Chemistry - 4.7 amino acids, peptides and proteins
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What are amino acids?
molecules containing an amine group and a carboxylic acid group
What is the general formula of naturally occuring a-amino acids?
RCH(NH2)COOH
What is an a-amino acid?
when the amino group is attached to the 2nd carbon next to the carboxyl group
What is a b-amino acid?
when the amino group connected to the third carbon
Amino acids are amphoteric, what does this mean?
they have both acidic and basic properties - contain 2 functional groups
what are the reactions of amino acids?
reacting with acids
reacting with bases
esterification with alcohols
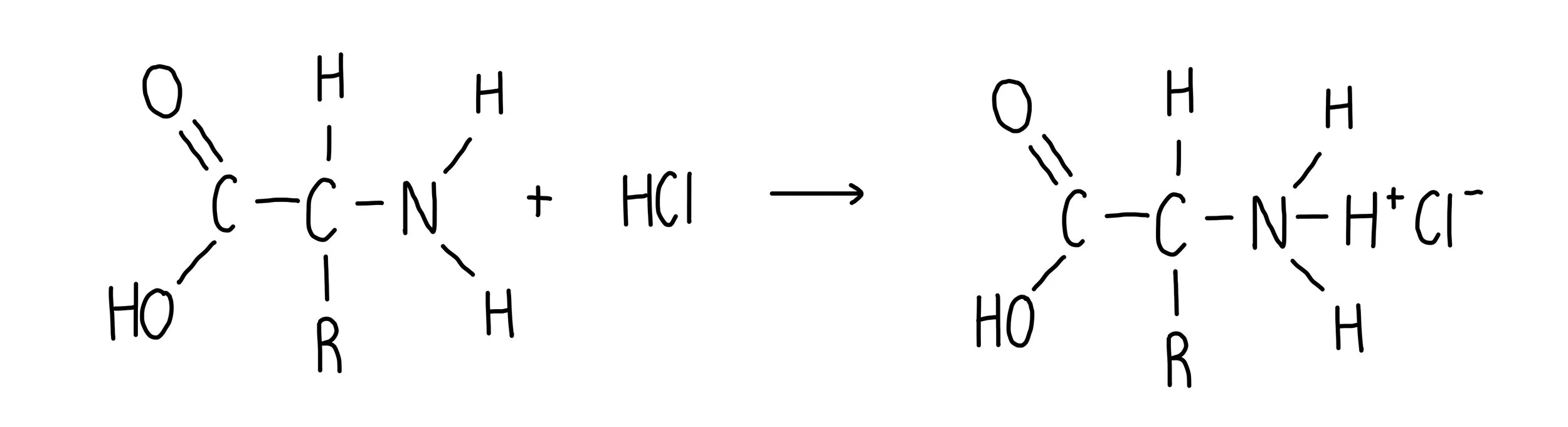
What is the reaction of amino acids with strong acids?
