Lecture 6: Suture Materials & Patterns
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
What is suture’s important role in wound repair?
provides hemostasis
supports healing tissue by apposing and supporting tissue layers
What determines the requirements for suture support?
type of tissue
anticipated duration of healing
How long should a suture be functional for different tissues?
vessel ligation: hours (until clot is formed)
muscle, SQ tissue, skin: few days
fascia: weeks
tendon: months
What characteristics of individual patients may cause the healing of their wounds to be delayed?
infection
obesity
malnutrition
neoplasia
drugs (ex. steroids)
collagen disorders
hypoproteinemia
radiation therapy
What is the major function of suture?
maintain apposition of tissues until wound’s tissues strength returns
The ideal suture is:
Easy to handle and reacts minimally in tissue
Inhibits bacterial growth
Holds securely when knotted and resists shrinking in tissue
Absorbs with minimal reaction after the tissue has healed
Noncapillary, Nonallergenic, Noncarcinogenic, and Nonferromagnetic
What is the smallest vs largest USP suture size?
smallest: 12-0
largest: 7
True or false: 3-0 suture is larger than 2-0.
false
Why should the smallest diameter suture that will adequately secure wounded tissue be used?
minimize trauma as the suture is passed through the tissue
reduce the amount of foreign material left in the wound
True or false: There is no advantage to using a suture that is stronger than the tissue to be sutured.
true
What are flexible sutures indicated for?
ligating vessels or performing continuous suture patterns
Nylon and surgical gut are relatively _____ compared with silk suture; braided polyester sutures have _______ stiffness.
stiff; intermediate
What suture characteristics influence the ease with which it is pulled through tissue (“drag”") and the amount of trauma caused?
surface characteristics
Why are smooth sutures particularly important in delicate tissues, such as the eye?
smooth sutures are pulled through tissue more easily and cause less friction/drag → less trauma
What is the downside of using sutures with smooth surfaces?
require greater tension to ensure good apposition of tissues
have less knot security
Braided materials have more ______ than monofilament sutures.
drag
Why are braided materials often coated?
reduce capillarity
provide smooth surface
What is the process by which fluid and bacteria are carried into the interstices of multifilament fibers?
capillarity
What type of sutures are considered noncapillary?
monofilament
What type of suture should NOT be used in contaminated or infected sites?
capillary suture

Which type of suture are these?
left: monofilament
right: multifilament or braided
True or false: tensile strength of the suture should not greatly exceed the tensile strength of the tissue.
true
What is the holding capacity of a suture expressed as a percentage of its tensile strength?
relative knot security
What is the strength required to untie or break a defined knot by loading the part of the suture that forms the loop?
knot-holding capacity
What is the strength required to break an untied fiber with a force applied in the direction of its length?
tensile strength
How are suture materials usually classified?
structure:
monofilament
multifilament
behavior in tissue:
absorbable
nonabsorbable
origin:
synthetic
organic
metallic
What type of suture has less tissue drag, does not have interstices that may harbor bacteria or fluid, and care should be used when handling because damaging the material with sx instruments may weaken it and predispose it to breakage?
monofilament
What type of suture is more pliable and flexible and may be coated to reduce tissue drag and enhance handling characteristics?
multifilament
Compare and contrast the memory, wicking, and handling of monofilament vs mutlifilament suture?
monofilament
nonwicking
more memory
does not handle as well
multifilament
wicking
less memory
good handling
What are the two major mechanisms of absorption resulting in the degradation of absorbable sutures?
suture of organic origin are gradually digested by tissue enzymes and phagocytized
suture manufactured from synthetic polymers are principally broken down by hydrolysis
What effect does fibrous tissue have on nonabsorbable sutures?
