Anatomy and Physiology of Pregnancy Overview
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Gravida
Indicates the number of times a person has been pregnant regardless of outcome.
Nulligravida
Never Pregnant
Primigravida
First time pregnant
Multigravida
Two or more times pregnant
Para
The number indicates the number of times a person has given birth, including living/stillborn and excluding abortions.
Parity
Number of pregnancies in which fetus or fetuses have reached 20 weeks of gestation
Nullipara
No completion of pregnancy >/= 20 weeks of gestation
Primapara
Completion of one pregnancy >/= 20 weeks of gestation
Multipara
Completion of two or more pregnancies >/= to 20 weeks of gestation
Grand Multi Para
Completion of >/= 5 pregnancies greater than period of viability
Viability
Capacity of fetus to live outside the uterus (22 - 25 weeks of gestation).
Preterm
20 weeks of gestation to 36 weeks + 6 days of gestation.
Late Preterm
34 weeks to 36 weeks + 6 days of gestation.
Term
37 weeks of gestation to 40 weeks + 6 days of gestation.
Early Term
37 weeks to 38 weeks + 6 days of gestation.
Full Term
39 weeks to 40 weeks + 6 days of gestation.
Late Term
41st week of gestation.
Post Term
≥ 42 weeks of gestation.
Extremely Preterm
Less than 28 weeks of gestation.
Very Preterm
28 weeks to 32 weeks of gestation.
Moderate to Late Preterm
32 to 37 weeks of gestation.
LMP
Last menstrual period
Gestational Age (GA)
LMP to current duration in pregnancy.
5-Digit Method
A method to calculate obstetrical history: G (gravidity), T (term), P (preterm), A (abortions), L (living children).
2-Digit Method
G/P= Gravidity (Number of pregnancies)/Para (Number of pregnancies carried to age of viability) - Not recommended.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
Earliest biomarker for pregnancy; starts production on implantation day, detected 8-10 days after fertilization, peaks at 9-10 weeks of GA, stabilizes at 20 weeks GA.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Most popular test for detecting pregnancy.
The results are affected by last menstrual period and a host of other factors.
Medications like anticonvulsants and tranquilizers can lead to false positives, while Diuretics and promethazine can lead to false negatives
Gestation Trophoblastic Disease
Abnormal placental (trophoblast/Chorionic villi) development with no viable fetus. Usually Benign (3% can develop into Choriocarcinoma).
Types include Hydatidiform mole and Gestational trophoblastic Neoplasia
Hydatidiform mole (Molar pregnancy)
A type of Gestation Trophoblastic Disease which can be complete or partial.
Gestational trophoblastic Neoplasia
An invasive type of Gestation Trophoblastic Disease including invasive mole, Choriocarcinoma & Placental site tumour.
Risk factors for Gestation Trophoblastic Disease
Previous history, Blood groups A/AB, Extreme reproductive age, Asians.
Signs and Symptoms of Gestation Trophoblastic Disease
Vaginal bleeding
Enlarged Uterus
Ovarian cyst/torsion
Hyperemesis Gravidarum
signs of Pre-eclampsia,
Increased hCG levels - hyperthyroidism.
Investigation for Gestation Trophoblastic Disease
Increased beta hCG level
Transvaginal U/S - 'snowstorm appearance',
Close follow-up with repeated hCG level monitoring, Chemotherapy.
Management of Gestation Trophoblastic Disease
Evacuation of uterus (ERPC) and histology,
Close follow-up with repeated monitoring of serum hCG levels
Chemotherapy
Counselling (no pregnancy for min of 3 months, not take OCT/HRT, can recur, histology with each future pregnancy, psychological well-being)
Surgery - tumor removal/Hysterectomy.
Signs of Pregnancy - Presumptive
Subjective feelings from the person, these signs can be cause by other issues in the body aside from pregnancy.
Breast Changes (3-4 weeks)
Amenorrhea (4 weeks)
Nausea/Vomiting (4-14 weeks)
Urinary Frequency (6-12 weeks)
Fatigue (12 weeks)
Quickening (16-20 weeks).
