REDOX REACTIONS PT.3
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Electrolytic cells are spontaneous or non-spontaneous
Non-spontaneous
Difference between galvanic cell and electrolytic cell in terms of energy conversion
Chemical energy to electrical energy
Electrical energy to chemical energy
Define electrolytic cell
Is an electrochemical cell in which non-spontaneous redox reactions occur at the electrodes. Electrical energy is converted to chemical energy
What must be applied in order to maintain the electrode reactions and does this affect the spontaneous aspect
Electrical energy with a DC current (external source)
Yes,this is why electrolytic cells are non-spontaneous
True/false
In a electrolytic cell the reaction is also exothermic and the cell potential is positive
False
Endothermic and negative
What must the electrolyte be(2)
Ionic substance
Molten/dissolved in distilled water
Why is an electrical current needed
Since ionic substances are in crystal lattices(ions can't move freely). The charges from current can move freely and therefore causing the reaction
Define electrolysis
Electrolysis is the chemical process in which electrical energy is converted to chemical energy. It is the use of electrical energy to produce a chemical change
What are two unreactive electrodes in electrolytic cells
-graphite
-carbon
What's ONE MAJOR thing about the electrodes
Anode is positive
Cathode is negative
But reduction is still at the cathode and oxidation still at anode
What's the state symbol for molten substances and state symbol for dissolved
-(L)
-(aq)
Anions are attracted to ___and are oxidised there
Cations are attracted to___ and are reduced there
Anode
Cathode
Are you free to move when substance is melted or dissolved
109% yes
What happens during the oxidation of water
What happens during the reduction of water
Oxygen gas forms by anode
pH decreases( more H3O ions since presence of H ions increase and bind with water )
Hydrogen gas forms by cathode
pH increases(more OH ions)
For low anion concentrations (lots of water,few anions)
For high anion concentrations(saturated solution)
Strongest reducing agent will oxidise
Anion will always oxidise
At the negative cathode
Strongest oxidising agent will always reduce
What are the 3 main applications of electolysis
Electroplating
Electrofing of copper
Preparation of chlorine gas,hydrogen gas and sodium hydroxide
What is electroplating
What is it literally
Whats the tow uses
Are the half reactions done with the same metal
Covering metal object with a thin layer of another metal
Make it look better+protect cheap metal(nickel/bronze)
Both half reactions are from the same metal
What's the anode,cathod and electrolyte mixture
Precious metal rod(gold/silver)
Object that needs plating(i.e nickel spoon)
Precious metal nitrate and potassium cyanide
What two things does cynadie help with
Keeping consistent precious metal concentration
Increases electrical conductivity
Ensures effective plating
How does electroplating work

What remains constant during electroplating
The concentration of previous metal
What is electrorefining of copper
Impure copper being purified through electolysis
The deposits on cathode is the pure copper
Impure copper is used for anodes
What is anode silt
Less reactive(weaker reducing agentslike silver,gold and platinum) sink to the bottom of the cell
Which solution is normally used for copper electrorefining
Acified copper sulphate
The electrolysis of concentrated NaCl solution is used in the chloro-alkali industry
What's another name for [NaCl(aq)]
What is formed from this type of electrolysis
Brine
Cl gas
NaOH
H gas
NaOH(aq) (caustic soda)
How does membrane cell work
Oxidation half-call and reduction half cell are separated by the cation exchange membrane
Membrane only allows cations through
Na+ move from anode half cell to cathode
OH ions can't move to anode from the cathode
NaCl is pumped Into oxidation half-cell
What's formed at the anode and what forms at cathode at the membrane cell
And what is sodium
Cl gas cause it's very concentrated so will oxidise instead of H2O
Hydrogen gas(from water) since it's a stronger oxidising agent
Sodium ions are spectator ions
Advantages of membrane cell
Most Environmentally friendly cell
Cheaper than other two
Produces very our product
Disadvantages of membrane cell
Cl gas can't be inhaled
H gas is combustible
NaOH is corrosive and should not be in ground water
High tech membrane can get clogged by impure cations
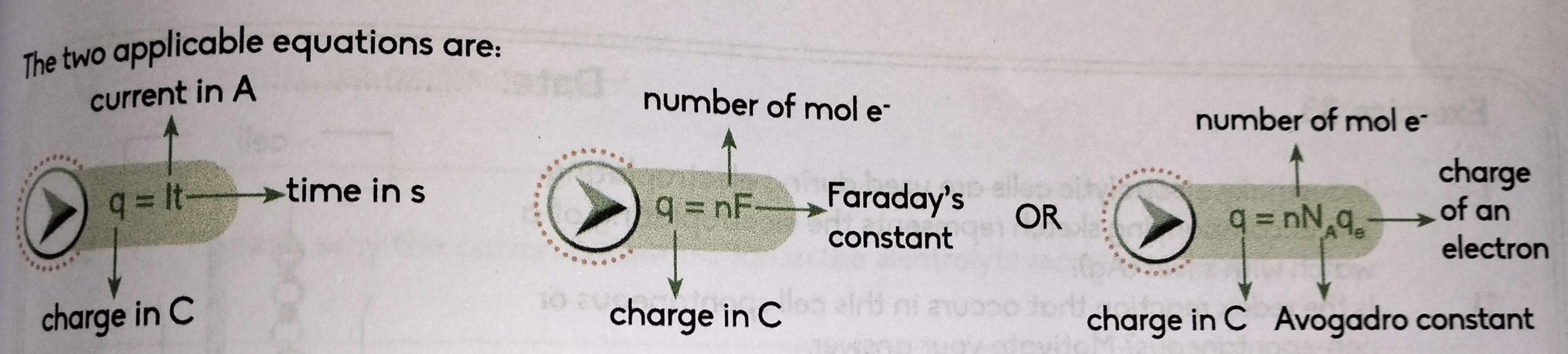
What 3 formulas can you use to find charge