The Changing Economic World
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
what is development?
improvement in a country’s capacity to produce goods and services for it’s population.
HIC examples
USA, UK, Germany
LIC examples
Somalia, Ghana, Nepal
NEE examples
Brazil, China, India
Measures of development
GNI
Literacy rate
Access to safe water
People per doctor
Birth/death rates
Life expectancy
Human development Index
Infant mortality rate
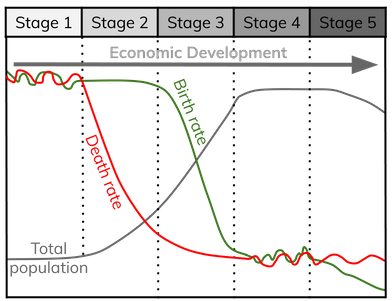
The Demographic Transition Model
(Death rates usually fall first as countries become more developed)
Natural increase
more births than deaths (increased population)
Natural decrease
more deaths than births (decreased population)
What does the DTM show?
how the population of a country changes throughout economic development
Stage 1
birth rates high
death rates high
Stage 2
birth rates high
death rates begin to fall
Stage 3
birth rates begin to fall to death rate level
death rates fall
Stage 4 & 5
birth rates low
death rates low
what is the development gap?
the widening difference in levels of development between the richest and poorest countries
Factors affecting the development gap
poor climate
few raw materials
natural hazards
colonisation
war
poor trade links
political instability
ways to reduce the development gap
investment
aid
intermediate technology
free trade
fair trade
debt relief
microfinance loans
advantages of tourism
brings people to a country
boosts local economy
preserving culture
gives locals jobs
develops infrastructure from money made
helps develop countries
disadvantages of tourism
potentially damages environment
locals may not like how busy it is
most money goes towards flights to get there which won’t benefit locals
can be costly & wasting money if it doesn’t take off
Case Study: Tanzania GNI
$174.5 billion
Case study: Tanzania
68 million
high population density
young country - half under 18
Case study: why travel to Tanzania?
excellent safari location
amazing beaches and ancient towns
cultural/unique
ancient history
landmarks - Mt. Kilimanjaro, the Serengeti
endangered species