Quickening
First fetal movement feels like a flutter in the belly.
Signs of Pregnancy - Probable
Objective changes assessed by an examiner
Goodell Sign (5-6 weeks),
Chadwick's Sign (6-8 weeks),
Hegar Sign (6-12 weeks),
Osiander sign (8 weeks),
Positive pregnancy test Serum (4-12 weeks),
Positive pregnancy test urine (6-12 weeks),
Braxton Hicks (14-16 weeks),
Ballottement (16-28 weeks).
Goodell Sign (5-6 weeks)
Softening of the cervix.
Is brought about by increased vascularity, slight hypertrophy, and hyperplasia
Chadwick’s Sign (6-8 weeks)
Purplish blue appearance of the cervix
Hegar Sign (6-12 weeks)
Softening of the lower segment of the uterus (isthmus)
Osiander Sign (8 Weeks)
Feeling of pulsation in the walls of the vagina
Braxton Hicks (14-16 weeks)
Painless uterine contractions that help with circulation. Later on, it develops to false labour pains
Ballottement (16-28 weeks)
When the baby is tapped, the baby bounces on the uterine wall and then bounces back.
Signs of Pregnancy - Positive
Fetal Visualization by U/S (5-6 weeks)
Fetal heart tone using U/S (6 weeks),
Fetal Visualization using radiography (16 weeks),
Fetal heart tone using doppler U/S stethoscope (8-17 weeks),
Fetal heart tone using fetal stethoscope (17-19 weeks),
Fetal movement palpated (19-22 weeks),
Visible fetal movement (Late pregnancy).
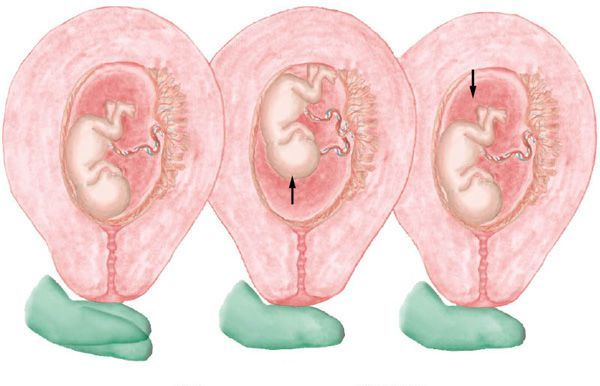
Uterine Enlargement
Early uterine enlargement results from increased vascularity and dilation of blood vessels, hyperplasia and hypertrophy
Hen's egg - 7 weeks,
Orange - 10 weeks,
Grapefruit - 12 weeks.
After the third month, uterine enlargement is primarily the result of mechanical pressure of the growing fetus.
Shape of Uterus during Pregnancy
Upside-down pear - Conception,
Spherical - 2nd trimester,
Large/Ovoid - Later pregnancy.
Lightening
Between weeks 38 and 40, fundal height decreases as the fetus begins to descend and engage in the pelvis.
In Nullipara occurs in the last 4 weeks before labour
In Multipara it occurs at the start of labour
Height of Fundus
Factors affecting FH include:
Fetal position
Amniotic Fluid amount (Polyhydramnios, Oligohydramnios)
Number of fetus
Different examiner technique.
Reproductive system Adaptation to pregnancy
Chadwick sign
Leukorrhea
Increased progesterone/ Estrogen
Hyperplasia
Exfoliation of vaginal epithelium
Discharge
Operculum
Leukorrhea
A white or slightly grey mucoid discharge with a faint musty odour. This copious mucoid fluid occurs in response to cervical stimulation by estrogen and progesterone.
The fluid is whitish because of the presence of many exfoliated vaginal epithelial cells caused by the hyperplasia of normal pregnancy.
This vaginal discharge is never pruritic or blood stained. The mucus fills the endocervical canal, resulting in the formation of the mucous plug (operculum).
