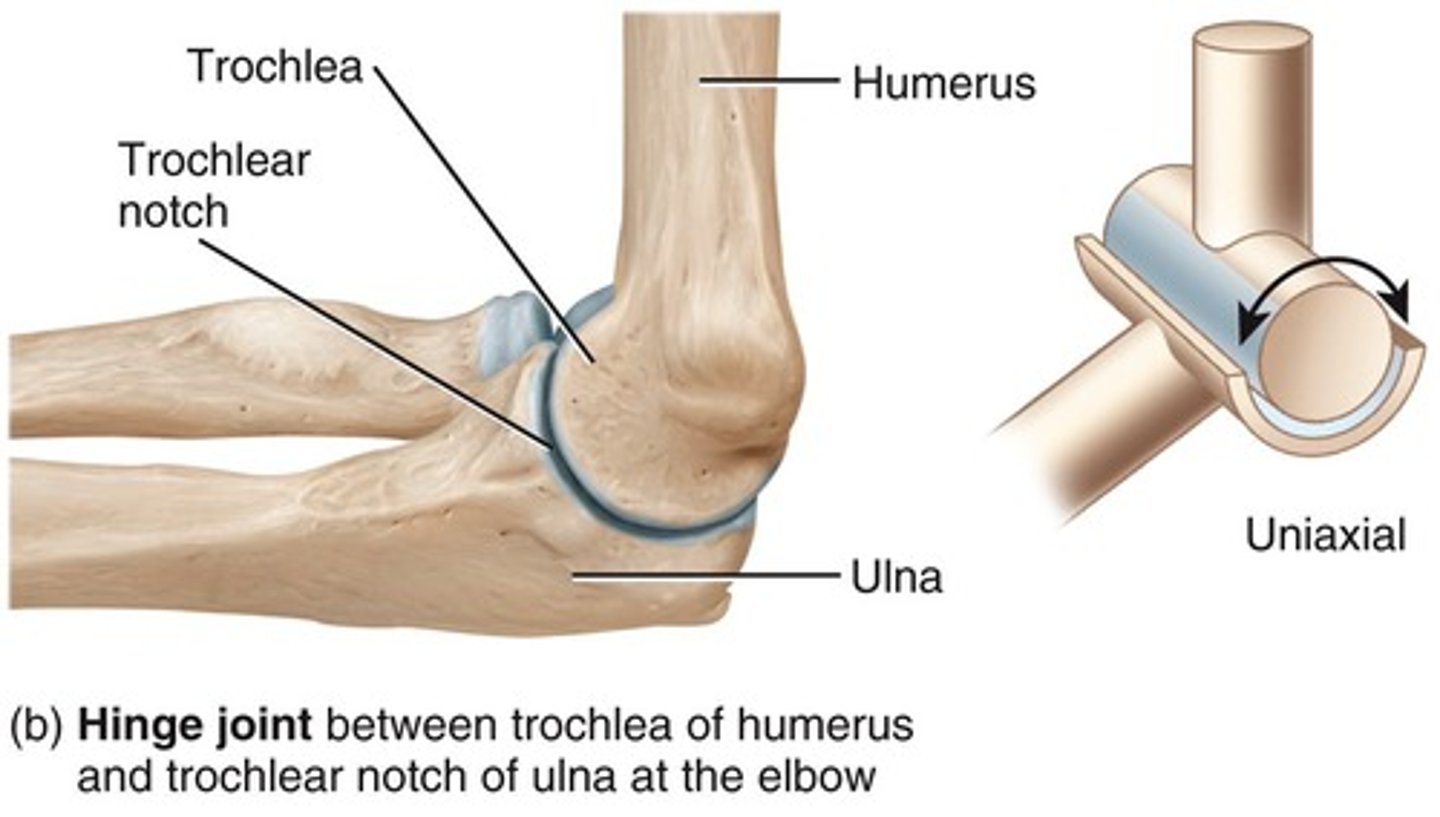
Hinge Joint
Convex surface fits into concave surface. Uniaxial: flexion-extension. Example: Elbow, ankle, and interphalangeal joints. Uniaxial: rotation. Example: Atlanto-axial and radioulnar joints.