exist in cationic (positive ion form)
NH2 becomes NH3+
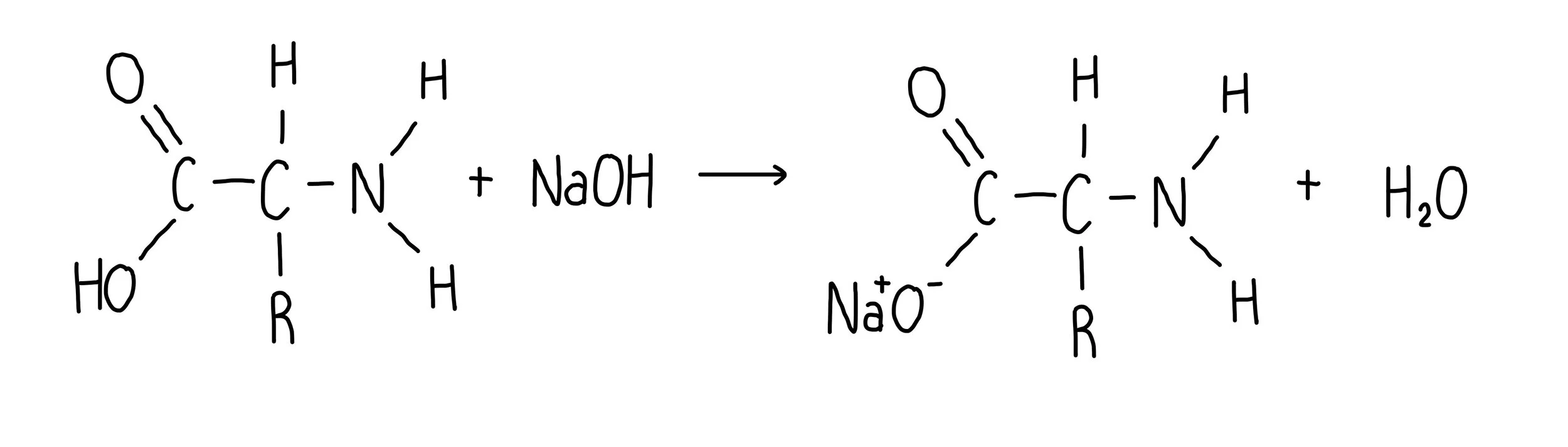
What is the reaction of amino acids with strong bases?
produce a salt and water
exists in anionic (negative ion form)
COOH becomes COO-
What is the reaction of amino acids with an alcohol?
easily esterified by heating an alcohol
in presence of concentrated sulfuric acid
amino group is protonated
H2NCH2COOH + C2H5OH + H+ → H3N+CH2COOC2H5 + H2O
What is a zwitterion?
a molecule that has both a positive and negative charge but no overall electrical charge
how does a zwitterion form in amino acids?
a hydrogen ion transfers from the -COOH group to the NH2 group forming COO- and NH3+
Why do amino acids have high melting points?
they have a strong electrostatic attraction (ionic bonds) between oppositely charged ions in the solide lattice requiring lots of energy to break