Vaginal Microbiome
The vaginal microbiome changes during pregnancy with an increase in at least four species of Lactobacillus and a decrease in anaerobic bacteria.
This results in a lower pH of vaginal secretions, ranging from about 3.5 to 6.0 (nonpregnant, 4.0 to 5.0).
Alterations in the vaginal microbiome help to prevent ascending bacterial infections of the uterus that contribute to preterm labour and birth.
Operculum
Mucoid plug
Discharged at the beginning of the labour and delivery process. Signifies the start of the process.
Breasts adaptations
Fullness, heaviness
heightened sensitivity from tingling to sharp pain
areolae become more pigmented
Montgomery's tubercles develop
Colostrum (16 weeks)
Colostrum
A form of milk produced during pregnancy, present from 16 weeks.
Cardiovascular system adaptations
Structural changes
Blood Volume
Heart Rate
Cardiac Output
Supine Hypotension Syndrome
Hypercoagulability
Varicose Veins
CV Adaptations: Structural Changes
Slight enlargement-reversed by 6 months postpartum
Diaphragm displaced upwards, elevated and shifted upwards, Apical impulse shifts laterally upward.
CV Adaptations: Blood Volume
Increases by 40-50%
CV adaptations: Heart Rate (HR) increase
The patient’s heart rate begins to increase at about 5 weeks of gestation, reaching a peak of 15 to 20 beats/minute over the prepregnancy baseline by 32 weeks and persisting until term.
This represents an increase of approximately 17% over the prepregnancy heart rate.
CV Adaptations: Cardiac output (CO) increase
Cardiac output increases from 30 to 50% during pregnancy and half of this increase occurs by 8 weeks of gestation.
A small decline occurs by term. Compared with nulliparous patients, parous patients have a significantly higher median cardiac output than that of patients with normal twin gestations, and cardiac output increases to an even greater extent from the mid-trimester of pregnancy
This elevated cardiac output is largely a result of increased stroke volume and heart rate and occurs in response to increased tissue demands for oxygen.
CV Adaptations: Blood Pressure
Increased cardiac output affects blood pressure during pregnancy.
CV Adaptations: Supine Hypotension Syndrome
Occurs when the ascending vena cava and descending aorta are compressed.
The labouring patient is at greater risk for supine hypotension if the uterus is particularly large because of multifetal pregnancy, hydramnios, or obesity or if the patient is dehydrated or hypovolemic. In addition, anxiety, pain, and some medications can cause hypotension
CV Adapations: Hypercoagulability
There is a greater tendency for blood to coagulate during pregnancy because of increases in various clotting factors
(i.e., factors VII, VIII, IX, and X, and fibrinogen) and decreases
in factors that inhibit coagulation (e.g., protein S).
This tendency, combined with the fact that fibrinolytic activity is depressed during pregnancy and the postpartum period, provides a protective function to decrease the chance of bleeding but also makes the patient more vulnerable to thrombosis, especially after Caesarean birth.
CVS Adaptations: Varicose Vein
Compression of the iliac veins and inferior vena cava by the uterus
causes increased venous pressure and reduced blood flow in the legs, except when the patient is in the lateral position.
