pathopharm clinical nutrition
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
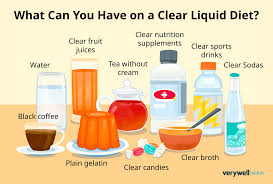
clear liquid diet
-no residual and liquid at room temp
-short term!!
-prevents dehydration
-nutritionally inadequate
ex) water, tea, broth, juices and etc
therapeutic nutrition
the role of food and nutrition in the treatment of diseases and disorders.

full liquid diet
more variety, still liquid at room temp
-short term!!
-nutritionally inadequate
-transition from liquids
ex) ice cream, strained cereal and pureed vegetables

pureed diets
-foods pureed to liquid form
-consistency varies
-for clients w/ chewing and swallowing difficulties
-nutritionally adequate

soft (bland, low fiber) diet
-whole foods, low fiber, (low residual) → not alot of fiber, easily digested
-smooth, creamy, non-gas forming

mechanical soft
-regular diet that is modified in texture
-minimal chewing
-excludes harder foods
vegetarian
-no food made from animals
ovo lacto
plant based with eggs and milk
vegan
plan based, no animal at all, came from or made from
pescatarian
-no red meat or chicken
-yes fish (maybe eggs and meat)
macrobiotic
plant based with sea food
kosher
guided by laws regarding preparation and eating of foods but not type
(dont mix dairy and meats together)
flexitarian
plant based with occasional consumption of fish, meat and dairy
dysphagia diets
-prescribed when swallowing is impaired ex: after stroke
what are manifestations sof dysphagia?
drooling, pocketing food, choking or gagging
what are the levels of liquid consistencies
level 0- thin
level 4- extremely thick
what are the levels of solid textures
level 3- liquidized
level 7- easy to chew
nursing actions in dysphagia diets
-HOB is in high fowlers (>60 degrees)
-no straws for liquids
-tilt head. forward when swallowing
-small bites throughly chew
ongoing assessment parameters
check daily weights, prescribed lab test, an evaluation of clients nutritional and energy needs and response to diet therapy
(can check albumin level or nitrogen balance or serum which looks at proteins)
-look at 7 days of nutrition
nurses should asses for _____ before advancing a clients diet.
-return of bowel function
(check for bowel sounds, may have passed gas which means bowl is awake n passing stool)
what are indicators of protein calorie malnourishment and need for clinical feedings
low protein: fatigue, weight loss, dry, brittle hair n nails
fluid shifts and edema ( low albumin and increased vascular permeability)
muscle mass and immunodef and illness
enteral feeding
used when a client cannot consume adequate nutrients and calories orally but has a GI system that functions partially.
-administer tube thru stomach
how do you know that the gut works?
listen for bowel sounds
nasoenteric tubes are used for how long?
less than 3-4 weeks (which is short term)
nasogastric
passed thru nose to stomach
nasoduodenal
passed from nose thru stomach and ends in duodenum
-used in pts who have high risk for aspirations/ delayed gastric emptying
nasojejunal
pass from nose thru stomach and ends in jejunum
-used in pts who have high risk for aspirations/ delayed gastric emptying
how long can the tube remain taped in place for?
30 days
which enteral feeding routes are long term
ostomies
gastrostomy tubes
jejunostomy tubes
ostomies
placed for clients requiring long term enteral feeding, who are high risk for aspiration or when a nasal obstruction makes insertion through the nose impossible.
-ostomy is a surgically created opening (stoma)
-can be used to deliver feedings directly in stomach or intestines
gastrostomy tubes
-endoscopically or surgically inserted into stomach
-gastrostomy feedings are well tolerated bc stomach chamber holds and releases feedings in physiologic manner which promotes effective digestion.
-dumping is usually avoided
jejunostomy tubes
-are surgically inserted into the jejunal portion of the small intestine (jejunum)
entereal formulas
feedings categorized by the complexity of the proteins
-GI tract must be functioning
standard feedings
composed of whole proteins
ex) meat, milk and eggs
hydrolyzed feedings
broken down (makes food easier to digest)
ex:people who have bowel disease or liver problems
disease specific feedings
has lower protein or potassium component
ex) kidney disease
modular formulas feedings
contains singular nutrients
ex) just protein or just carbs
-supplement for who cant get one specific nutrient
dumping syndrome
a condition in which food, especially foods high in sugar, moves from your stomach into ur small bowel too quickly.
side effects: diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dizzy, stomach cramping and heart palpitations
continuous delivery method
continuous rate over 24 hrs
-on feeding pump
-recommended for critically ill patients, lower risk of aspirations, keep energy at consistent lvl
cyclic delivery method
continuous rate for 8-20hrs usually during sleep
-used when not enough calories are needed
intermittent delivery method
every 4-6 hrs in equal portions (typically over a 30-60 mins time frame)
-thru syringe or IV pump
-cut up throughout the day
bolus delivery method
larger volumes over 15 mins for 4-6 times a day
-given with a large syringe directing in feeding tube
can use syringe of cans of food
preparing for feeding by…
verify presence of bowel sounds
verify tube placement and placement
make sure hob is at 30 degrees
residuals should be checked how often
every 4-6 hrs
steps for residual
1) stop feeding
2) determine total vol since last res check
3) draw back using 60 mL syringe
4) draw until empty (resistance)
5) if total is MORE than ½ total (need orders to adjust/slow/stop for a time)
if total is LESS than ½ total (continue feeding as ordered)
6) ALWAYS put feeding back that u withdrew
gastrointestinal complications
-constipation, diarrhea, cramping, pain
nursing action for gi complications
consider changing formula
decrease formula, increase free water
formula should be at room temp
mechanical complications
-tube replacement, dislodgment, aspiration, irritation, clogging (NOT PATENT)
mechanical nursing actions
-confirm placement prior to feedings
-elevate hob to 30 degrees or higher
-bolus over 15 min
-flush tube with 30 ml water every 4 hrs
-check residuals every 4-6 hrs
-dont mix formula with meds
metabolic complications
dehydration, hyperglycemia, electrolyte imbalance, fluid overload, refeeding syndrome
refeeding syndrome
starvation state to feeding -can be fatal
food contamination actions
wash hands before, clean equipment, replace feeding, tube, and any equipment every 24 hrs!!
fill generic bags with only 4 hrs worth of formula
when gi is not working use _____ feeding
parental
-given thru blood stream (vein)
total parenteral (TPN)
central
-long term use
-in the inferior or super vena cava
-used for more complete nutrition
peripheral parenteral nutrition (PPN)
short term use
can only go to 10% dextrose
not nutritionally complete
if hypertonic (>10% dextrose) must be administered through ______
central vein
you should only use bloodstream when stomach cannot be used. true or false?
true
carbs (dextrose) for PPN
-2.5-10%
carbs (dextrose) for TPN
>10% (up to 70%)
lipids for parenteral nutrition
10-30%
what functions determine the amount of protein provided?
clients estimated requirements and liver n kidney function
insulin can be added
to reduce potential for hyperglycemia
heparin can be added
to prevent fibrin buildup on the catheter tip
glutamine can be added
based on individual client needs
pn can be used when….
client is unable to consume enough calories
prep of the client
review the clients weight, bmi, nutritional status, diagnosis and current lab data
nursing care is..
focused on preventing complications thru consistent monitoring
when monitoring ongoing care you should…
-verify solution with second RN
-change bag and tubing every 24 hrs
nursing actions & complications
monitor for effectiveness
protein= albumin levels !!
feed enterally whenever possible. true or false?
true! (if gut works use it)