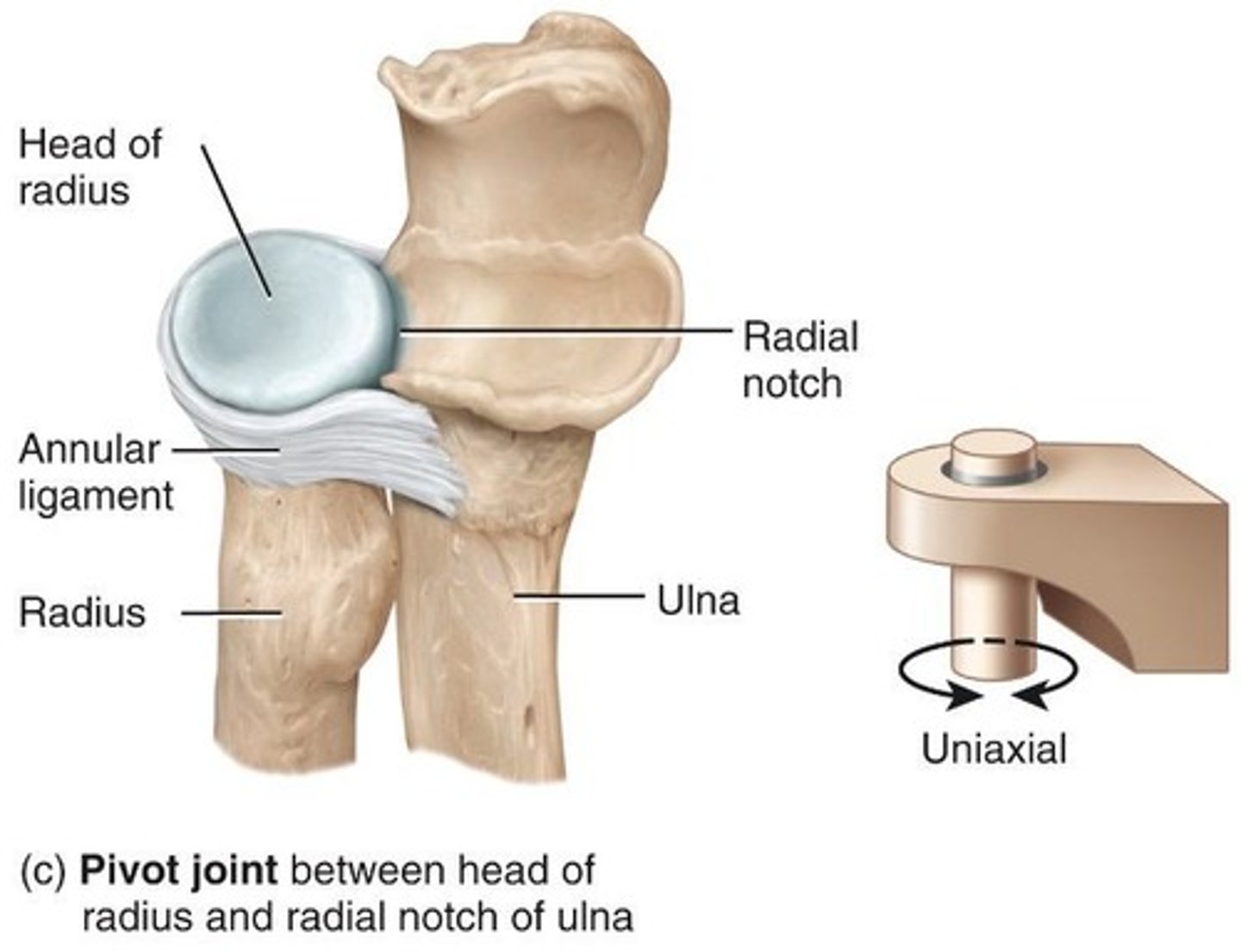
Pivot Joint
Rounded or pointed surface fits into ring formed partly by bone and partly by ligament.
