PHYS 371 FINAL
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
explain the characteristics of energy conversion in the sun or a star
energy passing through the giant sphere each second must equal to the energy passing out of the sun’s surface each second which must be equal to energy created in suns core each second
What represents the efficient of a refrigerator?
Coefficient of performance, K, want it as close to one as possible
What are the byproducts of heat engines?w
Work and heat
is this true or false: nuclear reactions happen in the sun because its hot
false
TRUE or FALSE: the sun is hot because nuclear reactions within
true
how do we measure angular size of the sun?
conversion factor for degrees x (physical size/distance)
how do we calculate the physical size of the sun?
distance x (angular size/conversion factor for degrees)
how do we measure how hot the sun is?
sun’s energy output is measured with spectrograph and thermal radiation spectrum revealing that surface temperature of photosphere is about 5800K
who discovered the orbital rules of motion?
kepler and newton
what are the characteristics of the interior surface of a star?
deeper you go inside the higher the gas pressure needs to be to support the weight of all the gas above it
what is the principle of hydrostatic equilibrium in relation to the sun?
deeper you go inside the higher the gas pressure needs to be to support the weight of all the gas above it
what can the hydrostatic equilibrium principle and ideal gas law derive for a star’s center?
core temperature, (1/2) GMstar/NaKbRstar
what does the hydrostatic equilibrium principle and ideal gas law in the center of a star depend on?
stars radius and mass (and fundamental constants)
what was the temperature of the center of the sun known to be?
15 million K before we knew nuclear fusion happens there
what are the characteristics of energy balance in a star?
for stars to remain stable there needs to be a constant flow of energy from center to the surface, if thermodynamics were alone stars would cool of with time and shrink, so there is a giant source of energy in the center of stars
what are the characteristics of energy conversion in a star?
nuclear energy processes create deadly radiation, fluffy buffer that converts deadly radiation to a thermal spectrum, buffing process takes a long time
what does the joining of two protons form?
one proton becomes a neutron plus a positron pls a neutrino
can two protons stay together as an atomic nucleus?
no
what is a deuterium?
isotope of hydrogen
what is the mass of a photon
zero
what is a positron?
anti-matter counterpart of an electron, has same mass but positive charge
what happens to the newly formed positron when protons combine?
quickly collides with an electron, mutual annihillation results in two gamma ray photons
how do neutrinos travel?
escape the sun at nearly the speed of light
what is the mass of two protons?
2.014553 amu
what is the mass of a proton and neutron?
2.015941 amu
what is the mass of a deutron?
2.013551 amu
where does the missing mass from the proton proton chain go?
mass difference is converted to mass and energy of the positron and neutrino following einsteins equaion, E = change in mass x c2
what is step one of the proton proton chain?
two protons fuse to make a deuterium nucleus (1 proton and 1 neutron), occurs twice in reaction
what is step two of the proton proton chain?
deuterium nucleus and a proton fuse to make a nucleus of helium-3 (2 protons, 1 neutron), occurs twice in overall reaction
what is step three of the proton proton chain?
two helium 3-nuclei fuse to form helium-4 (2 protons, 2 neutrons) releasing two excess protons in the process
what does the proton proton chain reaction result in the formation of?
gamma rays
how do we measure the rate of mass conversion for the sun?
sun luminosity/energy created per kg
how do we measure the nuclear lifetime of the sun?
suns mass/mass conversion rate
what can we conclude about the suns energy consumption?
theres enough fuel in the sun to keep it shining with its current power for at least another 5 billion years
what is another important factor in the energy conversion and balance in the sun?
suns core temperature is regulated to stay constant because the. gas in it obeys the ideal gas law of thermodynamics
what is the characteristic of energy release from nuclear fusion?
releases energy in form of very fast particles and gamma ray photons, at surface the sun emits mostly photons in visible part of spectrum
what are the actions of gamma ray photons in the sun?
in core of sun travel only few nm before deflected in collision with another electron or photon, overtime these interactions convert one energetic photon into many lower energy photons, takes long time for energy released by nuclear fusion to reach surface
is the net energy output of the sun variable?
super constant and very stable
does the sun follow gas like behaviour and if so what does this imply?
yes, if nuclear reaction rate increases the sun expands and cools, if rate lowers it is compressed and heats up back to average temp
What happens when a positron meets an electron?