Nonabsorbable sutures are ultimately encapsulated or walled off by fibrous tissue
When do absorbable suture materials lose most of their tensile strength?
within 60 days
How do absorbable suture materials eventually disappear?
they are phagocytized or hydrolyzed
What is catgut suture made of?
submucosa of sheep intestine or the serosa of bovine intestine
What notable reaction does catgut elicit?
inflammatory
What may happen to catgut when wet?
knots may loosen
Where is surgical gut rapidly removed?
infected sites or areas where it is exposed to digestive enzymes and is quickly degraded in catabolic patients
How are synthetic absorbable sutures broken down? What reaction does this elicit?
broken down by hydrolysis, causing minimal tissue reaction
True or false: Infection or exposure to digestive enzymes significantly influences the rate of absorption of most synthetic absorbable sutures.
false
What type of sutures are relatively stable in contaminated wounds?
Polyglactin 910 and polyglycolic acid
What type of synthetic absorbable suture may be rapidly degraded in infected urine?
polyglycolic acid, polyglactin 910, poliglecaprone
What type of suture is acceptable for use in sterile bladders and those infected with E. coli?
polydioxanone, polyglyconate, and glycomer 631
What is the most common organic nonabsorbable suture?
silk
What suture is made by a special type of silkworm?
braided multifilament
Why is organic nonabsorbable suture often used in cardiovascular procedures?
it has excellent handling characteristics
Why is silk suture contraindicated for use in vascular grafts?
does not maintain significant tensile strength after 6 months
What site should silk suture NOT be used in?
contaminated sites
Synthetic nonabsorbable suture, braided multifilament or monofilament threads, are typically strong and induce _____ tissue reaction.
minimal
What is the most common type of metallic suture?
stainless steel
True or false: surgical steel is strong and inert with minimal tissue reaction.
true
What are the downsides of metallic sutures?
knot ends evoke an inflammatory reaction
tendency to cut tissue
may fragment and migrate
What type of suture is stable in contaminated wounds, the standard for judging knot security, and the standard for judging tissue reaction to suture materials?
stainless steel
What are the considerations for suture selection?
Length of time the suture will be required to help strengthen the wound or tissue
Risk of infection
Effect of the suture material on wound healing
Dimension and strength of the suture required
What type of sutures should be used in skin and why?
monofilament to prevent wicking or capillary transport of bacteria to deeper tissue
What type of sutures used in skin generally have good relative knot security and are relatively non-capillary?
synthetic monofilament nonabsorbable
Why should absorbable sutures used in skin ultimately be removed?
absorption requires contact with body fluids
What type of sutures are used to obliterate dead space and reduce tension on skin edges? What suture material is preferred for this?
subcutaneous sutures; multi or monofilament absorbable suture
Most surgeons routinely close the rectus fascia with a simple continuous suture pattern. What type of suture should be used for this?
a strong non absorbable or standard absorbable monofilament suture with good knot security (ex. polypropylene, polybutester, etc)
What size suture should be used for a continuous suture pattern?
one size larger suture than would normally be used
How many knots should be placed for abdominal closure?
3-4 square knots (6-8 throws)
Why is standard absorbable suture usually preferable when selecting suture for abdominal closure?
to prevent large amounts of foreign material from remaining permanently in the incision
True or false: muscle has poor holding power and is difficult to suture.
true
What suture material should be used for muscle?
absorbable or nonabsorbable
Why should consideration be given to the type of suture pattern chosen for suturing muscle?
sutures placed parallel to the muscle fibers are likely to pull out of muscle
What characteristics should suture material used for tendon repair have?
strong, nonabsorbable, and minimally reactive
largest suture that will pass without trauma through tendon
Suturing with what type of needle is generally less traumatic for tendons?
taper or taper-cut needle
What type of suture material is usually selected for parenchymal organs (liver, spleen, and kidneys)?
absorbable monofilament suture (multifilament tends to cut through this type of tissue because of the increased drag)
What type of suture should be selected for hollow viscus organs (trachea, GI tract, or bladder)?
Absorbable monofilament sutures generally are recommended to prevent tissue retention of foreign material once the wound is healed
Why should non absorbable suture not be used for hollow viscus organs (trachea, GI tract, or bladder)?
may be calculogenic when placed in the urinary bladder or gallbladder
may be extruded into the lumen when implanted in intestine
What type of suture rapidly dissolves when incubated in sterile urine (6 days) or infected urine (3 days)?
polyglycolic acid (Dexon)
What sutures are selected for infected or contaminated wounds? What sutures should be avoided?
