AP Human Geography 1st Semester Vocab Review
1/219
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocab from units 1, 2, and 3; Krinhop's class
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
220 Terms
Connectivity
Degree of direct linkage between one location and other locations in a network.
Sense of Place
Feelings, perceptions, and emotions that people associate with a particular location (Personal feelings).
Ghost town
Abandoned town or city that once had civilization/population.
Remote sensing
Process of collecting date about Earth’s surface from satellites or aerial platforms/views.
GIS
Computer system that captures, stores, analyzes and display geographic data/spatial data (Computer analysis)
Mental maps
Personal internal representations of spatial information and locations based on individual/personal experience.
Reference maps
Show general features like boundaries, cities, and physical landscape, used for navigational purposes.
Political maps
Maps that show human created boundaries, like countries, states, and cities.
Physical maps
Show natural features of Earth’s surface such as mountains, rivers, and lakes.
Road maps
Maps that depict highways, streets, and transportation routes for navigation (GPS)
Plat maps
Detailed maps that show property barriers/rooms, show divisions and boundaries of a piece of land.
Locator maps
Location of a geographic region within a larger context, used in various types of maps to mark locations.
Thematic maps
Highlights a specific theme like population density, climate, economic activities, or specific information for situations.
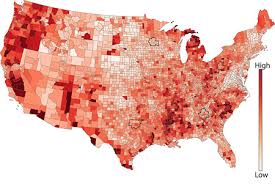
Choropleth maps
Display divided geographic areas or regions with toned shades of colors. They represent data values, such as population or income, through varying shades or patterns.
The map shown is a choropleth map
What kind of map is shown?
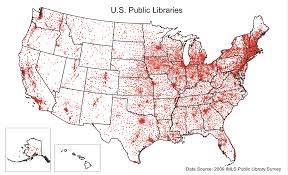
Dot distribution maps
Maps that use dots to show the presence or quantity of a phenomenon.
The map shown is a dot distribution map
What kind of map is this?
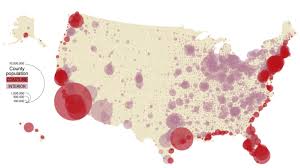
Graduated symbol maps
Uses symbols of various sizes to show quantitative differences between mapped features.
The map shown is a graduated symbol map
What kind of map is this?
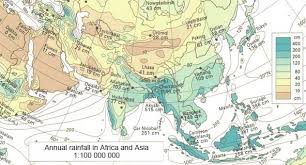
Isoline maps
Use lines to connect points of equal value to show gradual or continuous data.
This image shows an isoline map
What kind of map is this?
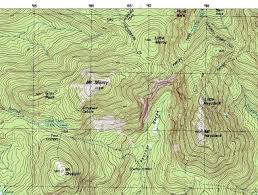
Topographic maps
Record of a land area using contour lines to show elevation and data/elevation changes.
The map shown is a topographic map
What kind of map is this?
Cartogram map
Statistical information is shown in a diagrammatic form, geographical size is/can be altered to be directly proportional to a selected variable.
The map shown is a Cartogram map
What kind of map is shown?
Cultural landscape
Geographic areas that have been shaped by human activity, cultural practices, beliefs, and values of the people who live/lived there.
Built environment
Human made surroundings like buildings/infrastructure that provide a setting/structure for human activates.
Human - Environment interaction
Ways humans use/interact/adopt with surrounding/natural environment and how humans alter environment/environment altering humans
Formal region
An area with official boundaries and a shared characteristic.
Uniform region
Everyone shares the same characteristics, like language, climate, or boundaries.
Functional region
Area organized around a central point of activity, also known as a node.
Perceptual/Vernacular region
A region defined by people’s beliefs or feelings, like the South for the US.
Mercator projection
Projection of a map of the world on to a cylinder but drawn in a grid with latitude lines being more spaced out as they touch the poles. Distortion in size but good for navagating.
Peter’s projection
Rectangular, equal area map projection that distorts shape but keeps proportional sizes.
Robinson projection
Most commonly used, oval shaped projection that shows the entire world but has minor distortion in all areas.
Conic projection
View from a pole, shaped like a semicircle. Things look smaller at the top, creating distortion.
Goode-homolosine
Interrupted map, often used in atlases an equal-area (equivalent) projection. Shapes, directions, angles, and distances are generally distorted.
