Electrolysis
- ^^Electrolysis:^^ The breakdown of an electrolyte (ionic compound, molten or aqueous solution) by passing an electric current
- This is possible due to the presence of mobile electrons
^^Components of an Electrolytic Cell:^^
Electrodes: Metal or graphite rods that aid the flow of electricity in and out of the electrolyte
Anode: Positive electrode
- ^^Oxidation of negative anions happens at the anode^^
Cathode: Negative Electrode
- ^^Reduction of positive cations happens at the cathode^^
Anion: Negatively charged ion that moves to anode
Cation: Positively charged ion that moves to cathode
Electrolyte: substance that conducts electricity when dissolved in water and is broken down by electrolysis
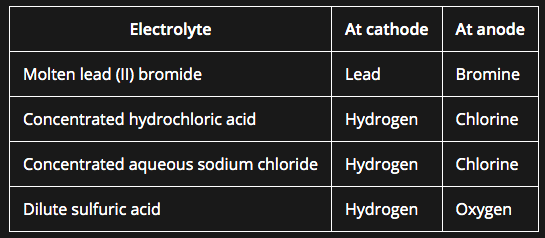
Positive electrode (anode)
- Non-metal ions (other than hydrogen) are attracted to the positive electrode
- Non-metal ions will lose electrons to form the non-metal
- The product formed depends on which ion loses electrons more readily, with the more reactive ion remaining in solution
Negative electrode (cathode)
- H+ and metal ions attracted to the negative electrode but only one will gain electrons
- Either hydrogen or metal will be produced
- If the metal is above hydrogen in reactivity series, then hydrogen will be produced and bubbling will be seen at the cathode
- ^^In molten ionic compounds the metal is formed at the cathode and the non metal is formed at the anode^^
In Aqueous Solution
Positive Electrode:
- Negatively charged OH– ions and non-metal ions are attracted to the positive electrode
- ^^If halide ions and OH- are present then the halide ion is discharged at the anode^^
- If no halide ions are present, then OH- is discharged at the anode, gains electrons and forms oxygen gas
- The concentration of the solution also affects which ion is discharged:
- ^^If a concentrated halide solution is being electrolysed, the halogen forms at the anode^^
- ^^If a dilute halide solution is being electrolysed, oxygen is formed^^
Negative Electrode (cathode)
Positively charged H+ and metal ions are attracted to the negative electrode but only one will gain electrons
Either hydrogen gas or metal will be produced
^^If the metal is above hydrogen in the reactivity series, then hydrogen will be produced and bubbling will be seen at the cathode^^
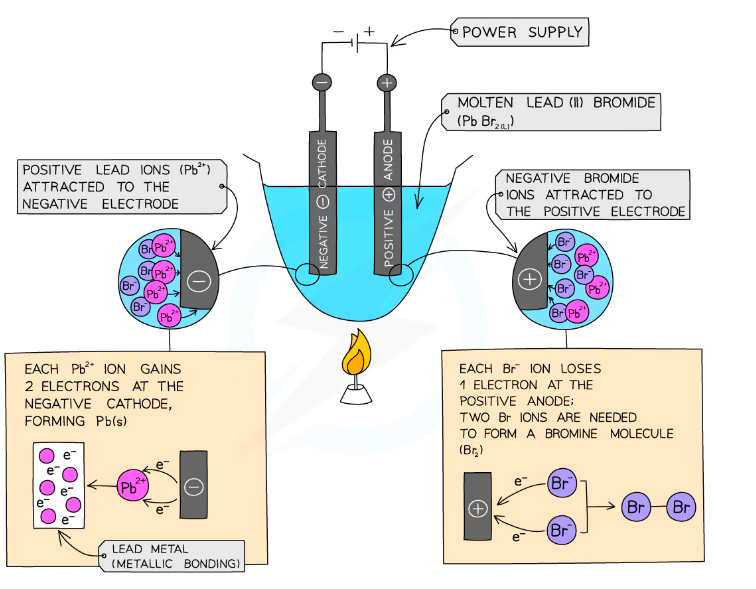
Electroplating
**^^Electroplating:^^**The process of coating the surface of a metal (more reactive) with another metal (less reactive) using electrolysis \n
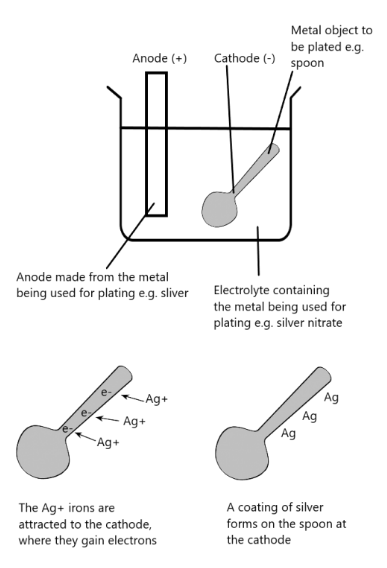
Refining Metals
- Cathode: thin strip of pure metal
- Anode: impure metal
- Electrolyte: Aqueous Salt Solution of metal
- The refining of copper: Impure copper as the anode and pure copper as the cathode; the aqueous copper (II) sulfate helps the copper ions move from the anode to the cathode. Here the ions gain electrons and become copper atoms, making the pure copper cathode thicker.
Reaction at Anode: Cu – 2e Cu2+ (mass decreases)
Reaction at Cathode: Cu2+ + 2e Cu (mass increases)
Extraction of Aluminum
The main ore of aluminum is bauxite – high m.p.
^^Aluminum (III) oxide (alumina) is dissolved in molten cryolite (Na3AlF6) – this mixture has a lower m.p.^^
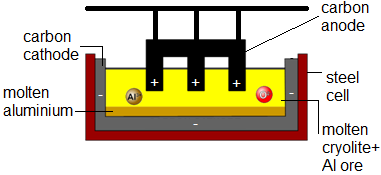
During electrolysis aluminum ( Al3+ + 3e- → Al ) is produced at the carbon cathode and oxygen ( 2O2- - 4e- → O2 ) at the carbon anode.
Due to the high temp. the oxygen reacts with the carbon in the graphite anode to form CO2 and so anode has to be periodically replaced
Electrolysis of Brine
^^Brine: concentrated aqueous NaCl solution^^
Ions present: Na+, H+, Cl- and OH-
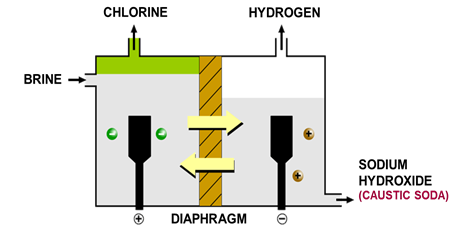
| At the anode | At the cathode |
|---|---|
| Made of titanium | Made of steel |
| Cl- ions; Chlorine gas | Hydrogen cations reduced to H2 molecules |
Na+ and OH- ions are left in solution forming sodium hydroxide