Unit 2 Exam
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
please don't use only this to study go practice ur math calculations and notations and stuff
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
metals
the red parts are..
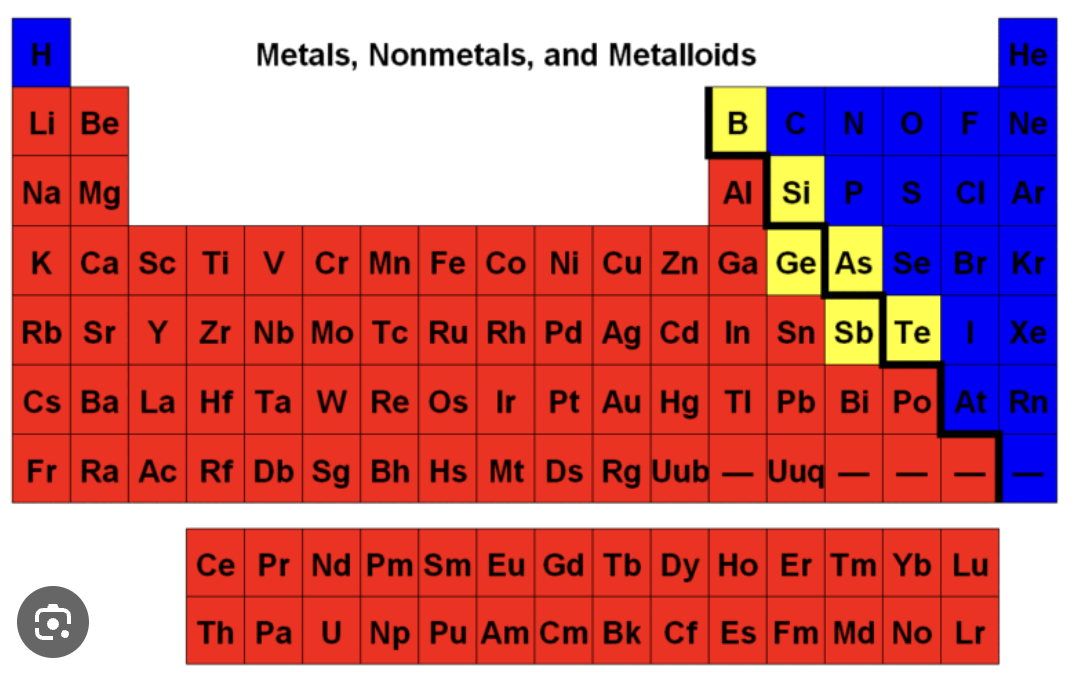
metalloids
the yellow parts are..
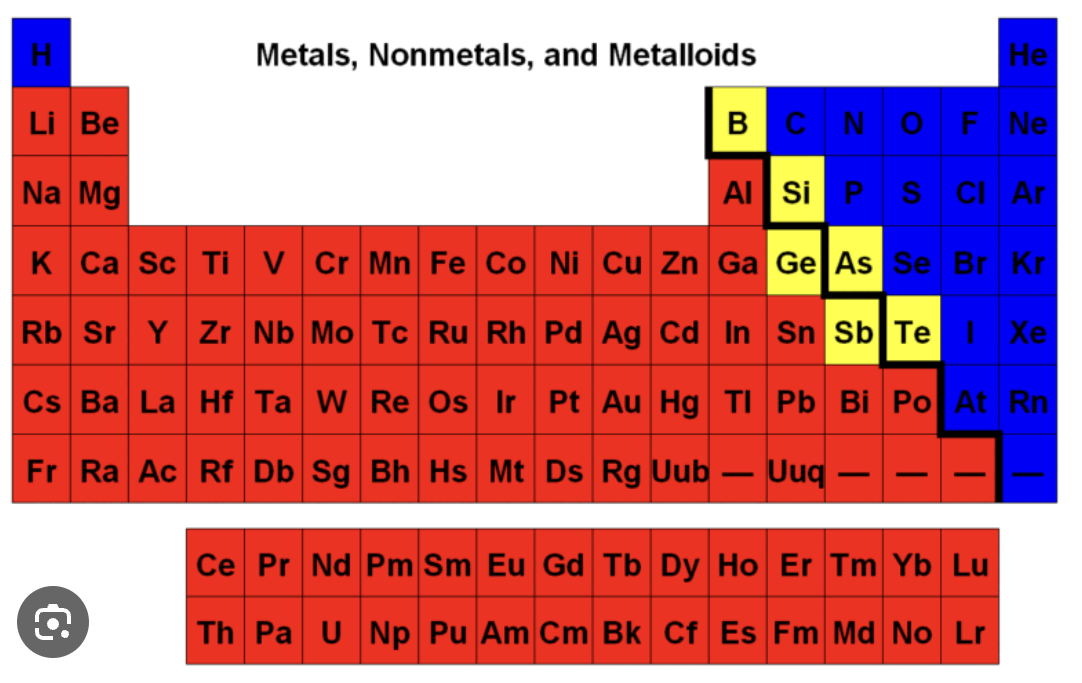
non-metals
the blue parts are…
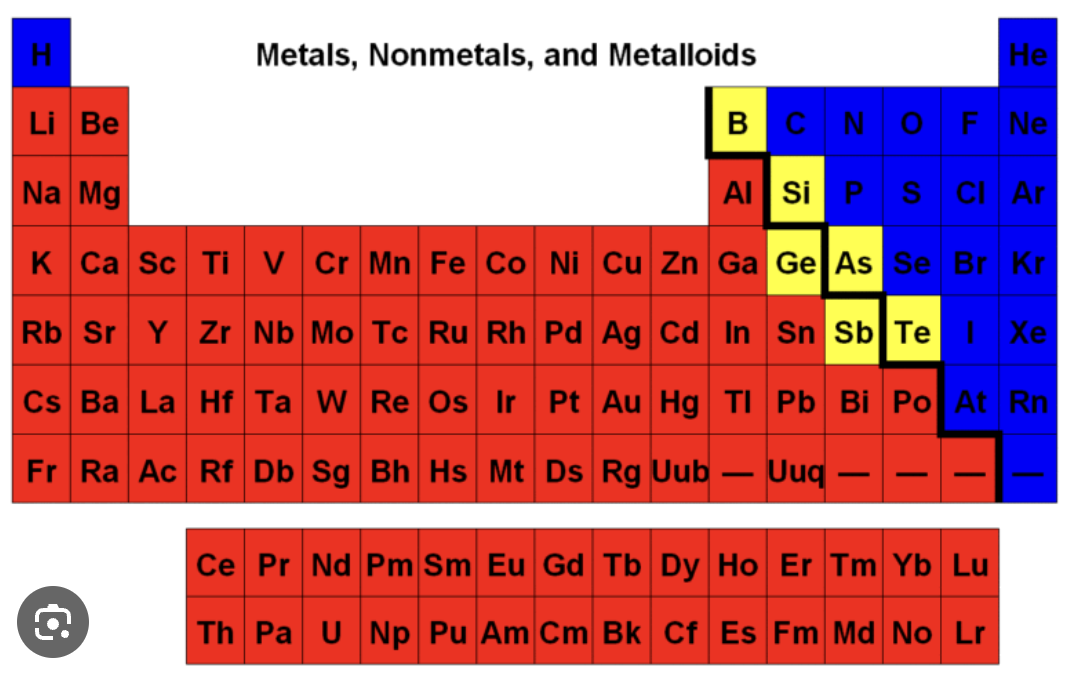
groups
elements in the same ____ have similar chemical properties
Group 1
What group(s) is Alkali metals?
Groups 3-12
What group(s) is transition metals?
Group 18
What group(s) is noble gases?
Group 17
What group(s) is halogens?
57-70
what elements by atomic number are Lanthanides?
89-102
what elements by atomic number are Actinides?
Lanthanides and Actinides
The two types of Transition metals
atom
the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element
electron, proton, neutron
the three smaller parts that atoms are split into
In the electron cloud orbiting the nucleus
Where are electrons?
inside the nucleus
where are protons and neutrons?
The nucleus / protons + neutrons
What makes up the majority of the mass of an atom?
proton
the positively charged subatomic particle of an atom
electron
the negatively charged subatomic particle of an atom
neutron
the subatomic particle of an atom with a 0 charge
Democritus
proposed that everything was made of tiny, indivisible particles called atomos
John Dalton
discovered that different elements were made of different types of atoms; atoms cannot be created or destroyed; all atoms of one type of element are the same
JJ Thompson
Discovered the electron; electrons are negative and protons are positive; believed that protons and electrons were mixed together throughout the atom
Ernest Rutherford
Gold foil experiment; the negatively charged electrons surround the positively charged nucleus of the atom
Niels Bohr
Electrons orbit the nucleus at fixed energy levels; sometimes referred to as the “planetary model”
Werner Heisenberg
cannot pinpoint the exact location of electrons around the atom. Electrons exist in general areas instead.
Atomic Theory
the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that the same numbers of electrons and protons but different numbers of neutrons
always stay the same
In isotopes, Atomic number will….
top
in Nuclear Symbol notation, mass goes on the _____