These alterations contribute to the dependent edema, varicose veins in the legs and vulva, and hemorrhoids that may develop in the latter part of term pregnancy and can lead to increased risk for venous thromboembolism
CVS Adaptations: Physiological Anemia
Because the plasma increase is greater than the increase in RBC production, there is a decrease in normal hemoglobin and hematocrit values which leads to an anemic state
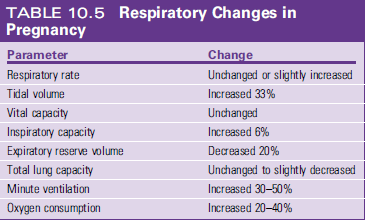
Respiratory System Adaptation
Increase in tidal volume by 40%
Increase in O2 consumption and CO2 Production by (20-30%)
Shortness of Breath
Renal System Adaptation
Increased progesterone leads to increased vascularities of afferent arterioles which leads to increased blood flow to the glomerulus, increasing GFR which leads to increased urine and size of ureters and nephrons
Increased progesterone also leads to decreased ureter motility which leads to increased urinary stagnation, increasing bacterial colonization which leads to increased risk of UTI/Nephiritis/ Blood Infection
Integumentary System adaptations
Anterior Pitituary Hormone Melanotropin causes Hyper pigmentation. Leads to:
Chloasma
Linea nigra
Striae gravidarum
Palmar Erythema
Polymorphic eruption of pregnancy/ Pruritic Urticarial Papules and Plaques of pregnancy
Chloasma
Also known as the mask of pregnancy, a skin condition characterized by a blotchy, brownish hyperpigmentation
of the skin over the cheeks, nose, and forehead, especially
in pregnant patients with dark complexions
Linea nigra
A dark line that appears on the abdomen during pregnancy.
Striae gravidarum
Stretch marks that can occur during pregnancy, often with a familial tendency.
Polymorphic eruption of pregnancy (PEP)
Also known as pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy (PUPPP), a skin condition that can occur during pregnancy.
and is associated with increased weight gain in the pregnant patient, multiple gestations, hypertension, and induction of labour Although it can cause significant discomfort, it is not associated with adverse outcomes for the pregnant patient or fetus.
Neurological Adaptation
Carpel Tunnel Syndrome
Decreased sensation
Tension Headache
Syncope
Postural Hypotension
Carpel Tunnel Syndrome
Edema involving the peripheral nerves during the last trimester. The syndrome is characterized by paresthesia (abnormal sensation such as burning or tingling) and pain in the hand, radiating to the elbow.
The sensations are caused by edema that compresses the median nerve beneath the carpal ligament of the wrist. Smoking and alcohol consumption can impair the microcirculation and may worsen the symptoms.
Decreased sensation
Compression of nerves due to enlarging uterus.
Tension Headache
Anxiety/uncertainty.
Fainting/Syncope
Common & usually due to postural hypotension; care when getting up.
Appetite changes during pregnancy
Nausea/Vomiting (N/V), smells can trigger, subsides by end of 3rd month.
Hyperemesis Gravidarum
Excessive vomiting leading to weight loss, electrolyte imbalance, nutritional deficiency (0.3-3%).
PICA
Nonfood craving (clay, ice, detergent) that can affect nutrition.
Esophageal regurgitation
Heartburn (Pyrosis).
Constipation
Common gastrointestinal issue during pregnancy.
Hemorrhoids
Swollen veins in the rectal area that can occur during pregnancy.
Gallbladder changes in pregnancy
Increased progesterone decreases gastric motility leading to bile stagnation and cholestasis.
Signs/Symptoms of Hyperemesis Gravidarum
Protracted vomiting, retching, severe dehydration, weight loss requiring hospitalization.
Management of Hyperemesis Gravidarum
Includes small frequent diet, support, oral fluids, IV fluids, medication therapy (antiemetics, steroid, Vit B6, multivitamin), emotional support.
Human chorionic gonadotropin
A hormone produced during pregnancy.
Progesterone
A hormone that helps maintain pregnancy.