Why are amino acids soluble in water?
their charged ions interact with polar water molecules (forming ion-dipole bonds) helping them dissolve
what is the isoelectric point?
the pH at which amino acid exists as a zwitterion and has no overall charge
why do different amino acids have different isoelectric points?
because their R groups are different and affect how easily they gain or lose protons
How do you form amides?
reacting acyl chloride with ammonia and amines
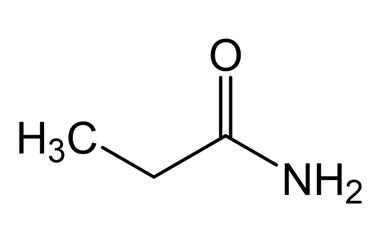
example of primary amide
propanamide
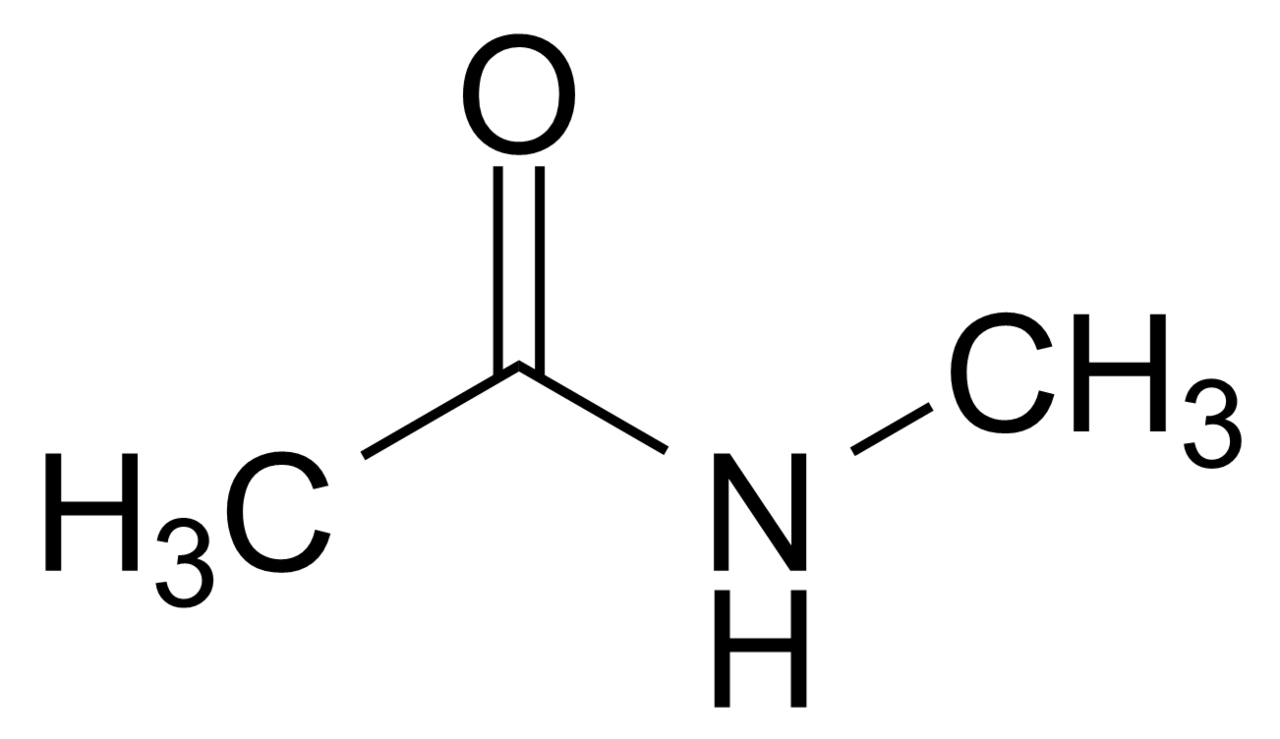
example of secondary amide
N - methylethanamide
example of tertiary amide
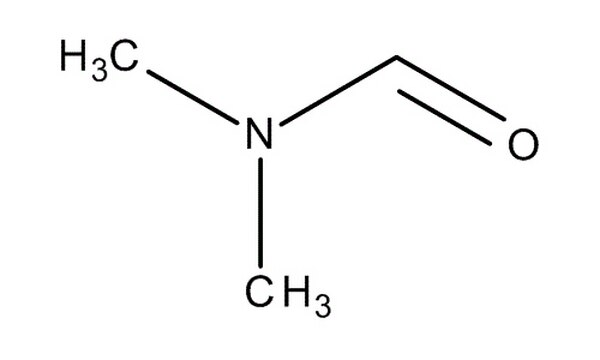
N.N - dimethylmethanamide
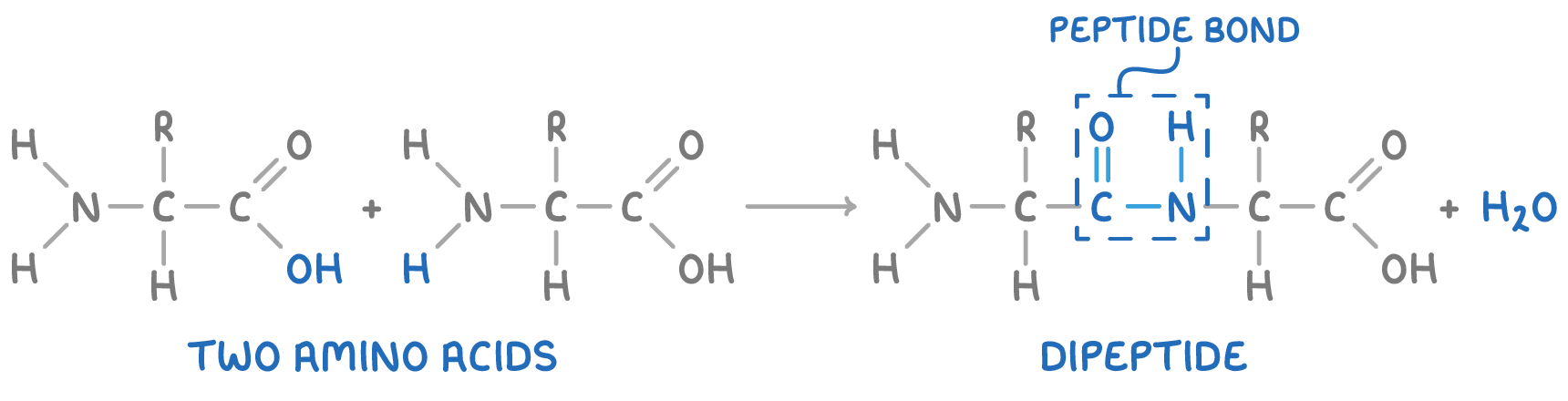
How is a dipeptide formed?