bottom
in Nuclear Symbol notation, atomic number goes on the _____

Hyphen notation
name or symbol of element followed by mass number

Isotopes having different masses
Why are atomic masses on the periodic table not whole numbers?
mole
a counting unit used to describe a very specific number of particles
6.02 × 10^23
Avogadro’s number
Molar mass
moles in a substance related to mass; the mass of one mole of an element
electromagnetic radiation
energy that travels and spreads out as it goes
how atoms emit light
excited electrons fall back from an excited state to a ground state and emits a photon
electromagnetic spectrum
a continuum of all the electromagnetic waves arranged according to frequency and wavelength
increases; frequency
in wavelengths, as energy ___ so does ____
gamma rays, x rays, ultraviolet
wavelengths that are smaller than visible light (in order of smallest to largest)
radio waves, microwaves, infrared
wavelengths that are larger than visible light (in order of largest to smallest)
electrons in the elements differ
why do different elements emit different color light?
spherical
shape of s orbital
dumbbell
shape of p orbital
cloverleaf
shape of d orbital
flower
shape of f orbital
within each subshell, 2 at a time, with opposite spins
where are the electrons in orbitals?
Aufbau principle
electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first; orbitals within a sublevel have equal energies; for a given main energy level , s < p < d in levels of terms of energy
Pauli Exclusion principle
each orbital can hold 2 electrons with opposite spins; no two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers
Hund’s rule
Within a sublevel, place one e- per orbital before pairing them, all electrons in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin
2e-
needed total number of electrons to fully occupy n=1
8e-
needed total number of electrons to fully occupy n=2
18e-
needed total number of electrons to fully occupy n=3
32e-
needed total number of electrons to fully occupy n=4
orbital notation
orbitals are represented as boxes; name of orbital written below the line or box; shows spin
full electron configuration
number of electrons in each sublevel show as the superscript; sum of superscript = total number of electrons
noble gas configuration
shows the outermost electrons; writes name of previous noble gas in brackets before completing notation
electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first
Why do electron configurations for some elements differ