Site
The actual location of a settlement/place on a map. (Physical characteristics and attributes) (The place itself)
Situation
Position of a settlement/place in relation to the surrounding area
Geographic Model
Theoretical frameworks that let us predict things like spatial relationships, interaction with or across space, and other issues of geography (Basically a model/show of geographic data)
Spatial
Relating to or occupying space, the position of things in the world, and how they relate to each other
Non-spatial
Not relating to or involved in the perception of relationships (as of objects) in space
Space-time compression
The way that the worlds seems to be getting smaller as communication, travel, and transport improves
Hydrosphere
Total amount of water on a planet
Resource
A source or supply of energy/support/material
Sustainability
Using natural resporces responsibly, so they can support both presesent an future generations
Linear pattern
Structures built in a line, usually along a major transport route such as a road or body of water
Centralized patterns
A patterned cluster that forms around a single or central location/node
Random pattern
Settlement with no correlation, distributed w/o discernable pattern
POSSIBILISM
Belief that environment is one factor that can determine culture but human innovation can overcome environment
ENVIRONMENTAL DETERMINISM
Belief that environment determines culture
Physical Geography
physical attributes of land like geographical features
human geography
study of human activity, and its affects or influences on earth’s surface
International date line
Imaginary line at 180 latitude where day changes when crossed
Greenwitch mean time (GMT)
Mean solar time at median 0 (used as a global standard)
North and South poles
90 degrees latitude n/s
Density
number of people or objects per unit area or volume
Cartographic
Related to the science of making maps
Scala of Data
Level of detail or representation of data in maps (Local to global ranges)
Scale
Relationship between distance in model and in real life
small scale
Shows LARGE amount of land/data
large scale
shows SMALL amount of land/data
Relative location
Location of object related to other locations
Useless boi
Enjoy the brain break bc I accidentally made 2 identical cards :)))
LONGITUDE
NORTH TO SOUTH - made of medians
LATITUDE
EAST TO WEST - made of paralells
Demographic regions
Areas defined by population characteristics like age, birth rate, or death rate
Population distributions
The pattern of where people live; the density of the inhabitants over an area.
Age distribution
The proportionate representation of different age groups within a population.
East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, Europe
Examples of major population clusters
East US and Southeast Canada, West Africa
Examples of emerging population clusters
Sparsely populated areas
Areas that are too wet, too dry, too hot, too cold, or too hilly.
Diffusion of fertility control
The spread of birth control in an area.
Disease diffusion
When a disease is spread into a new area.
Maladaption
A trait diffusion and adopted by a place that is harmful or nonbeneficial to the people involved or the environment.
Locations of high and low
High areas with high population densities, in major cities and by bodies of water, low areas that are much more sparsely populated in less habitable areas.
Demographic equation
Population = Starting population + natural increase + net migration
Rate of natural increase (NIR)
Crude birth rate - crude death rate (Can be negative or positive)
Overpopulation
When human population surpasses the quantity the environment is able to support
Underpopulation
A situation where a region has a population that is too low to effectively utilize the available resources.
Population projection
An estimated future population size based on current demographic trends, including birth rates, death rates, and migration patterns
Spatial analysis
The study of the characteristics, location, and relationships between places and features on Earth's surface, examining how these spatial patterns influence and explain human behavior and geographic distribution across different areas
Anti - natalist policies
Methods adopted by the government to PREVENT the population from having children, such as sterilization, free birth control, free abortions, and propaganda.
Pro - natalist policies
Methods adopted by the government to ENCOURAGE the population to have children, such as tax breaks for parents, free or cheap and accessible childcare, and propaganda.
Voluntary migration
Migrants who chose or volunteered to migrate.
Forced migration
Migrants who have to move due to factors like persecution, natural disasters, or government.
Intercontinental migration
The movement of people from one continent to another.
Interregional migration
Migration from one region to another.
Rural to urban migration
When people migrate from rural areas to urban ones in pursuit of economic success.
Intervening obstacles
A geographical or social barrier that hinders or prevents a migrant from reaching their intended destination
Intervening opportunities
A positive event or situation that a migrant encounters while traveling to their destination that may cause them to settle there instead
Cyclic movement
A type of migration pattern where people regularly move away from their home base for a short period of time and then return, following a repeated pattern, often based on seasonal changes
Migratory movement
The movement of people from one place to another, often with the intention of settling permanently in a new location
Periodic movement
A type of migration where people move away from their home for a significant period of time, but eventually return, often following a recurring pattern or cycle
Internal migration
The permanent movement of people within the boundaries of a single country
Recent trends
The current and emerging patterns or developments happening in human geographic phenomena like population distribution, migration, urbanization, economic activity, or cultural practices
Demography
The statistical study of human populations, analyzing characteristics like size, distribution, and changes over time, including factors like birth rates, death rates, and migration patterns
Population densities
The measurement of how many people live within a specific unit of land area
Natality
The birth rate - The number of live births per 1,000 people in a population over a specific period of time
Mortality
The death rate - per 1000 individuals over a specific time period.