They are oppositely charged so they attract each other. But when they touch they convert purely to Energy in the form of two photons, leaving no mass behind.
what is thermal efficiency?
fraction of heat that becomes useful work, represented as W/QH or energy of task/energy available, power of task/power available
in the formula for thermal efficiency what does W stand for?
Useful work
In the formula for thermal efficiency what does QH stand for?
total heat energy input from hot source
what is the efficiency of heat engines?
heat engines operate at 30-50% efficiency due to practical limitations, impossible to achieve 100% efficiency according to second law of thermodynamics
Can heat engines achieve 100% efficiency? Why?
impossible to achieve 100% efficiency because some waste heat is always produced in a heat engine but we can increase efficiency
What is Carnot efficiency?
max attainable efficiency of a heat engine derived by Sadi Carnot, 1 – (TL/TH)
in the formula for Carnot’s efficiency what does TL stand for?
temperature of cold sink
In the formula for Carnot’s efficiency what does TH stand for?
temperature of heat reservoir
what does the Carnot efficiency describe?
efficiency of idealized engine, lower sink temp or higher source temp = more work availed from heat engine
how do temperature changes impact carnots efficiency?
Greater temp change, greater decrease in fluid and greater energy availed to do work
What is waste heat?
unused heat given to surrounding environment by heat engine, increases greenhouse gas emissions and contributes to global warming
How do the laws of thermodynamics relate to waste heat?
second law of thermodynamics – waste heat must be produced when converting temperature difference into mechanical energy
What formula relates waste heat to work and input heat?
QH = QL + W, Energy available = Energy of task + energy lost, input heat to system from a given fuel = useful work + waste heat
What is cogeneration in thermal efficiency?
combined heat and power, uses heat and electricity for beneficial tasks for more efficient use of fuels, efficiency of up to 80%
What is a cogeneration cycle?
uses waste heat generated by thermodynamic process to heat homes, cars, and other appliances
What is the purpose of thermoelectrical devices?
use to convert temperature difference to electrical energy, change in temp across semiconductor material creates voltage that causes electricity to flow (peltier seebeck effect)
what is the main difference between the moon and earth?
the moon has no atmosphere
what is the goldilocks zone?
area where you can plant a planet and have it turn into liquid form
how close to protons need to be to collide?
10^-15m before strong force can kick in and get them to stick, only fastest protons with most head on trajectories undergo step one of proton proton chain
are protons particles or waves and how does this impact them?
protons are waves, these waves overlap when close enough and increase their probability of colliding
what is the tunnelling effect for and what does it mean?
for protons, how rate and wave like nature helps them collide, rate of fusion reactions is high enough to explain suns radiative power
what did george gamow do?
discovered the tunnelling effect of protons, created graph to show shape of overlap between speed distribution curve and tunnelling curve
do we see nuclear fission in the sun?
no, nuclear fusion is seen
what is efficiency?
describes the energy that a certain system can extract and make useful from its energy source, ratio of power out to power in
what is the general understanding of what a heat engine is?
system that transfers thermal energy to do mechanical or electrical work using a cycle (thermodynamic cycle)
What is a refrigerator?
Open system that dispels heat from a closed space to a warmer area by decreasing its temperature and allowing other items to remain cool
What is one thing that violates second law of thermodynamics?
Refrigerator
How does a refrigerator work?
Work is inputed compressing coolant increasing temperature above room temp, heat flows from coolant to air in room to reduce temp of coolant, coolant expands and cools down below temp inside refrigerator, heat flows from refrigerator to coolant decreasing temperature above inside
What is K?
Coefficient of performance, K=Qc/Win
What is a heat engine?
Type of engine that produces macroscopic motion from heat, take energy from being warm and turn that into motion, move energy form a hot to cold place and divert some into mechanical energy
What processes can be used by heat engines to produce heat?
