Reactivity 2.3.1 Dynamic Equilibrium
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Dynamic Equilibrium
A reaction takes place at the same rate as the reverse reaction so no net change is observed
Two Equilibrium systems
physical and chemical systems
eg physical equilibrium
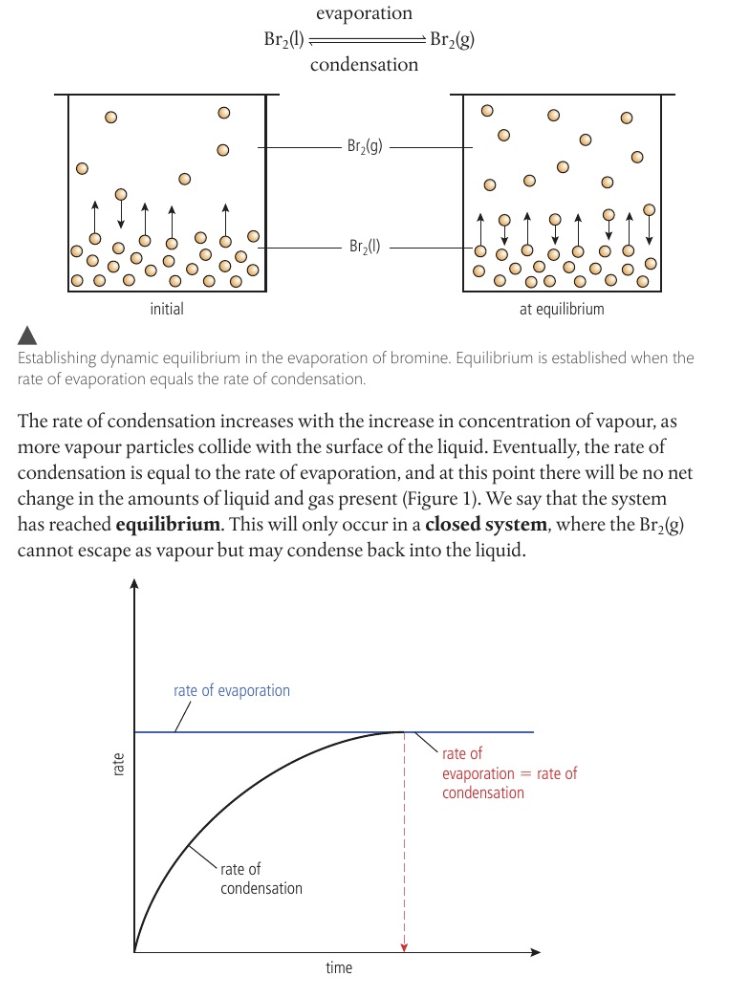
bromine= volatile liquid; liquid to gaseous through condensation and evaporation
explanation: rate of condensation increasing with increasing concentration of vapour as more vapour particles collide with the surface of the liquid - eventually rate of condensation is equal to the rate of evaporation
eg chemical equilibrium
reaction of dissociation between HI and H2/I2
just what youd think
equilibrium mixture
the result of a dynamic equilibrium
forward reaction
reaction from left to right
reverse reaction
reaction from right to left
equilibrium is dynamic
reaction has not stopped but forward and backward reaction are at the same rate. products and reactants get produced and destroyed at the same rate
equilibrium is achieved in a closed system
equilibrium is reached where both reactants and products can react and recombine with each other
at equilibrium there is no change in macroscopic properties
they dont change as they depend on the concentrations of the components of the mixture
macroscopic properties
such as colour, density (observable properties)
equilibrium can be reached from either direction
will result under the same conditions no matter if the reaction is started with all reactants, products or both.
difference between concentration being constant and equal
constant eg always 1:3
equal eg 2:2
equilibrium position
proportion of reactant to product
reaction where the mixture is predominantly products and a l’envers
“lies to the right” “lies to the left”