Sutures should be avoided in highly contaminated or infected wounds.
Multifilament nonabsorbable sutures should not be used in infected tissue.
Absorbable suture material is preferred.
Surgical gut should be avoided
What type of sutures may elicit less infection in contaminated tissue than metallic sutures?
synthetic monofilament nylon and polypropylene sutures
What type of suture should be selected for vessels and vascular anastomoses?
Vessels should be ligated with absorbable suture material.
Vascular anastomoses are typically performed with monofilament nonabsorbable suture material such as polypropylene
What does selection of a surgical needle depend on?
type of tissue to be sutured
topography of the wound
characteristics of the needle
Why are most surgical needles made from stainless steel wire?
strong
corrosion free
does not harbor bacteria
What is the amount of angular deformation a needle can withstand before becoming permanently deformed?
surgical yield
What is the needle’s resistance to breaking under a specified amount of bending?
ductility
What is related to the angle of the poitn and the taper ratio of the needle?
sharpness of needle
How are curved needles selected?
evaluate depth and diameter of a wound
¼ circle needles primarily used in ophthalmic procedures
3/8 and ½ circle needles = most commonly used in vet med
What curved needle is easier to use in confined locations?
½ circle or 5/8 circle needle
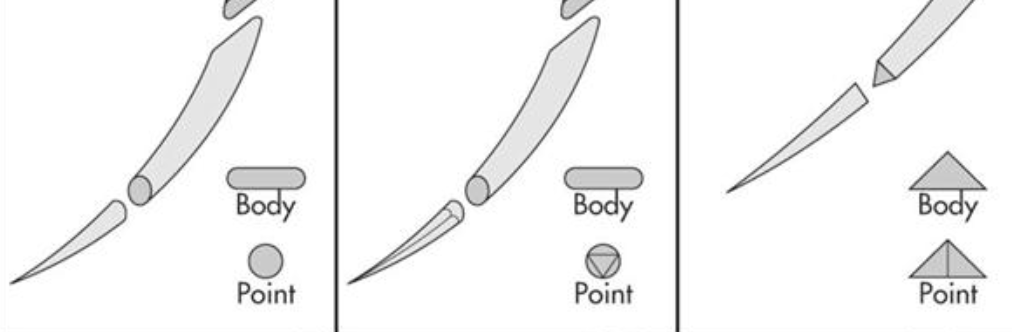
What are these types of needles?
taperpoint, tapercut, and regular cutting
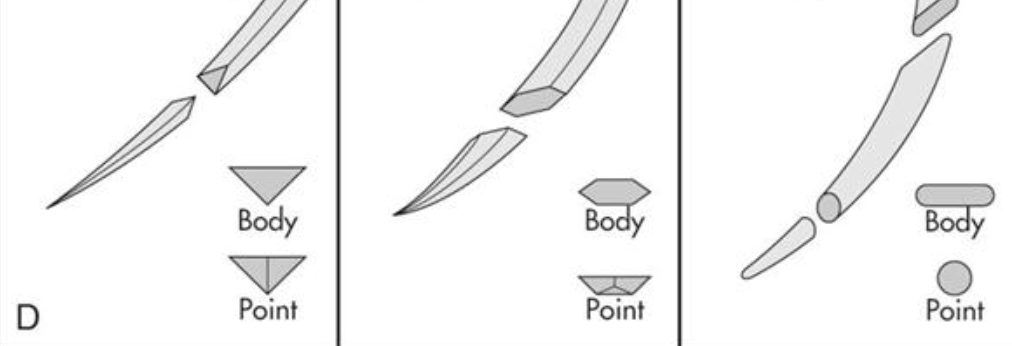
What types of needles are these?
reverse cutting, spatula point, blunt point
How are sutures classified by the way they appose tissue?
• Appositional – one tissue edge apposed to another
• Everting - turn the tissue edges outward, away from the patient and toward the surgeon.
• Inverting - turn tissue away from the surgeon, or toward the lumen of a hollow viscus organ.