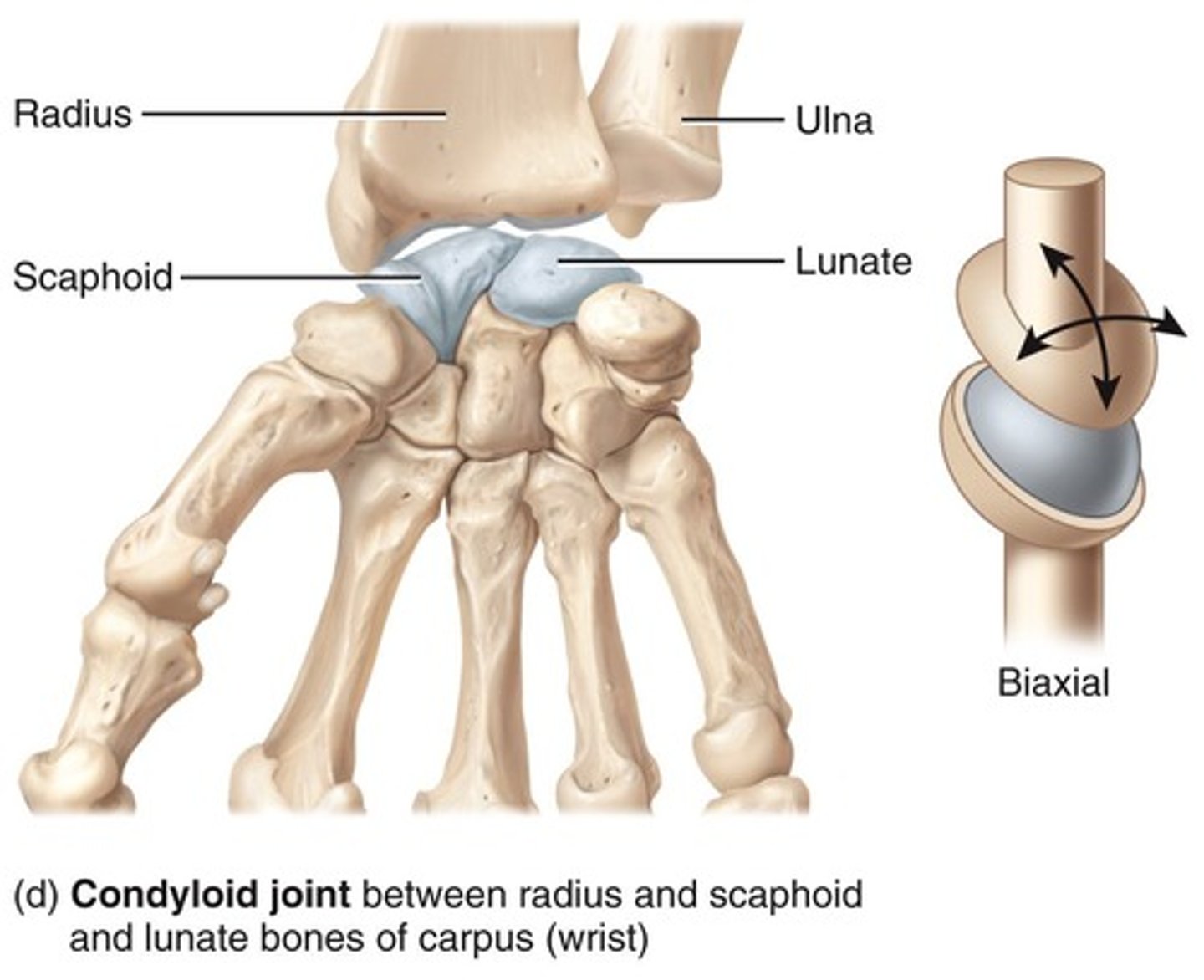
Ellipsoid (Condyloid) Joint
Oval-shaped projection fits into oval-shaped depression. Example: Radiocarpal and metacarpophalangeal joints. Biaxial: flexion-extension, abduction-adduction.