Igniting fuel through combustion, using energy from nuclear processes to produce heat
What are internal combustion engines?
Most common heat engine, fuel ignited to do work inside engines and same fuel and air mixture is emitted as exhaust, fuel burns inside engine itself
What is an external heat engine?
Steam engines, heat source is separate from the gas that does work, fuel burned outside engine and heat is transferred to working fluid
How do internal heat engines work?
Gas ignites inside a piston, does work, then is expelled
What is Albedo?
Fraction of light reflected by a body, ratio of energy reflected by an objected divided by the energy incident
What does a high vs low albedo mean? How do we calculate albedo?
Very reflecting body had a high albedo approaching one, very absorbing body had a low albedo approaching 0, energy reflected/energy incident
In terms of albedo how do we see how much energy is absorbed?
Energy reflected + energy absorbed = energy incident SO energy absorbed equals 1-albedo
What is geometric albedo?
Measuring brightness when illumination comes from directly behind the observer
What is bond albedo?
Total proportion of electromagnetic energy reflected
What is the energy balance equation when discussing thermal efficiency?
Win = QH-QC
How does energy get things done?
engine draws heat from high temp reservoir, works fluid like. Gas or liquid absorbs heat and expands pushing on component like a piston, expansion performs mechanical work, after work substance releases its remaining heat to a low temp reservoir cooling down and returning to initial state
What unit of temperature is used in carnots efficiency?
K
what are two requirements for formation of a Carnot engine?
To return to initial state without increasing entropy engine needs to me in thermal equilibrium the whole time, mechanical interactions (no energy lost in friction, no heat transfer, adiabatic process), thermal interaction (heat transfers really slow, quasi-static)
Wwhat is meant by a Carnot engine?
perfectly reversible engine with max thermal efficiency
what is a stars habitable zone?
where water could exist in liquid form (between 0 and 100C), cooler stars have closer zones, most basic definition involves radiative equilibrium without other factors, going by that the earth isn’t habitable
what is the earths global average measured surface temp?
15C, earth is loaded with liquid water and has an above OC global average temperature by a long shot
if you stripped all the water off the earth and rolled it up into a ball and held it up to next to the original earth how would its shape change?
it would shrink
what are the main greenhouse gase?
CO2, water vapour, methane
what are greenhouses transparent to? Opaque to?
transparent to visible light, opaque to infrared light
how do atmospheres screw up astronomical data?
photons interact with molecules and particulates, the amount of air you’re looking through over a duration changes and this air absorbs light
what explains how the atmosphere can trap heat?
greenhouse effect, radiative energy fights to get down to the ground from space and this can be illustrated at 50% of absorption on a graph
is earth kind of like a greenhouse?
yes because it traps heat, acts as a black body
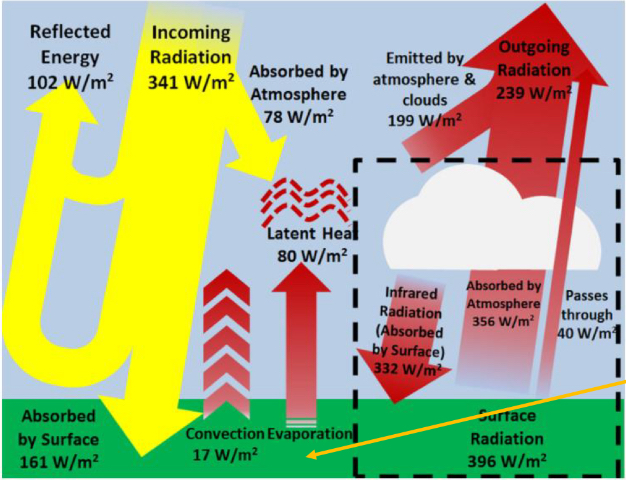
What does this image show you?