two amino acid molecules reacting together
condensation reaction
forms peptide bond/amide link - CONH
eliminates one molecule of water
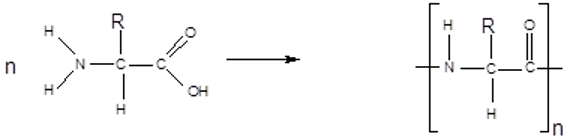
How do you form polypeptides?
Multiple amino acids reacting in condensation reactions to form polymers called polypeptides
called polyamides
How you can break the peptide link in proteins?
heating in a strong acid or strong alkali
describe acid hydrolysis of proteins
heat under reflux with strong acid
amino acids produced are in cationic form (NH2 to NH3+)
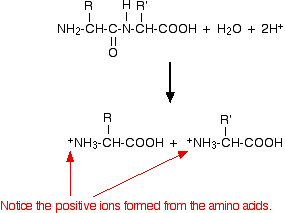
describe alkaline hydrolysis of proteins
heat under reflux in strong alkali
amino acids are produced in anionic form (COOH to COO-)
What are the structure levels of proteins?
primary structure
secondary structure
tertiary structure
what is the primary structure of proteins?
the sequence of amino acids in the protein chain
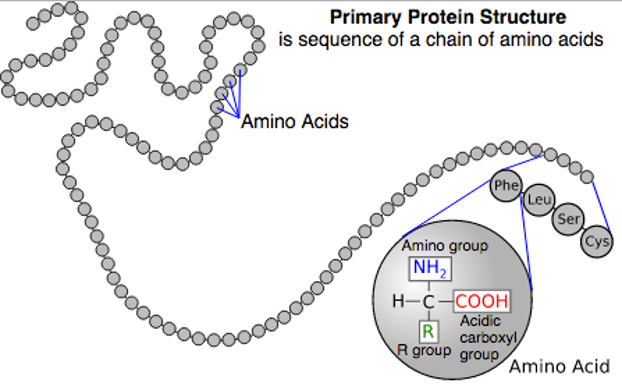
what is the secondary structure of proteins?
a primary polypeptide chain folded into an alpha helix or a beta pleated sheet
describe the structure of the alpha helix in the secondary structure of a protein
polypeptide chain is coiled into a spiral
shape is maintained by hydrogen bonds between the N-H hydrogen atom of an amide group and the C=O carbonyl oxygen of another amide group
found in muscle and wool
describe the structure of the beta pleated sheet in the secondary structure of a protein
maintained by hydrogen bonds but the C=O and N-H groups are in different chains
van der waals forces are responsible for producing a pleated sheet rather than a flat arrangement
what is the tertiary structure of a protein?
alpha helix structure of a protein bent, twister or folded into a particular shape - e.g. coiled into another spiral or super helix
what are enzymes?
biological catalysts (proteins)
what is the role of enzymes?
to maintain life by speeding up the rate of reactions
without them reactions would be too slow
what are some things proteins are found in in living organisms?
nails
skin
collagen of cartilage
2 examples of proteins and their importance
Amylase (enzyme)
found in human saliva
catalyses the breakdown of starch into sugars during digestion, allowing energy to be released in respiration
Haemoglobin
found in red blood cells
transports oxygen around the body by binding to oxygen
allows oxygen to be carried from the lungs to respiring tissues - essential for aerobic respiration.