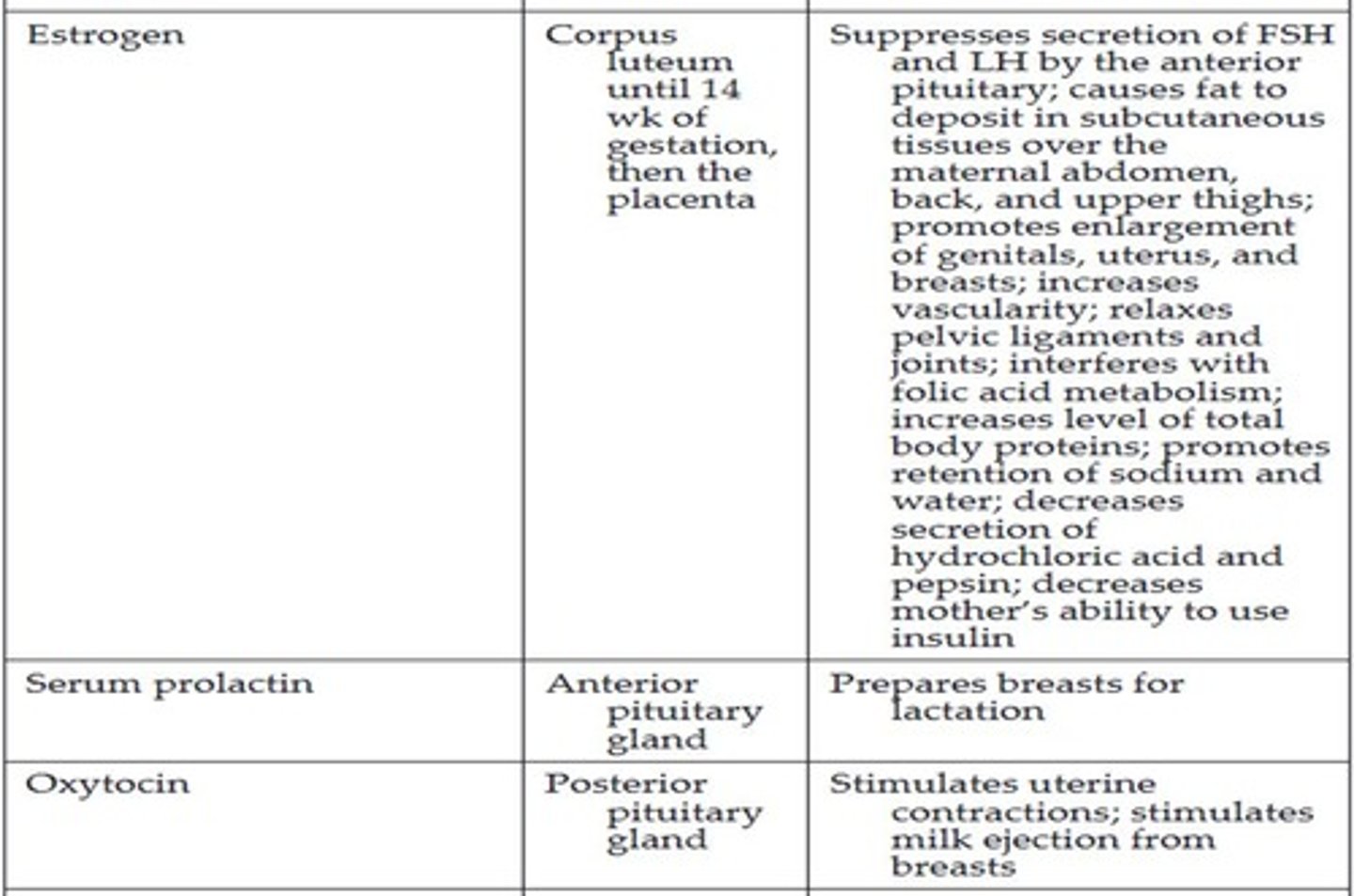
Estrogen
A hormone that plays a key role in pregnancy.
Serum prolactin
A hormone involved in lactation.
Oxytocin
A hormone that stimulates uterine contractions during labor.
Human placental lactogen
Previously called chorionic somatomammotropin, it helps regulate metabolism during pregnancy.