incoming and outgoing energy in a balanced example of earths energy budget, general flow of energy on surface of atmosphere are shown best representing greenhouse effect in dashed box, global average picture of star planet interaction over long time periods
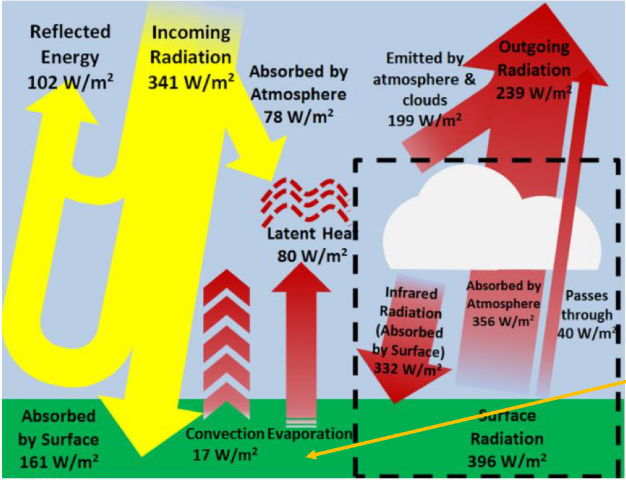
what does the 341W/m² represent in the incoming and outgoing values of the earth?
global average amount of incoming radiation weighted by the area of a circle divided by the area of a sphere
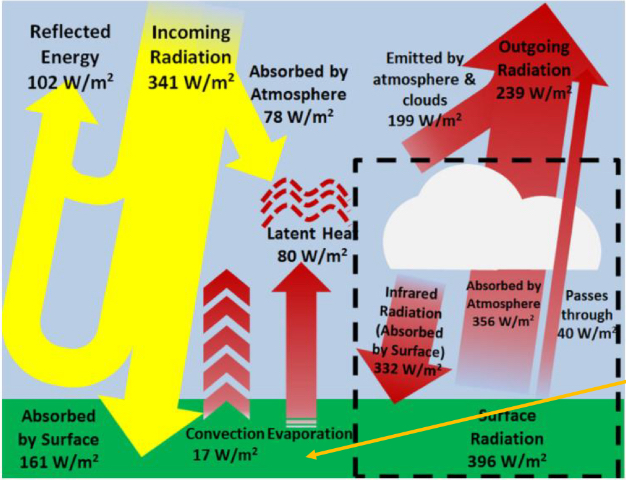
what is the albedo of the earth in this diagram? Where is the energy reflected back?
0.299, 102W/m² is reflected back to space from clouds and ground, it distributes 161 W/m² absorbed by the ground and the atmosphere absorbs 78W/m²
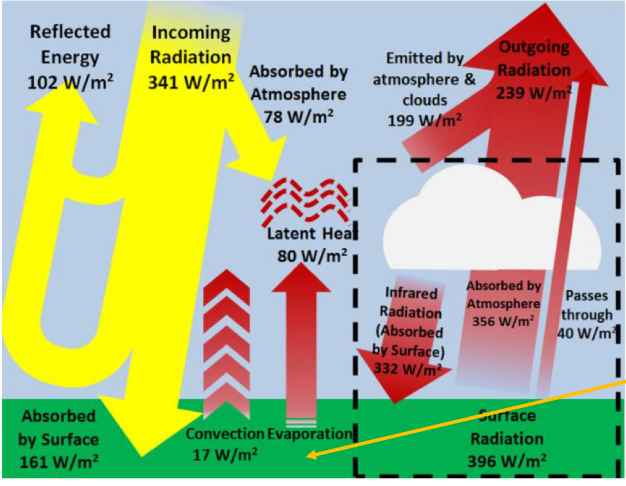
where does the energy absorbed by the atmosphere come from?