What suture pattern is generally used for subcutaneous tissue?
simple continuous
What may be used in place of skin sutures to reduce scarring and eliminate the need for suture removal?
subcuticular sutures
How are subcuticular sutures?
suture line is begun by burying the knot in the dermis
suture is advanced in the dermal tissue
bites are parallel to the long axis of the incision
suture line is complete with a buried knot
What type of suture material and needle are used for subcuticular sutures?
absorbable suture materials with a cutting needle
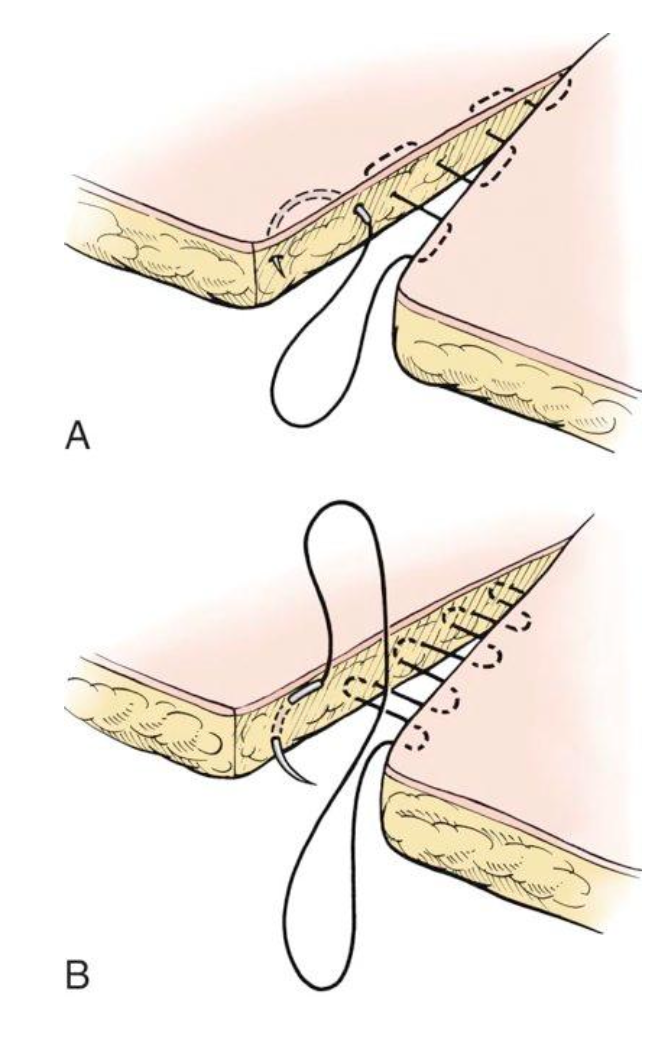
What are these suture patterns?
A. subcuticular
B. subcutaneous
What are the interrupted suture patterns?
simple interrupted
horizontal mattress
cruciate
vertical mattress
halstead
gambee
Why is the knot of a simple interrupted offset?
so it does not rest on top of the incision
For a simple interrupted suture, approximately how far should they be placed away from the skin edge?
2-3mm
What type of suture pattern is simple interrupted sutures?
appositional
What are the pros and cons of simple interrupted sutures?
pros: disruption of a single suture does not cause the entire suture line to fail
cons:
simple interrupted sutures take more time than continuous patterns
result in more foreign material (knots) in the wound
When are horizontal mattress sutures used?
used primarily in areas of tensions
Horizontal mattress sutures often cause tissue _____.
eversion
How are horizontal mattress sutures performed?
sutures should be angled through the tissue so that it passes just below the dermis
generally, are separated by 4-5mm
can be bolstered using rubber stents and buttons
What appositional suture is formed when two simple interrupted sutures are placed parallel to each other and then tied across the incision to create an “X”?
cruciate
What are the benefits of using a cruciate suture?
can relieve low to moderate tension across an incision
less suture material is used to close a skin incision than with simple interrupted
affords the security of an interrupted pattern
What stitch is preferred when addressing tension in skin closure and causes less disruption to the blood supply of the wound edges?
vertical mattress
What is placing padded material beneath the suture loops?
stenting