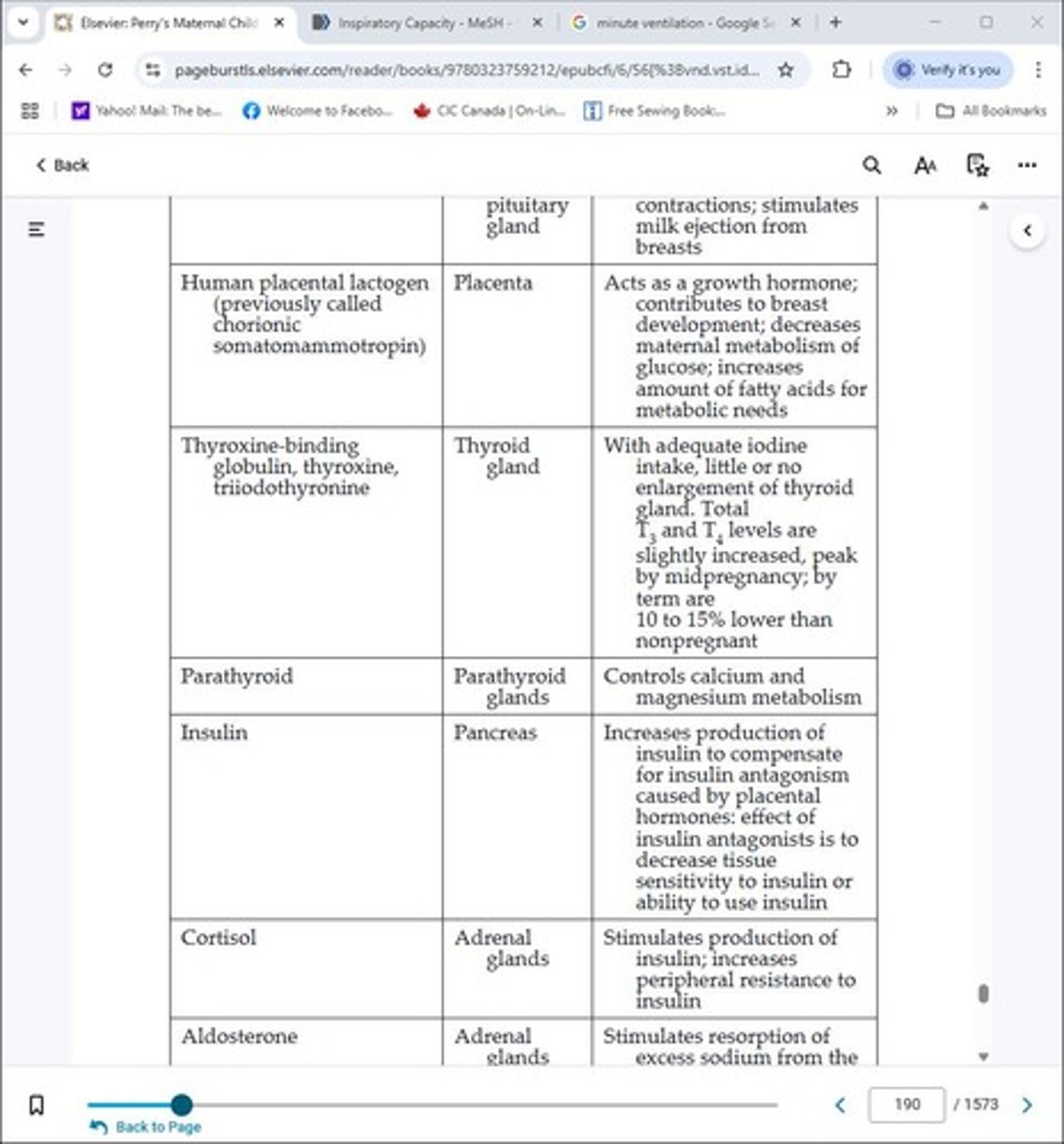
Thyroxine-binding globulin
A protein that binds thyroid hormones.
Thyroxine
A hormone produced by the thyroid gland.
Triiodothyronine
Another hormone produced by the thyroid gland.
Parathyroid
Glands that regulate calcium levels in the body.