Sunlight, convection, evaporation, the infrared emission from the earths surface
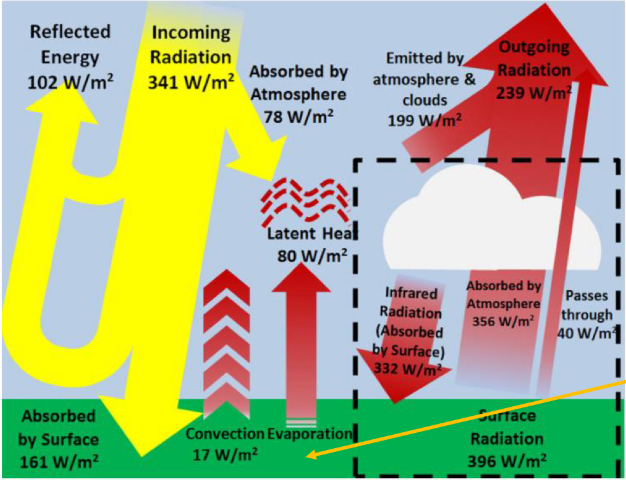
where does energy emitted by the atmosphere head to?
earth and space
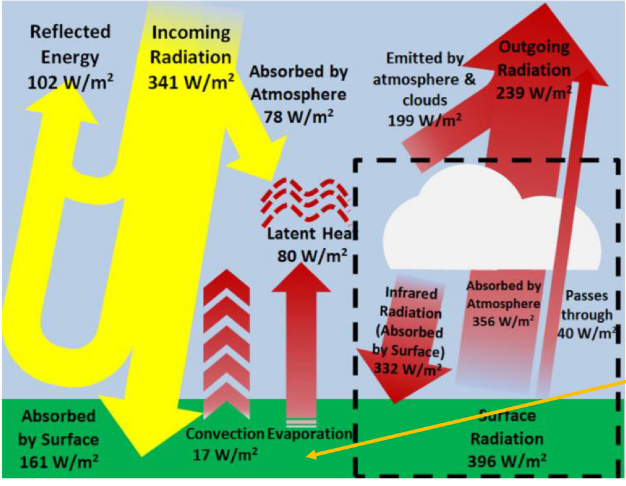
where does the energy absorbed by the surface of the earth come from?
sunlight and infrared emissions
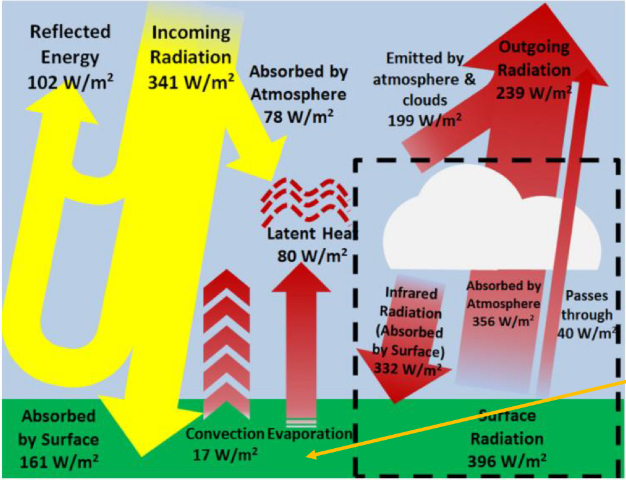
where does energy emitted by the surface of the earth come from?
convection, evaporation, thermal infrared
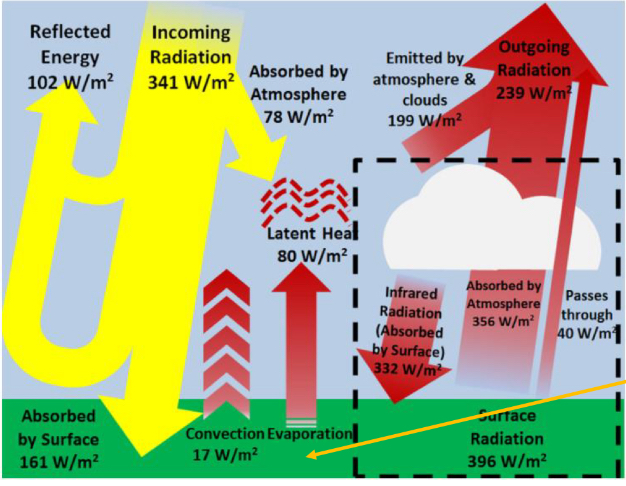
how does the energy absorbed by the atmosphere relate to thermal IR?
energy absorbed by atmosphere and the energy passing through the atmosphere equals the thermal IR radiation from the surface