Saddle Joint
Articular surface of one bone is saddle-shaped; articular surface of other bone 'sits' in saddle.
Ball-and-Socket Joint
Ball-like surface fits into cuplike depression. Example: Glenohumeral and hip joints. Triaxial: flexion-extension, abduction-adduction, rotation.
Factors Affecting Contact and Range of Motion at Synovial Joints
1. Structure and shape of the articulating bones. E.g., hip joint. 2. Strength and tension (tautness) of the joint ligaments. E.g., knee joint. 3. Arrangement and tension of the muscles. E.g., hip joint. 4. Contact of soft parts. E.g., elbow joint. 5. Hormones. E.g., relaxin, a hormone released by the placenta and ovaries, increases the flexibility of the fibrocartilage of the pubic symphysis and loosens the ligaments between the sacrum, hip bone, and coccyx towards the end of pregnancy. 6. Disuse. Disuse of a joint for an extended period may limit the range of motion of that joint. Disuse may also result in decreased amount of synovial fluid, diminished flexibility of ligaments and tendons, and muscular atrophy (reduction in size or wasting of a muscle).
Suture Joint
Between skull bones. Fibrous. None.
Atlanto-occipital Joint
Between superior articular facets of atlas and occipital condyles of occipital bone. Synovial (ellipsoid). Flexion and extension of head; slight lateral flexion of head to either side.
Atlanto-axial Joint
(1) Between dens of axis and anterior arch of atlas; (2) between lateral masses of atlas and axis. Synovial (pivot) between dens and anterior arch; synovial (planar) between lateral masses.
Intervertebral Joint
(1) Between vertebral bodies; (2) between vertebral arches.
Intervertebral
(1) Between vertebral bodies; (2) between vertebral arches.
Movements of Intervertebral Joints
Flexion, extension, lateral flexion, and rotation of vertebral column.
Classification of Intervertebral Joints
Cartilaginous (symphysis) between vertebral bodies; synovial (planar) between vertebral arches.
Vertebrocostal
(1) Between articular facets of heads of ribs and costal facets of bodies of adjacent thoracic vertebrae and intervertebral discs between them; (2) between articular facet of tubercles of ribs and transverse costal facet of thoracic vertebrae.
Classification of Vertebrocostal Joints
Synovial (planar). Slight gliding.
Suture
Between skull bones. Fibrous. None.
Sternocostal
Between sternum and first seven pairs of ribs.
Movements of Sternocostal Joints
None between sternum and first pair of ribs; slight gliding between sternum and second through seventh pairs of ribs.
Classification of Sternocostal Joints
Cartilaginous (synchondrosis) between sternum and first pair of ribs; synovial (plane) between sternum and second through seventh pairs of ribs.
Lumbosacral
(1) Between body of fifth lumbar vertebra and base of sacrum; (2) between inferior articular facets of fifth lumbar vertebra and superior articular facets of first vertebra of sacrum.
Movements of Lumbosacral Joints
Flexion, extension, lateral flexion, and rotation of vertebral column.
Classification of Lumbosacral Joints
Cartilaginous (symphysis) between body and base; synovial (planar) between articular facets.
Sternoclavicular
Between sternal end of clavicle, manubrium of sternum, and first costal cartilage.
Classification of Sternoclavicular Joints
Synovial (plane, pivot). Gliding, with limited movements in nearly every direction.
Acromioclavicular
Between acromion of scapula and acromial end of clavicle.
Classification of Acromioclavicular Joints
Synovial (plane). Gliding and rotation of scapula on clavicle.
Radioulnar
Proximal radioulnar joint between head of radius and radial notch of ulna; distal radioulnar joint between ulnar notch of radius and head of ulna.
Wrist (radiocarpal)
Between distal end of radius and scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum of carpus.
Classification of Wrist Joints
Synovial (ellipsoid).
Movements of Wrist Joints
Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, circumduction, and slight hyperextension of wrist.
Intercarpal
Between proximal row of carpal bones, distal row of carpal bones, and between both rows of carpal bones (midcarpal joints).