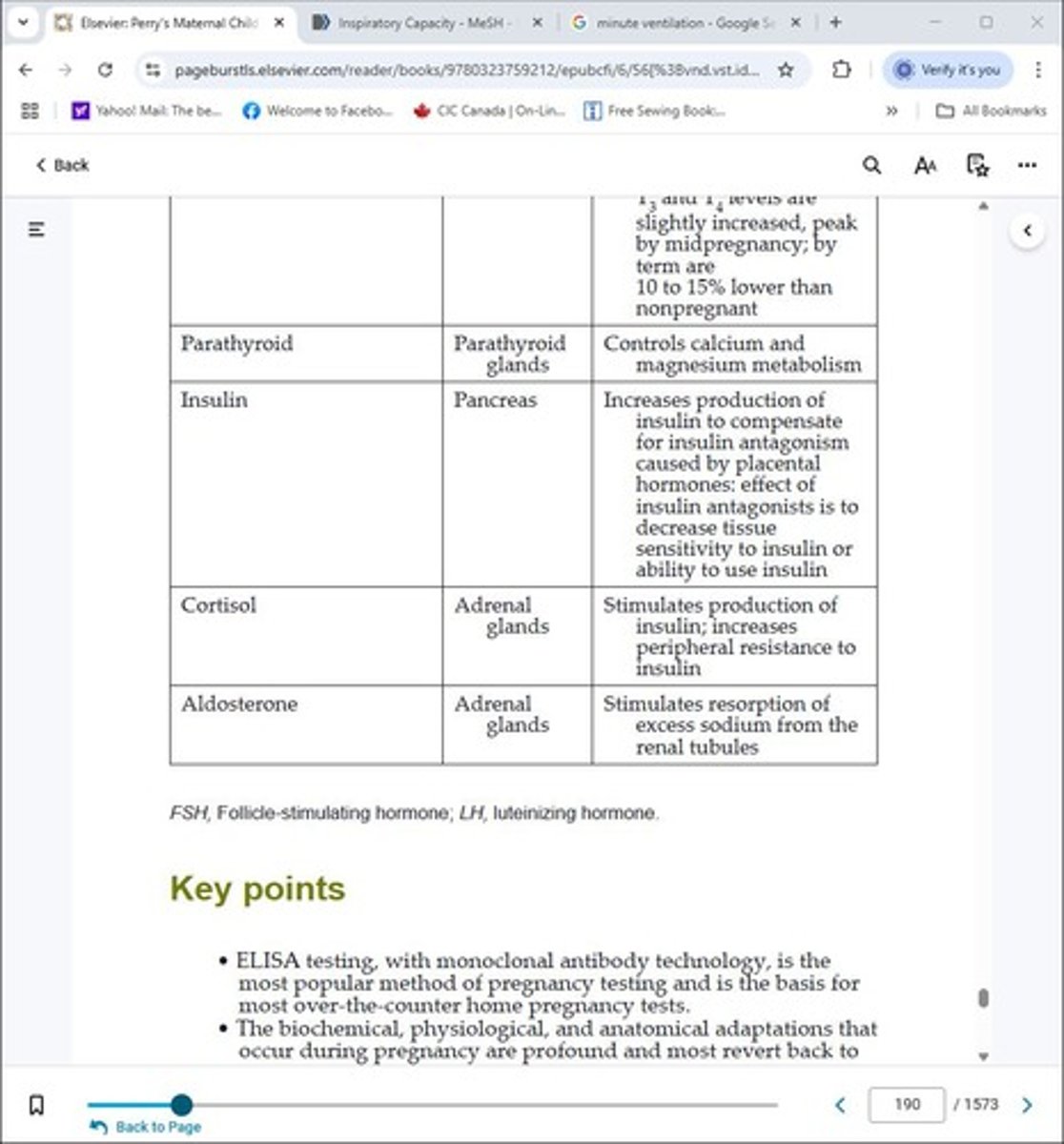
Insulin
A hormone that regulates blood sugar levels.
Cortisol
A hormone that helps manage stress and metabolism.
Aldosterone
A hormone that regulates sodium and potassium levels.